Pasture management through rotational grazing [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Malgorzata Conder
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Deborah Niggli, David Streiff
technologies_1585 - Tayikistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
03/09/2012
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Rotational grazing on private grazing land used as daily pastures
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
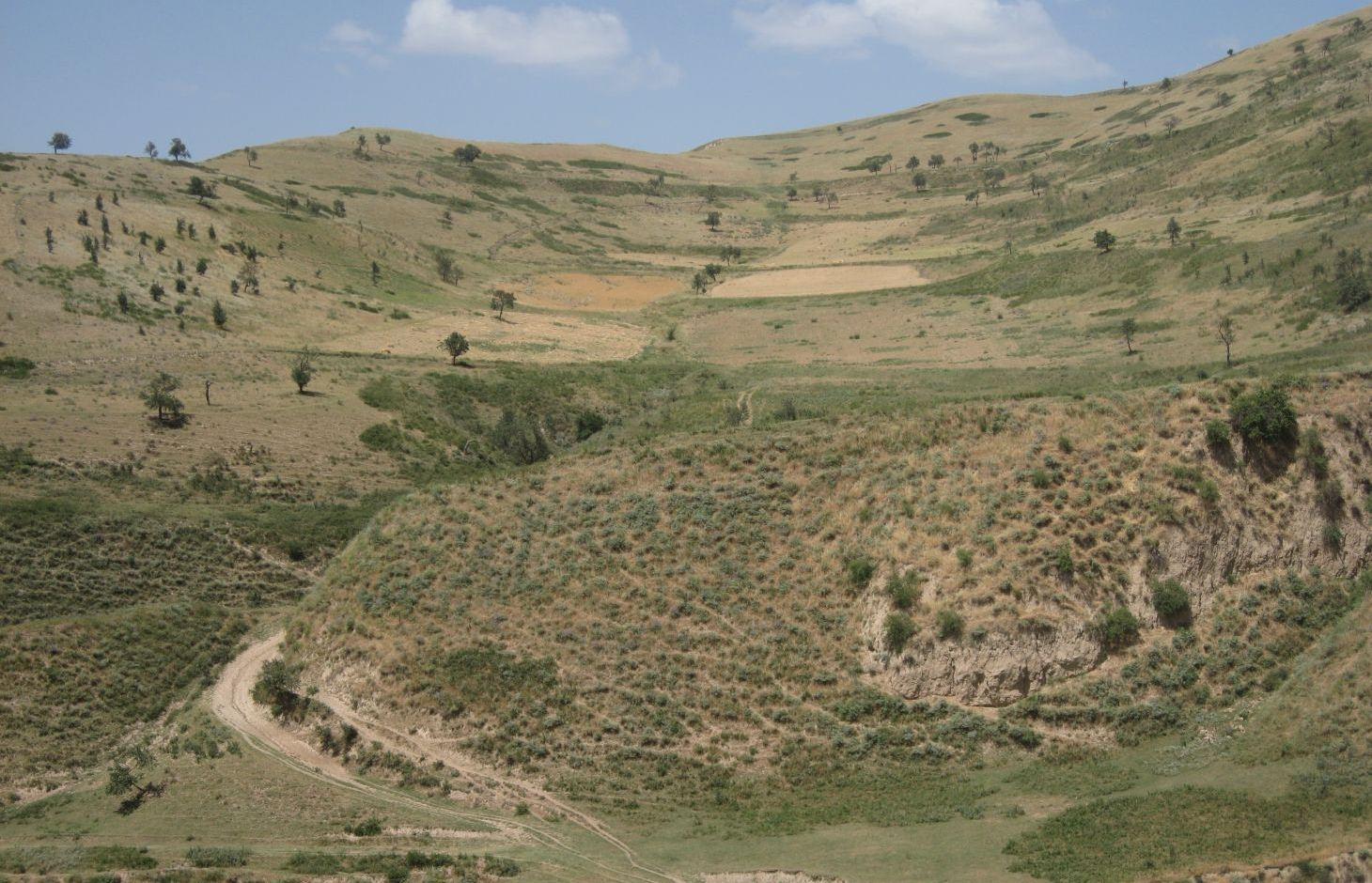
A riverbed divides the pasture where rotational grazing is practiced with the village Chargii poyon, where the certified land user and owner of the pasture lives. From a view point nearby his house, he has a good view on and hence a good control over the pasture area. This allows him to keep intrusive livestock outside, having a limited number of grazing livestock in the pasture. The area encompasses 119 ha, from which 5 ha are rented out as crop land.
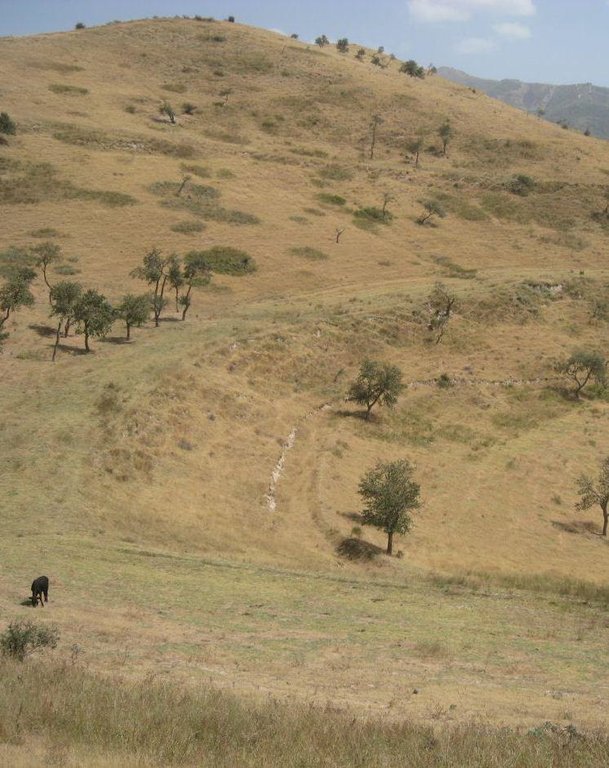
Land tenure conflicts about this pasture existed over many years, because there wasn’t declared any owner. The certified land user of Chargii poyon claims to possess the pasture since 1999. It is unclear how he got the land transferred. Being aware of the ongoing degradation of this land, the certified land user divided the area into 3 parts and introduced controlled grazing in 2007. While one part is being grazed the other two lie fallow. After one to two months of grazing in one area, the herds move to the next area. The rotation phases depend on the availability of grass. In June 2012, at the moment of documentation, there were 145 cows and some 30 goats and sheep. The number of animals is varying seasonally, with a higher amount of animals in summer than in winter. Compared to other pastures in summer, more grass in available on the pasture with rotational grazing. In winter grass availability is comparable between the pastures. This may explain why a higher number of livestock is recorded on the pasture with rotational grazing in summer.
The pasture is controlled by the farmer and further 4 people to avoid livestock intrusion.
In a seminar organized by Caritas Switzerland, the farmer learned about increasing long-term productivity of pastures by vegetation recovery. The idea of pasture rotation convinced him in order to raise productivity on long-term. The main reasons for changing the pasture management were the advanced stage of deforestation, increasing overgrazing, and the additional source to get the land taxes paid. The management of the pasture by rotational grazing on three areas allows the non-grazed areas to rest and recover. Less grazed and trampled areas result in an increase of the vegetation cover and thus to higher fodder quality, as well as increased soil stability and therefore a reduced risk of disasters, such as floods.
The farmer expected that the implementation of land conservation measures would stop the on-going pasture degradation and would assure long-term and sustainable use of the land. Despite the rotating system, the grazing land is still overgrazed and shows signs indicating moderate erosion, but it is less degraded than other pastures in the watershed. The area being the most far away from the settlement is in best conditions. The closer to the riverbed the more degraded and eroded the pasture is.
Additional measures are necessary to reduce soil erosion and gully formation in the area
Livestock owners have to pay a fee to the farmer for grazing cows, but not for grazing sheep and goats. The amount of the fee depends on the provenance of the herder. Fees vary greatly between the villages. Because of solidarity, Chargii villagers pay much less than herders from villages located further away. Momandion villagers pay 3 times, Dilolo villagers even 9 times more than Chargi villagers. But the certified land user claims to be flexible in the amount of fees for poor herders. He has to pay taxes to the government for the property and salary to the surveillants. If more money is available, also generated by the fees, the certified land user claims to invest a part of the money into the pasture. He would like to build another water point and to plant trees in the upper area. Livestock could graze in more remote areas which would reduce the pressure on the pastures in the lower area and decrease the soil compaction.
The pasture is located in the middle zone of the Obishur watershed and on the foothill above the riverbed plain. This pasture, located between the villages of Chargi poyon, Chargi bolo and Momandion and not far from Dilolo village, is a reachable place for many livestock of private households. In the riverbed, the only water point is installed where livestock is watered at midday. Due to tree cutting in the past, only a few shady places exist. Vegetation cover varies depending on the exposition of the slopes and the accessibility of the pasture. North-facing slopes have a more abundant vegetation cover. Some flanks are difficult to reach because of dense thorn bushes. A big gully, hardly accessible by livestock, is about to be covered again by naturally re-growing bushes and trees. Nevertheless, signs of erosion and rill building can be observed. Due to the closeness to the villages and to the pressure on natural resources it is crucial to sustain a controlled pasture management.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Especifique más el lugar :
Muminabad
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Idea of how to improve ground cover was initiated by a workshop from Caritas, but the rotational grazing was introduced by the farmer himself in 2007
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierra de pastoreo
Tierras de pastoreo extensivo:
- Semi-nomadismo/ pastoralismo
- rotational grazing
Especies y productos animales principales:
sheep/goats and cows
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazed pasture with frequent big gullies, rills and trampled areas. Almost complete deforestation of the grazing land.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water availability and water points for grazing livestock. Gradual degradation and erosion of the pasture which has to be stopped.
Grazingland comments: Rotation within 119 ha of grazing land
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180, Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept/Oct
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- sistemas de rotación (rotación de cosecha, cosecha rotatoria con descanso, agricultura migratoria)
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 1-10 km2
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.14 m2.
Total area is 119 ha, but 5 ha out of it are rented for cropping
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, governance / institutional (No/ Insufficient management planning and control), livestock pressure (Due to subsistence of the population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (impact of overgrazing and deforestation), education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
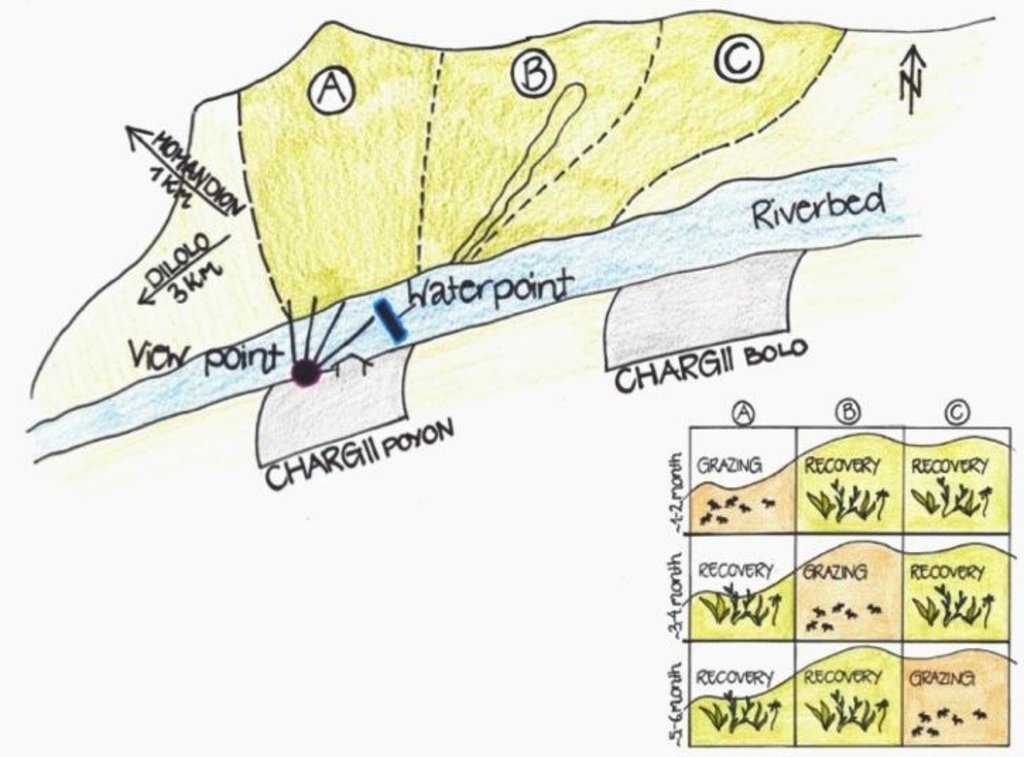
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
The hilly pasture of 114 ha in total is divided more or less vertically in 3 areas. In each area, the pasture between the ridge and the riverbed is covered. After having grazed one area for approximately one to two months, the herd moves to the next part. This means that two areas rest and grasses recover, while one is being grazed.
Location: Chargii poyon. Muminobod, Kathlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (When benefits of pasture management are known and understood, high technical knowledge isn't required)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (When benefits of pasture management are known and understood, high technical knowledge isn't required)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Change of land use practices / intensity level: In 2007 controlled and rotational grazing was introduced where no pasture management existed before
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
12.40
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Introduction/information of pasture management among the herders | Manejo | once in 2007 |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Introduction/information of pasture management among the herders | - | 1,0 |
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Salary for 5 people to guard pasture and herders: Monthly salary 70 Som/pers, pers d unknown | Manejo | every day, from spring until autumn |
| 2. | Annual Rent | Manejo | once a year |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Guarding pasture and herders | Persons/6months | 5,0 | 86,96 | 434,8 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Annual rent | ha | 114,0 | 1,359649 | 155,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 589,8 | |||||
Comentarios:
Costs which concern the information transfer to the herders is not calculated, as it is done informally. Only guardening by the employed people is monetarised.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The farmer already owns the land user certificate for the property and only has to pay annual taxes and the people who control the pasture. He covers these costs with the rent he gets for the grazing livestock.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Totally 800mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season (At 1200mm asl, wheater station Muminabad). Precipitation increases 60mm per 100m of altitude in average.
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Slopes on average: Some flanks over 40%
Slopes on average: Also rolling
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility: Low-medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: Poor-medium
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Water quality (untreated): For livestock, surface water in spring (because of snow melting and rainfall), in summer ground water at one water point
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Tree cutting, due to grazing more and more uneatable species
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- rico
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Men are taking decisions and administrating the property whereas women are working on the field. Privileged land user because he owns a big area.
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2% (Farmer owns a big property of 119 ha).
Off-farm income specification: Additionally bee-keeping
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
Comentarios:
3.2 ha if 7.7 pers/household for totally 4100 ha pasture
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- arrendamiento
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Comentarios:
Land ownership is based on the land user certificate conferred by the government.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
área de producción
manejo de tierras
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
disparidades económicas
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
instituciones comunitarias
mitigación de conflicto
Livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
The farmer possessing the user certificate of the land states that even poor families are allowed to graze their livestock for a low rent and thus this pasture management seems to lead to more equity among the farmers of different economic classes. The better the livestock is fed, the higher the value of livestock and the wealthier the households are. But this statement could not be verified and should be taken with precaution.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
escurrimiento superficial
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
diversidad de hábitats
Otros impactos ecológicos
Hazards towards adverse events
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no se sabe |
Comentarios:
Thanks to a better vegetation cover, the infiltration of rainwater is facilitated which results in an increase in soil moisture and thus to a higher resilience to droughts or higher temperatures.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Establishment and maintenance cost are low. Input consists mainly of the establishment of a pasture management which is based on dissemination of knowledge and information
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
1 Household
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 90-100%
Comentarios:
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
At the time of documentation it wasn't known if there exist other land users with a similar technology. There are more farmers grazing on that rotational pasture than in the very beginning.
Precondition is a big grazing land property, but only a small amount of farmers do own such a property.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Equity amongst the farmers through flexible renting prices |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| No high establishment and maintenance cost |
| No high physical inputs required |
| Economic (better fodder quality) and ecological benefits (grass recovery, erosion reduction) can be seen as a direct result of pasture rotation |
| It is a good platform to share and spread knowledge of good practices, as over time many farmers come regularly to graze |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Other cost intensive investments required like building another waterpipe and planting trees |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Precondition for such a setup is that one farmer owns the user certificates for a big grazing land, which is unusual. It is not clear how he got the user rights. | Ideally communal grazing land would be divided among several households sharing access to pastures |
| The pasture shows still a lot of signs of erosion and degraded areas. | Less livestock or division into more parts to allow the vegetation cover to rest for a longer time span. Enhance a homogeneous grazing of upper and more distant parts of the pasture. Control if pasture management is adhered consequently. Additional conservation measures such as resowing of specific areas, or fencing of badly degraded areas such as gullies. |
| This system works when there are communal pastures in the surrounding area. On the here documented pasture, less livestock is kept than on communal pastures. This lower density of livestock is not realistic at watersheds level, because it might raise the pressure on land in the other pastures. | Rotating within the grazing land just combats the fact that there is too much livestock compared to the available area |
| It is not clear whether the main motivation of this private pasture is to stop degradation or to collect the renting fees | Elaborate an investment plan showing how the collected fees will be reinvested into grazing land infrastructure and how much is taken for reimbursing the efforts of the certified land user. |
| It is not known whether the different fee levels according to the herders provenance does not create discontentment | Transparent price structure |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos