Two Room Stove [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: shane stevenson
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1518 - Tayikistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Pochoev Mirzokurbon
mirzo_pochoev@camp.tojikiston.com
CAMP
Tayikistán
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership (CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership) - Kirguistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
11/07/2011
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
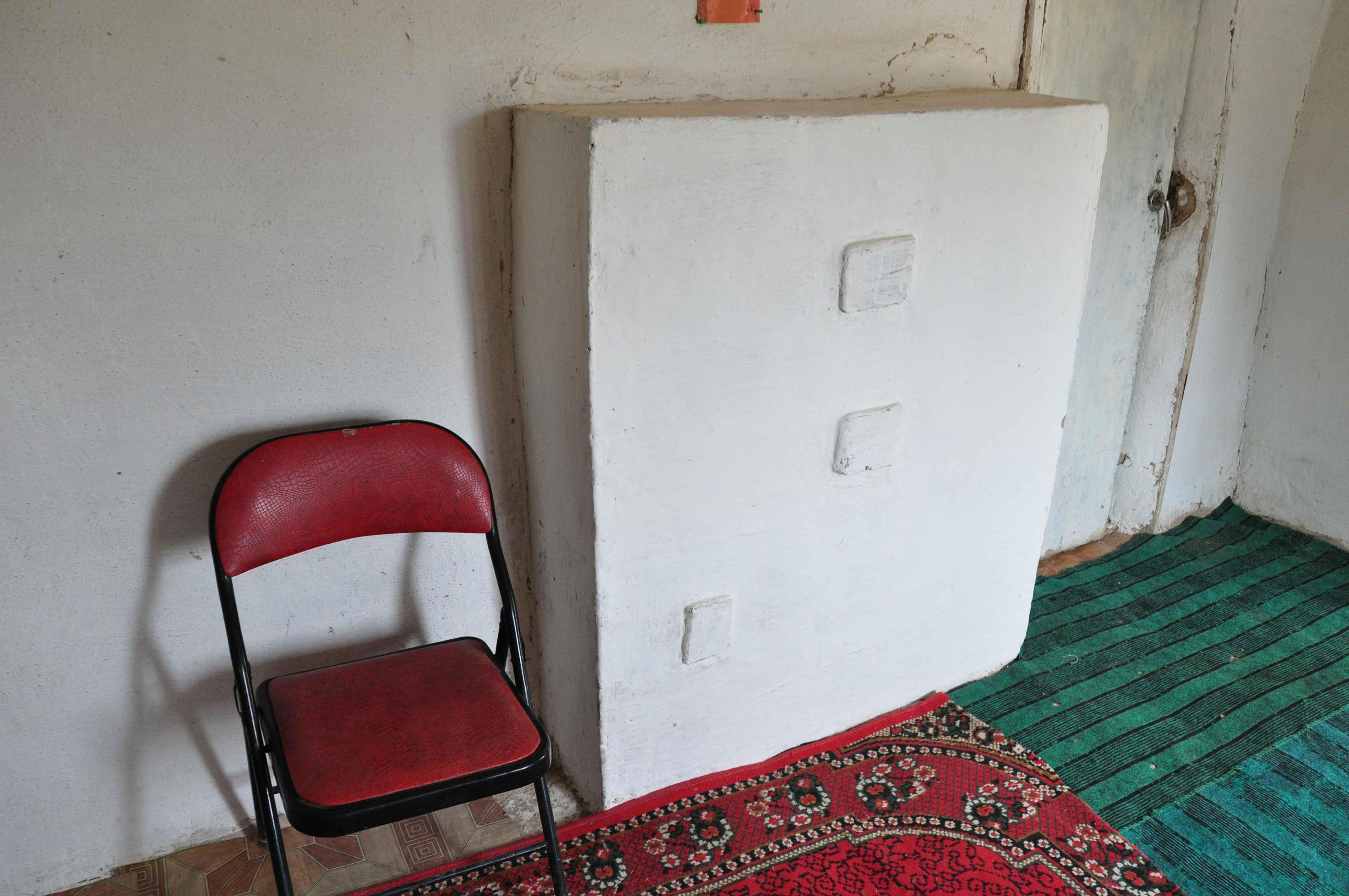
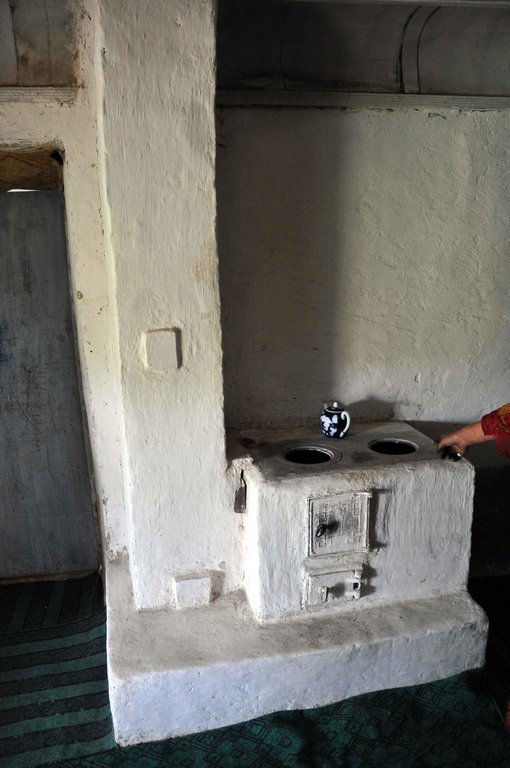
A brick stove that is built into the existing internal wall, that will heat the two rooms and can be used for cooking.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
The 2-room stove is a brick based structure that filters hot air into a second room, hence maximising the heating potential of the fuel. The basic stove is built of fire bricks, house bricks, cement and coated with a natural mix of straw and mud. It is a traditional concept based upon former soviet stoves, that was modernised and adapted to improve the energy efficiency, and make use of the materials that are available to the people. It is able to burn coal, wood, and tapac, and is designed to reduce the amount of natural resources used to meet the household energy needs.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the 2-room stove is to replace the traditional cast iron pig style of stove, with a more modern and energy efficient stove that can be used effectively for cooking and the heating of two rooms. The 2-room stove is designed to filter the hot air between the rooms and the use the bricks as a thermal sink for heat retention. As most of the houses are made of mud bricks, the heat from the stove will conduct through the walls, which will act as radiators to emit warmth into the room. The 2-room stove also means that cooking activities can be conducted inside the house in a smoke free environment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The stove requires basic training in construction by a skilled technician, however after a three day training course the local trades people are able to build their own stoves with limited supervision. The stove is constructed from 45 fire bricks and 400 household bricks, the hot plate and stove doors are bought second hand from the markets, and metal bars are used to reinforce the structure. There are two smoke vents in the wall between the two rooms to allow the smoke to filter its way along the snake like chimney until it vents through the roof. The final structure is coated in straw and mud which acts as an insulation layer.
Natural / human environment: There is a high reliance on natural resources in Shahtuti Bolo. The average family burns several tons of tapac (straw dung mix) and wood each year. The surrounding mountain area is sparsely vegetated and does not even provide enough fuel for the village during the harsh winter months. This is supplemented by buying wood from the neighbouring villages. One tapac weighs one kilo, this is organic matter that can no longer be used for soil enhancement, but for fuel purposes. It is estimated that the 2-room stove will reduce the amount of fuel burnt by 20-40% depending upon the household.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Hakimi Jamoat, Nurobod
Especifique más el lugar :
Regional Subordination of Tajikistan
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The two room stove is modernisation of a traditional design, therefore the concept is not new to the people.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reduce energy
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierra de pastoreo

asentamientos, infraestructura
- Asentamientos, edificios
Comentarios:
The technology is implemented in the households
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The over exploitation of natural resources that have lead to soil erosion and degradation of the soil structure.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land has become increasingly unproductive over the last few decades. There is not enough pasture to feed our animals.
Constraints of settlement / urban
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April - October
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- tecnologías de eficiencia energética
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comentarios:
The village of Shahtuti Bolo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S11: Otros
Comentarios:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
- Wm: movimiento de masas / deslizamientos de tierra

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bh: pérdida de hábitats
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides, Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Failure to use organic fertilisers), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Removal of natural resources to meet local energy needs.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (as above), overgrazing (Areas became over grazed as productivity declined), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (removal of vegetation leads to increased run off from the mountain slopes.), poverty / wealth (There is a lack of money for investment), labour availability (Two thirds of the households in the village have people working abroad.), war and conflicts (There has been substantial political unrest in the area.)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (There is a perception that there are more extreme rainfall events.), population pressure (Popualtion in the area is increasing), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge on good land management.)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Autor:
S. stevenson, CAMP Kuhiston, apt19 h 131 Rudaki ave, 734003, Dushanbe
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
A simple view of the main part of the stove used for cooking. There are two cast iron doors, the lower is for air circulation and the upper is the combustion chamber for the fuel. There are two hot plates for cooking. The smoke travels from the fire vent towards the chimney and then through a 10cm sq hole to the brick structure on the other side. The smoke snakes it way around the the second structure which acts as a radiator as the bricks warm up. The smoke then returns into the chimney in the main room, heating the chimney as it vents.
Location: Shahtuti Bolo. Nurobod
Date: 13.07.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The technical design requires a high level of knowledge)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (With training the land user would be able to build their own two room stove)
Main technical functions: reduces the amount of dung and wood used as fuel.
Structural measure: 2-room stove
Construction material (other): fire bricks and regular house bricks, covered in mud are the main materials.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
Stove
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
4.00
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of stove | Estructurales | any |
| 2. | None | None |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Construction of stove | Persons/day | 6,0 | 5,333333 | 32,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tools | pieces | 5,0 | 4,0 | 20,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Bricks | bricks | 400,0 | 0,225 | 90,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Fire bricks | bricks | 45,0 | 1,4 | 63,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Metal bar | bars | 5,0 | 3,4 | 17,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Fire cement | cub m | 3,0 | 8,333333 | 25,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Ceramic tiles | tiles | 24,0 | 1,0 | 24,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Metal cooking plates | plates | 1,0 | 63,0 | 63,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Stove doors | doors | 2,0 | 22,5 | 45,0 | |
| Otros | Transports | vans | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 429,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning the stove | Estructurales | annually |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Cleaning the stove | Persons/day | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 4,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
The costs are based upon 2011 prices and are based on constructing only one stove.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The main cost is the fire bricks. These have to be transported from the capital. However, in some regions of Tajikistan, materials are available from stoves that were constructed several decades ago which could be reused.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low-medium
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
< 5 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Availability of surface water: is good for the village because there is a stream and medium for other areas which have access to te stream.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- muy pobre
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Training is provided on he construction of the stove. This is only attended by men.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are poor and own 95% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: 44 out of the 58 households are reliant on remittances from Russia, however all the families have livestock which they buy and sell in the local markets and a small household plot for vegetables.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Comentarios:
Four people have the majority of the land user rights in a village of 58.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
producción de madera
generación de energía
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved cooking conditions i.e. no smoke.
Ingreso y costos
carga de trabajo
Otros impactos socioeconómicos
Demand on natural resources
Comentarios/ especifique:
On average around 30% reduction
Impactos socioculturales
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
Do not need to cook outside and improve the internal living conditions.
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
Leaves natural resources for the community benefit.
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Helps prevent inter village conflicts over natural resources.
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
The project is targeted at the most vulnerable in the community.
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
It has reduced the time, effort and money spent on fuel whcih can be up to 50% of the household's budget in extreme cases. It has improved the heating in the household and created a smoke free environment for cooking.
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
cubierta del suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduction in the burning of dung.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
Comentarios:
The stove is able to take other fuel sources in the event that natural resources are not available.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
There is a high initial outlay in the building materials and labour costs, but once the two room stove is constructed it only requires annual cleaning which can be done via hatches already included in the design.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
10 households in an area of 0.1 - 1 km2 (ca. 596 habitants)
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: All land users given support have constructed a stove. The project will build a further 11 stoves in the local district for the most vulnerable families.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: To early in the project to say, but several memebers of the community are trained to build the stove.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
It keep the house warm and for longer. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Thermal insulation techniques and energy efficiency training may support reduced fuel use. |
| I do not have to cook outside in the winter months. |
| It is easy to clean. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
It improved the household heating system dramatically, as the previous cast iron stove does not retain the heat after the fire dies. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The room could be insulated using traditional techniques or modern materials that are starting to appear on the market. |
|
The brick design will retain the heat for several hours and will heat two rooms. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Doors and windows in the rooms could be sealed to prevent drafts. |
|
The stove will last for 25yrs with minimal maintenance. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the stove became popular a small brick making factory could be established. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| It is expensive, and I need an expert to help me. | Remittances could be used to fund the initial set up costs. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| There is a high initial investment that has required project funding. | Collective building of the stoves will reduce the cost. Micro-finance loans could be made available to help cover the initial costs. |
| The stove requires technical training in its construction. | A booklet could be produced to support self building of the stoves. |
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos