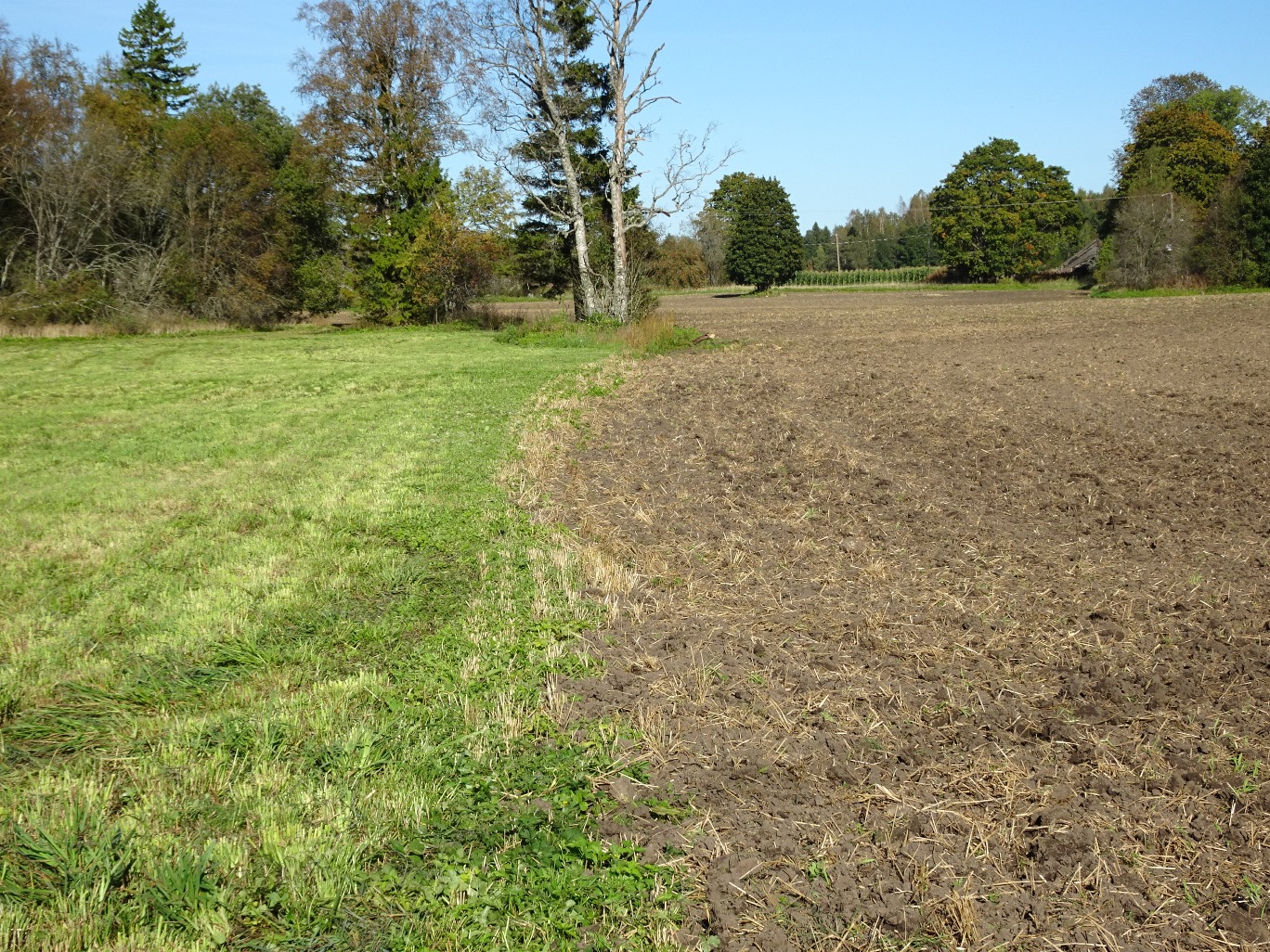
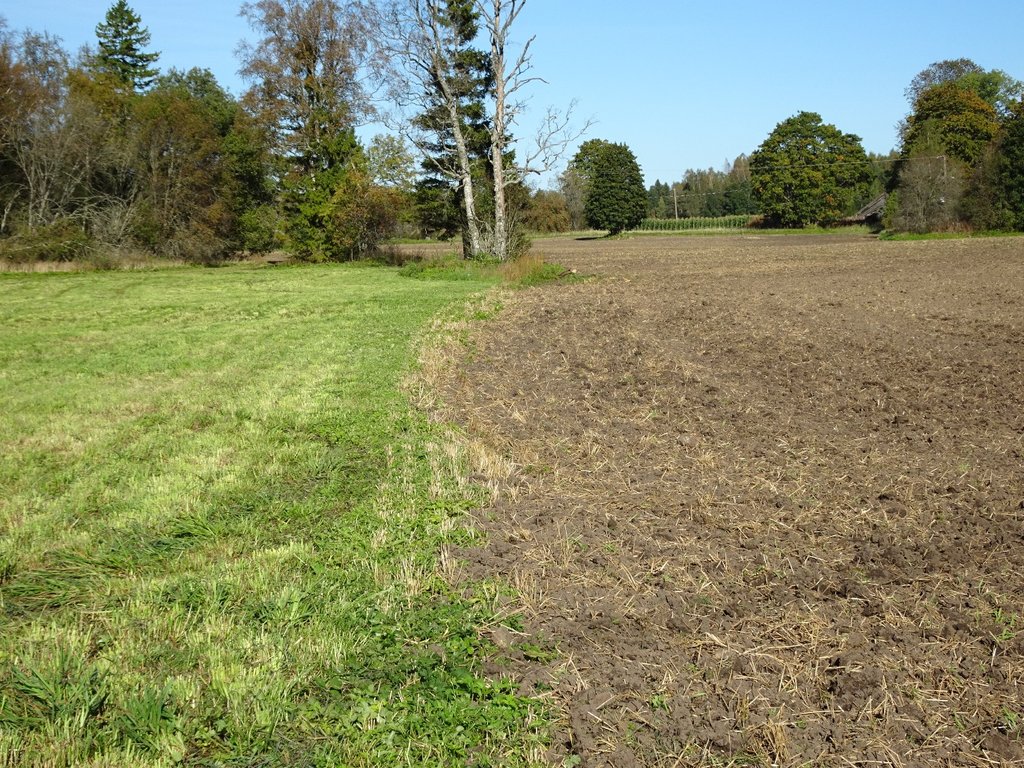
Permanent grassland on peaty and eroded soils [Estonia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Endla Reintam
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch
Püsirohumaa turvas- ja erodeeritud muldadel
technologies_3113 - Estonia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
usuario de la tierra:
Selge Are
+37257863250
are.selge@emu.ee
Hummuli Agro
Tiigi 3b, Hummuli, 68410 Valga maakond
Estonia
researcher:
Penu Priit
+3725156165
priit.penu@pmk.agri.ee
Agricultural Research Centre
Teaduse 4/6, 75501 Saku, Harjumaa
Estonia
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences (IAES/EMÜ) - Estonia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
04/06/2017
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
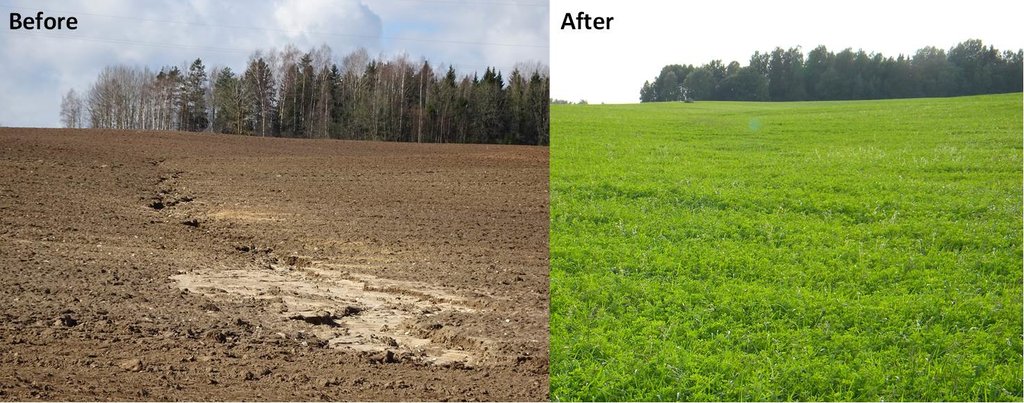
A permanent plant cover is maintained or established to protect soil against erosion or peat decomposition.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
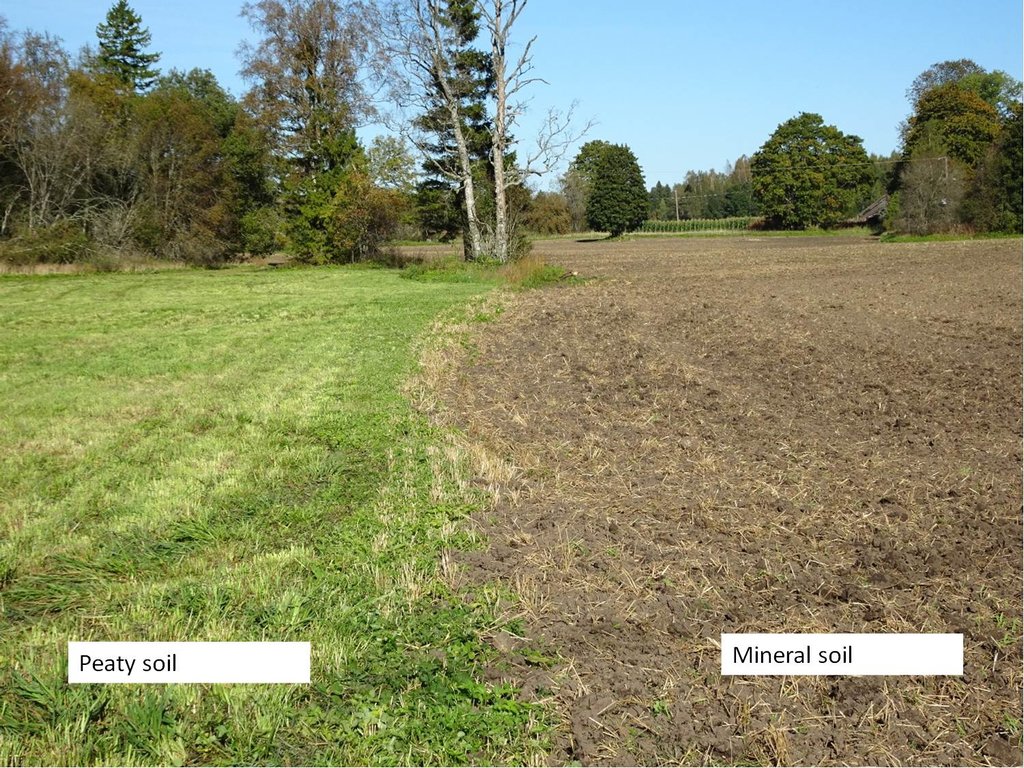
The technology is applied in sub-humid climate with an average of 696 mm of precipitations per year, from which more comes from July to October and less in March and April. Average annual temperature is +4 C, length of the growing period is 180-195 days. The territory is mostly flat to slopes of 6-10%. Average altitude from the sea level is 50 m. About half of the Estonian territory is above 50 m and half is below it. Soils are from very shallow (less than 0.1 m) inthe north to very deep (> 120m ) in the south. Soil cover is very variable. The peat cover of peatlands varies from 0.3 m to more than 10 m from well decomposed to poorly decomposed peat. On hilly areas the soils are medium textured with low (< 1%) organic matter in topsoil. Groundwater in near the surface in peatlands and deep in hilly areas. Biodiversity of these areas is medium. Market orientation of production system is mixed and off-farm income less than 10%. Relative level of wealth is average from individual households to cooperatives. Soil management is mechanized. Land belongs to land users but is leased also in case of bigger farms (over 1000 ha).
In the agricultural land the area will be excluded from intensive tillage by establishing a permanent plant cover, mainly with grass. The aim is to protect the slopes over 10% against erosion and peaty soils from further intensive decomposition of organic matter and with that the reduction of CO2 emission. The farmers should maintain permanent plant cover in the areas mentioned, or establish permanent plant cover. Renewing of the grassland is allowed from the top (without ploughing) once in a 5 year period. Government pays support of 50 EUR/ha if the area is bigger than 0.3 ha. The technology reduces intensively tilled area and thus the possibility to grow cash crops and/or reduces the yield from grassland. On the other hand it allows to still use wet areas for agriculture (i.e. fodder production).
The rules of the technology are fixed with the Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014-2020 under activity "Support for regional soil protection" (https://www.agri.ee/et/eesmargid-tegevused/eesti-maaelu-arengukava-mak-2014-2020) related to the reguation of the European Parliment and of the Council 1305/2013, article 28. The regulation is relevant more to the South-Estonia in case to reduce erosion, as the landscape is more hilly there. The exclusion of peatlands from agricultural use is relevant more in West-Estonia where the share of peatlands of the total area is the highest. However, it can be applied in whole Estonia if the area of peatland is bigger than 0.3 ha.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Estonia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
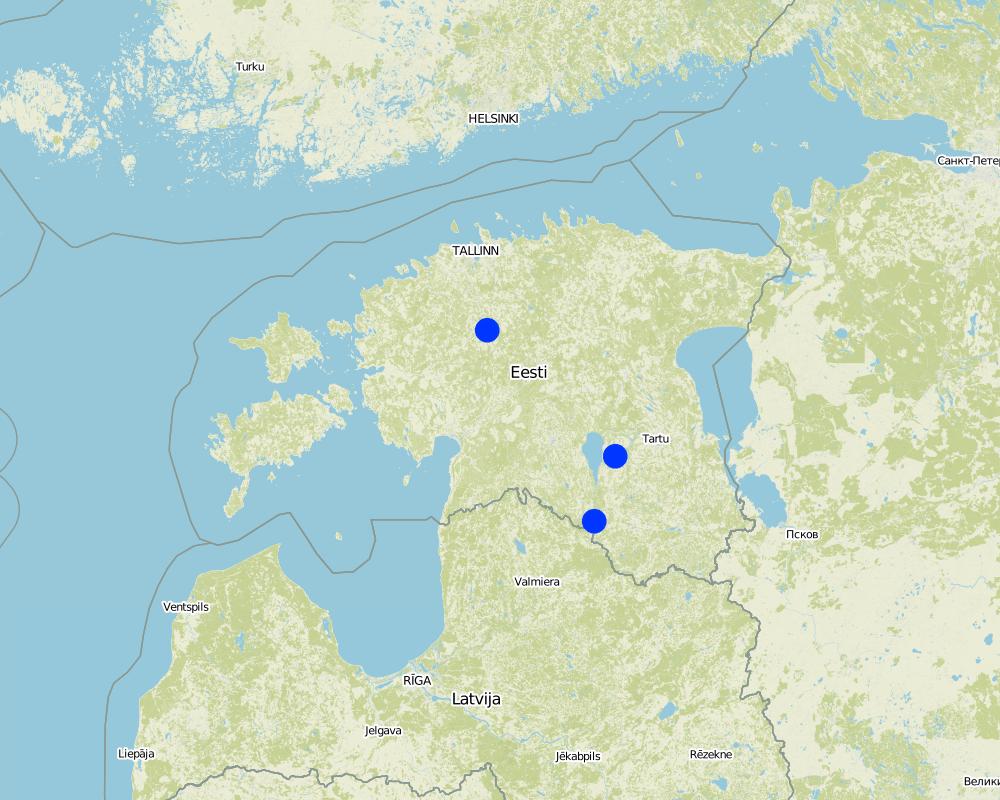
One site at Rapla, second at Tartu, third at Valga (erosion)
Especifique más el lugar :
One site: Rapla county, Pae; second site Tartu county, Annikoru, third site Valga county, Hummuli
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
- Governmental tool
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The tool is a part of Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014–2020 for soil fertility.
The survey was done by the Soil Survey Bureau of the Estonian Agricultural Research Centre (http://pmk.agri.ee/). The results presented here are partly from this survey and from the work done by the project iSQAPER.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- mitigar cambio climático y sus impactos
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas principales (comerciales y de subsistencia):
barley, wheat, rye, oat, oilseed rape, pea, bean, corn for silage, vegetables - potato, carrot, cabbage

Tierra de pastoreo
Tierras de pastoreo extensivo:
- Ganadería de hacienda
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Pastoreo mejorado
Especies y productos animales principales:
Species: cattle, beef cattle, sheep,
Products: milk, beef, lamb
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Usually before the implementation of the technology the land was intensively tilled and used for annual crop plantation. After implementation the grasslands can be used for cutting and grazing.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
On Histosols the groundwater is close to the surface.
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
For the cereals one harvest per year, for grasslands 1-4 cuts per year. For hay 1 cut, for silage 2-4 cuts depending on the year
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- perturbación mínima del suelo
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 1-10 km2
Comentarios:
To get the governmental support the area should be larger than 0.3 ha. Othervise the size is not important, depending on the area covered by hilly area or wet soils in the landscape.
In 2016 it was 10554 ha Histosols and only 40 ha of eroded soils covered with this technology in Estonia. This area excludes grasslands on another soil types. On specific sites: in Rapla county in Pae the size of the field is ca 3.2 ha, at Tartu county, Annikoru 2.8 ha.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A3: Tratamiento de superficie del suelo

medidas vegetativas
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
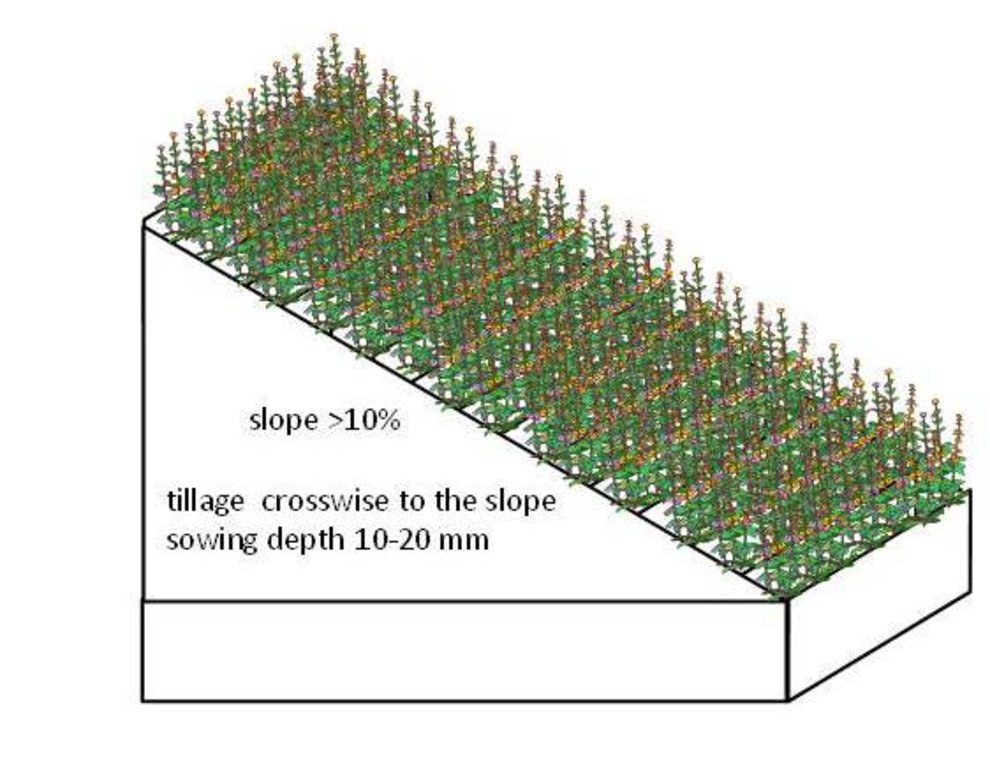
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
The requirements to create a permanent grassland depends on soil type.
Species mixture suitable for the permanent grassland on wet soils (Histosols): Bromus sitchensis 30%, Phalaris arundinacea 45%, Phleum pratense 20%, Poa pratensis 5%. Sowing rate 20 kg/ha.
For the drier areas (eroded soils) the next mixture is suitable: Dactylis glomerata 65%, Phleum pratense 26%, Poa pratensis 9%. Sowing rate 23 kg/ha.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
per hectar
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
EUR
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
1,18
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
36-40 EUR/day + taxes
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage (ploughing, cultivation) | Agronómicas | in spring |
| 2. | Collecting stones, slip (by demand) | Manejo | in spring |
| 3. | Fertilization | Agronómicas | in spring complex fertilizer |
| 4. | Sowing | Agronómicas | in spring |
| 5. | Rolling | Agronómicas | in spring |
| 6. | Cutting the weeds | Agronómicas | during growth (summer) |
| 7. | Fertilization during growth period | Agronómicas | after every cut of grass, if cutted grassland, N-fertilizer |
Comentarios:
If renewing the grassland, there will be no ploughing, collecting the stones and sliping. Only chisel plowing and/or sowing with fertilization. If the grassland will be use for grazing, no need for fertilization during growth period.
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Driver (machinery work) | person day | 0,5 | 36,0 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Equipment (machinery) cost on establishment year | year | 1,0 | 207,0 | 207,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds | kg | 22,0 | 2,47 | 54,34 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Complex fertilizer | kg | 500,0 | 0,42 | 210,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Ammonium fertilizer | kg | 100,0 | 0,33 | 33,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 522,34 | |||||
Comentarios:
For tillage and other operations it is calculated 14-18 EUR/ha.
If to hire equipment the labour costs should be included to the machinery costs - for cutted grassland 225 EUR/ha, for grazed grassland 162 EUR/ha
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting or grazing the grass | Vegetativas | 1-4 times per vegetation period |
| 2. | Fertilization | Agronómicas | in spring in the beginning of season and after every cut N-fertilizer, after each second year complex fertilizer |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipo | Grasslands for cutting - machinery costs | year | 1,0 | 141,0 | 141,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Ammonium fertilizer | kg | 200,0 | 0,33 | 66,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Complex fertilizer | kg | 200,0 | 0,42 | 84,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Materials for hay making | year | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 306,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
The governmental support to establish and to maintain the grassland is 50 EUR/ha.
If to use the land for the grazing, the machinery cost per year is 38 EUR/ha.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Fuel price.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
696,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Average 696 mm, almost equally spread over the year, more from July to October, less in March and April
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Tartu Tõravere
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
LGP 180-195 days
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones convexas
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Eutric Histosol, well decomposed peat, drained area.N 2.32%; C32.89%; C/N14.20%; P2,62 mg/100g; K 13.73 mg/100g; Ca 1762.32 mg/100g; Mg 166.98mg/100g
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
< 5 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Histosols biodiversity depends on the base saturation and level of groundwater (degree of drainage). Diversity is higher at higher pH and better drainage.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
- cooperativa
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
- ancianos
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- gran escala
Comentarios:
There are also small-scale and medium-scale farms applying the technology. At Pae, the farm have 4900 ha of land, from which 1800 are grasslands, at Annikoru the farm have 2320 ha of land from which 390.5 ha are grasslands.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- arrendamiento
- individual
- individual/open access
Comentarios:
Groundwater belongs to the state. Smaller water bodies can be in individual use, larger are usually open access
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The area will be excluded from crop production and it means no cash crops can be cultivated on this area. Instead of crops hay or silage is possible to sell.
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
As it is not allowed to renew these grasslands intensively, the quantity of grass will drop. For short term clover+grasses mixture the average yield is 16 tons/ha per year, for long-term grass mixtures 5.2 tons/ha per year.
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to the change of species in the mixture, the protein level will drop. Instead of red clover grasses will be used in the mixture of long-term grasslands.
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to the changes in silage/hay quality (protein) there can be reduction of milk and meat production if the differences will not be covered with other fodder.
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
In case of crop orientation, there are new products to sell - grass, hay, silage, or grasslands to rent.
manejo de tierras
Comentarios/ especifique:
Depending on the farm it can be simplified or hindered. If focus was on crops, then new machinery is needed to manage grasslands (for cutting, hay or silage making).
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
As renewing of grassland is after every 5 years, there is no need to buy seeds every year, as well as pesticides and to till the soil.
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to the reduction of the inputs costs, the income my increase. Also the government pays support 50 EUR/ha for the land under these measures.
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Next to the yield (grass, silage, hay) the support from the government (50 EUR/ha)
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
It may decrease due to no need of every year tillage and sowing and due to the change from 2 year short-term grasslands to the permanent grasslands. However, if not managed grasslands earlier it may increase the workload as cutting and collecting the grass is needed.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
More land under grasslands than under crops. Grasses are suitable for animals feeding, not for human direct consumption.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
If land was eroded before and soil was on the road, everybody can see the differences after establishment of the grasslands. It is not so severe in case of peatlands, however, less tractors will stuck in to the mud on rainy period.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
In case of erosion, no soil will be washed down to the hill as plant cover protects soil surface and increases infiltration. In case of peatlands, grass cover creates better structure and increases water infiltration thus decreases surface runoff during heavy rainfall.
drenaje de agua en exceso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Grass creates protection to the soil surface and raindrops can't destroy the soil structure any more. Also grass roots create better porosity and structure in the soil leading to better water drainage.
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The difference in soil moisture between mineral and organic soils under cereals and under grassland was ca 5% and 25%, respectively, in favour to the grasslands in autumn 2016.
cubierta del suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
40%
Cantidad luego de MST:
100%
Comentarios/ especifique:
Under spring cereals soil is covered only 4-5 months per year, under grasses soil is covered 100% of the year.
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
On the slopes depending o the crop and the amount of precipitations, the loss varied from 3 to 60 tons/ha, under permanent grass cover it is less than 0.05 tons/ha per year. Without every year tillage there is no intensive decomposition of the peat, as well as no wind erosion.
acumulación de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Under grasses we can increase the soil organic matter content by 0.35 t/ha in 5 year period in peatlands. In eroded soils we can increase 0.02% per year.
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
As plants protect soil surface, raindrops can't destroy the soil structure and there will be no crust formation
compactación de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Under the grasslands the bulk density was lower by 0.1-0.2 g/cm3 compared to tilled soil.
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the intensive decomposition of the peat stops or there will not be any leaching by water, more nutrients remain in the soil. Also the permanent plant cover during the whole year stops nutrient leaching.
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Under permanent grasslands the Corg increases by 0.35 t/ha per 5 year period.
acidez
Comentarios/ especifique:
Without periodic liming the acidity of peatlands starts to increase. If no CaCO3 in mineral part, also pH of previously eroded soils starts to decrease slowly, as organic acids form during decomposition process.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Thanks to the permanent plant cover there is no period of the year without vegetation.
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
If previously the plant residues were mixed with the soil by tillage, now there will always some extent of plant mass be left above ground (5-10 cm), even if the most is removed for hay or silage.
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Long-term grassland includes at least 4 species in the mixture, short-term mixtures 2-3 species. However, compared with the cereals, the annual weeds will disappear and the diversity may decline.
diversidad animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
There are more spiders, ants, beets.
especies benéficas
Cantidad antes de MST:
2 species of earthworms
Cantidad luego de MST:
3-4 species of earthworms
Comentarios/ especifique:
Under grasslands were 1-2 more earthworm species than under tilled management. More spiders and ground beetles were found there compared to the tilled soil.
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
Grasslands create untilled patterns to the landscape.
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
Grasses surpress many soil born crops diseases and pests, also annual and perennial weeds.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de sequías
Comentarios/ especifique:
Grass roots go to the deeper soil and they are not so sensitive to the drought.
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Under permanent grasslands reduced CO2 emission by 1.10 t/ha per year compared to the tilled areas.
riesgo de incendio
Comentarios/ especifique:
If the grass will not be cutted before winter, the dry grass has the risk of higher landscape fires in the spring.
micro-clima
Comentarios/ especifique:
The changes of soil temperature as well as moisture content are smaller under permanent grass cover than under tillage.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios/ especifique:
All year plant cover helps to bind nutrients and stop their leaching from the soil. Higher amount of organic matter in the soil increases water holding capacity.
sedimentos transportados por el viento
Comentarios/ especifique:
Organic peat particles are light and are easy subject of wind erosion in dry conditions by tillage. Permanent plant cover stops such kind of erosion
daño a campos de vecinos
Comentarios/ especifique:
On hilly landscape no extra soil is flushed to neighbours fields. In case of peatlands no dust is carried around.
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
Comentarios/ especifique:
In case of erosion, no soil is carried by water or wind to the ditches and on the roads.
impacto de gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Under permanent grasslands reduced CO2 emission by 1.10 t/ha per year compared to the tilled areas.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | moderadamente | |
| temperatura estacional | invierno | incrementó | moderadamente |
| temperatura estacional | primavera | incrementó | moderadamente |
| lluvia anual | incrementó | no se sabe | |
| lluvia estacional | invierno | incrementó | no se sabe |
| lluvia estacional | otoño | incrementó | no se sabe |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | moderadamente |
| tormenta local | no se sabe |
| granizada local | no se sabe |
| tormenta de nieve local | moderadamente |
| tormenta de viento | no se sabe |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| ola de frío | no se sabe |
| condiciones extremas de invierno | moderadamente |
| sequía | moderadamente |
| incendio | no muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | moderadamente |
| marea tormentosa/ inundación costera | moderadamente |
| deslizamiento | bien |
Desastres biológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| enfermedades epidémicas | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
ligeramente positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
ligeramente positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- más de 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
In 2016 two hundred four households got the governmental support, in total 10554 ha
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 10-50%
Comentarios:
Anyway, the use of Histosols and Gleysols is limited due to their properties and regular use of these soils is for grazing or grass cutting.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Better soil protection |
| Possibility to earn money in unsuitable soil conditions. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Reduces soil erosion on hilly landscape |
| Reduces the decomposition of peat on Histosol |
| Reduces CO2 emission from agricultural land. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Loss of income | Governmental support (50 EUR/ha) |
| Problems with the grass (farms without animals) | Cooperation with neighbours, selling the hay for energy production |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Farmers don't want to use the technology | More effective lobbying |
| Wrong declaration of the land under the technology | Better advisory system and improvement of electronic databases |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
5 within iSQAPER project but more than 20 during another projects
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
10 within iSQAPER project but more than 20 during another projects
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
8
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Bender, A. (koostaja) 2006. Eritüübiliste rohumaade rajamine ja kasutamine. I. ja II. osa. Jõgeva
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Bender, A. 2010. Heintaimede sordiaretus ja seemnekasvatus. Jõgeva Sordiaretuse Instituut
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Older, H. 2011. Kohalikud söödad. Eesti Rohumaade Ühing.
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014–2020
URL:
https://www.agri.ee/en/objectives-activities/estonian-rural-development-plan-erdp-2014-2020
Título/ descripción:
Kattetulu arvestused taime- ja loomakasvatuses 2016. Koost: Marju Aamisepp, Helle Persitski. Maamajanduse infokeskus. 2017.
URL:
http://www.maainfo.ee/data/trykis/kattetulu/KATTETULU2016.pdf
Título/ descripción:
Statistics Estonia
URL:
https://www.stat.ee/en
Título/ descripción:
Eesti maaelu arengukava 2007-2013 2. telje ning Eesti maaelu arengukava 2014-2020 4. ja 5. prioriteedi püsihindamiseks 2016. aastal läbiviidud uuringute aruanne. Põllumajandusuuringute keskus. Saku 2016.
URL:
http://pmk.agri.ee/mak/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/09/aruanne_uuringud_2015.pdf
Título/ descripción:
Eesti tuleviku kliimastsenaariumid aastani 2100
URL:
https://www.envir.ee/sites/default/files/kliimastsenaariumid_kaur_aruanne_ver190815.pdf
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos