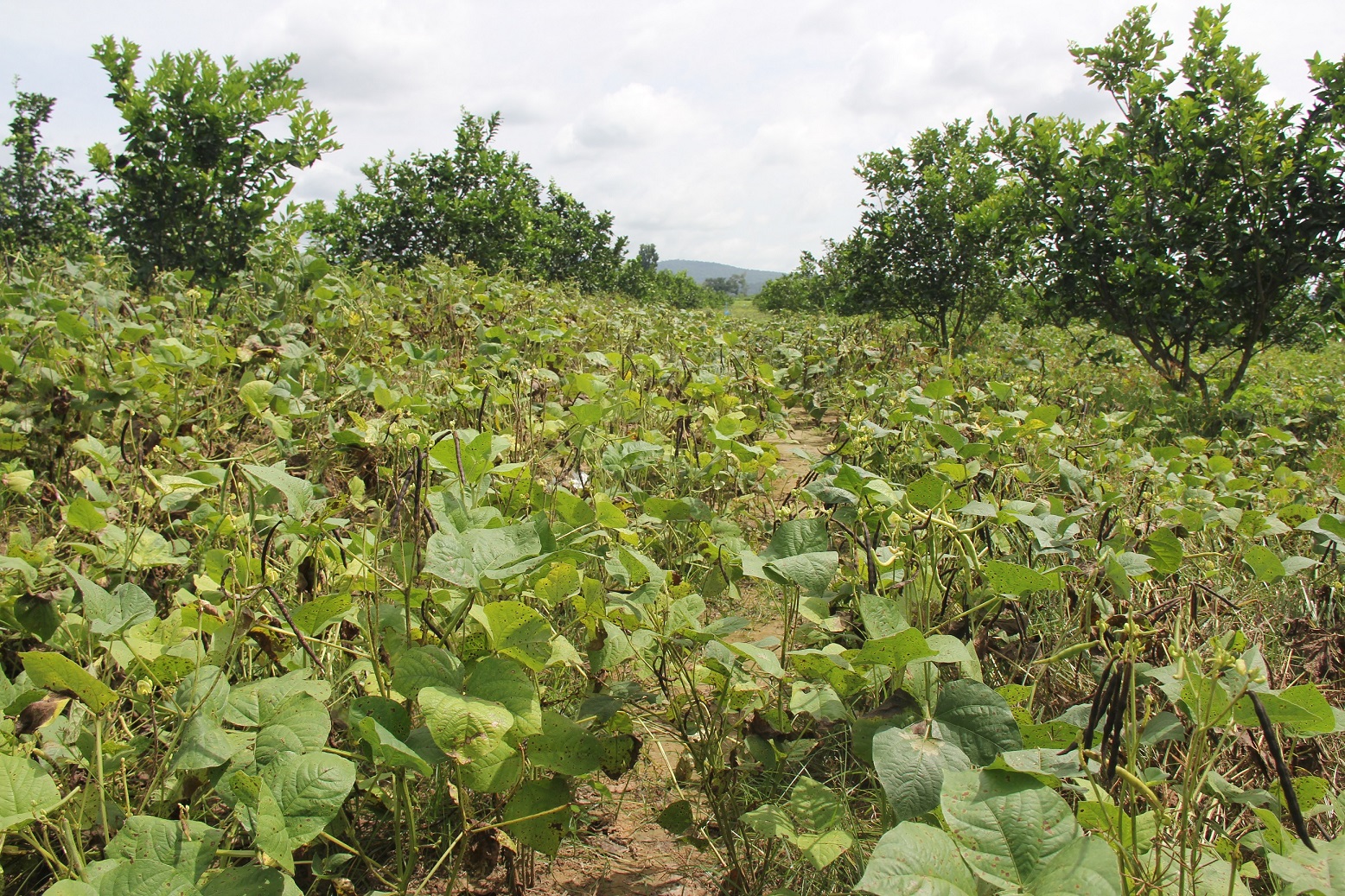
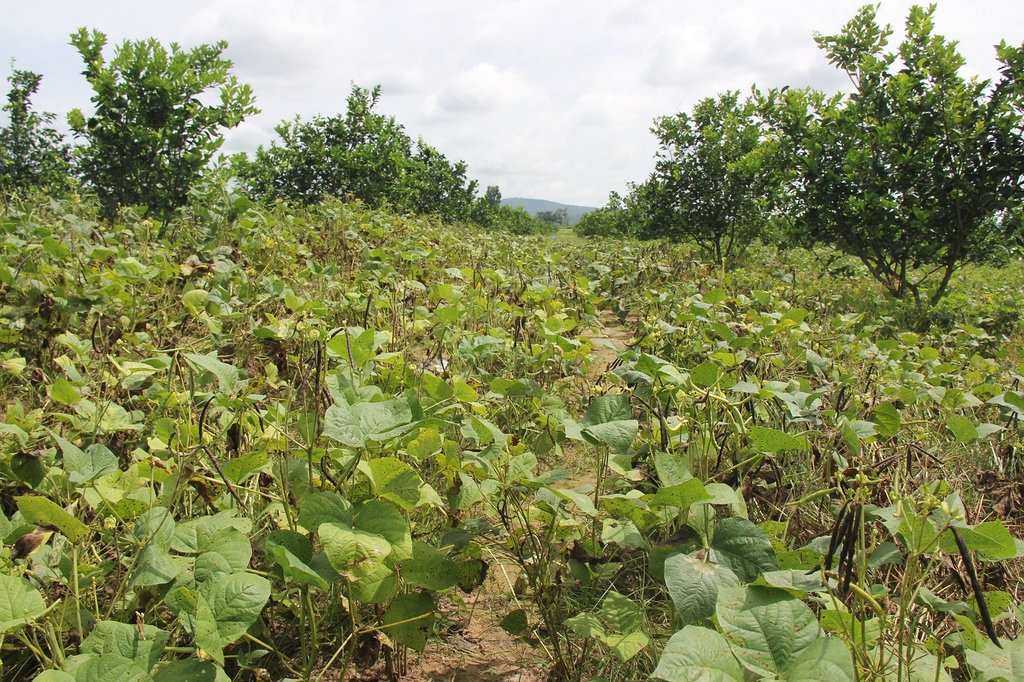
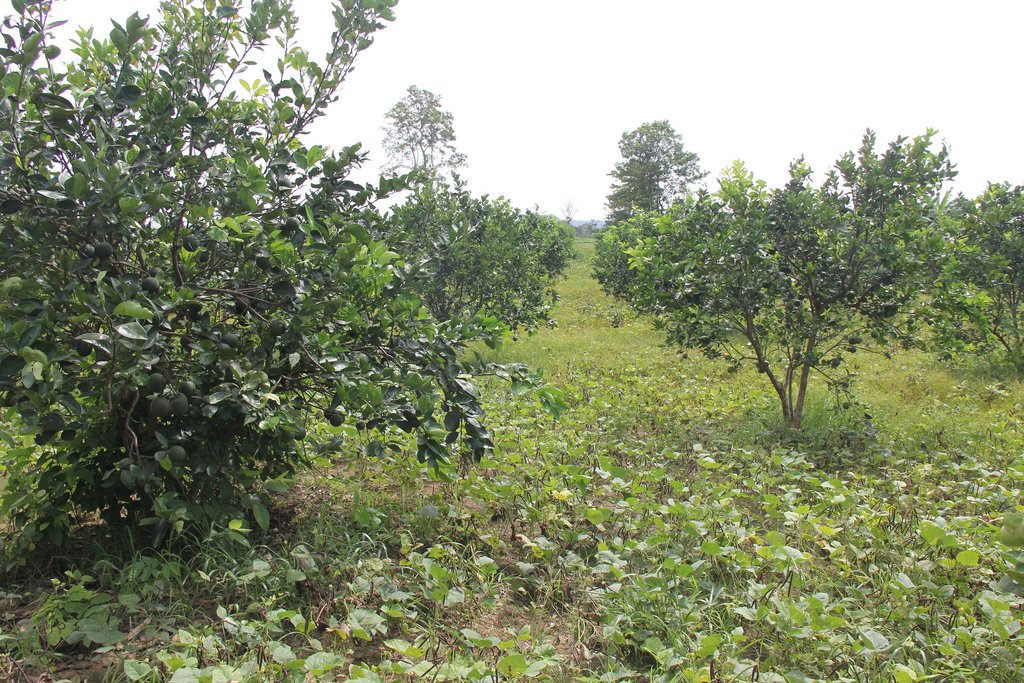
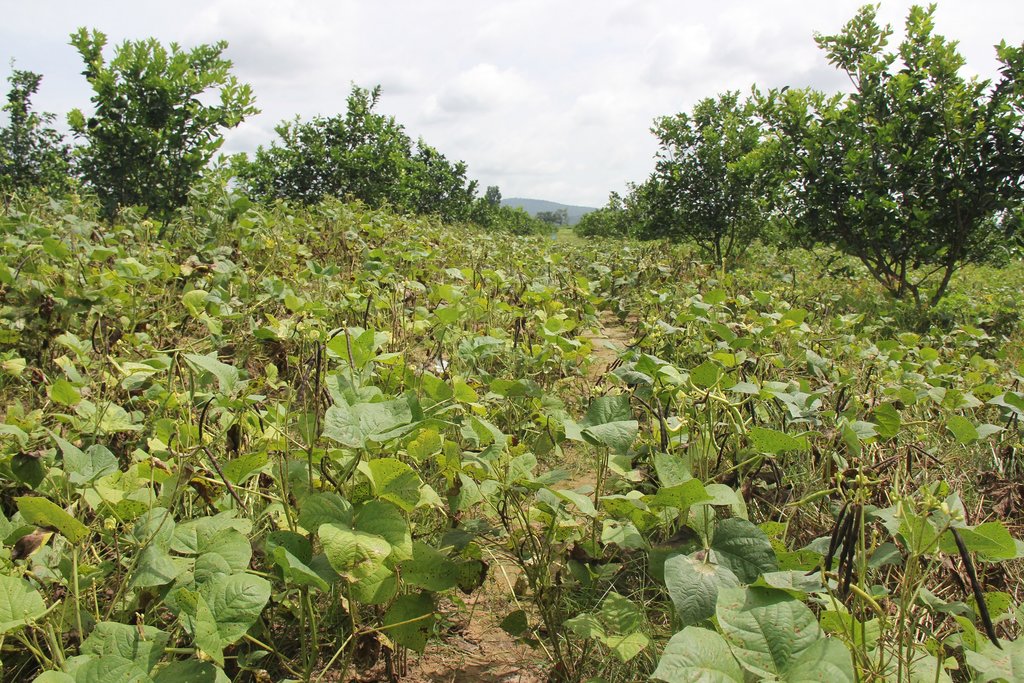
Intercropping of orange trees with mungbean in mountainous areas [Cambodia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Navin Chea
- Editores: Sophea Tim, Sok Pheak
- Revisores: Nimul CHUN, SO Than, Ursula Gaemperli
Intercropping
technologies_3146 - Cambodia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
Chea Sarith
(+855) 97 5734083
N/A
Land User
Ongkrong Village, Samrong Commune, Phnum Kravanh District, Pursat Province.
Cambodia
Acting Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh:
Doung Phanny
(+855) 97 44 222 78 / (+855) 12 17 89 577
N/A
District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh.
Prey Khlong Village, Rokat Commune, Phnum Kravanh District, Pursat Province.
Cambodia
Chief Office of Agricultural Extension at Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pursat:
Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Bakan:
Agronomic Official at District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Kandieng:
Seng Kompheak
(+855) 96 43 52 665
N/A
District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Kandieng
Kandieng village, Kamdieng Commune, Kandieng District, Pursat province
Cambodia
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
04/07/2017
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Intercropping of mungbean between orange trees improves soil fertility and generates income before the orange trees bear fruit.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Agroforestry is a farming practice that can involve growing of a mixture of woody perennials like trees, shrubs, palms, bamboos, etc. with crops and/or animals, on the same land-management units. Agroforestry systems play an important role in ecological and economical interactions between the different land use components (Lundgren and Raintree, 1982). It represents an interface between agriculture and forestry, and encompasses mixed land-use practices. Agroforestry systems are composed of three attributes:
1. Productivity (improved tree products, yields of associated crops, reduction of cropping system inputs, and increased labor use efficiency);
2. Sustainability (beneficial effects of woody perennials);
3. Adoptability (MoE/Adaptation Fund/UNEP, 2016).
In Cambodia, mungbean grows throughout the whole year almost, depending on the moisture factor. Mungbean is short maturity crop which can be grown both in sloping upland and in lowland areas. In upland areas farmers usually plant their second crop in August and harvest it in October. Mungbean is a crop that can be grown on many soil types, but grows best on alluvial, sandy, and volcanic soils which well drained containing high levels of nutrients (incl. N, P, K, Ca, Mg) and organic matter (MAFF, 2005). Mungbean crop duration depends on the variety, with short-term, medium-term and long-term being harvested between 60-65 days, 65-75 days, and 75-80 days, respectively.
Mungbean residues can make an active contribution to improvement of soil quality through nitrogen fixation and subsequent incorporation of this nitrogen into the soil after root and nodule degeneration by Rhizobium bacteria. The incorporation of the organic root material also improves the soil structure (MAFF, 2005, Chadha, 2010, IRRI-CIMMYT Alliance, 2009). The taproot of the mungbean can penetrate the soil to a depth of 50-60 centimeters. Sometimes, some land users grow mungbean as a green manure crop specifically to improve soil quality (Tauch Ung, 2010).
Mr. Chea Sarith is one example of land user who practices intercropping of orange trees with mungbean since 2013. The main purpose is to improve soil fertility, to prevent soil erosion, and to generate income before the orange trees provide fruit. In addition, it eases the weed control. After the harvest the farmer leaves the plant residues on the soil to provide organic matter. With the objective not to harm the roots of the orange trees, he avoids tilling the soil. In general, mungbean grows twice a season depending on the rainfall distribution and soil moisture.
The average yield of direct seeded mungbean as an intercrop between orange trees is about 1,200 kg/ha (harvested 3 times per crop). If mungbean is grown as a single crop the yield is usually ranges from 1,300 to 1,400 kg/ha. The market price for mungbean grain is usually about 4,500 to 5,000 Riel/kg.
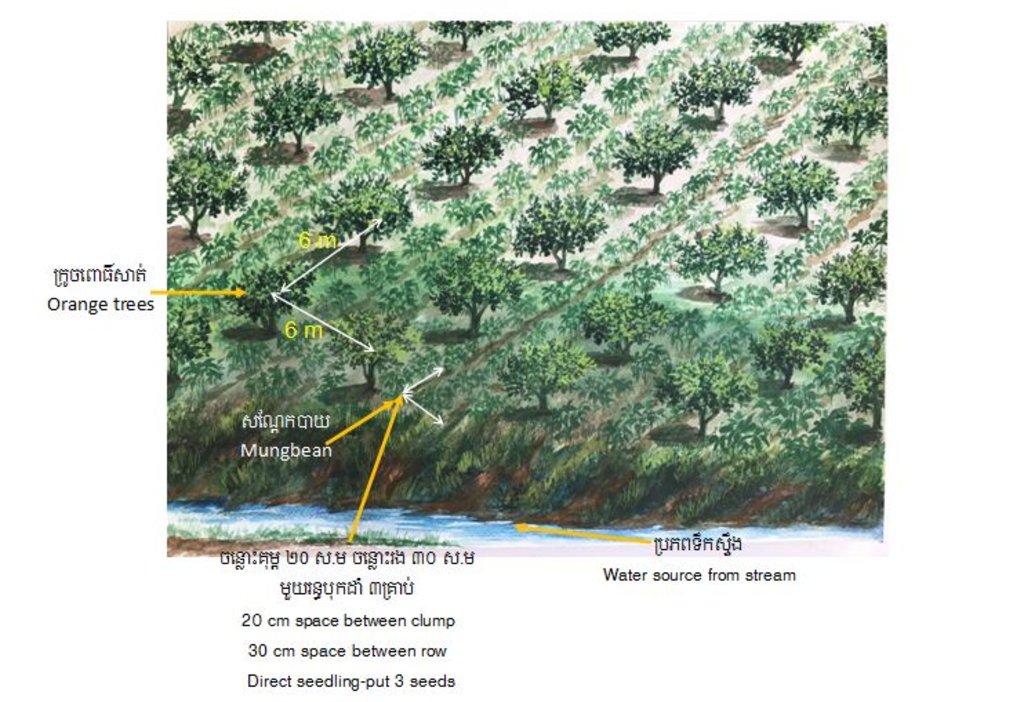
Before planting orange trees the soil requires two turns of ploughing. After first ploughing the soil should dry during 1-2 months, before it can be ploughed again by a wheel harrow. Orange trees then are planted in rows into pits of 1 m x 1 m, with a depth of 70-80 cm. The spacing between the trees, as well as between the rows is usually 6 meters. Before planting, the orange tree seedlings (bought from outside) are usually kept at the farm site for 15 to 20 days, which to allow them to adapt to the conditions of the growing environment. The farmer installed a water pipe in the underground to irrigate the fruit orchard. The nearby stream serves as water source. After the tree plantation, mungbean is sown by direct seeding on the remaining bare soil. This is done by putting 3 to 4 seeds into the seed holes (3 to 4 cm sowing depth at a plant spacing of 20 cm and a row spacing of 30 cm. After harvest the residues of the mungbean plants are squashed by machine and left to rot on the soil surface until is the next mungbean cycle starts by direct seeding.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Cambodia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Ongkrong Village, Samrong Commune, Phnum Kravanh District, Pursat Province.
Especifique más el lugar :
Phnum Kravanh of Cambodia.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2013
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
- durante experimentos/ investigación
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Through farmers experience, investigation on cropping and natural fertilizer application.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Agroforestería
Principales productos/ servicios:
Orange and mungbean.
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Degraded forest, soil from termite mound.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Comentarios:
There is a stream near the farm for supply the water for orange trees.
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Orange trees belong to the long lifespan crop which provide fruit at the age of 4 years. The lifespan of getting fruits is approximately 20 years. Then in general, the farmer cuts the trees down and grow it again. However, it depends on the yield it provides. Mungbean can be harvested within two months and half and can be harvested 3 times per crop cycle.
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- agroforestería
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A3: Tratamiento de superficie del suelo

medidas estructurales
- S7: Equipo para cosechar agua / provisión de agua/ irrigación
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
The former degraded forest soil was rehabilitated by the rotten residues of the mungbean, the deep penetration of its taproots, and by the nitrogen fixation through the symbiotic association of nitrogen fixing bacteria in the nodular roots of the mungbean. Thus, the soil structure and the soil fertility were improved little by little.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
The area of implementing this technology is 4 hectares with 1096 orange trees. The pit of planting orange trees is 1m x 1m, with a depth of 70-80 cm. The spacing between trees and between rows is usually 6 meters to get enough sunlight. The mungbean is planted by direct seedling by inserting 3 to 4 seeds per hole (the hole is 3-4 cm in depth). The spacing between the holes is 20 cm and the row spacing is 30 cm. The farmer of this farm also installed an irrigation system by setting up a pipe under the ground.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
4 hectares
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
KHR (Riel)
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
4000,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
20000
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clear degraded forest | Estructurales | January |
| 2. | Clear the termite mound to flatten the area | Estructurales | Dry season |
| 3. | Drying the soil by sunlight | Agronómicas | Dry season |
| 4. | Buy orange trees and adapt them to the condition of the area | Agronómicas | Dry season |
| 5. | Planting orange trees | Agronómicas | August |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Clear the degraded forest soil | Person-day | 80,0 | 2000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Collect the residue of forest and then burn | Person-day | 60,0 | 20000,0 | 1200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Clear 40 termite mounds in 4 hectares | Person-day | 48,0 | 20000,0 | 960000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Hire labor to carry the soil of termite mound to put in the hole of orange tree for planting | Person-day | 180,0 | 20000,0 | 3600000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Grass cutting marchine | piece | 2,0 | 1200000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Two wheel tractor | piece | 1,0 | 12000000,0 | 12000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Orange seedlings | seedling | 1026,0 | 6000,0 | 6156000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Pumping machine | piece | 1,0 | 1200000,0 | 1200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Irrigation system such as big tube, small tube etc | set | 1,0 | 8000000,0 | 8000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Planting orange trees | Person-day | 51,0 | 20000,0 | 1020000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Pesticide sprayer machine | piece | 3,0 | 600000,0 | 1800000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Spraying pesticide hand pump sprayer | piece | 1,0 | 280000,0 | 280000,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 38776000,0 | |||||
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering during dry season in the first year of planting orange trees | Agronómicas | Two times per day during dry season |
| 2. | Spraying pesticides when there is present of insects on orange trees | Agronómicas | Spray once time per season |
| 3. | Pruning some branches of orange trees | Agronómicas | When the orange trees 2 years (One year cut some branches once time) |
| 4. | Apply organic fertilizer for the orange trees | Agronómicas | When the orange trees are 4 years |
| 5. | Spray against weeds | Agronómicas | Spray once time per half month. |
| 6. | Spray pesticides on mungbean plants | Agronómicas | When mungbean flowering |
| 7. | Direct seeding of mungbean | Agronómicas | August |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Watering the orange trees | Person-day | 11,0 | 20000,0 | 220000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Pruning some branches of orange trees | Person-day | 100,0 | 20000,0 | 2000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Hire labor to spray pesticides | Person-day | 8,0 | 20000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Hire labor to harvest mungbean when mature | Person-day | 120,0 | 20000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Mungbean seed (1 hectare need 25 kg of mungbean) seeds) | hectare | 4,0 | 312500,0 | 1250000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Pesticides for orange trees | bottle | 4,0 | 40000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Chemicals for improving of stem of mungbean | package | 60,0 | 1500,0 | 90000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Pesticide to kill worms on mungbean | bottle | 2,0 | 40000,0 | 80000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Direct seeding of mungbean | Person-day | 56,0 | 20000,0 | 1120000,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 7480000,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
The maintenance costs then depend on the age of orange trees. The cost calculation of maintenance of orange trees is for year period, but the the recurrent costs for mungbean cultivation is calculated only for one crop cycle (two months and half).
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The establishment of an orange tree orachard requires a lot of money.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1225,70
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
In 2015 the annual rainfall is 1225.7 mm, in 2014 is 1128.1 and in 2013 is 1316 mm.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Ministry of water resources and meteorology, 2015
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
On Phnum Kravanh mountain area.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
PH=6
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
Comentarios:
The total crop land is 15 hectares.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
Comentarios:
There is free access of water stream nearby. He never has water usage conflict.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The soil fertility was improved, so that the crop production increased steadily. In addition, the farmer now doesn't grow only orange trees, but he also grows mungbean.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The residues of mungbean contain many nutrients, which is suitable for getting good crop quality.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the farmer plants more than one crop on the plot now, it reduces the production failure. This means that farmer get income from mungbeans before the orange trees provide fruits. The better weed control also reduces insects, which could be harmful to the crop.
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
There are mungbean and orange trees, now.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced chemical fertilizers on orange trees and mungbean, because after harvesting mungbean residues are kept on the soil which is very good green manure for soil.
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
The farm income increases considerably due the intercropping system, as both mungbean and orange trees provide yield. In addition, mungbeans provide yield two times per year. Last but not least , mungbean play a key role as green manure which reduces the input of chemical fertilizers and therefore cost.
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The mungbean and orange tree cultivation does not consume much of labor force because he doesn't have to spend a lot of time for weeding (as instead of weed mungbeans cover the soil now). On the other hand, the farmer mentioned that the orange plantation is time consuming at the beginning, when the orange trees has to be planted. As well the mungbean need more time at the moment when the plot has to be prepared for first direct seedling. But the technology as a whole entails not a lot of maintenance workload as he uses machinery such as pesticide sprayer machine and mungbean squash machine to facilitate the labor.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
The diversification of the crops (oranges and mungbean) has considerably raised the income and therefore strongly prevent food insecurity situations.
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
The reduction of chemical fertilizer and pesticides provides safer products that improves the health situation. In addition, mungbean and orange fruit deliver many nutrition benefits to human health.
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
He has joined the orange trees community to sell the orange fruits. Many researches are convinced of his success and the tastiness of his oranges; as for example researchers from the District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh, Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pursat etc.”
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
By doing the farmer learned that degraded soil can be rehabilitated by the mean of mungbean residues acting as green manure. And from the moment the soil is rehabilitated he can see that this green manure prevents soil degradation at high degree.
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Mungbean and orange trees keep the soil moisture, prevent the evaporation to the atmosphere.
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Orange trees and mainly the mungbean intercrop cover the soil almost entirely all year around.
compactación de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The residue of mungbean reduce soil compact by improving the soil structure through providing organic matter to the soil. The increased amount of soil organisms make the sol less compact.
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
The residues of mungbean left on the soil after harvesting are transformed to organic matter by the process of decay and therefore contribute essentially to increased soil organic matter.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Orange trees and mungbeans are the vegetation cover to avoid bare land, so the sunlight will not come directly to the the soil.
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
There is more than one crop (orange trees and mungbean).
especies benéficas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Now, the soil is somewhat richer in termites, ants, earthworms, crickets ect.
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
Orange trees and mungbean cultivation promote soil organisms in the habitat.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien | |
| temperatura estacional | estación húmeda/ de lluvias | incrementó | moderadamente |
| temperatura estacional | estación seca | incrementó | bien |
| lluvia anual | incrementó | moderadamente | |
| lluvia estacional | estación húmeda/ de lluvias | incrementó | moderadamente |
Comentarios:
Change in rainfall. If there is too much rain, the soil will be saturated and the root will be spoiled what reduces the yield of mungbean.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
When the orange trees grow bigger, it will provide very high income.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 90-100%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Get income from the mungbean before orange trees provide fruit as a potential source of income. |
| The residues from the mungbean plants help to improve soil fertility. |
| The potential market of orange tree fruits is good, with traders buying directly from producers at the farm. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Residues of mungbean improve soil fertility, reduce soil degradation and help rehabilitate the degraded land. |
| In the initial 3 to 4 years of growth of orange trees it is important to grow short term crops like mungbean to provide an income source. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Orange trees require a lot of water. | Grow near a water source such as a stream or river, or dig ponds to hold water. Land users need to consider a potential water source. |
| When the soils become saturated due to excessive rain, the mungbean plant roots can degenerate and result in low grain yields and low grain price (due to poor grain quality). | There is little that farmers can do to improve the performance of the mung bean crop in conditions of soil moisture saturation. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| As the orange trees grow bigger there is reduced opportunity for intercropping with mungbean. | Grow intercrops that do not require much sunlight, such as ginger or galanga |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
One place
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
one person.
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
4 persons
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Chadha, M. L. (2010). Short Duration Mungbean : A New Success in South Asia.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
N/A
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
MoE/Adaptation Fund/UNEP. (2016). Forest Restoration and Rehabilitation “ Enhancing Climate Change Resilience of Rural Communities Living in Protected Areas in Cambodia .”
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Ministry of Environment(MoE). Free of charge.
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
MAFF. (2005). Mung bean.
URL:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from http://www.maff.gov.kh/agri-tech/56-ដំណាំឧស្សាហកម្ម/ការដាំដុះសណ្តែក/1519-ដំណាំសណ្តែកបាយ.html
Título/ descripción:
Tauch Ung. (2010). Overiew of mung bean.
URL:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BwhP4tVirBPsOTM3OWFiMzktZTdmNi00NjMyLTg1NjktMzFhYzhmMzUyMjVl/view?hl=en
Título/ descripción:
IRRI‐CIMMYT Alliance. (2009).The importance of legumes in cereal cropping systems.
URL:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/images/pdfs/the_importance_of_legumes_in_cereal_cropping_systems.pdf
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos