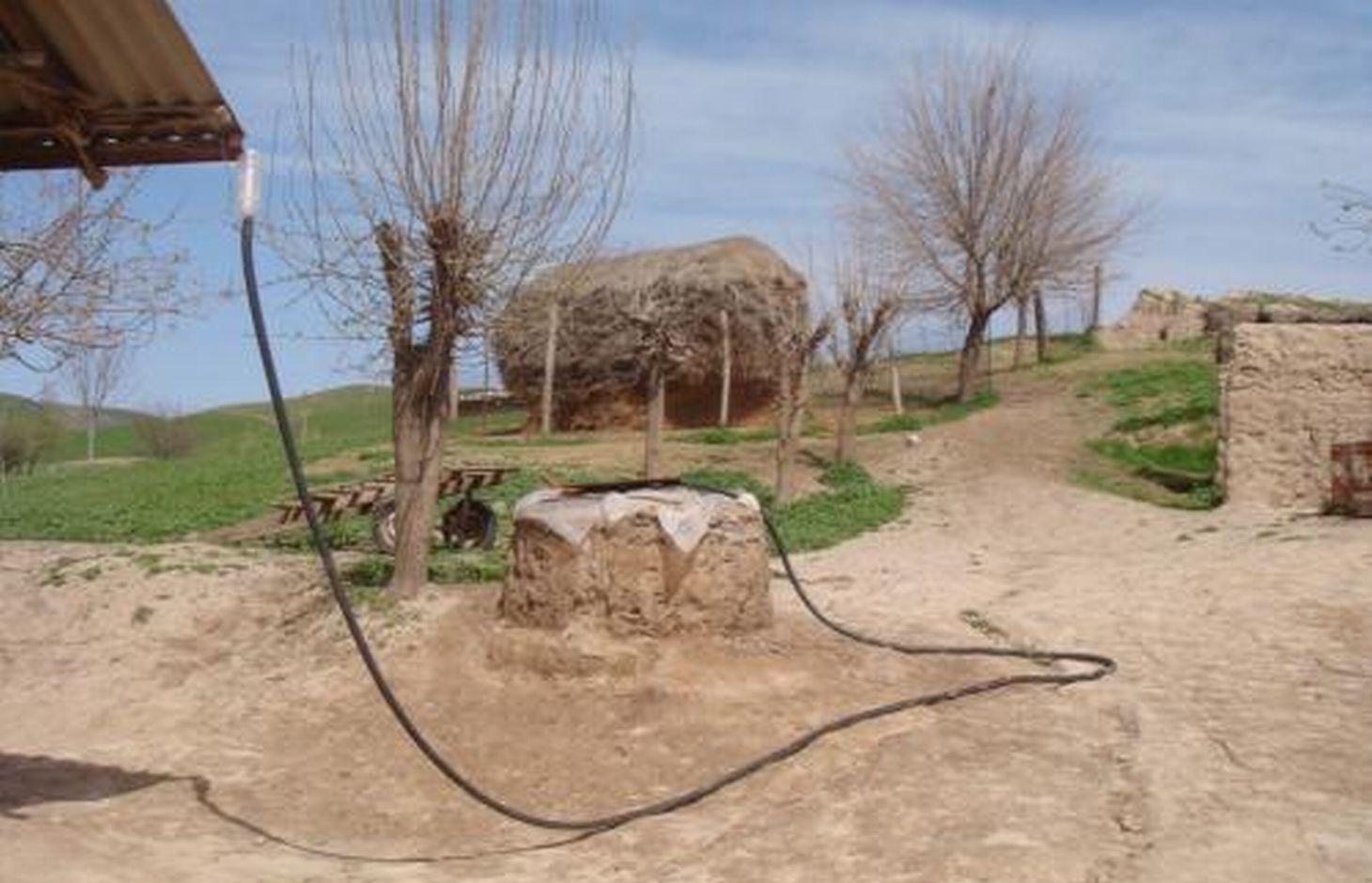
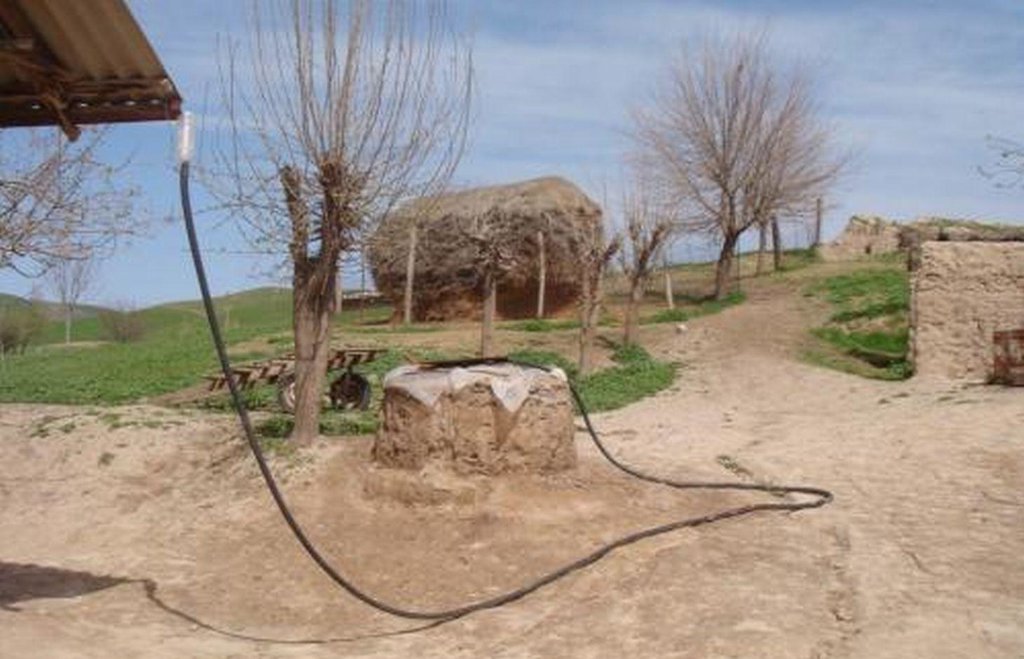
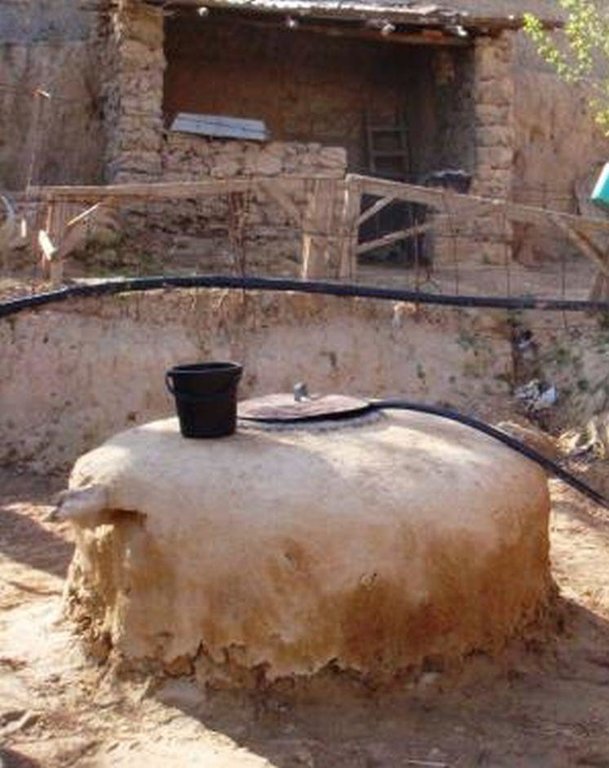
Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank. [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Daler Domullojonov
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
Чамъоварии оби борон аз руи боми хона
technologies_1446 - Tayikistán
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 2 de noviembre de 2021 (public)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 4 de abril de 2018 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 15 de agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 19 de julio de 2017 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 6 de mayo de 2017 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 14 de marzo de 2017 (inactive)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe (Welthungerhilfe) - TayikistánNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience Tajikistan (PPCR Tajikistan) - Tayikistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
06/04/2011
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
The use of an earth tank lined with a polyethylene sheet to retain rainwater collected from the roof of the house.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
An earth retention tank is a simple low cost structure that can be used to retain rain water from the rooftop. A hole is prepared and lined with a polyethylene sheet to prevent leakage. The top of the hole is covered with a metal lid for access. The roof of the house is fitted with a plastic guttering that captures the rainwater and funnels the water via a plastic pipe into the earth tank. The water in the earth tank then can be utilised for the irrigation of crops (especially during the hot dry summer months), sanitation, and potentially drinking water.
Purpose of the Technology: The population in Southern Tajikistan consists largely of subsistance farmers and are thus highly reliant upon their kitchen garden plots. As the population in the area continues to expand, the pressure on the land increases. The latter is already in a poor state, because it is becoming degraded through deforestation, overgrazing and general over exploitation. There is much precipitation during the rainy season from autumn until spring in Southern Tajikistan, but the scarcity of water from late spring to the end of autumn poses a problem with water shortages.
During the rainy season, a lot of water is lost as surface runoff, this water can be saved in a retention tank to be utilised during the dry season. It can be used to water crops to help increase yields as well as crop diversity and quality. The additional water can also be used for sanitation, drinking water and watering of livestock.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of such a retention tank several steps are needed. In preparation, a rough estimation of the potential volume of harvested rainwater needs to be calculated. Thereafter, a location for the tank needs to be selected so that expenses are minimised and it is easy to access. The establishment of ponds near big trees is not recommended, because the polyethylene layer might be punctured by the roots.
Natural / human environment: The actual steps of constructing the tank involve:
(1) digging the pond, (2) plastering the inside walls with a fine soil and water mixture to smooth them, (3) lining the pond’s walls with double polyethylene layer, (4) connecting the inside polyethylene sheets with the pond coverage through a piece of cord, so that it can be taken out of the pond any time to be cleaned of sediments, (5) covering the pond with any available material such as a soil, water and straw mixture, reinforced by several poles, leaving an opening of 0.25 x 0.25m to extract water, (6) finally connecting the roof to the pond with a plastic pipe. To avoid dirty water flowing from the roof into the pond, the pipe should only be connected to the pond some time after the rainfall has started.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Khatlon province
Especifique más el lugar :
Temurmalik, Baljuvon
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology was developed through a Welthunger Hilfe Project and promotion in the local communities started in 2008.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

asentamientos, infraestructura
- Asentamientos, edificios
Comentarios:
Kitchen garden
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Inefficient natural resource management, which is mainly visual because people throw potential organic fertilisers away instead of spreading them on the fields. Incorrect ploughing techniques which leads to the acceleration of erosion, deforestation and waste of fuel materials in inefficient stoves and ovens. Overgrazing leading to pasture degradation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): lack of water
Constraints of settlement / urban
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cosecha de agua
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 10-100 km2
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques
Comentarios:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de subterráneas
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification, Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Inproper land management), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Cutting trees and shrubs), overgrazing, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (poor water supply)
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure (the population is increasing over time.), poverty / wealth (lack of funds)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Autor:
Daler Domullojonov, 14, Giprozem str., Dushanbe, Tajikistan
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Harvesting water from the household roof to an earth built retention pond with plastic sheet lining. The retention pond is covered with a removable metal plate for access.
Location: Davad village, Vatan jamoat, Temurmalik district,. Khatlon province, Tajikistan
Date: June 2009
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (No special knowledge is needed for implementation)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Any farmer can implement, once they understand the basic concept.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Construction material (earth): digging in earth, plastering and cover
Construction material (wood): pole for cover
Construction material (other): polyethelene sheets, plastic pipe
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 3.96m3
Catchment area: 72 m2m2
Beneficial area: 0.2h.am2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:0.5
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
TJSomoni
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
4,5
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
6.60
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Manual digging of pond;smoothing and plastering;covering pond | Estructurales | once in the beginning |
| 2. | polyethylene sheet and pipe procurement, preparation and placement; | Estructurales | once in the beginning |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Manual digging of pond | Persons/day | 2,0 | 30,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Placing sheet | Persons/day | 0,1 | 30,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Wooden poles for pond | poles | 4,0 | 5,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Earth | tons | 0,1 | 45,0 | 4,5 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Polyethylene sheet | square meters | 10,0 | 2,3 | 23,0 | 50,0 |
| Material de construcción | Cord | meter | 20,0 | 0,025 | 0,5 | 50,0 |
| Material de construcción | Plastic pipe | meter | 5,0 | 2,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Bucket | pieces | 1,0 | 4,5 | 4,5 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 125,5 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of pond (washing out sediments) | Estructurales | once every year |
| 2. | Changing polyethylene sheet;covering | Estructurales | once every 2 years |
| 3. | Changing polyethylene sheet;covering | Manejo | once per 2 years |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Cleaning of pond (washing out sediments) | Persons/day | 0,1 | 45,0 | 4,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Changing polyethylene sheet (every 2 years) | Persons/day | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Polyethylene sheet | square meters | 10,0 | 2,3 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Cord | square meters | 1,13 | 8,85 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Earth | tons | 0,05 | 45,0 | 2,25 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 49,75 | |||||
Comentarios:
The above costs were calculated for the building of one retention tank. One household could have several ponds in one kitchen garden.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The type of earth in Tajikistan is very good for making the retention ponds, the labour is provided by the land user, and the plastic pipes can be manufactured out of empty plastic bottles. The polythene sheet and cord have to be purchased from the shop.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Average annual precipitation is 575 mm (according to data from the last 15 years), most of which falls between late autumn and spring time.
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate. 3 months below 5 degrees, 7 months above 10 degrees
Continental conditions
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zone: Mainly communities in this range
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is medium and if it is not overused the fertility can be increased.
Topsoil organic matter: Usually locals collect cow dung and use it as fuel.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium because the loess material contains clay material
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table can also be below 50 m.
Availability of surface water is so poor du to deforestation the natural water balance is disturbed.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: In this example the farmer's son has migrated to Russia.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- individual
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
producción de forraje
producción animal
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Cantidad antes de MST:
120 litres
Cantidad luego de MST:
12000 litres
Comentarios/ especifique:
Water storing capacity of household increased
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
100
Comentarios/ especifique:
vegetables and greens are available for own consumption
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
no need to carry water
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
more water available
cosecha/ recolección de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
more water available
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
only in kitchen garden
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
Comentarios:
To minimise the damage to the polyethylene waterproofing layers and, reduce evaporation rates, pond is covered. As the pond is dug into earth the temperature remains fairly stable. If precipitation decreases less water can be harvested.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Before the implementation of this technology, one family would spend an avarage of $44.5 on one truck of water per month. A pond costs around $25 to build, and should provide families with around 4 months worth of water after the rainy season.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- más de 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
600 households (in an area of 10-100km^2)
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 10-50%
Comentarios:
58% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
350 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: In the initial stages of the project, they were provided with 50% of the costs of the polyethylene sheets and cord only.
42% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: After observing the benefits of the technology and the high cost benefit ratio, many people in the community and surrounding villages have replicated this technology themselves.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Easy and quick to establish, and maintain. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
It is a low cost technology and can be made from many locally available materials. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To disseminate these ideas in areas with water scarcity through local Extension Service providers / NGOs or local inhabitants. |
|
It reduces the time and effort to collect water and also the cost to buy water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promotion of different water saving methods and technologies by interested and line departments. |
| More water available for gardening and household purposes |
|
Increases access to water for drinking and sanitation purposes. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Construction of larger and/or more tanks. |
|
Provides water for irrigation during the hot dry months, therefore improving crop diversity and yields. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training and education on kitchen garden farming techniques to optimise the use of the extra water supply. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The polyethylene only lasts for 2-4 years. | To increase the number of layers or use a thicker polyethylene sheet |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The plastic layers have a limited lifespan. | To find thicker and more hardy materials, or apply multiple layers. |
| Th waterproof layer can easily be degraded by mice and large insects. | |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Brochure - Converting drought prone areas into productive gardens! Low cost options to improve rainwater harvesting in Southern Tajikistan rain fed areas …. and beyond! 2009
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Welthungerhilfe, Temurmalik office,
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Training film - Simple ways to improve management of kitchen gardens in Southern Tajikistan rain fed areas …. and beyond. 2009
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Welthungerhilfe, Temurmalik office
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Welthungerhilfe project final narrative report (144-912) - 2010
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Welthungerhilfe, Temurmalik office
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos