Slope erosion control using wooden pile walls [Armenia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Hanns Kirchmeir
- Editor: Artur Hayrapetyan
- Revisor: Ursula Gaemperli
technologies_4092 - Armenia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Mnatsyan Aghasi
+374 (0)96001193
aghasi.mnatsyan@giz.de
GIZ
4/1 Baghramyan Street, 0019 Yerevan, Armenia
Armenia
Especialista MST:
Khachatryan Hrant
+374 94 839083 / +374 91 926092
hkhachatryan84@gmail.com
ESAC NGO, Armenian National Agrarian Univercity
Yerevan, Davit Anhaght 23
Armenia
Especialista MST:
Huber Michael
0043463504144-24
huber@e-c-o.at
E.C.O. Institute of Ecology
Lakeside B07b 9020 Klagenfurt
Austria
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Integrated Biodiversity Management, South Caucasus (IBiS)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
03/10/2018
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST

Estabilización de laderas de manera participativa [Honduras]
La bioingeniería comprende una serie de técnicas que utilizan materiales vegetativos vivos para prevenir la erosión y el deslizamiento de laderas y taludes. Las obras de bioingeniería se aplican a base de un análisis integrado de riesgo, son de multi-uso en su conjunto, tienen un bajo costo de construcción y …
- Compilador: Helen Gambon
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Small horizontal wooden structures and terraces on eroded slopes built to mitigate sheet or rill erosion and slow down water run-off. The technology is easy to apply and efficient to mitigate erosion processes of the upper soil layer and to stop small rock falls.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
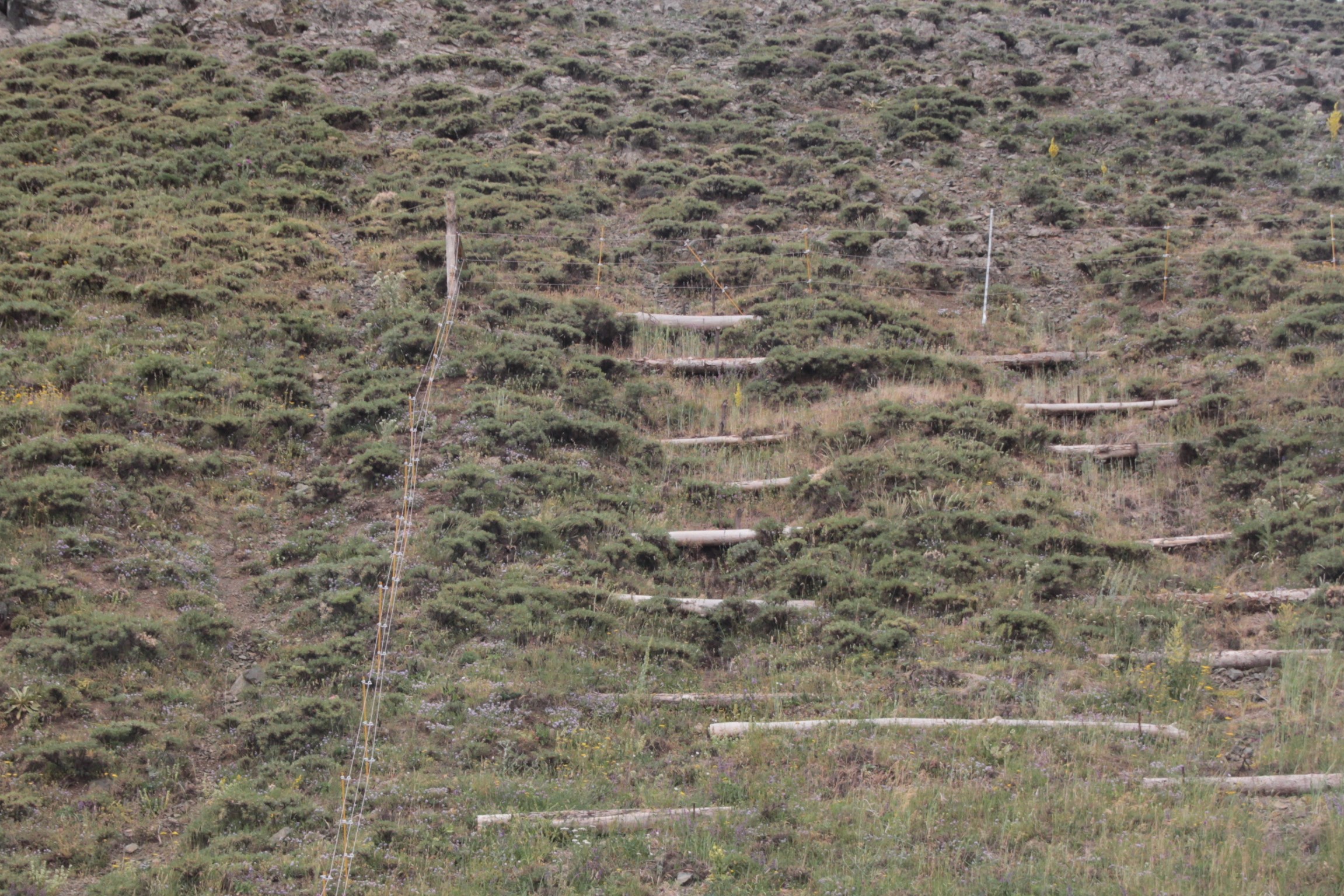
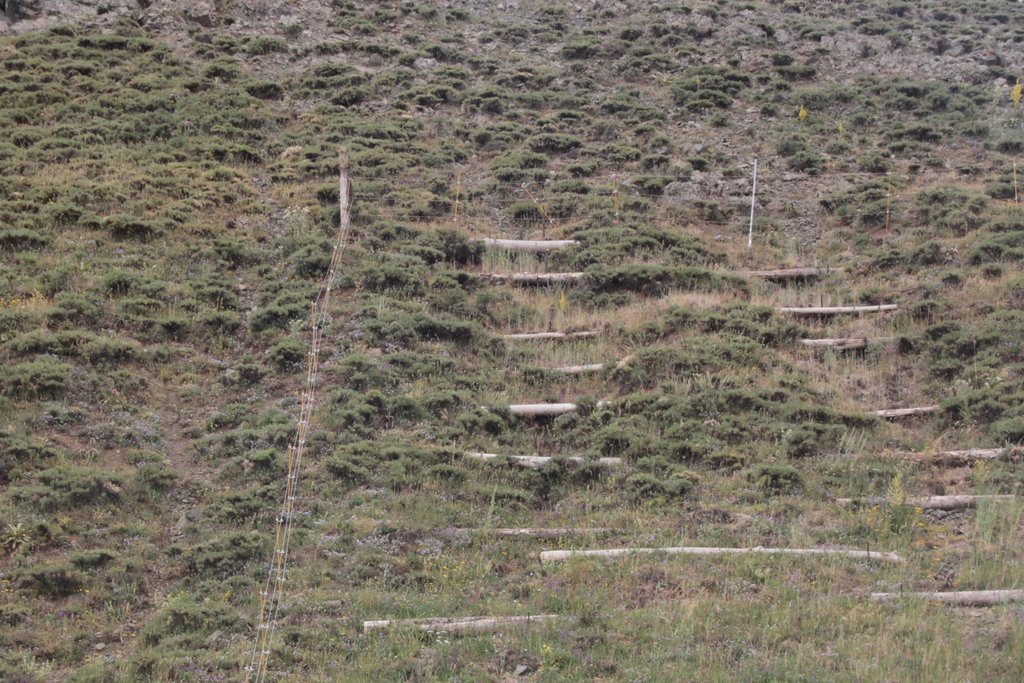
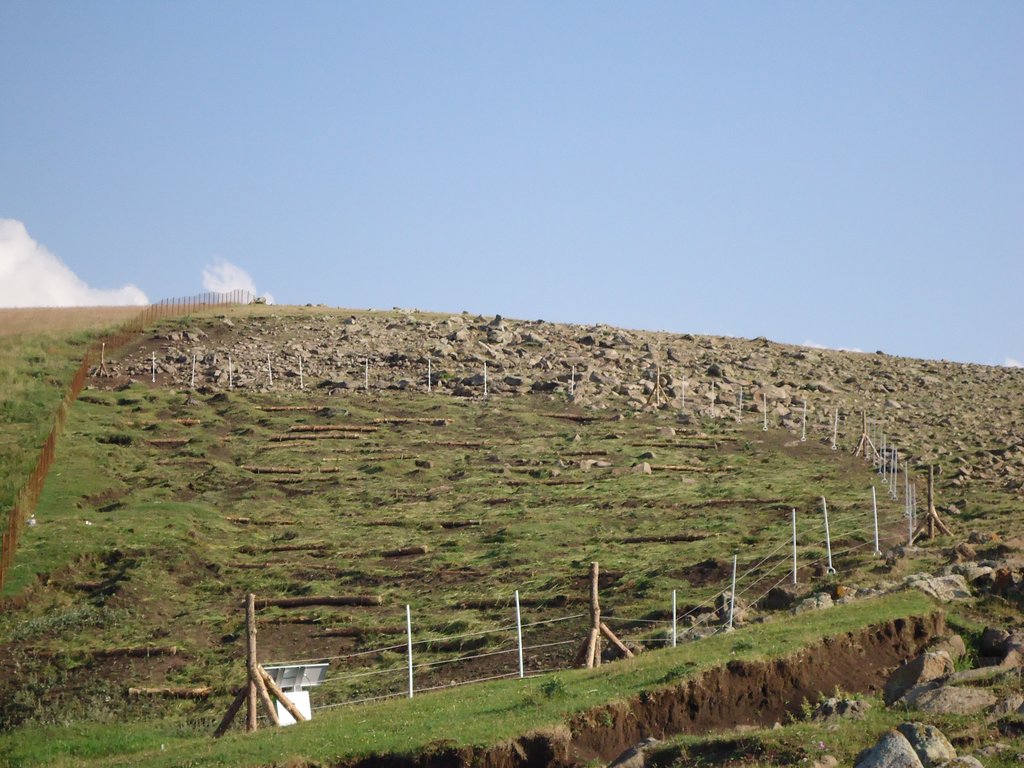
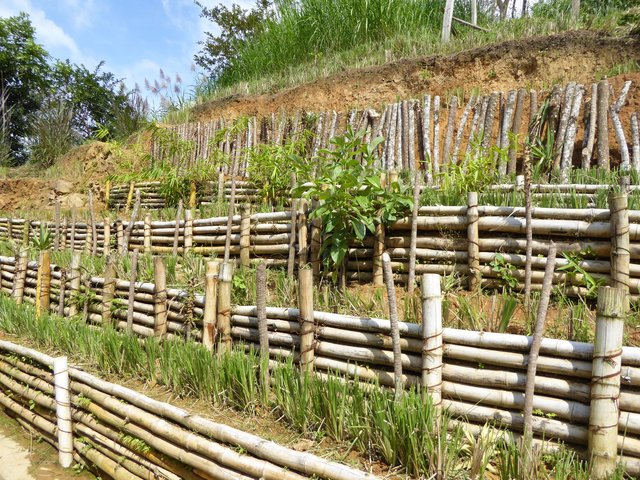
In the provinces of Aragatsotn and Shirak in Armenia, the weather is cold and temperate with dry summer. Steep slopes, pastures and some autochthonous oak forests make up the area. Farmers make most of their income with grazing by manual labour. The carrying capacity of pastures in the vicinity is regularly exceeded, and they degrade more and more. In order to stabilize the steep eroded slopes, pile walls were established. Pile walls are horizontal constructions along a slope, functioning as erosion control measures by slowing down the superficial water runoff, retaining materials and supporting the rehabilitation of vegetation.
The major advantages are: It is not expensive since mostly locally available materials can be used, and a positive effect can already be observed within a year. Also, the pile walls can be established relatively easy without any need of heavy machinery or specific knowledge and, therefore, allow the involvement of the local population.
In the case of the implementation in Armenia, the exact location for the pilot measures was selected in such a way that grazing activities were almost not impaired. For temporary exclusion of livestock, electric fencing was used. Within the fenced area, pile walls were established in the washed-out rills along the slope to address the water erosion phenomena.
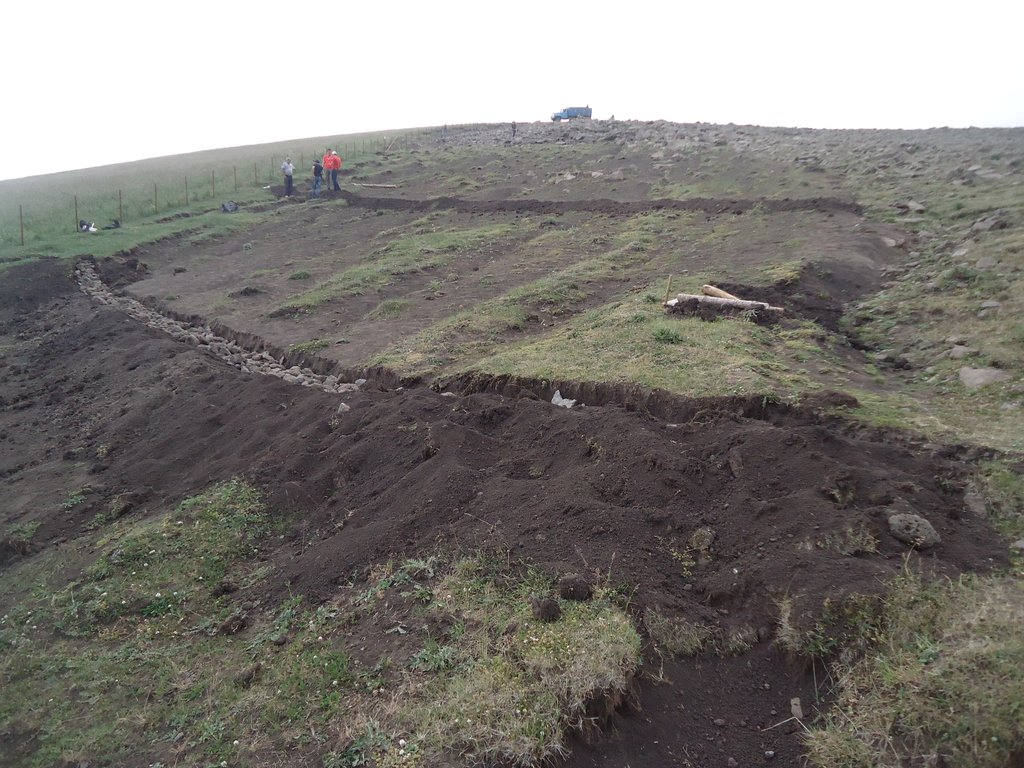
The technical requirements and workload for the construction of a pile wall are relatively low. The needed resources require iron piles, a hammer, wooden logs (or a bundle of branches) and tree cuttings. First, the wooden logs were cut in 1-2 m length to fit into the irregular rills of the slope. After identifying the locations of individual pile walls, the team fixed the logs with iron poles of about 70-100cm length. The distance between the pile walls varies between 1-3m, depending on the topography: the steeper the slope, the closer the distance. The space behind the logs was filled with soil, plant material and rocks to stabilize the construction and to reduce the risk of water washing out the soil and passing below the logs. As a last step, the terraces were covered with hay to provide protection against precipitation and to accelerate re-growth of grass through the seeds contained in the hay residuals.
Community members were surprised how easy and quick the pile walls could be established. A team of two workers established a pile wall within 30 min. Since these areas are usually intensively used and thus are of high importance for the community, even a temporary exclusion from use must be thoroughly discussed and agreed upon.
The measure slows down vertical water-run off and provides steps for cattle. Due to temporary fencing and the application of hay mulch vegetation is recovering on these parts.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Comentarios, descripción breve:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Apt2D9i18a0
ESAC Project Video
Fecha:
27/03/2018
Lugar:
Argatsotn/Shirak Marz
Nombre del videógrafo:
ESAC
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Armenia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Aragatsotn and Shirak Marzes (Provinces)
Especifique más el lugar :
Lusagyugyh, Hnaberd, Ghegadhzor, Saralandj, Mets Mantash
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierra de pastoreo
Tierras de pastoreo extensivo:
- Semi-nomadismo/ pastoralismo
Especies y productos animales principales:
cattle (and sheep)
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
0.89-1.30 pasture load/ha
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- perturbación mínima del suelo
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas estructurales
- S1: Terrazas
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
- Wm: movimiento de masas / deslizamientos de tierra

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
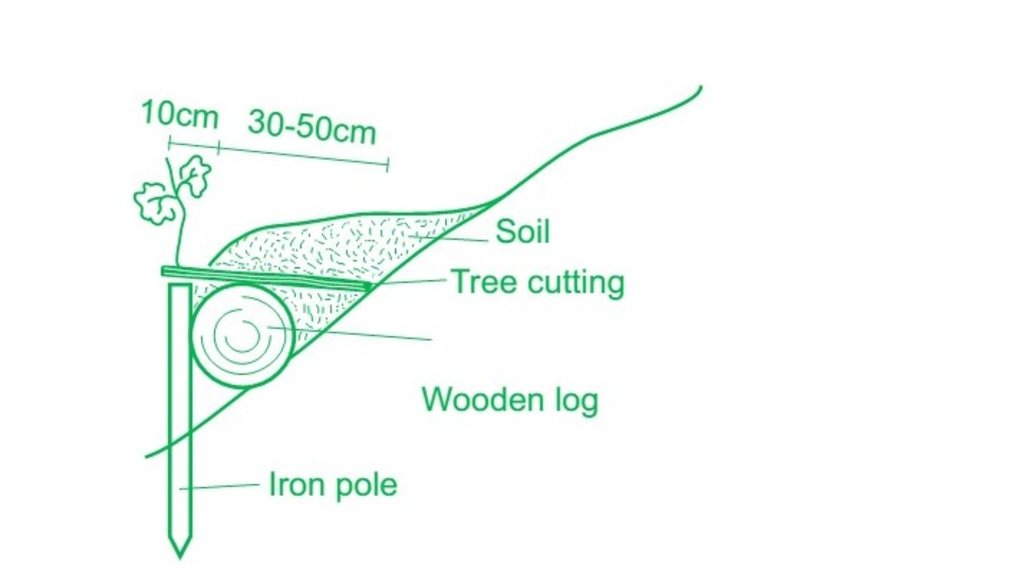
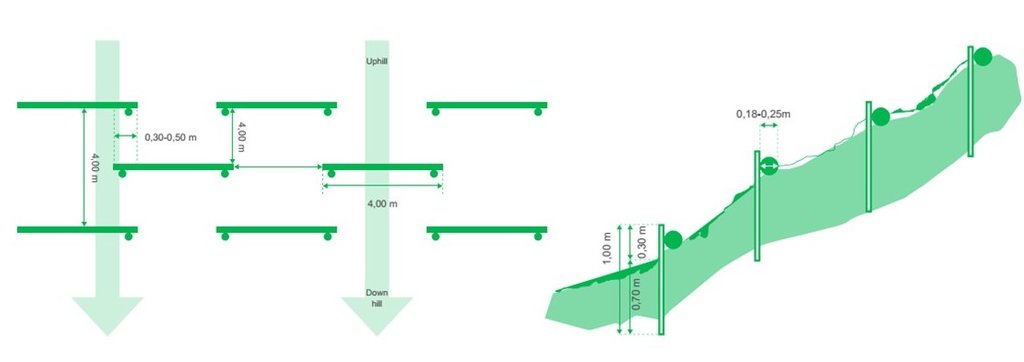
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Required materials for 1 pile wall:
- 2 iron poles (0.7-1m) and a hammer
- 1 wooden log (ca. 4 m, 20-25cm diameter)
- 10-20 shrub cuttings (e.g. Salix species)
Selection of appropriate sites for pile walls (where and how to put them):
The logs are being spread on the slope as indictated in the scheme of the figure. The steeper the slope the narrower the vertical spacing in between (max. 4m, min. 1-2 m). On uneven slopes, place the along the depressions as these are the areas where water-run off is strongest. Parts which show no erosion signs can be left out to not destroy existing vegetation cover. The location of the pile walls is determined by the slope and serves to stabilize the slope at superficial level (10-30 cm). It landslides occur that involve deeper soil layers, this technology is not efficient.
Building process:
After placing the logs, those are fixed with two irons at the end (alternatively wooden posts can be used as well). After fixing the logs, the space behind needs to be filled (slight terracing of the slope). Additionally, either shrub seedlings or living cuttings from species such as willows (ca. 50cm long, 2-5cm diameter) should be integrated. Finally, the open soil should be covered by a layer of 2-5 cm of hay/grass containing seeds and eventually additional seeds (from local species) to promote the re-establishment of vegetation. This has also the benefit that this cover keep humidity in the soil, which is particularly important in (semi-)arid areas.
Species used/density:
At least 20 cuttings per pile wall should be planted. Depending on the survival rates, it can be also more. Shrubs additionally stabilize the slope and are to some extent protected by the pile wall.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
0.15 ha
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
ca. 20 USD per worker and day (unskilled local workers), 120 USD per day (local expert)
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of eroded sites and size | Manejo | anytime |
| 2. | Clarification of land user rights | Manejo | anytime |
| 3. | Calculate amount of logs and irons needed | Manejo | anytime |
| 4. | Materials check: Local materials and procurement of other materials | Manejo | anytime |
| 5. | Place logs on the eroded slope (favor depressions where water flows are) | Estructurales | anytime (best in spring and autumn) |
| 6. | Fix logs with two iron poles at both sides of the log | Estructurales | anytime (best in spring and autumn) |
| 7. | Fill the space behind the log with soil, rocks and (willow) cuttings | Estructurales | early spring or late autumn (willow cuttings without leaves) |
| 8. | Flatten the area behind the log (small terracing) | Estructurales | anytime (best in spring and autumn) |
| 9. | Use additional hay/grass mulch to cover open soil and add additional seeds | Vegetativas | best in spring (alternatively in late autumn) |
| 10. | If it is grazing area: Fence the area for at least 2-3 vegetation periods | Manejo | during grazing period |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Unskilled worker: Implementation of field measures | person days | 30,0 | 21,0 | 630,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Skilled expert (Implementation supervision and project management | person days | 14,0 | 120,0 | 1680,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Transportation costs (truck, experts) | rental days | 12,0 | 54,0 | 648,0 | 10,0 |
| Mano de obra | Administration costs | month | 1,0 | 127,0 | 127,0 | |
| Equipo | Consumables | set | 1,0 | 59,0 | 59,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipo | Electric tools | set | 1,0 | 424,0 | 424,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipo | P3800 Fence energizer + Box and equipment | set | 1,0 | 345,0 | 345,0 | |
| Equipo | Solar Panel for fence energizer | piece | 1,0 | 233,0 | 233,0 | |
| Equipo | Battery and fence tester | piece | 1,0 | 203,0 | 203,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Cuttings (20 per pile wall) (not used as it is being grazed) | pieces | ||||
| Material para plantas | Hay/grass for mulch cover (Bales ca.20kg) | kg | 800,0 | 0,08 | 64,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Wooden logs (3m, 20cm diameter) | pieces | 50,0 | 17,0 | 850,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Iron poles (0.7-1m, 10 mm diameter) | pieces | 150,0 | 2,1 | 315,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Electric Fence Polywire | m | 1300,0 | 0,3 | 390,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Electric Fence Corner donut insulator | pieces | 27,0 | 1,0 | 27,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Earth stakes | pieces | 3,0 | 22,0 | 66,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Electric Fence Spring Gate Set | piece | 1,0 | 42,0 | 42,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Wooden Posts | pieces | 9,0 | 6,4 | 57,6 | 20,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 6160,6 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
GIZ Project
Comentarios:
Initial costs were comparatively high as it is a pilot project. Thus, staff costs and the procurement of electric fence equipment made costs rather high. If materials can be obtained locally costs go down as far as 23 USD/pile wall (including material and work).
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Regular check of fence | Estructurales | Once per two weeks |
| 2. | Installation and deinstallation of electric fence | Estructurales | Once per year |
| 3. | Changing the broken posts | Estructurales | once per year |
| 4. | Optional refill of stones and/or soil if washed out | Estructurales | twice per year |
Comentarios:
Almost all maintenance activity refer to the maintenance of the electric fence (which is being removed in winter) and needs to be re-established during the grazing period. The pile wall itself does not need maintenance measures.
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Regular check of fence | workdays | 8,0 | 21,0 | 168,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Installation and deinstallation of electric fence | workdays | 8,0 | 21,0 | 168,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Changing the broken posts | workdays | 1,0 | 21,0 | 21,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Optional refill of stones and/or soil if washed out | workdays | 3,0 | 21,0 | 63,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 420,0 | |||||
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Grazing (if fencing is needed it is the most costly part)
Wooden logs (if bought). This can be turned to zero by either using local wood (if permitted) or bundles of branches of specific species (e.g. willows).
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
521,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
In Aparan, the climate is cold and temperate. Aparan has a significant amount of rainfall during the year. This is true even for the driest month. Precipitation peaks are in May and June.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Aparan, Aragatsotn Marz, Armenia
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
According to Köppen and Geiger, the climate is classified as Dfb (Cold/continental, no dry season, warm summers). Annual mean temperature is 5.2. °C. The warmest month of the year is August, with an average temperature of 16.4 °C. January has the lowest average temperature of the year with -6.9 °C.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
The technology is applicable on hills and steep slopes with an inclination between 10° and 30 (40)°
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
There are substantial amounts of water (seasonally) from water from melted snow of Aragats mountain
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
The area is widely used as pasture and shows some degradation signs (e.g. inpalatable plants spreading, open soil, decreasing number of plant species, spreading of Astragalus). On some slopes, autochtonous oak forests (Quercus macranthera) still exist. The area consists of typical sub-alpine to alpine grasslands with medium species diversity.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- jóvenes
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
The land owners are the communities in the target region on behalf of community mayors.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- arrendamiento
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
The erosion control masures stopped top soil Erosion and Gully Erosion in the pasture land.
Ingreso y costos
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The workload for implementing the measures does not pay off within the first view years but is a long term investment in saving soil productivity.
Impactos socioculturales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
The intervention raised awareness to soil erosion and new technologies have been trained to village stakeholders (pile walls, electric fencing)
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Water run off is decreased and soil moister is increase by better infiltration of water into the soil.
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
The increase of vegetation leads to an increase of evaporation-transpiration.
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Water run off is decreased by pile walls and better vegetation cover and soil moister is increase by better infiltration of water into the soil.
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Decrease of water run off by pile walls and increased vegetation cover leads to decrease of soil loss.
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increase of vegetation leads to more root activity and humus increase by increase of litter.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
The stop of grazing and trampling by the fence leads to fast increase of vegetation cover.
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
The stop of grazing leads to significant increase of above ground biomass.
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
On heavily eroded sites the measure lead to increase of plant species.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
riesgo de incendio
Comentarios/ especifique:
The increase of above soil biomass increase the risk of grass-fire in autumn during or after the dry season.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios/ especifique:
through increased vegetation cover and reduced speed of superficial water-runoff and increase of water capacity of the slope above the village.
sedimentos transportados por el viento
Comentarios/ especifique:
partially improved through increased vegetation cover and less open soil
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | no muy bien | |
| temperatura estacional | invierno | incrementó | no muy bien |
| temperatura estacional | verano | incrementó | no muy bien |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | ||
| lluvia estacional | primavera | incrementó | no muy bien |
| lluvia estacional | otoño | incrementó | no muy bien |
| lluvia estacional | invierno | disminuyó | no muy bien |
| lluvia estacional | verano | disminuyó | no muy bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
| incendio | no muy bien |
Comentarios:
Seasonal raifall is different, but the annual rainfall has decreased. The impact of technology is minor, since the area is very small.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Comentarios:
On the short term there is a significant increase of work load and needed resources to establish the pile walls and fencing the site. Recovery of vegetation, increase of soil carbon content and increase of productivity will need 2-5 years to be effective and give increase fodder yields of the site.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
There are interested households who want to adopt the technology, but indeed there is nobody who implemeted the technology by himself/herself.
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
Due to unavailablity of local seeds, local hay/grass was used to provide mulching cover and add locally adapted seeds
On one site an additional drainage trench was prepared as the soil was very compacted and vegetation cover was completely destroyed. The trench was filled with rocks which are available in abundance.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Improvement of road of animals, improvement of quality of pasture and vegetation cover, overcome of erosion, regulation of water flow, better view of the area, dissemination of seeds to other areas |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Technology is easy to apply and works mostly with local materials and requires no specific knowledge. Materials can be adapted (e.g. if timber is scarce, bundles of willow branches can be used as alternative) |
| Technology is able to stabilize superficial erosion processes and support recovery of vegetation on steep slopes. It can also stop small rock falls. |
| Technology can also be adapted to fortify/stabilize paths and cattle paths on slopes (e.g. when a walking path is crossing a small gully section). Thus, it can also stop erosion processes caused by trampling or hikers |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Limited availability of material such as electric fence, solar panels, etc in the local market | At the moment they can be imported |
| relatively high cost for material | Using cheap and local material |
| Limitation of cattle road | Use other alternative road for animals |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| If not installed properly, water flows on the sides of the pile walls and below and the barrier becomes ineffective |
Take care during construction that the space below the logs is filled appropriately. Take care of appropriate re-establishment of a vegetation cover |
| If area is being grazed, it is challenging to re-establish vegetation. Cuttings which further stabilize the slope are unlikely to succeed. |
Temporary fencing of the area or permanent fencing and use of area for hay making |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
3-5 informants
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Handbook on Integrated Erosion Control A Practical Guide for Planning and Implementing Integrated Erosion Control Measures in Armenia, GIZ (ed.), 2018, ISBN 978-9939-1-0722-6
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
GIZ Armenia
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Project website of the GIZ program
URL:
http://biodivers-southcaucasus.org/
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Estabilización de laderas de manera participativa [Honduras]
La bioingeniería comprende una serie de técnicas que utilizan materiales vegetativos vivos para prevenir la erosión y el deslizamiento de laderas y taludes. Las obras de bioingeniería se aplican a base de un análisis integrado de riesgo, son de multi-uso en su conjunto, tienen un bajo costo de construcción y …
- Compilador: Helen Gambon
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos