Small Irrigation System for Highland Rice Terraces [Tailandia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Pitayakon Limtong
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Checkdam for highland rice terrace
technologies_4114 - Tailandia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Srisomkhew Sasirin
662 579 1409 / 669 8269 6410
sasirin0928@gmail.com / sasirin0928@gmail.com
Land Development Department
Paholyothin Road, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10999, Thailand
Tailandia
SLM Consultant:
Limtong Pitayakon
66 89 444 6599
pitaya@ldd.go.th / pitaya49@msn.com
Land Development Department
Paholyothin Road, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10999, Thailand
Tailandia
usuario de la tierra:
Kayanyaiyie Mr.Vitoon
668 7188 0798
Soil Doctor Volunteer
Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
Tailandia
usuario de la tierra:
Kongvili Mr.Boonpan
668 4740 1550
47 Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
Tailandia
usuario de la tierra:
khangJing Mr.Suchat
668 3660 0272
1/2 Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
Tailandia
usuario de la tierra:
KangJing Mr.Somnuek
668 8764 1683
Village Headman
1 Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
Tailandia
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Land Development Department LDD (Land Development Department LDD) - Tailandia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
11/09/2018
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
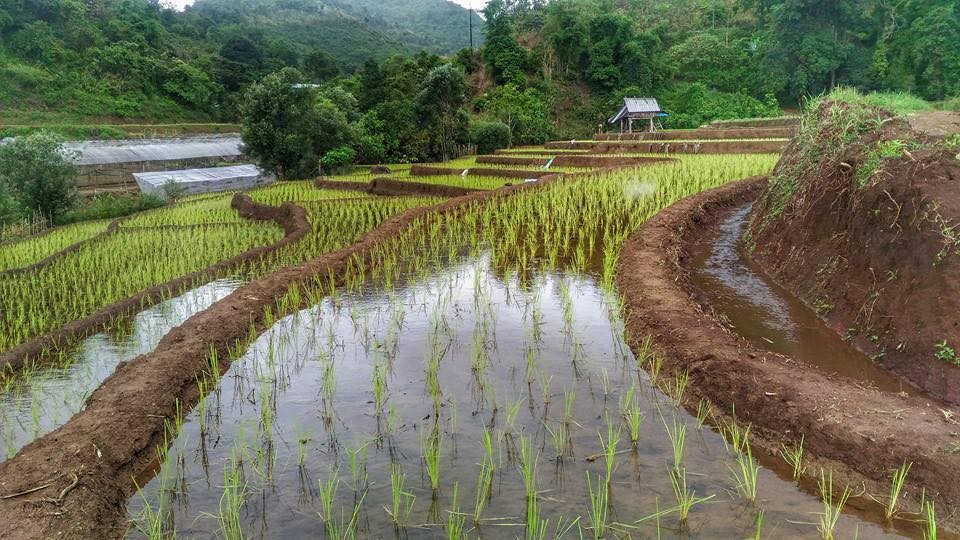
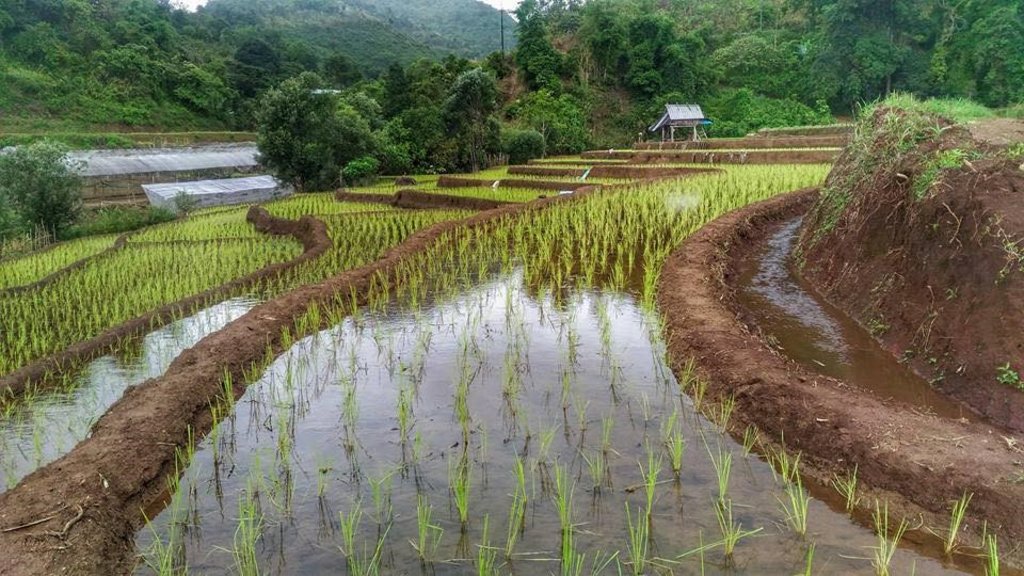
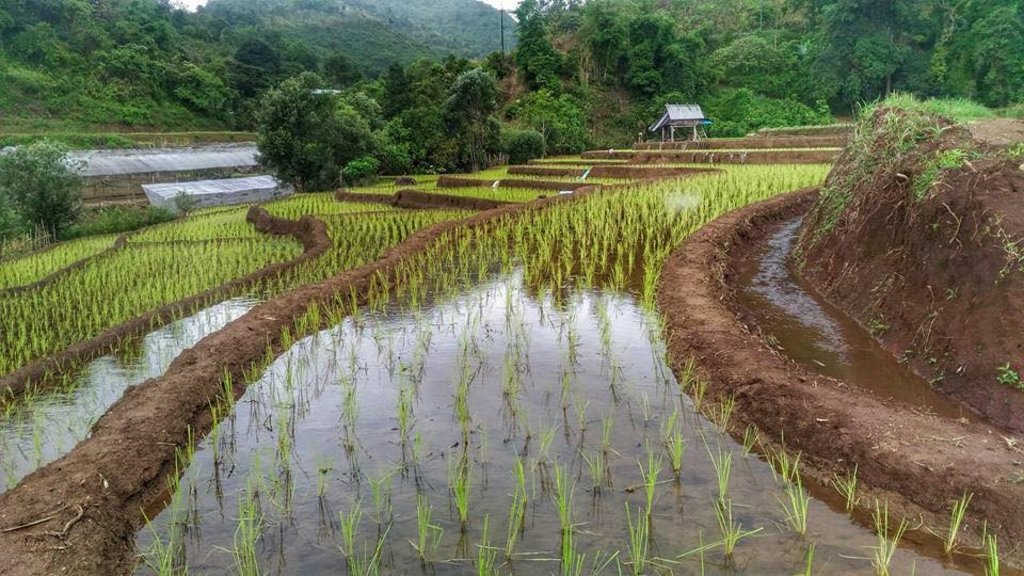
Water supply systems in the high landscape rice terraces can prevent land degradation and also land users can utilize this area for producing rice in limited agricultural land. Because this system slows down the water flow, it reduces soil erosion into water courses and controls the amount of water that flows from the forest upstream to the rice terraces. This system increases water available to the rice terraces and improves the utilization of water, thus maximizing benefits for growth and yield of rice.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
An irrigation distribution system to highland rice terraces is required for agriculture on these highland slopes. It is based on the principles of water management in the area by diversion of water from natural watersheds upstream to the agricultural land - with regulation by village community consensus.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
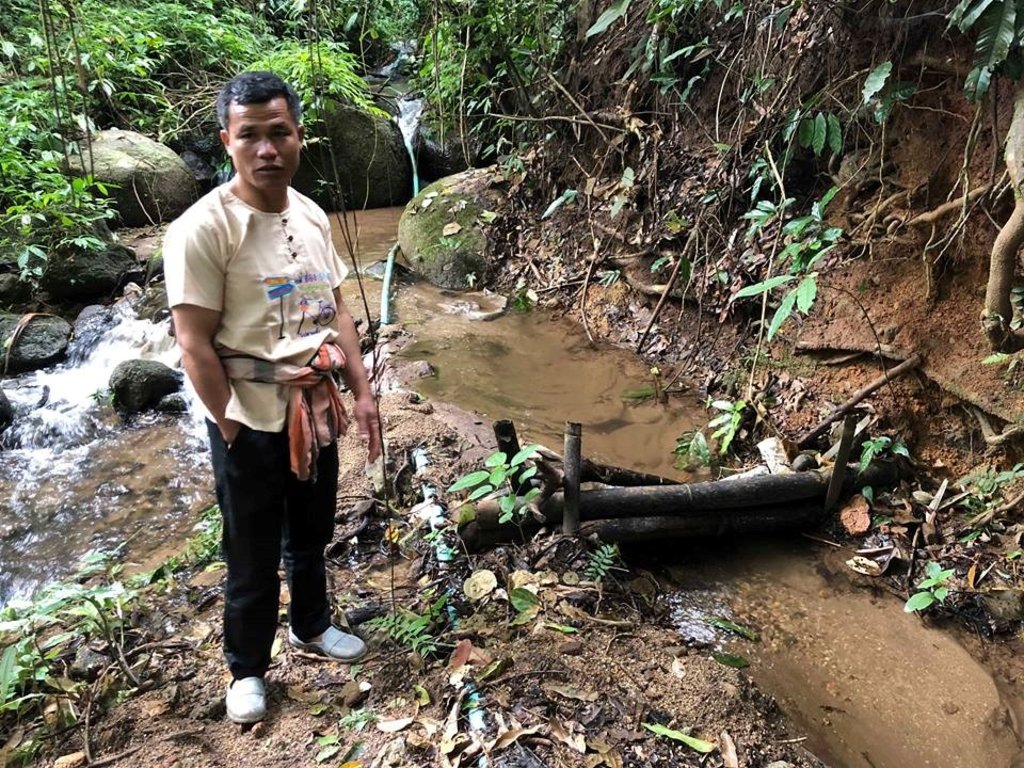
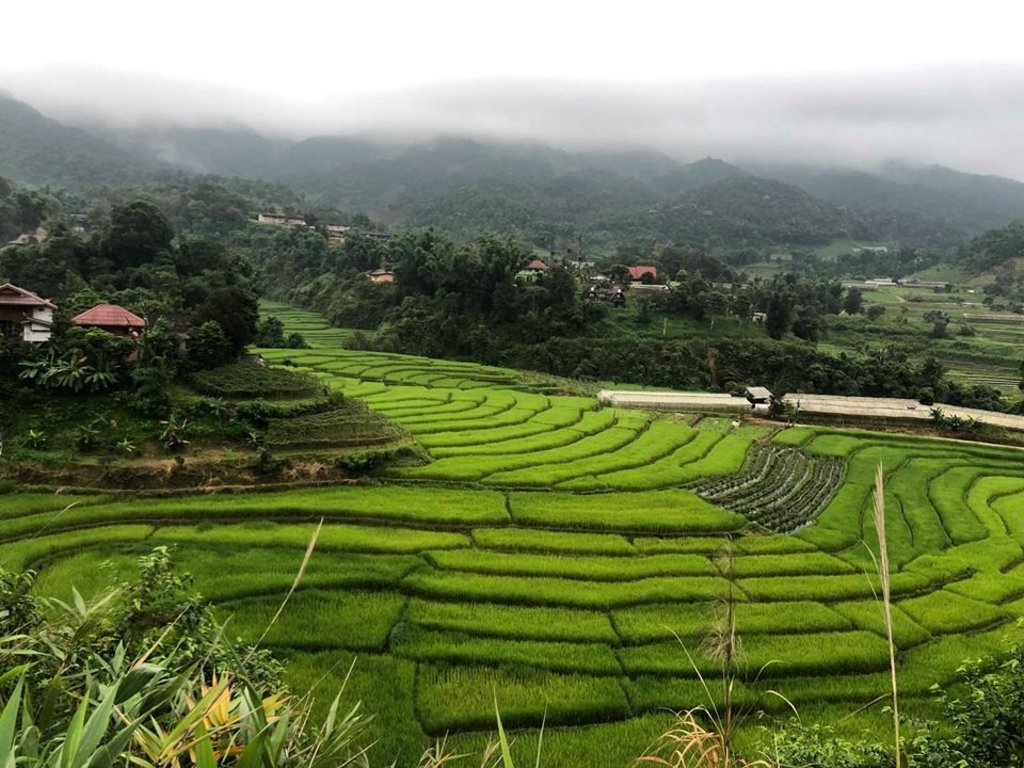
The topography of this mountainous area, Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, is complex. The height ranges from 994 -1,100 m above sea level (m asl). The main river is Mae La Noi. The climate is cool all year round. The annual average temperature is 25 degrees Celsius (⁰C), maximum temperature is 37⁰C in April, and minimum temperature is 8⁰C during December. The annual average rainfall is 1,500 mm and lasts from June to October. The number of households is 147, with total population of approx 763, 400 (Mae La Noi Royal Project Development Center, 2561). An irrigation distribution system to highland rice terraces is required for agriculture on these highland slopes. It is based on the principles of water management in the area by diversion of water from natural watersheds in the upstream areas to the agricultural land - with regulation by village community consensus. The steps of preparation are as follows. 1. Site selection: Rice terraces should be on suitable slopes, not more than 60 degrees, otherwise it will be difficult to excavate the slope and rice fields become very narrow. 2. Reshaping and leveling the slope: The sloping land for rice terrace should be reshaped and levelled by either manpower or mechanical means. The terraces can extend up to 50 m long, be as little as 1 m wide and 0.5 m deep, depending on the slope. The leveling of soil surface in the plot is done by releasing water into that plot and adjust the soil surface until a good level is attained. 3. Soil improvement: Generally, soil structure and fertility in the plots is very low because of reshaping and leveling. It is therefore necessary to restore and improve by application of organic matter, compost, animal manure, legumes, etc. Soil pH must be adjusted, and nutrients such as phosphorus and potassium should be added based on soil analytical results. 4. Rice cultivation: In the first years of cultivation, the terraces may not store water at the desired level, so rice is planted in small holes. Normally, farmers plant rice seedlings (3-5 seedlings per hole) at a spacing of 20 x 20 cm. 5. Fertilizer application: In this highland area focus should be on organic fertilizers to reduce costs, because people can find materials locally such as animal manure and plant residues. 6. Water supply system: Distribution of water to the rice terraces is managed by small dams or weirs to release suitable amount of water through a small water channel to rice terraces. This water distribution system will spread water to all land users in this area, and there is sufficient water for farming throughout the year. 7. Disease and insect control: Most rice varieties are native, so they have high resistance. But there could be some disease/insect outbreaks; they have to be protected according to instructions. The submerged condition in the paddy field can help control weeds, but some labour is still needed. 8. Maintenance: For small dams or weirs, small water channels and terraces, it is necessary to restore and maintain twice a year, i.e. before and after harvest.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Fecha:
11/09/2018
Lugar:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
Nombre del videógrafo:
Ms.Sasirin Srisomkhew
Fecha:
21/03/2018
Lugar:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
Fecha:
11/09/2018
Lugar:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
Nombre del videógrafo:
Ms.Sasirin Srisomkhew
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tailandia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- mitigar cambio climático y sus impactos
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas principales (comerciales y de subsistencia):
Paddy rice and vegetables such as chili, cabbage

vías fluviales, masas de agua, humedales
- Líneas de drenaje, vías fluviales
Principales productos/ servicios:
Small dams or weirs with small water channels to supply/distribute water to rice terraces.
Comentarios:
Farmers in the area will grow rice in the rainy season for household consumption. The duration of cultivation until harvesting is about 6 months. In the dry season, the farms are converted to several kind of vegetables under support by the Royal Project Foundation.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
The system of water supply of this technology distributes water resources from forest upstream to the rice terrace.
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 3
Especifique:
Paddy rice once a year and vegetables 1-2 crops a year
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- medida de pendiente transversal
- diversión y drenaje de agua
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
Comentarios:
This water system covered around 200 households, each household covers an area of 0.5 hectare.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S1: Terrazas

medidas de manejo
- M7: Otros
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Autor:
Ms.Sasirin Srisomkhew
Fecha:
25/09/2018
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
The irrigation water distribution system for highland rice terraces by farmers in the village is suitable for highland, sloping agriculture, with slopes ranging from 5-60 degrees. It is based on the principles of water management in the area by diversion of water from natural watersheds in the upstream zone to the agricultural land through the consensus of community members. Distribution of water to the rice terraces is managed by small dams or weir which are used to divert and release suitable amount of water through small water channels to rice terraces. The terraces can extend up to 50m long, 1m (or more) wide and 0.5m deep, depending on the degree of the slope. This water distribution system will spread water to all land users in this area, and there is sufficient water for farming throughout the year.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
0.48 hectare for each farmer
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Baht (THB)
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
32,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
300
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | prepare small dam and water canal | Estructurales | in the first year |
| 2. | prepare terraces and land leveling | Estructurales | in the first year |
| 3. | cultivation | Estructurales | before rainny season |
| 4. | soil improvement | Manejo | after preparing and cultivating the soil |
| 5. | rice planting | Vegetativas | rainy season |
| 6. | fertilizer application | Manejo | after planting |
| 7. | irrigation | Manejo | after planting |
| 8. | disease, pest and weed control | Manejo | after planting |
| 9. | havesting | Agronómicas | when rice grains are mature |
| 10. | None | None |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
Si fuera posible, desglose los costos de establecimiento de acuerdo a la siguiente tabla, especificando insumos y costos por insumo. Si usted no pudiese desglosar los costos, proporcione un estimado de los costos totales para establecer la Tecnología:
98100,0
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | prepare dam and canal | 7x10 | 70,0 | 300,0 | 21000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | planting | 7x1 | 7,0 | 300,0 | 2100,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | maintainance | 20x2 | 40,0 | 300,0 | 12000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | harvesting | 20x7 | 140,0 | 300,0 | 42000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | tractor | set | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | fuel | liter | 20,0 | 30,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | rice seed | bag | 3,0 | 100,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | chili seed | plant | 5000,0 | 2,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | fertilizer 21-0-0 | bag | 3,0 | 400,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | fertilizer 15-15-15 | bag | 3,0 | 700,0 | 2100,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | fertilizer 16-20-0 | bag | 3,0 | 600,0 | 1800,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | animal manure | bag | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 98100,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Labour of small and canal preparation was paid in the first year, after that paid for maintain all of these structuer.
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | restoration and maintain dam, canal and terrace | Estructurales | 2 times a year |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Si fuera posible, desglose los costos de mantenimiento de acuerdo a la siguiente tabla, especificando insumos y costos por insumo. Si usted no pudiese desglosar los costos, proporcione un estimado de los costos totales que se necesitan para el mantenimiento de la Tecnología:
1800,0
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | restoring and maintaining the dam, water canal and terraces | 2dx3m | 6,0 | 300,0 | 1800,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 1800,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Land user spend their money for 100% of costs
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The most important factors that affect the costs is the labour factor, where farmers need to hire labourers for rice cultivation such as planting, fertilizer application, maintaining the system and harvesting, including, the excavation and restoration of the small dam, water channels and terraces.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1500,00
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones convexas
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
en superficie
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
- ancianos
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
calidad de cultivo
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
calidad de agua potable
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
calidad de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
derechos de uso de la tierra/ agua
oportunidades culturales
oportunidades recreativas
instituciones comunitarias
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
calidad de agua
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
drenaje de agua en exceso
nivel freático/ acuífero
Suelo
pérdida de suelo
acumulación de suelo
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
acidez
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
diversidad animal
especies benéficas
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
impactos de sequías
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
inundaciones río abajo
colmatación río abajo
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
impacto de gases de invernadero
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | moderadamente | ||
| temperatura estacional | verano | no muy bien | |
| lluvia anual | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | moderadamente |
| tormenta local | moderadamente |
| granizada local | moderadamente |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| incendio forestal | moderadamente |
Desastres biológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| enfermedades epidémicas | nada bien |
| insectos/ infestación de gusanos | nada bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- más de 50%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 90-100%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The villagers are self-reliant by living in balance between demand and supply to meet their own needs. So every household will grow rice for their consumption and solve some problems in water management of these rice terraces by their community. |
| Villagers have knowledge and technology of water management and systematically and continuously transfer to other land users from generation to generation, causing a connection between kinship and community. There are groups to solve the main problems of the community. |
| Villagers have a stable and strong mental state with the hard thinking to fight the obstacle in the way of living, to achieve a more prosperous life. Individual communities have strength in self-reliance, and also have strong mind in learning, having virtue and rationality in thinking and decision-making. |
| They have the ability to promote agriculture with natural resources and ecological tourism and develop the communication system for visitors to access the local information and facilities. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The selection of appropriate technology can solve the problem of soil degradation, reduce soil erosion and manage adequate water supply to agricultural area for the whole year. |
| The villagers have to rely and trust on each other with high willingness to share their knowledge and experience. |
| Communities have the ability to use existing natural resources in maximizing benefits, and at the same time they try to conserve and prevent soil degradation in this area. |
| Community networking allows them to conduct activities to achieve self-reliance. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Land users’ lack of ownership of the land that cannot be legally owned by individuals, as the area is located in a preserved forest. The villagers therefore might be afraid to move out of the area in the future. | The community leaders and villagers need to solve this problem, one thing being that they should ask the government to help. |
| Lack of opportunities for children to have education caused by the poverty of their parents. | Schools in the area have increased educational opportunities for poor children by sponsoring underprivileged children. |
| Lack of social and health welfare because this area is far from the city. Villagers will not be able to reach the hospital in time in the case of emergency. | Villagers take the right treatment from the gold card or project 30 baht free treatment of all diseases for emergency situations. |
| Lack the coverage of energy and communication system in this area. Some areas still lack electricity, telephone and internet facilities. | Some villagers purchased and installed solar panels for their own use. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The villagers lack the ownership of the land, which located in the conserved forest. That means they do not have right to hold the land. | The government has a policy to solve these problems, and at the same time serve and arrange this preserved forest as natural resource. |
| Lack of educational opportunities, The study site is located in a remote area. Children living there lack opportunities in education. | The government has a policy to give underprivileged children equal education to children. |
| Villagers lack social and health welfare because of the remoteness of the place that they live. It is difficult to access medical treatment and hospital. | The government has set up and supported the budget to develop district health promotion hospitals in the sub-district level. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Ecological tourism of Mae La Noi Development Center, Royal Project
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=818zn7JMKsU
Título/ descripción:
Mae La Noi Royal Project Foundation
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M8pFfl18fC8
Título/ descripción:
Mae La Noi Development Center of Royal Project Foundation
URL:
http://www.mhsdc.org/interest510.htm
Título/ descripción:
History of Mae La Noi Development Center
URL:
http://www.mhsdc.org/rypmaenoi.htm
Título/ descripción:
Mae La Noi Project for tourism of beautiful paddy rice terrace
URL:
https://mgronline.com/travel/detail/9590000106920
Título/ descripción:
Mae La Noi Development Center of Royal Project Foundation
URL:
http://royalprojectthailand.com/maelanoi
Título/ descripción:
Rice terrace in highland
URL:
http://www.ricethailand.go.th/rkb/management/index.php
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos