Introduction of Crop Rotation [Georgia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Hanns Kirchmeir
- Editor: Kety Tsereteli
- Revisor: Ursula Gaemperli
technologies_4275 - Georgia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
co-compiler:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural area (L-SLM Project)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Regional Environmental Centre for the Caucasus (REC Caucasus) - Georgia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
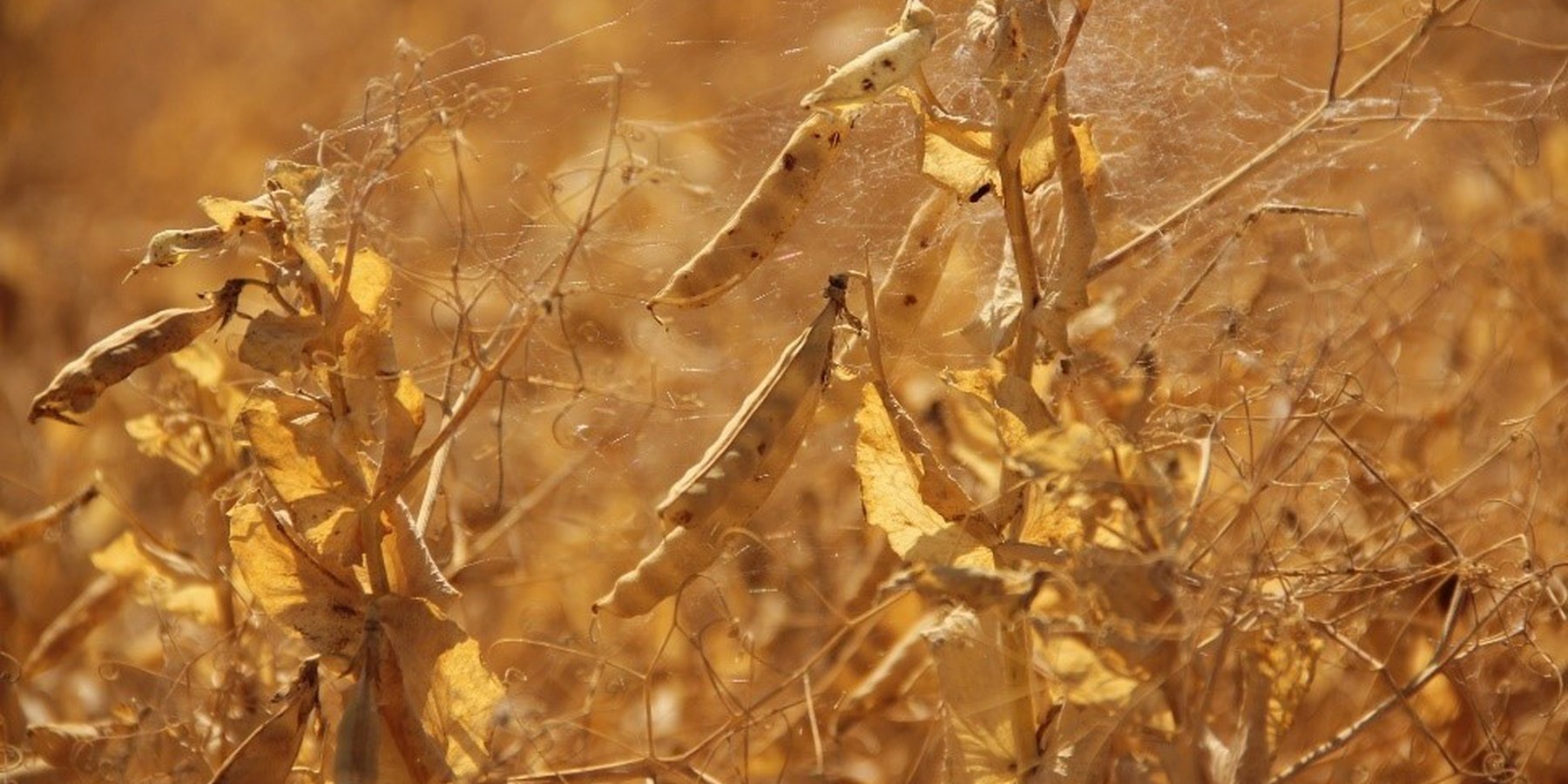
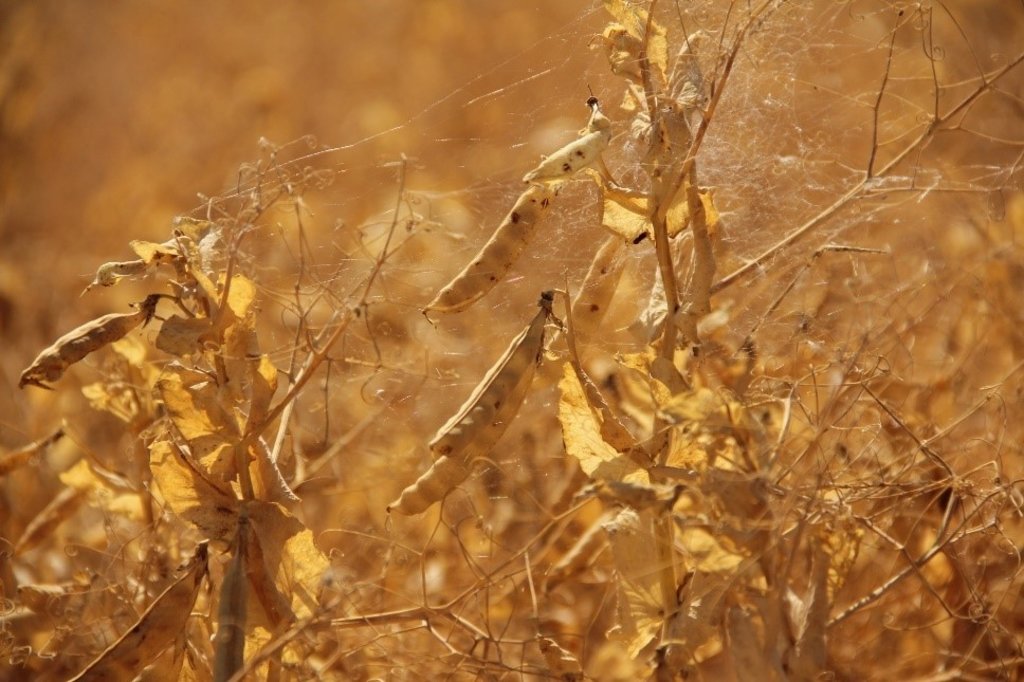
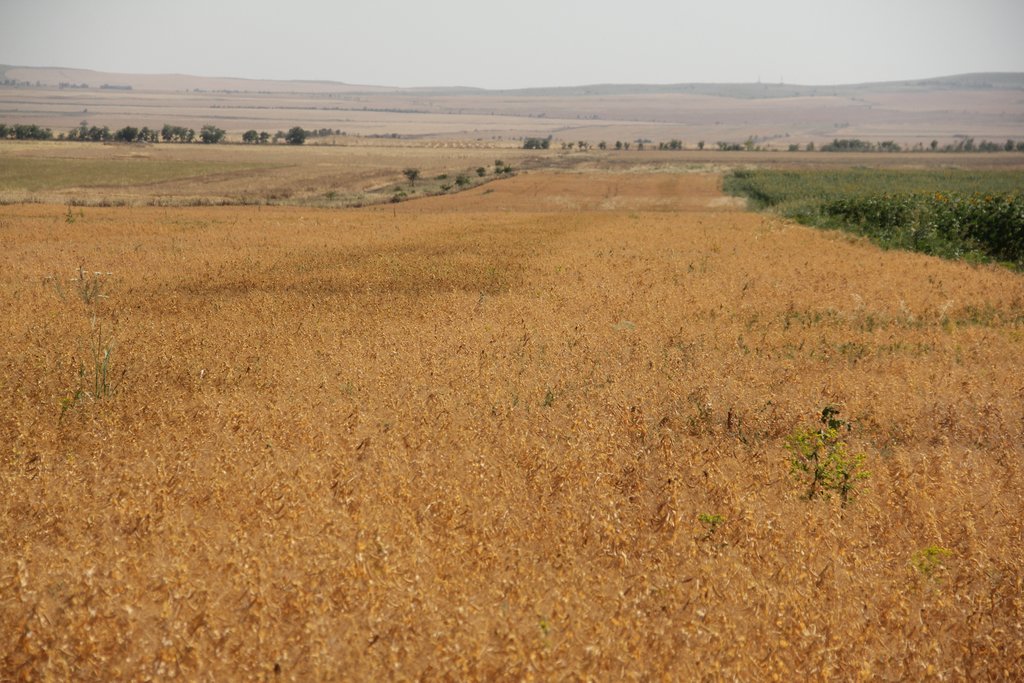
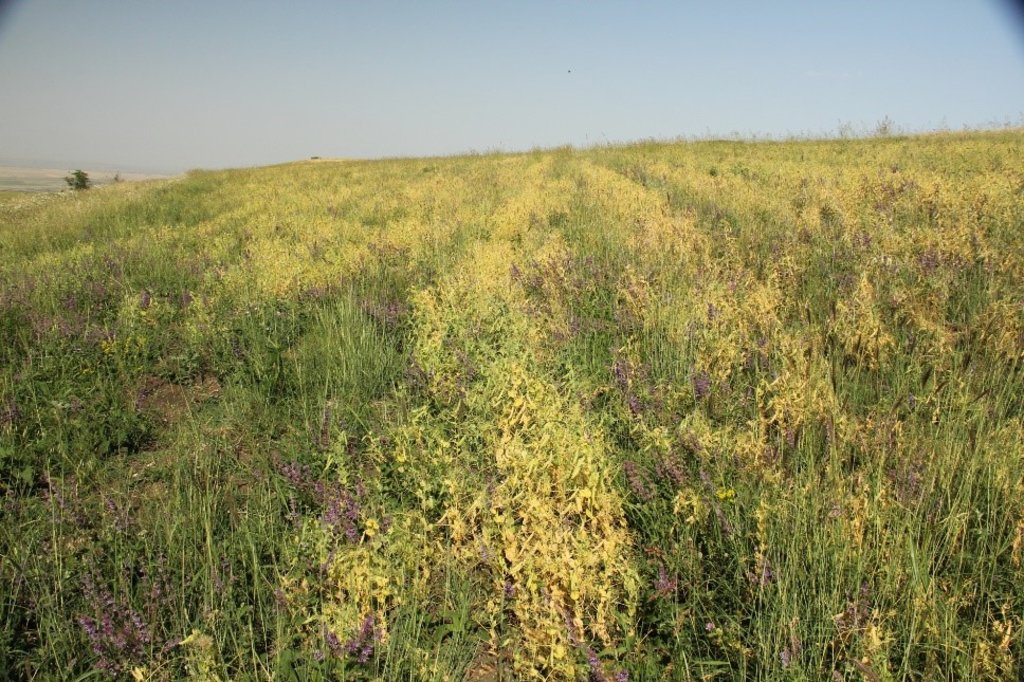
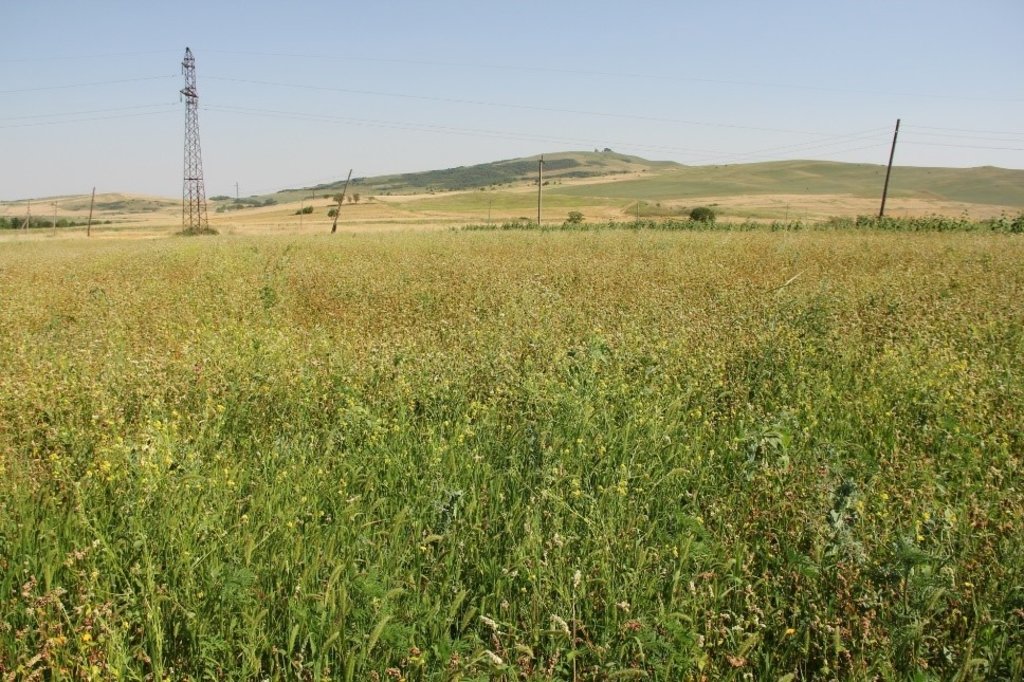
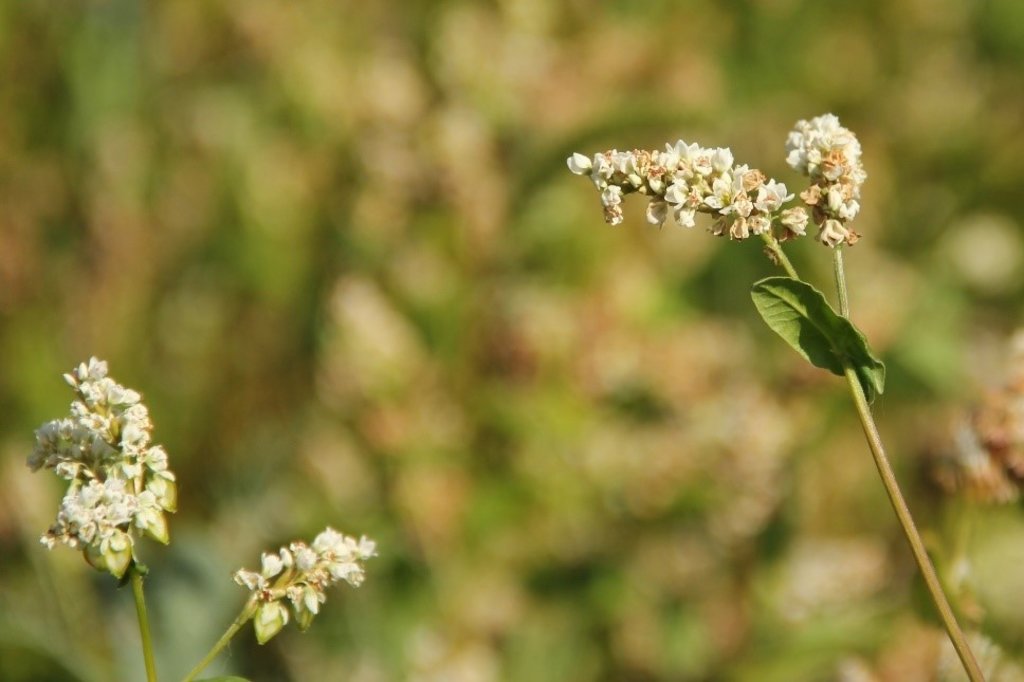
In the municipality of Dedoplistskaro, Georgia, 100 ha of land have been cultivated with peas on approx. 25 fields (each 1-10 ha in size). The introduction of peas as an alternative crop that is now used in rotation with wheat, helps to increase soil fertility sustainable and ecologically.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
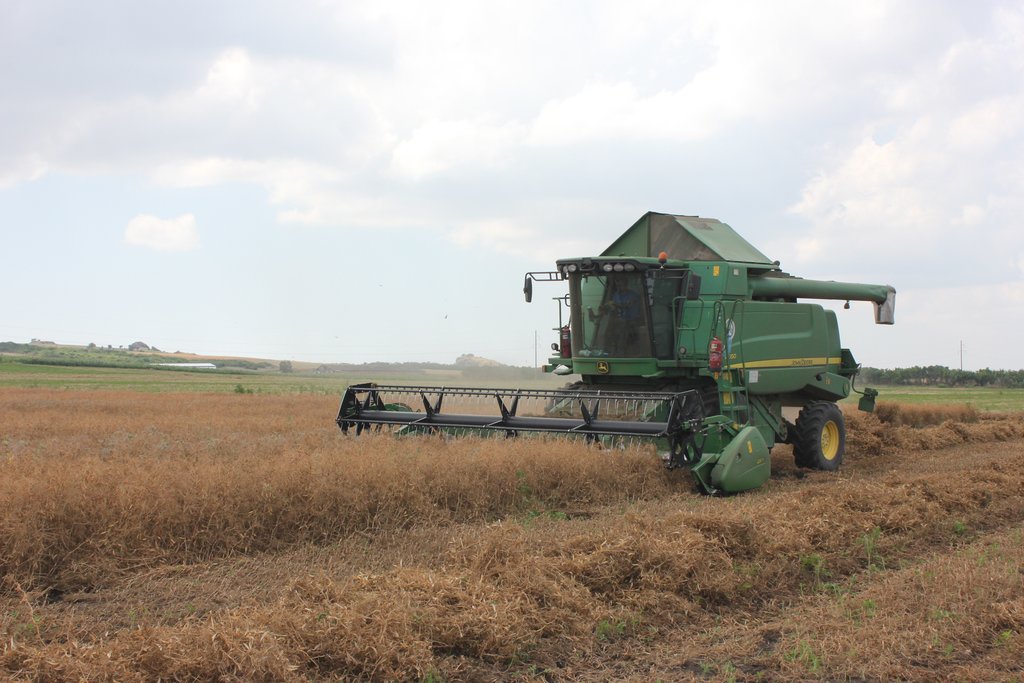
Dedoplistskaro is located in the Shiraki Plain, in eastern Georgia, and consists of steppes, where grain crops are cultivated and livestock is grazed in the winter. The steppic soils are dominated by Chernozems and Kastanozems, the climate is warm and temperate and the small-scale land (2-5 ha) is in individual ownership. The labour including plowing, seeding and harvesting is fully mechanised, the machines are mainly borrowed from agricultural machinery cooperatives and less often from private machinery suppliers. For the inhabitants of Dedoplistskaro municipality, agricultural production is an important source of income. 74% of the Georgian wheat production is located in the Kakheti region. Shiraki valley has a great share of this. The area of wheat production in Dedoplistskaro is 13,693 ha (Census 2014). Securing the productivity of arable land and stopping degradation due to the loss of soil fertility is of local and national importance. The introduction of pea as an alternative crop, which can be used in rotation with wheat or other crops, should help to increase soil fertility in a sustainable and ecologically viable way. Pea is a plant from the legume plant family. The root system of Pea can thus fix nitrogen from air by symbiotic bacteria. This helps to increase the C/N ratio in the soil leading to higher decay rates of organic carbon (e.g. from straw residuals) and higher fertility of soils. Most farmers sowed on 23 and 24 March 2018 - some until 29 March 2018. Later sowing led to lower yields.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Georgia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Kakheti
Especifique más el lugar :
Dedoplistskaro
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la Tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente a lo largo de un área, especifique el área que cubre (en km2):
1,0
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2018
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - trigo (verano)
- leguminosas y legumbres - arvejas
- buckwheat
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Crop rotations with wheat, pea and buckwheat. Different systems, one example: Year 1: Wheat, Year 2: Pea, Year 3: Wheat, Year 4: Wheat, Year 5: Buckwheat, Year 6: Wheat, Year 7: Wheat, Year 8: Pea, Year 9: Wheat
Comentarios:
Before the implementation of the technology wheat was cultivated without intercropping or crop rotation.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - trigo (verano)
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No
Comentarios:
It is envisaged to continue with crop rotation in the following years.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- sistemas de rotación (rotación de cosecha, cosecha rotatoria con descanso, agricultura migratoria)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo
Comentarios:
The nitrogen fixing capabilities of the pea-roots will increase fertility of the soil additionally to the crop-rotation effect.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)
Comentarios:
The permanent cultivation of wheat on the same field leads to degradation of fertility.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
The crop rotation will reduce and/or prevent from land degradation by permanent wheat cultivation.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Proposed rotation schema for wheat, pea and buckwheat
Autor:
Hanns Kirchmeir
Fecha:
07/02/2018
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
100 ha
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
20
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of farmers and fields according to the selection schema and signed subsidy contracts to all farmers | Until January 2018 |
| 2. | Scientific assessment of soil fertility before seeding | October 2017-Novembver 2018 |
| 3. | Seeding, maintaining and harvesting | March-October 2018 |
| 4. | Scientific assessment of soil fertility before seeding | October 2018 |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | plowing | ha | 100,0 | 35,71 | 3571,0 | 40,0 |
| Mano de obra | harrowing | ha | 100,0 | 14,29 | 1429,0 | 40,0 |
| Mano de obra | seeding | ha | 100,0 | 8,93 | 893,0 | 40,0 |
| Mano de obra | harvesting | ha | 100,0 | 35,71 | 3571,0 | 40,0 |
| Material para plantas | pea-seeds (250kg) | ha | 100,0 | 133,93 | 13393,0 | 40,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | herbicide (1l) | ha | 100,0 | 5,36 | 536,0 | 40,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 23393,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 23393,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
60% of the cost have been added as a subsidy payed from GEF project funds.
Comentarios:
The funding was organised in a public call. Farmers from the Dedoplitskaro region have been invited to apply for a 60% co funding of the pea/buckwheat planting.
The costs stated in the section "Labour" for plowing, harrowing, seeding and harvesting include costs for labour and for equipment. The work was done partly by the farmers themselves and partly by an agricultural contractor such as for driving the harvester. The machines are mainly borrowed from a local machinery cooperative, but also from private machinery suppliers.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
Comentarios:
The full production cycle (plowing, harrowing, seeding, harvesting including the application of pesticide have been included in the 'establishment' section.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Comentarios:
The full production cycle (plowing, harrowing, seeding, harvesting including the application of pesticide have been included in the 'establishment' section.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
It was a challenge to organised the high amount of pea-seeds, as they are not commonly available in the region.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
697,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The driest month is January, with 25 mm of rainfall. The greatest amount of precipitation occurs in June, with an average of 108 mm. The difference in precipitation between the driest month and the wettest month is 83 mm.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Dedoplistskaro Met. Station
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
The climate is warm and temperate in Dedoplistskaro. The average annual temperature in Dedoplistskaro is 11.3 °C. The warmest month of the year is July, with an average temperature of 22.7 °C. The lowest average temperatures in the year occur in January, when it is around 0.1 °C.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
In the region steppic soils are dominating (Chernozems and Kastanozems)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
The landscape is intensively used by agricultural purpose. The former network of windbreaks was massively reduced in the last decades. Re-establishing could support the habitat diversity significantly.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
The local farmers-association was an important partner in promoting the imitative.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
No
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The average yield of peas 3 t/ha, 98 t pea yield was taken from the pilot plots. Some of the farmers will sow the peas in other plots to improve soil fertility on another land under their ownership. Buckwheat was sown only on 2 plots, 450 kg at all. The farmers who had opted for the concept of starting the crop rotation with buckwheat cultivated the green mass in the soil to improve their fertility. The harvest of peas/buckwheat was very variable between the different farmers depending on their timing of measures: 1. The farmers who could not use the possibility to seed the crops in March - 1 farmer, because of rainy weathers afterwards, seeded pea later , in the middle of April. This farmer could not get yield from the plot. The others (2-3 farmers) who could not harrow the soil after seeding (as we recommended to harrow), they got the small yield.
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
When peas are used as a intercrop between winter wheat cultivation, this would have a positive effect on wind erosion. Since the implementation of the crop rotation just started in 2018, evidence-based further impacts are only expected in the following years, e.g. impacts on soil quality.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
No off-site effects are expected.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Comentarios:
Maintenance costs were not applied.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
It is a very new technology. But success of the first year will help to spread it across the region.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The project gave farmers the opportunity to try the new crops (peas and buckwheat) for the community of Dedoplistsakro, as they only sow wheat and barley over the years. They had the opportunity to get advice on how to sow peas and buckwheat and how to improve the soil fertility of their land. They invested through ploughing, harrowing and maintenance, as well as by taking over the yields. They were also interested in maintaining the yield from the proposed crops, using this seed for further plots next year and passing on the knowledge to other farmers. Some farmers sold harvested peas as forage, some gifted others for the same purposes to improve soil fertility. |
| The farmers, who sow the peas in time and cultivate them with appropriate agrotechnical measures, harvested 3.5-4t/ha. The profit was 12 250 - 14 000 GEL/ha. The yield rate was as follows: 3.5.5 t/ha yield - 4.8 yield rate; 4 t/ha --- 5.5 yield rate. |
|
The expected yield of barley per hectare in the years following pea sowing will be 7-9 tonnes. Income ratios - 9.6 for 7 t/ha yield; 12.4 for 9 t/ha yield. The expert calculated the expected yield on the basis of yield data from the davit Nateladze area in Dedoplistskaro, where peas were sown in 2017 and then 5.5 t barley/ha instead of 1.5 t barley/ha (in previous years before peas were sown) was harvested. As part of the pilot project, 23,750 kg of peas were sown on 92 ha in Dedoplistskaro in 2018. 98 t of peas were harvested in mid-July in the municipality of Dedoplistskaro. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The machinery for preparing the soil and seeding are available. |
| Especially pea has a very positive effect on soil fertility. |
| Most of the farmers used the technology for next year(2019). They seeded the harvested pea in spring 2019 at another plots in Dedoplistsakro municipality (about 100 ha). This confirms the positive impact of the approach on soil fertility and guarantees the sustainability of the project. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Some farmers (2-3) sow the pea later than others. They did not get a good yield because of the sowing in April. The reason for the delay was 1. rainy weather; 2. lack of machinery. Timely harvesting was also the problem because of the lack of machinery, since Dedoplistskaro is called the barn of wheat and there are not enough machines in the community. The problem of the realization of peas and buckwheat was also the problem because of the lack of companies for peas and buckwheat not only in the municipality but throughout the country. | The farmers asked for a support for the municipality in the development of such enterprises to process the mentioned crops for realization. |
| Of the 3 schemes proposed, 19 farmers choose the first scheme to sow the peas in the first year. The second scheme was not chosen at all. The 3rd scheme to start crop rotation in the 1st year with buckwheat was chosen by 2 farmers. A farmer ploughs the yield of buckwheat as a green mass in the soil and improves the fertility of the soil. Another harvested and prepared 120 hay presses. The farmers improved the soil, but the expenses were at 1 ha / 2 645 GEL, 1 press / 7 GEL, the income ratio 0,31. The sowing of buckwheat to prepare the press is ineffective to benefit from the harvest. The farmers who opted for the third scheme (start of croprotation with buckwheat) were geared towards improving soil fertility, but most farmers prefer to do the rotation in order to benefit from the yield. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| There is no local marked or seller for peas and it is difficult to sell the product for the local farmers. | It needs national support to develop a pea-processing industry. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Two field visits.
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Interviews with the implementing national field expert.
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
Documentation from the field expert
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
12/09/2018
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos