Establishment of a paddock system and improvement of degraded pastureland. [Georgia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Hanns Kirchmeir
- Editor: Kety Tsereteli
- Revisor: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_4276 - Georgia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
co-compiler:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural area (L-SLM Project)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Regional Environmental Centre for the Caucasus (REC Caucasus) - Georgia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Rehabilitation of Pasture Land through fencing [Tayikistán]
The approach demonstrates the effect and importance of rotational grazing by fencing certain areas of land in pasture areas as well as it demonstrates the rehabilitation process in comparison to the open space which is overgrazed. The approach involves mobilizing communities to observe the rehabilitation process by not grasing in …
- Compilador: Askarsho Zevarshoev
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
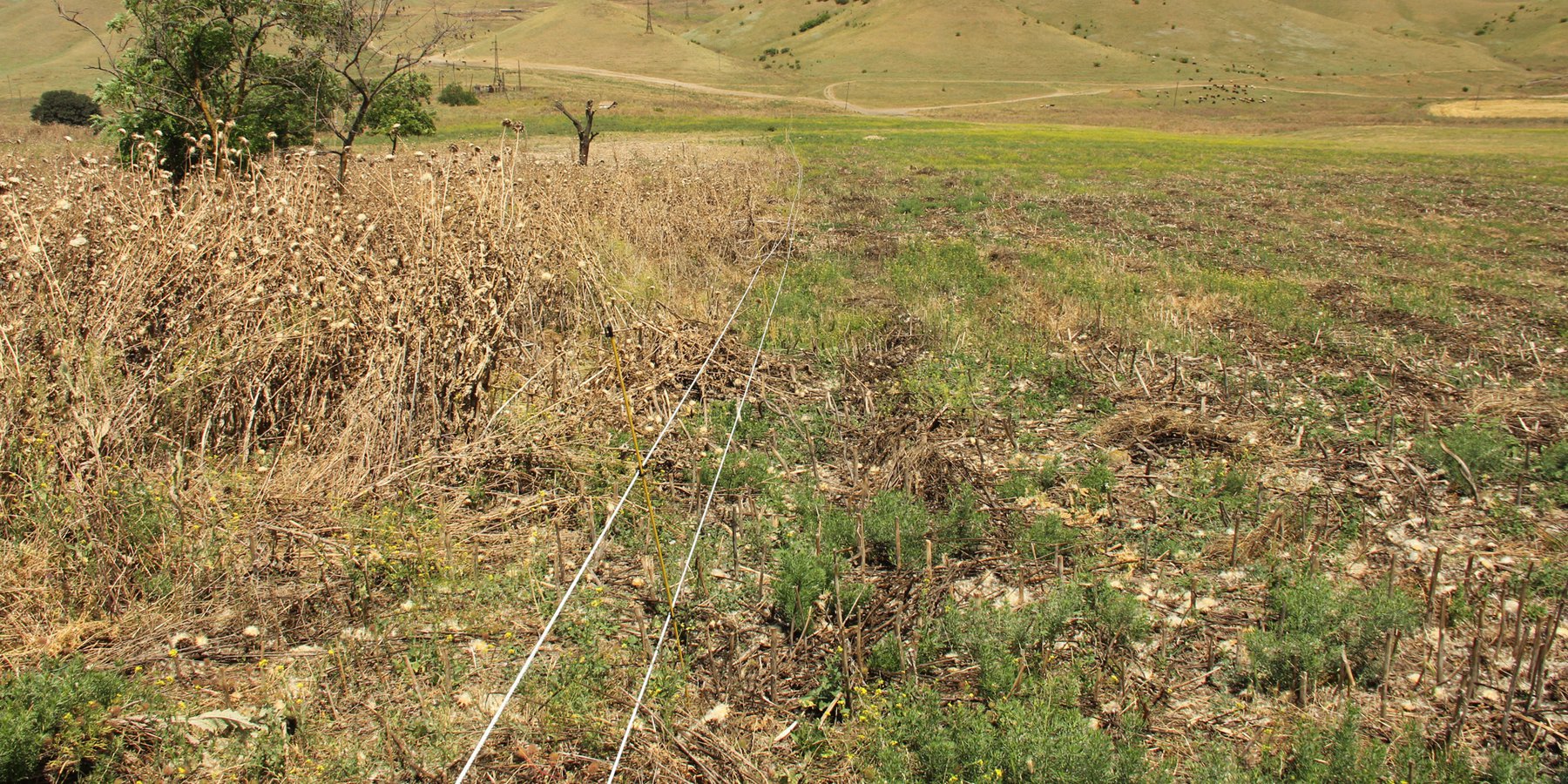
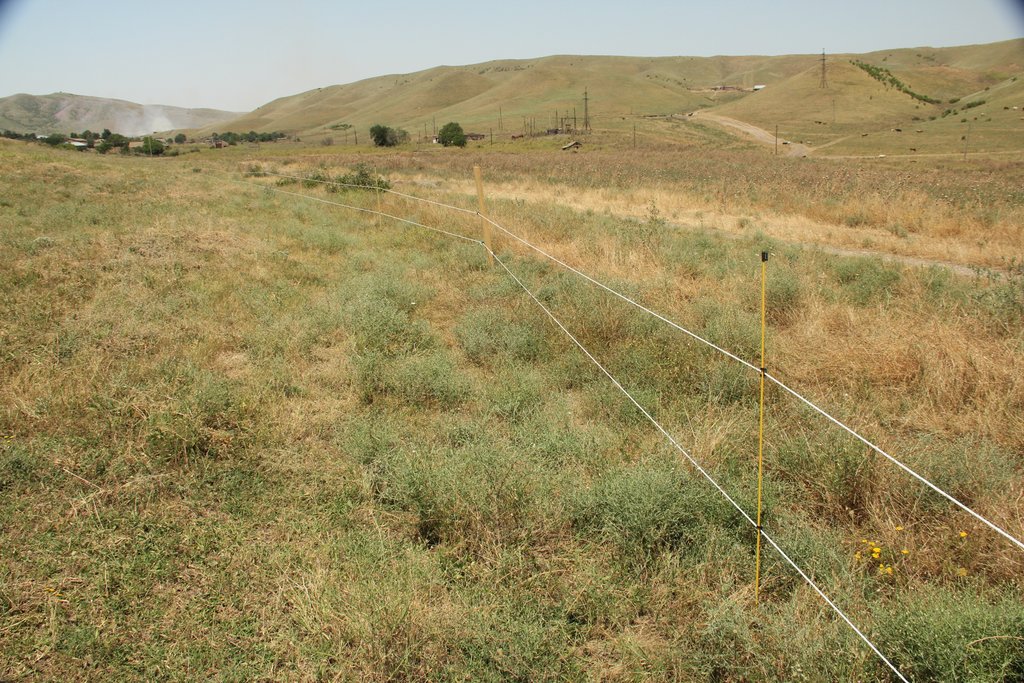
In a pilot project, degraded pastureland near the settlement of Kasristskali was regenerated by introducing a fencing, mowing and grazing regime that favours the growth of forage plants instead of weeds and, where necessary, reseeding forage plants.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
This showcase is part of the project "Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural areas", implemented by the Regional Environmental Center for the Caucasus (REC C).
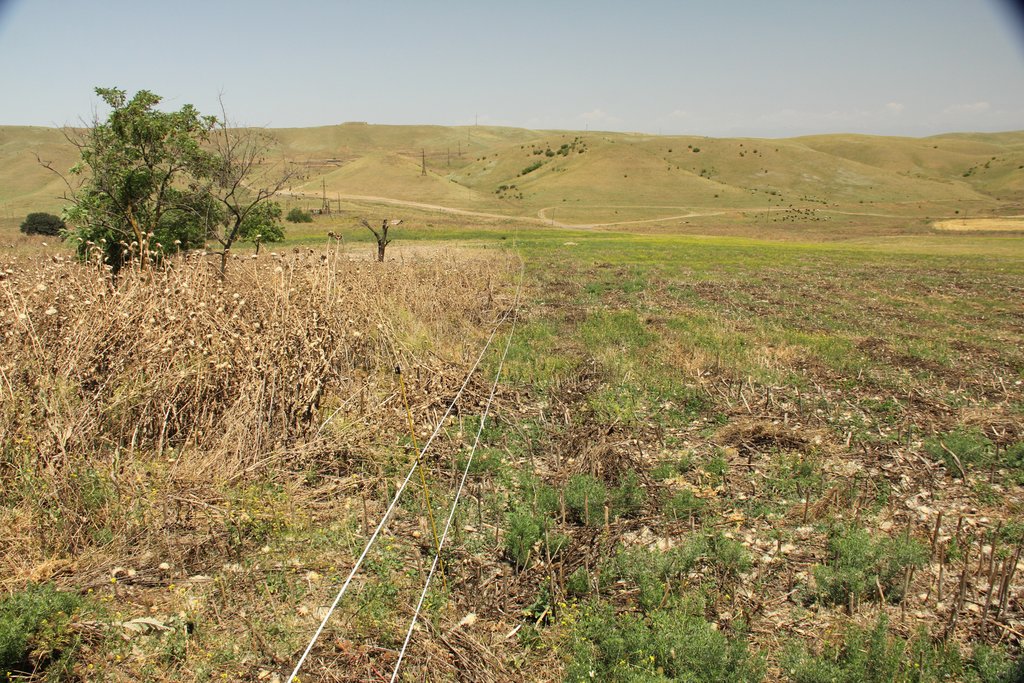
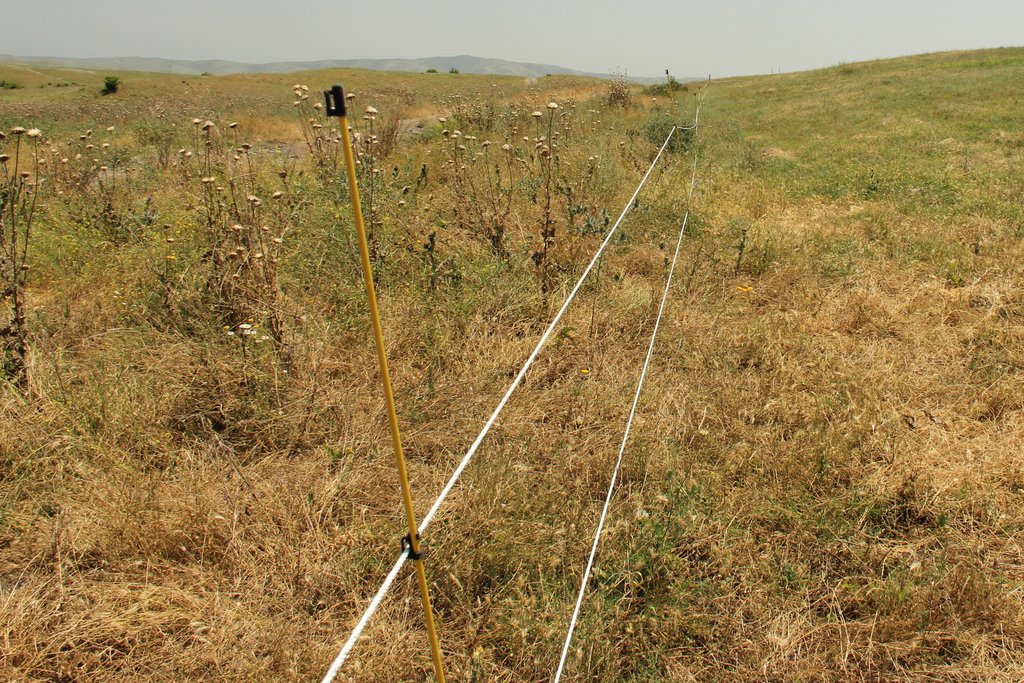
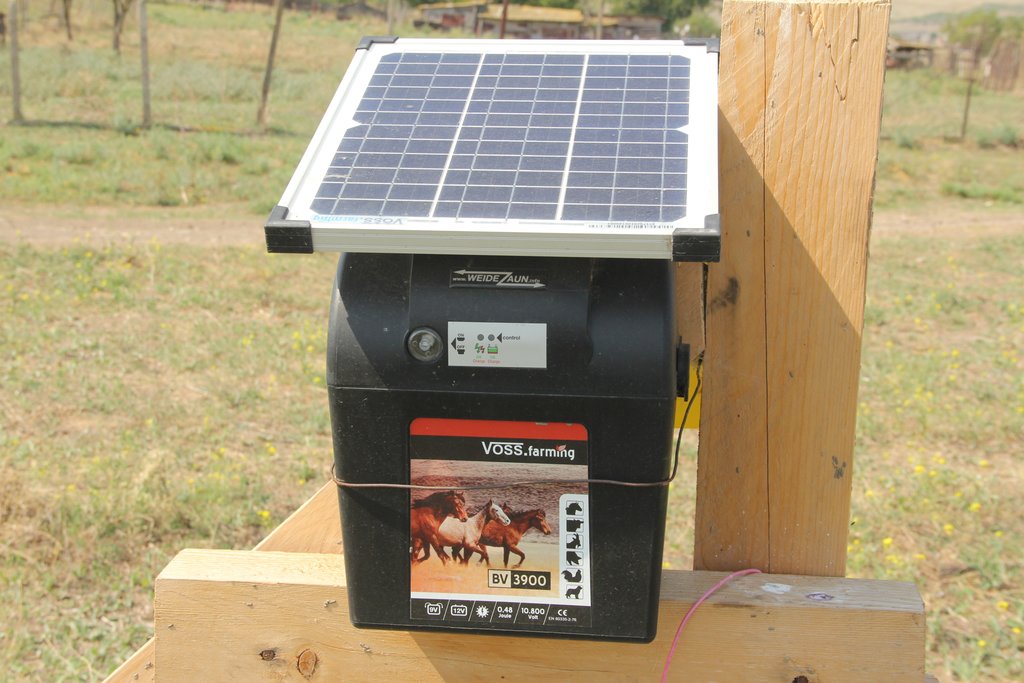
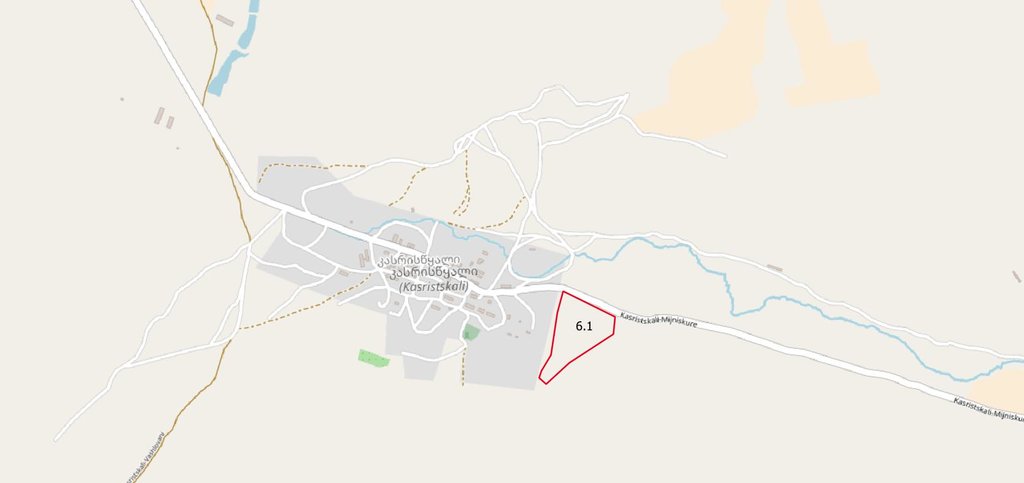
The implementation site was selected by national experts together with stakeholders from the village. This site is located close to the settlement Kasristskali. It is community pastureland, which was abandoned and not maintained for many years. The site had been dominated by thistles and weeds before the intervention took place and was not suitable for grazing. 30% of the area was previously used to store manure and is rich in nutrients. To reclaim the pastureland for cattle, an area of 6.1 ha was mowed twice and equipped with an electric fence (two lines of electric wire and a solar-powered energizer brand Voss). This was done to regenerate the area so that a grazing regime could be introduced later. An electric fence was chosen because wood is not available in the area and a wire mesh fence would be more expensive. Furthermore, an electric fence is flexibly adjustable, which is essential for a rotational grazing system. It is important to remove the residues after the mowing to reduce the amount of weed seed. The time of mowing should be before the flowering of the most common weed species. An ongoing mowing and grazing regime was set up to favour fodder plants instead of weeds: Since the cows only eat the fodder plants and leave the weeds standing, the weeds have a clear advantage. To counteract this, the weeds are mowed, and fodder plants are sown. Mowing is needed for the first 2 years and after that, it is enough to control the quality of pastureland by a grazing system. For maintenance purposes, the area was cut once in early spring and a second time in summer. The evaluation in September, after the pastureland was recultivated, showed that the northern and eastern parts now have a grass and herb cover suitable for grazing, while the central, western and southern parts are still overgrown by weeds. This is due to the fact that these parts were very rich in nutrients from the very beginning and consisted exclusively of thistles. In order to improve the productivity of the site, it is recommended to cut the vegetation again in autumn, remove the residues, open the soil with a harrow and sow a pasture seed mixture adapted to the climatic conditions in February.
The local community farmers were involved in all activities. They were participated in development of local pasture management plan. The plan was approved by the community members and they are ready to follow the applied methodology and maintain the pastureland after the project completion. The farmers acknowledged the benefit from the proposed methodology and they invested to rehabilitate the additional area (6 ha) of pastureland with their own financial sources.
The 6.1 ha plot which was restored as pastureland with this technology is planned to be used as a paddock for alternating grazing between free-range and the paddock.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Georgia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Kakheti
Especifique más el lugar :
Municpalty of Akhmeta, Kasristskali village
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
The national park Vashlovani is nearby.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2018
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural areas; GEF funded, implementation by the Regional Environmental Center for the Caucasus (REC).
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierra no productiva
Especifique:
The area east of the village is rich in nutrients but was not maintained. A dense weed layer of milk thistle (Silybum marianum) was established.
Comentarios:
The main income of the village comes from agriculture in the plains of Shiraki Valley and livestock breeding in the hilly land east of the plains.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Pastoreo mejorado
Tipo de animal:
- ganado - lechero
- ganado - carne de res no lechera
¿Se practica el manejo integrado de cultivos - ganado?
No
Productos y servicios:
- carne
- leche
Especies:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Comentarios:
The 6.1 ha plot which was restored as pastureland with this technology is planned to be used as a paddock for alternating grazing between free range and the paddock.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- veda de zona (detener uso, apoyar la restauración)
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A7: Otros

medidas vegetativas
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes
- V4:reemplazo o eliminación de especies extrañas/ invasoras

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
- M5: Control/ cambio de composición de las especies
- M7: Otros
Comentarios:
The technology enables efficient weed control on common pasture land. The improvement of degraded pastures is achieved through weed control and sowing of fodder crops and the use of a rotational grazing system.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación biológica
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores
Comentarios:
The degradation is driven by excessive spread of milk-thistles on nutrient rich pasture land because of missing maintenance. Those thistle stand are of low plant diversity and have no fodder value.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
The technology supports the restoration of the weed dominated pasture land. This will increase biodiversity and productivity.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
The area on which the technology is applied is 6.1 ha. The paddock is on community rangeland and managed by the village people. It is located on a slightly north-oriented slope near the village. The area was used to store manure. The high nutrition values led to the enormous growth of weeds, especially thistles.
Autor:
Hanns Kirchmeir
Fecha:
22/03/2019
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
ha
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
13 USD/day
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | First mowing of the site, clearing from thistles and removal of hay/residuals | Early spring (March) |
| 2. | Establishment of electric fence | June |
| 3. | Opening the soil with a harrow | February of following year |
| 4. | Seeding of fodder plants | February of following year |
Comentarios:
It is important to remove the residues after mowing to reduce the amount of weed seed. The time of mowing should be before the flowering of the most common weed species.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Setup of fence | person-days | 2,0 | 13,0 | 26,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Open the soil with a harrow | person-days | 1,0 | 13,0 | 13,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Seeding of fodder plants | person-days | 1,0 | 13,0 | 13,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Mowing (1st time) an manual removal of thistles | person-days | 18,0 | 13,0 | 234,0 | |
| Equipo | Equipment for 1200m electric fence including energizer | set | 1,0 | 2547,0 | 2547,0 | |
| Equipo | Machinery for mowing (rental) | days | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | |
| Equipo | Machinery for harrowing (rental) | days | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Seeds (Onobrychis) | kg | 300,0 | 1,5 | 450,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 4083,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 4083,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The equipment, renting cost of machines and labor was financed by the GEF SLM project.
Comentarios:
The local village is very poor and lacks of infrastructure and financial capabilities.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Second mowing and removal of hay | July |
| 2. | Third mowing and removal of hay | September |
Comentarios:
The weed population is still very high. These are poisonous or spicy plant species which cannot be controlled by intensive grazing. To reduce the dominance of this weed, it is recommended to mow the entire area of 6.1 ha three times a year. The best time to mow is before the weed blossoms.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Mowing (2nd and 3rd time) | person-days | 2,0 | 13,0 | 26,0 | |
| Equipo | Machinery for mowing (rental) | days | 2,0 | 400,0 | 800,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 826,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 826,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
The community is very poor so the costs for maintenance was covered by the project. After the difficult removal of the thistles, the second and third mowing was done only by machinery and has not needed that much man power than the first time.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The most important factor was the equipment for the electric fence. Electric fencing material is not common in Georgia and there are no relevant national suppliers.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
697,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The driest month is January, with 25 mm of rainfall. The greatest amount of precipitation occurs in June, with an average of 108 mm. The difference in precipitation between the driest month and the wettest month is 83 mm.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Dedoplistskaro Met. Station
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
The climate is warm and temperate in Dedoplistskaro. The average annual temperature in Dedoplistskaro is 11.3 °C. The warmest month of the year is July, with an average temperature of 22.7 °C. The lowest average temperatures in the year occur in January, when it is around 0.1 °C.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
The pasture is located on top of a small hill and its north-eastern slopes.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
30% of area was used of manure storage before and is rich on nutrients.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Only a few weed species where dominating the area before the intervention.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
The village is very remote. Driving distance to the municipality is about 1h on bad roads.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
Community pasture land.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
1-2 t/ha
Comentarios/ especifique:
The fodder production will increase in the next few years as mowing and grazing affect weed control.
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
The fodder production will increase within the next years when mowing and grazing shows effect in the decrease of weeds.
área de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
0 ha
Cantidad luego de MST:
6 ha
Comentarios/ especifique:
6 ha of degraded and unused pastureland have been recultivated.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Community is equipped with electric fencing infrastructure (including training)
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
Most of the area could not be used for cattle grazing due to the dominance of weeds. Based on biomass harvesting experiments in Tusheti, it is expected that at least 1-2 tons of fodder per hectare will be available on the pasture.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
No significant effects are expected off-site
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lluvia estacional | verano | disminuyó | moderadamente |
Comentarios:
When temperatures rise and precipitation decreases, productivity falls. If productivity is below 1t/ha, the investment in an electric fence will not pay off.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
In the first two years, the forage harvest will be low, while the costs for erecting the fence and maintenance by mowing will be high. In the long run, unproductive land will be productive again. On the 6 ha, 6 to 12 tons of biomass per year can be expected (depending on rainfall in spring and summer). This is equivalent to 500-1000 USD/year.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
There is strong interest to establish a second plot for rotational pasture systems of 20ha near by. The financial capacity of the village is to low to cover the investment of the fencing material.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| improved pasture quality and new fencing technology introduced |
| raised production of fodder plants |
| pasture management plan is developed and local farmers are able to manage the pasture rotational system themselves. Also the farmers were trained in installation and maintenance of el-fence. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| A fertile land near the village, which was unusable, was turned back into productive land. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The pasture land has already been severely degraded (mainly by weeds) and it will take time and more resources to restore it. | Small grants to support the rental of machines for mower maintenance (topping cuts). |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The investments for the fencing cannot be made by the villagers. | Long-term microloans with low interest rates. |
| Seed of local, climate-adapted forage plants is not available. | Establishment of local seed suppliers in cooperation with the agricultural extension service. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
2 field visits in 2018
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
two interviews with local land users and one training on rotational pasture management, hands on training on installing and maintaining electric fence.
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Discussion with national field experts
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
12/09/2018
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural areas: Final report. 2017. Kirchmeir, H., Joseph, A., Huber, M
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
RECC Caucasus
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Rehabilitation of Pasture Land through fencing [Tayikistán]
The approach demonstrates the effect and importance of rotational grazing by fencing certain areas of land in pasture areas as well as it demonstrates the rehabilitation process in comparison to the open space which is overgrazed. The approach involves mobilizing communities to observe the rehabilitation process by not grasing in …
- Compilador: Askarsho Zevarshoev
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos