Using shallow wells for crops and lowering the saline groundwater table [Tailandia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Kaewjai Oechaiyaphum
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Samran Sombatpanit, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Pitayakon Limtong, William Critchley
shallow well
technologies_4391 - Tailandia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
SooPho Boonchu
Land user
Tailandia
co-compiler:
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Prawanna Prasit
Technical for Land Development Group , Land Development Regional Office 3 , Land Development Department.
Tailandia
National consultant:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - Tailandia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
Through this technology, farmers can pump water from shallow wells for agriculture throughout the year: it can lower the groundwater table and reduce salinity. This technology has resulted in reduction salinity in surrounding low land areas. Hence, shallow wells have been accepted by land users.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Pumping groundwater from shallow wells for agriculture can control the groundwater table in recharge areas. It helps to manage saline aquifers and reduce soil salinity. Such shallow wells range from 25 to 30 meters deep. This technology is very well-accepted by the land users.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
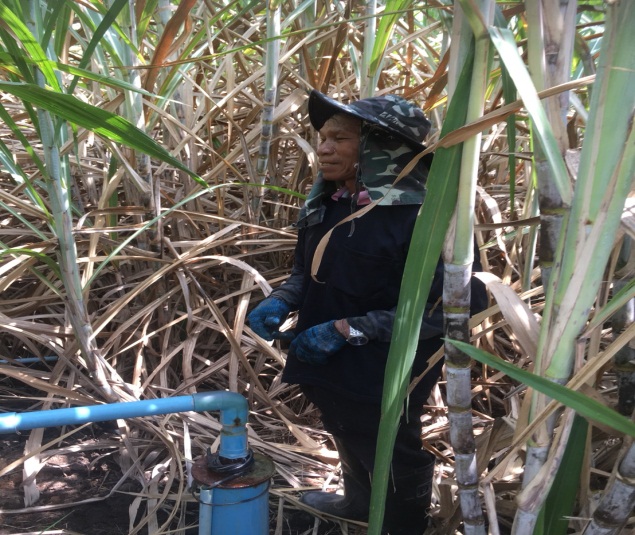
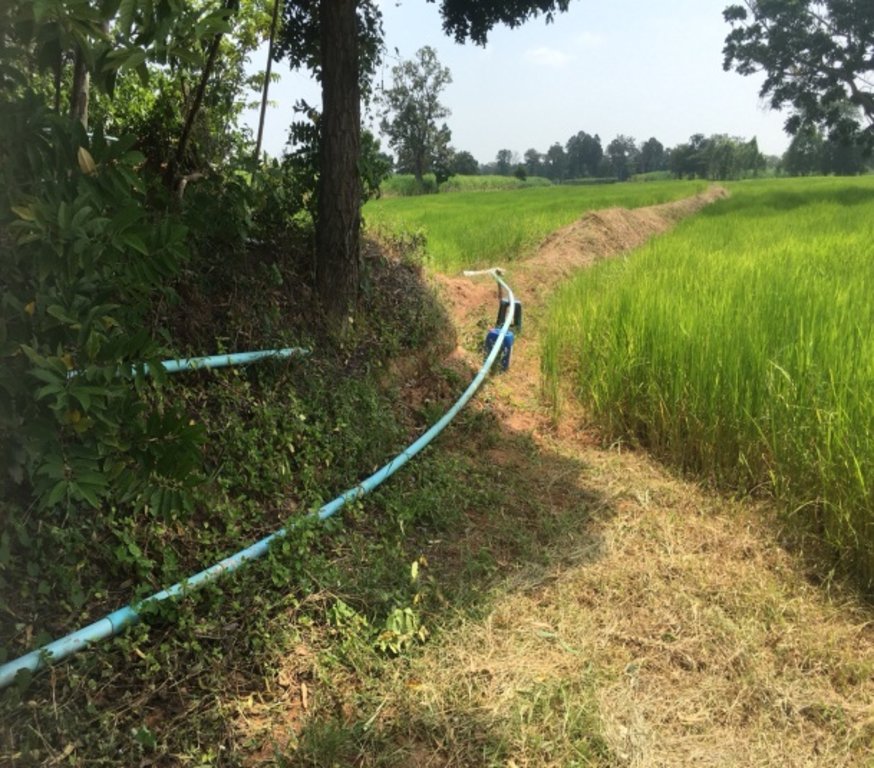
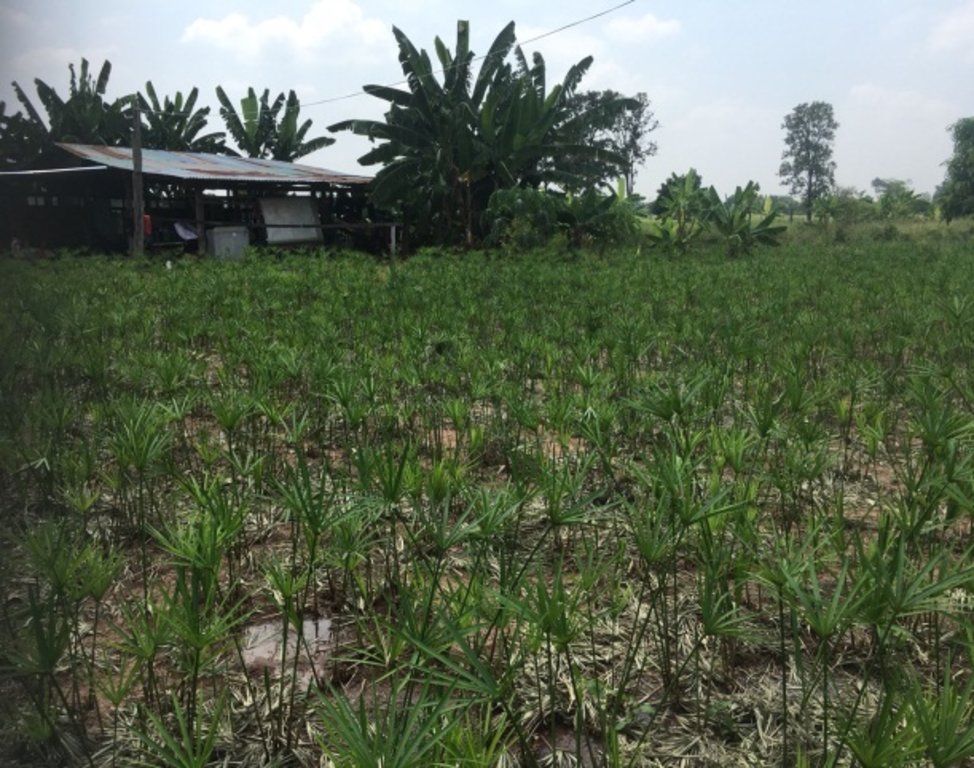
The shallow well is a structure created in the ground by digging or drilling to access water resources. This example of shallow wells is their use in recharge areas to lower groundwater tables. The technology is a subproject of a larger LDD initiative. The technology has been promoted by the Land Development Department at Bua Yai district Nakhon Ratchasima province since 2014. The objectives of the main project are (1) to provide water resources in recharge areas for agriculture: (2) to reduce the amount of saline groundwater and (3) to set up positive economic impact measures.
The process of technology establishment comprises 1) a recharge area survey in salt-affected areas, 2) drilling shallow wells to 25-30 meters depth, 3) installing 5.5 hp gasoline pumps and testing water quality, 4) pumping groundwater and distributing it to the cultivated areas.
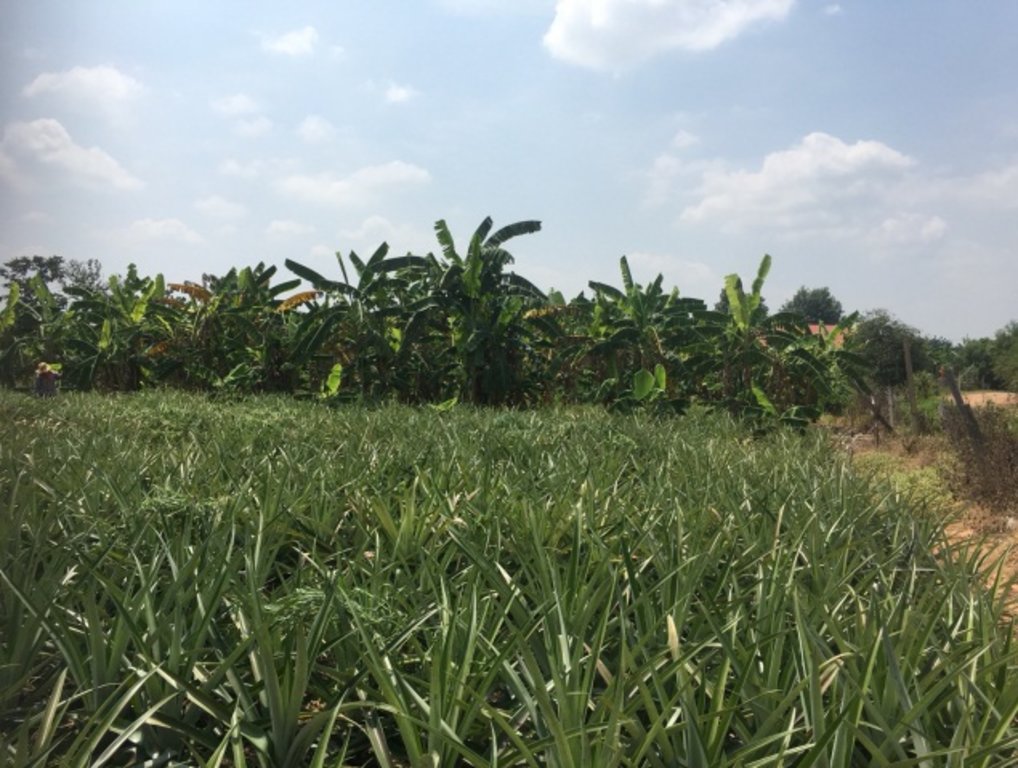
Shallow well technology has been implemented on the fields of Mr. Boonchu Supho, Ban Nong Mek, Moo 9, T.Dan Chang, A. Buayai, Nakhon Ratchasima Province. Mr. Boonchu Supho has 21 rai (approx. 3.4 hectares), undulating area with a 2-5% slope, situated at approx. 200 meters above sea level, with a tropical climate, and soil which is classified as being in the series of Kula Ronghai (Ki). This area is upland, and located in the recharge area. Mr. Boonchu Supho has 13 rai (approx. 2 hectares) of lowland rice fields and one shallow well.
In the past, water scarcity was the main issue with his land. Droughts resulted in water scarcity and low productivity. After excavating a shallow well in 2014, groundwater was used for 19 rai of cultivation. Due to soil salinity reduction, rice yields increased to 590 kg/rai (approx. 3700 kg/ha: an increase of approx. 47.4%). Sugar cane yield increased to 30 ton/rai. Moreover, land users can use land more efficiently with mixed plantations of banana, pineapples, sweet bamboo, chilies, galangal and lemongrass to generate income. Even with a drought in 2018, his land had enough water for cultivation, while rice fields in the surrounding area faced water scarcity problem.
In conclusion, the benefits of the shallow well are 1) lowering the groundwater table and reducing salinity, 2) enhancing rice and sugar cane yields, 3) ability to cultivate throughout the year and 4) better soil properties and a better environment. However, the disadvantage of the shallow well is that farmers have to pay for electricity (around 1,200 THB/ 9 months or 10,800 THB/year).
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
Using shallow well for planting in the recharge area
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Comentarios, descripción breve:
To interview Mr. Boonchu Supho
Fecha:
09/10/2017
Lugar:
Ban Koksa-ard Moo 9 T.Danchanget, A.Buayai, Nakhon-Ratchasima
Nombre del videógrafo:
.Jilayus Sommutram
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tailandia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Nakhon Ratchasima
Especifique más el lugar :
Ban Koksa-ard Moo 10 T.Danchang, A.Buayai
Comentarios:
Mr. Boonchu Supho has in total 21 rai, divided into 1) Recharge area, which is located in the upland zone. Land utilization comprises 2 rai of residence and shallow well, 1.5 rai of the sugar cane field, 1 rai of a banana field, 1 rai of sweet bamboo, 1 rai of pineapple and 0.5 rai of chillies, galangal, and lemongrass. 2) Discharge area, which is located in a low land area. This area has 13 rai of in-season rice
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2014
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The Land Development Department and local authorities created a demonstration plot to solve the saline soil problem under the LDD project (on preventing soil salinity and to lower the groundwater table in the recharge area) in Bua Yai district. Nakhon Ratchasima Province, since 2014
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- prevents soil salinity and to lower the groundwater table on recharge area
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- vegetable
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - arroz (humedal)
- vegetales - otros
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- banana/plátano/abacá
- piña
- caña de azúcar
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Land user growing rice 1 time/year, growing sugar cane 2 times/3 years and using of water punping for vegetable growing during rain delay season/ drought situation
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No

vías fluviales, masas de agua, humedales
Principales productos/ servicios:
shallow well
Comentarios:
An excavating shallow well on recharge area was to lower groundwater table and prevent soil salinity in recharge area. Groundwater was used for rice, sugar cane, banana, pineapple and vegetable growing. This technology has increased productivity up to 47.4% in rice: sugar cane has more than doubled its yields.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- vegetable
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - arroz (humedal)
- vegetales - otros
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- piña
- caña de azúcar
- sweet bamboo
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No
Comentarios:
An excavated shallow well in the recharge area was to lower groundwater table and prevents soil salinity in the recharge area. Groundwater was used for rice, sugar cane, banana, pineapple, and vegetable growing. This technology has increased productivity up to 47.4% in rice: sugar cane has more than doubled its yields.
3.4 Provisión de agua
otra (ej. post-inundación):
- shallow well
Comentarios:
Land users know how drought or rain can delay affect productivity. Hence, land users have decided to engage in this project
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- sistemas de rotación (rotación de cosecha, cosecha rotatoria con descanso, agricultura migratoria)
- manejo de agua subterránea
- desalination
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo

medidas estructurales
- S11: Otros
Comentarios:
Groundwater from the shallow well was used for 19 rai of plantation area. The result shows that this technology can increase soil moisture; make a better environment, crop residue from post-harvest can enhance soil organic matter and soil fertility
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cs: salinización/ alcalinización

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación
- Pk: desmoronamiento y encostramiento

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo

degradación del agua
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de aguas subterráneas
Comentarios:
There is not much organic fertilizing in 19 rai of land. Most organic fertilizer has been used in vegetable growing while other plantations are usually chemical fertilizing. Hence, increasing crop production needs more chemical fertilizing.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- adaptarse a la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
The land user has used shallow well technology during drought and rain delay situation since 2014-2018. They found that using shallow wells can reduce groundwater table which might dissolve saline aquifer and spread salinity. Hence, shallow well technology can reduce salinity in lower lying land. With less salt in the topsoil, rice yield has increased to 5-10%
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
21 rai own by one selected land user....(e.g. 24 acres, 4.5 hectares)
Si usa una unidad de área local, indique el factor de conversión a una hectárea (ej. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 hectare =…6.25 rai
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
THB
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
300 THB
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | To drilling shallow well with 25-30 meters depth | January 2014 |
| 2. | Sugar fields | May 2014, 2016, 2018 |
| 3. | Pineapple fields | May 2018 |
| 4. | Banana fields | May 2014 |
| 5. | Reed fields | May 2015 |
| 6. | Sweet bamboo fields | May 2015 |
| 7. | Chillies, galangal and lemon grass fields | May 2014-2018 |
| 8. | Rice fields | June 2014-2018 |
Comentarios:
No irrigation water therefore planting time depends directly upon the period of the early rainy season, which will be May to July
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Costs of labor for sugarcane cultivation | puddle | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Costs of labor for rice cultivation. | rai | 13,0 | 1150,0 | 14950,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Costs of labor for sugar cane cultivation. | rai | 1,5 | 1200,0 | 1800,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Costs of labor for pineapple cultivation. | rai | 1,0 | 1200,0 | 1200,0 | |
| Equipo | Costs of labor for Banana cultivation | rai | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | |
| Equipo | Costs of labor for Papyrus cultivation. | rai | 0,5 | 900,0 | 450,0 | |
| Equipo | Costs of labor for Sweet bamboo cultivation. | rai | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | |
| Equipo | Costs of labor for Chilli, galangal, lemon grass cultivation | rai | 1,0 | 900,0 | 900,0 | |
| Equipo | Cost of shallow water well drilling equipment | puddle | 1,0 | 100000,0 | 100000,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Bud seedling sugarcane | seedling | 2250,0 | 0,9 | 2025,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Bud seedling Pineapple | seedling | 2500,0 | 2,0 | 5000,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Bud seedling Banana | seedling | 100,0 | 10,0 | 1000,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Bud seedling Papyrus | seedling | 3000,0 | 0,2 | 600,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Bud seedling sweet bamboo | seedling | 25,0 | 80,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Bud seedling Chilli, galangal, lemon grass | seedling | 2000,0 | 1,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Seedling rice KDML105 | seedling | 65,0 | 25,0 | 1625,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Chemical fertilizer 15-15-15 | kg | 300,0 | 13,0 | 3900,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Chicken manure | kg | 2000,0 | 2,0 | 4000,0 | |
| Otros | Electricity charge | hr | 240,0 | 5,0 | 1200,0 | |
| Otros | Machinery | rai | 19,0 | 500,0 | 9500,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 155850,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 155850,0 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The Land Development Department supports expenses for drilling shallow wells approximately 100,000 THB. The land users are involved in the maintenance of shallow wells at the 2nd year about 2,000 THB and pay for cost of maintenance and electricity bills about 1,200 baht per month for 9 months. Moreover, land users have to paid for farm pond construction under farm pond project of LDD about 2,500 THB.
Comentarios:
Nong Mek Village, Moo 9, Dan Chang Subdistrict, Bua Yai District, Nakhon Ratchasima Province located on the recharge area which has totally 1,000 rai. Recharge area is a type of upland where use for cassava and sugar cane planting. Most land users have not much knowledge and motivation on shallow well drilling. Hence, Land Development Department comes to train, solution on salt-affected soil with the project on prevents soil salinity, and to lower the groundwater table on recharge area since 2014. The shallow well technology has been implemented through the demonstration plot, which is the first learning center of salt-affected soil management on the recharge area
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance | 1 Times/year |
| 2. | Electricity charge | 1 Times/month |
Comentarios:
Shallow well which supported by LDD is a type of 5.5 hp gasoline pump then, land users try to use the electric water pump instead. The use of electrical water pump can increases yield productivity and enhance land users’ income. This is resulting in a better life.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipo | electricity charge,5 baht per unit 8 hours per day, 360 days / year | time | 2880,0 | 5,0 | 14400,0 | |
| Equipo | Machinery | time | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 16400,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 16400,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Land users do maintenance this technology by themselves, without hiring labor. There has only cost of modifying.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Cost of shallow wells implementation at the 1st year consists of 100,000 THB of labor hiring, equipment, and installation. Besides, land users have to pay 2,500 THB for farm pond construction
The expenditure at the 1st year in 2014, pumping groundwater needs to use electricity 8 hours/ 270 day. The amount of water pumping has distributed to 13 rai of rice fields, 1.5 rai of sugar cane fields, 1 rai of chilies, galangal and lemongrass fields. The expenditure at the 1st year with 19 rai is 42,050 THB combine with electricity charge 10,800 THB. Thus, the grand total of expenditure is 52,850 THB.
The income from crop production at 1st year, land users sold rice yield and got 109,200 THB (the average amount of yield is 560 kg/rai, totally gain yield is 7,280 kg, price of rice yield is 15 THB/kg). Land users got 40,500 THB from sugar cane production (the average amount of yield is 30 ton/rai, totally gain yield is 45 ton, price of sugar cane yield is 900 THB/ton). Moreover, land users also got 2,000 THB/month or 24,000 THB/year from chilies, galangal, and lemongrass production. Thus, the grand total of income is 173,700 THB and net income is 120,850 THB
Cost and income at 2nd year in 2015 are described as following;
The expenditure at 2nd year in 2015, pumping groundwater needs to use electricity 8 hours/ 270 day. The amount of water pumping has distributed to 13 rai of rice fields, 1.5 rai of sugar cane fields, 1 rai of sweet bamboo, 1 rai of chilies, galangal and lemongrass fields and 0.5 rai of reed fields. The expenditure at the 2nd year is 40,475 THB combine with electricity charge 10,800 THB and 2,000 THB of water pump modifying fee Thus, the grand total of expenditure is 51,275 THB.
The income from crop production at the 2nd year, land users sold rice yield and got 109,200 THB (the average amount of yield is 560 kg/rai, totally gain yield is 7,280 kg, price of rice yield is 15 THB/kg). Land users got 40,500 THB from sugar cane production (the average amount of yield is 30 ton/rai, totally gain yield is 45 ton, price of sugar cane yield is 900 THB/ton). Moreover, land users also got 3,500 THB/month or 42,000 THB/year from reed, sweet bamboo, chilies, galanga, and lemongrass production. Thus, the grand total of income is 191,700 THB and net income is 140,425 THB
The expenditure at the 3rd year in 2016, pumping groundwater needs to use electricity 8 hours/ 270 day. The amount of water pumping has distributed to 13 rai of rice fields, 1.5 rai of sugar cane fields, 1 rai of sweet bamboo, 1 rai of chilies, galangal and lemongrass fields and 1 rai of reed fields and 0.5 rai of reed. The expenditure at the 3rd year is 40,800 THB combine with electricity charge 10,800 THB and 2,000 THB of water pump modifying fee Thus, the grand total of expenditure is 51,600 THB.
The income from crop production at 3rd year, land users sold rice yield and got 109,200 THB (the average amount of yield is 560 kg/rai, totally gain yield is 7,280 kg, price of rice yield is 15 THB/kg). Land users got 40,500 THB from sugar cane production (the average amount of yield is 30 ton/rai, totally gain yield is 45 ton, price of sugar cane yield is 900 THB/ton). Moreover, land users also got 3,500 THB/month or 42,000 THB/year from reed, sweet bamboo, chilies, galangal, and lemongrass production. Thus, the grand total of income is 191,700 THB and net income is 140,100 THB
The expenditure at the 4th year in 2017, pumping groundwater needs to use electricity 8 hours/ 270 day. The amount of water pumping has distributed to 13 rai of rice fields, 1.5 rai of sugar cane fields, 1 rai of sweet bamboo, 1 rai of chilies, galangal and lemongrass fields and 1 rai of reed fields and 0.5 rai of reed. The expenditure at the 4th year is 37,125 THB combine with electricity charge 10,800 THB and 2,000 THB of water pump modifying fee Thus, the grand total of expenditure is 47,925 THB.
The income from crop production at 4th year, land users sold rice yield and got 109,200 THB (the average amount of yield is 560 kg/rai, totally gain yield is 7,280 kg, price of rice yield is 15 THB/kg). Land users got 40,500 THB from sugar cane production (the average amount of yield is 30 ton/rai, totally gain yield is 45 ton, price of sugar cane yield is 900 THB/ton). Moreover, land users also got 3,500 THB/month or 42,000 THB/year from reed, sweet bamboo, chilies, galangal, and lemongrass production. Thus, the grand total of income is 191,700 THB and net income is 143,775 THB
The expenditure at the 5th year in 2018, pumping groundwater needs to use electricity 8 hours/ 270 day. The amount of water pumping has distributed to 13 rai of rice fields, 1.5 rai of sugar cane fields, 1 rai of sweet bamboo, 1 rai of banana, 1 rai of chilies, galangal and lemongrass fields,1 rai of reed
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1084,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Average annual rainfall from 2008-2013
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Meteorological Department
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Temperatures average 13-39 degrees Celsius, average relative humidity 55-89.%
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Geography The Bua Yai district is located in the north of Nakhon Ratchasima. On the Korat Plateau
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
The surface soil is sandy loam. The bottom soil is sandy loam soil. The pH is between 7.5 - 8.5. Salinity is at a salty level. Have salt stains on the surface throughout the year and have very low P and K.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
< 5 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
Sí
Especifique:
Slightly saline
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
saline groundwater
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Before drilling shallow wells there were very few animals living in this area. After 1 year of shallow well being implemented, there is an increase in food and plant sources, the habitat of living things. To implement the technology resulting in more organisms such as fish, birds, rats, earthworms, and insects
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- rico
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- ancianos
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users are diligent in their work and patient. They carried out crop rotation throughout the year. The, they get more revenue daily, monthly and yearly.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
Comentarios:
Land users drill a shallow well on the recharge area in order to pump groundwater for planting throughout the year to reduce expenses and increase family income
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
- Rainfed.
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Comentarios:
Land users can decide to use the land by themselves. They did crop rotation by using water pumped from shallow wells. The Land users could be an example for the other that could be shown by surrounding farmer want to engage in this project.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
calidad de cultivo
riesgo de fracaso de producción
diversidad de producto
área de producción
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
calidad de agua potable
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
ingreso agrario
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
derechos de uso de la tierra/ agua
oportunidades culturales
oportunidades recreativas
instituciones comunitarias
instituciones nacionales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
mitigación de conflicto
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
calidad de agua
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
drenaje de agua en exceso
nivel freático/ acuífero
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
acumulación de suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
salinidad
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
acidez
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
especies invasoras extrañas
diversidad animal
especies benéficas
diversidad de hábitats
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
deslizamientos/ fluyos de escombros
impactos de sequías
impactos de ciclones, tormentas de lluvia
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
riesgo de incendio
velocidad de viento
micro-clima
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
inundaciones río abajo
colmatación río abajo
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
sedimentos transportados por el viento
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
impacto de gases de invernadero
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Comentarios:
An opinion of the land user, there are many situations such as rain delay during 2014-2016, drought during December – April 201 and flood in rainy season while rain delay in 2018 can lead to water scarcity problem. However, that situation cannot impact farmland with shallow wells.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Land users to pay a 2,000 baht machinery as a long-term investment to operate for several years and pay the electric fee for water pumping but land users can have 10,800 THB and the revenue daily, monthly and annually and reduce costs in the household
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
Land user and other farmer have knowledge and understanding on an advantage of shallow well technology implemented. Some of them drill water well by themselves.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
otros (especifique):
changing practice
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
Land users have modified water pump machine by use electric pump instead of a gasoline pump
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Reduce soil salinity |
| Save money by bringing rice and vegetables grown into household food. |
| Increase sales revenue, rice, sugarcane, pineapple, Papyrus, banana, lemongrass, galangal, chili, and sweet bamboo. |
| Save money by bringing rice and vegetables grown into household food. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Pumping water from shallow wells for agricultural use, can reduce groundwater table and prevent salinity that is a great measure on land degradation mitigation |
| The land user can have food from plant production from their farms. The land user can reduce household expenses. Left to sell, resulting in a daily, monthly and annual income and make a better life. |
| Biodiversity enhancement, there are many plants and living things such as earthworms, birds, fish, frogs, and insects. This is resulting in a balanced ecosystem. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| After one year of shallow wells implemented, land users must take care and maintain shallow wells as usual. | Make an agreement on taking care of shallow wells after implemented. |
| To inform LDD when something is wrong |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Other land users who are not participating. will not get knowledge about the use of shallow well to reduce the level of underground water. | LDD staff / Land users participating in the project to advise or educate other farmers on how to join the project. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Visit 1 farmer/user's land
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Interview with 1 farmer.
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
The Land Development Department officers and planners (7)
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
03/09/2018
Comentarios:
To be clear on the result of the technology implementation there should be soil sampling as well.
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Evaluate the project using water from shallow wells to prevent. Distribution of saline soil as farmers participate in Bua Yai District,Nakhon Ratchasima Province (Kamolthip Sasithorn: 2017
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
http://www.ldd.go.th
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Study of groundwater level changes to rice production in an integrated saline soil development project area, Bua Yai District, Nakhon Ratchasima Province (Bowon Buakhao: 2017)
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
http://www.ldd.go.th
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/library/media/27/
7.4 Comentarios generales
Some part of the questionnaire is very complex such as the cost of input
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos