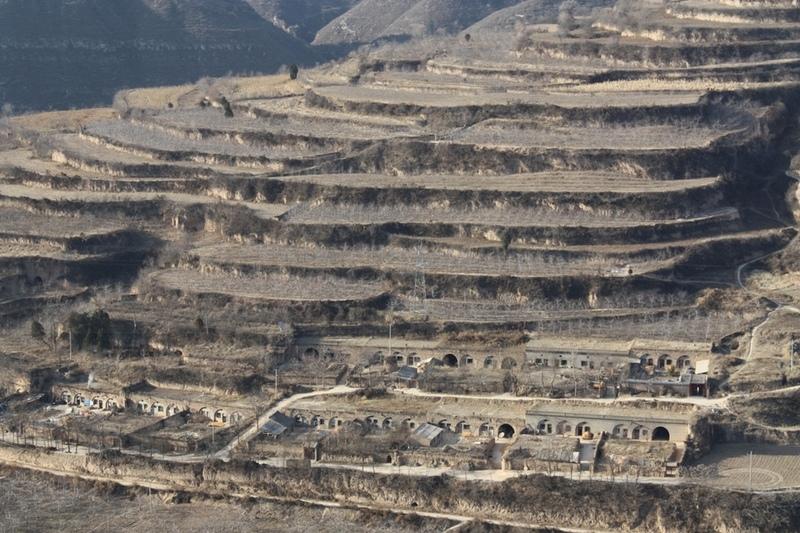
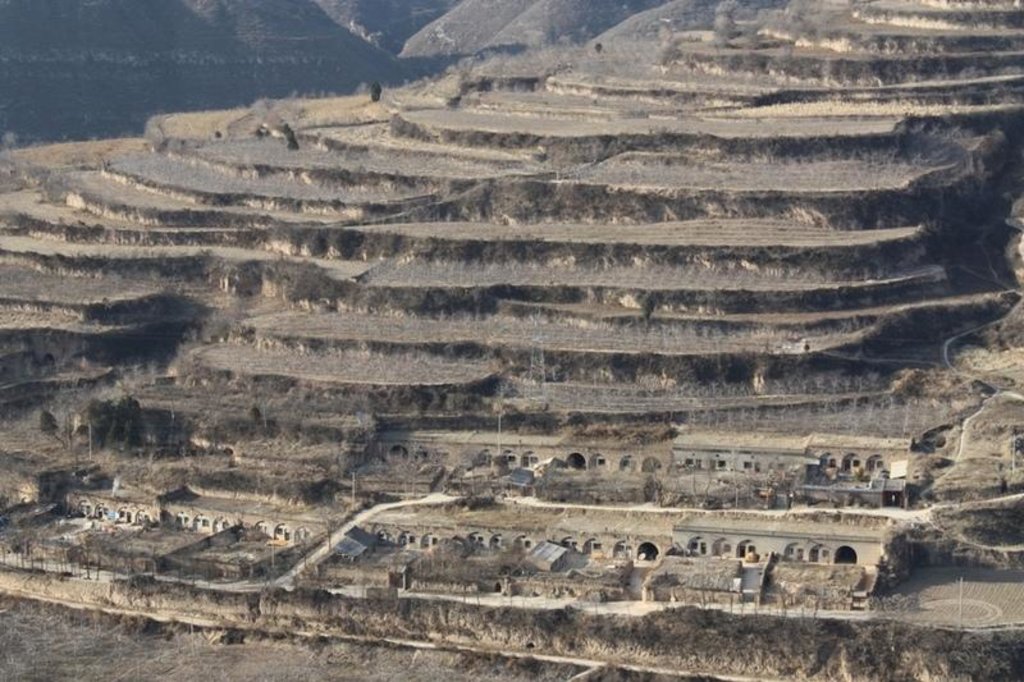
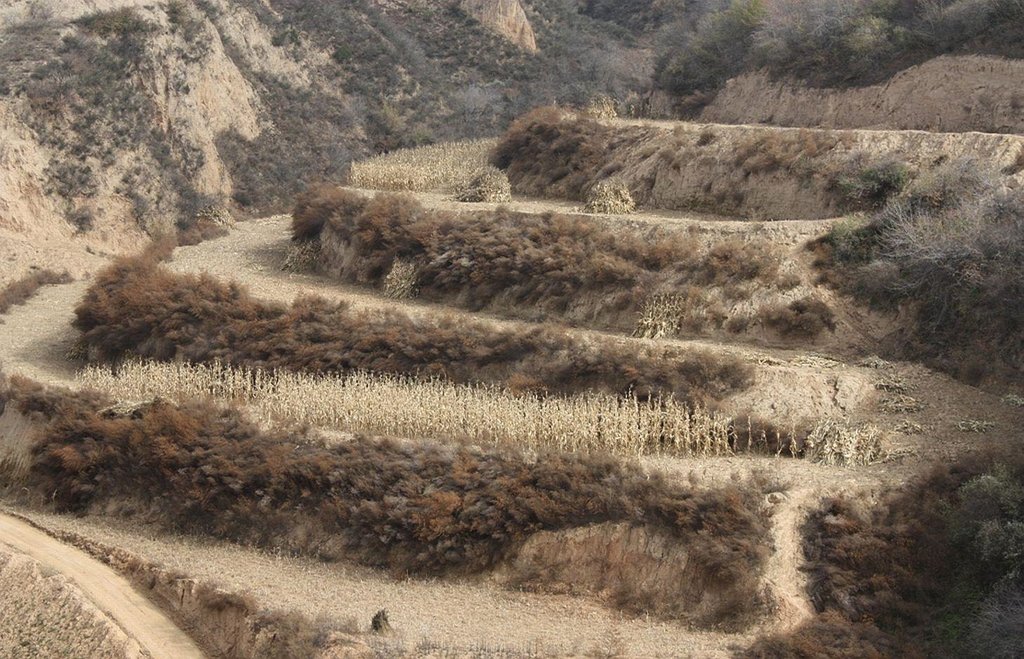
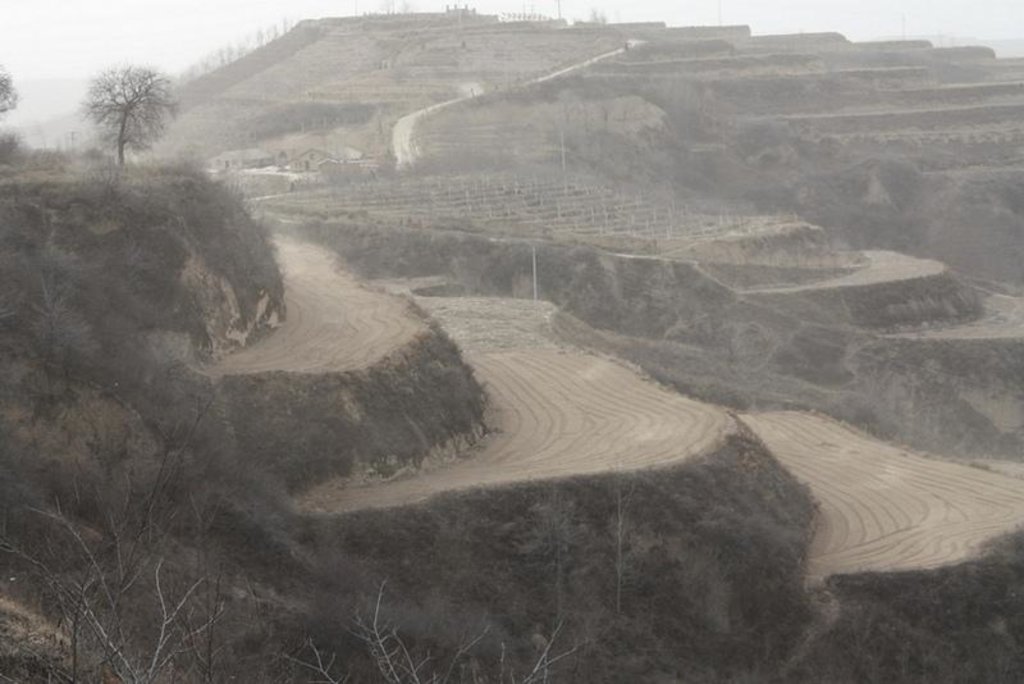
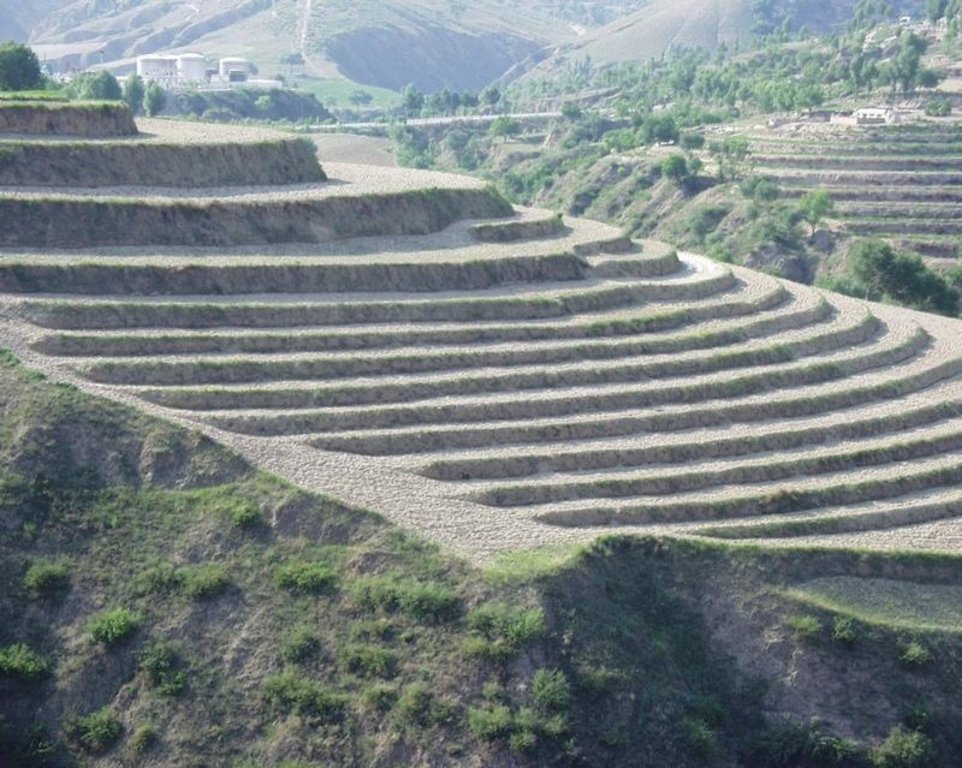
Bench terraces on loess soil [China]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Fei WANG
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
土坎梯田,梯地
technologies_1445 - China
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
A Terrace is a structural SLM practice with a raised flat platform built on the slope to reduce soil loss and runoff on the slope, increase the rainfall infiltration and yield.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
A terrace is a leveled section of a hilly cultivated area, designed as a method of soil conservation to slow or prevent the rapid surface runoff and erosion of topsoil. Often such land is formed into multiple terraces, giving a stepped appearance.
Purpose of the Technology: To change the landform for better agricultural condition of operation of tillage and harvasting, reduction of soil erosion and water loss and finally for higher production.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The building of a terrace in the loess plateau takes long because loess is very soft and deep and the severe soil erosion and shortage of water in agriculture hinders the process, as well. Previously, terraces were constructed by hand. These terraces weres narrow and damaged by the great storms. Now, the machinery is used to build wide terrace with high bank size in the loess plateau. The establishment of terrace needs a lot of money but it is a long-term investment. The maintenance of terrace is considerable economic because the major efforts are the annually improvment of terrace bunds.
Natural / human environment: The soil erosion is very severe because of the cohesionless loess soil and very intensive rainfall storms in the summer and autumn that would destroy the land surface into broken hilly area. Terrace is a kind of measure to resolve it combining with crops. The human activities here is very intensive because they must plant on the slopes that would make the soil erosion greater.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
China
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Shaanxi Province
Especifique más el lugar :
Yanhe River Basin
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la Tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente a lo largo de un área, especifique el área que cubre (en km2):
253,3
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 253.3 km2.
The total area with different measures is till to 2000. Yanhe River is a first class branch of Yellow River, China. The average channel slope is 3.26‰, and the area of whole basin is 7,687 km2. It is in the semi-arid North Temperate Zone with an average annual precipitation varying from 500 to 550 mm, and an average annual air temperature ranging from 8.5 to 11.4℃. It is in hilly gully area of the Loess Plateau covered by loess. The landform is seriously broken by cutting gullies induced by water erosion. The gully density (the length of channel in one km2) is amount to 2.1 to 4.6 km•km-2. The soil loss is severe all along.
The Ganguyi Hydrology Station (109°48′E, 36°42′N) located in the Ganguyi Town, Baota Country, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province. The area up Ganguyi Hydrology Station is 5,891 km2, including of Jingbian County(256km2), Zhidan County(708km2), Ansai County(2,699km2) and Baota County(2,228km2). The average annual runoff is 0.22 billion m3, and the runoff modulus accounting for 4,776.36 m3•km-2•yr-1. The average annual sediment flow is 4.776
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The terrace in this site has been formed since 1994 with machinery. The land is quite wide and large enough for agriculture in the hilly loess region,
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agroforestería

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- cereales - mijo
- cultivos florales
- cultivos para forraje - alfalfa
- leguminosas y legumbres - frijoles
- cultivos de semillas oleaginosas - girasol, colza, otros
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - patatas
- vegetales - otros
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- dátiles
- frutas de pepita (manzanas, peras, membrillo, etc.)
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 300Longest growing period from month to month: March to NovemberSecond longest growing period in days: 200Second longest growing period from month to month: April to October
Comentarios:
Main cash crops: Beans, sunflower, apple, Chinese date, alfalfa
Main food crops: Potato, millets, maize, buckwheat
other crops: vegetable
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water losses are alarming in this region. The loose loess, steep slopes, and intensive storms in the summer and autumn, accelerates this process. Aditionally, the lack of rainfall negatively impacts agriculture and vegatation. Sediment deposition could increase the river bed and diminish capacity of reservoirs. On one hand side floods occur frequently because of fast and large runoff and on other hand side sedimentation in rivers reduce their water carring capacity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The low yield of crops and the low income from land is more important for the local people. It is necessary to improve the agricultural conditions. The land, especially the tableland and gentle slope land could be convert into terrace.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: The composation of agriculture is very simple here.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)

Tierra de pastoreo
- Intensive grazing/ fodder production
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- medida de pendiente transversal
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas estructurales
- S1: Terrazas

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hw: reducción de la capacidad de amortiguación de las áreas humedales
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (The natural vegetation in this region is grass on theslope and trees on the gully and alluvial land. After the destroy of natural, the soil loss increases greatly.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (About 70% of annual rainfall is in the summer and autumn. The storm is very intensive.), population pressure (The population density account for 71 capita per square km.)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (The rainfall varies greatly in different year and different seasons. The drought happened frenquently.)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
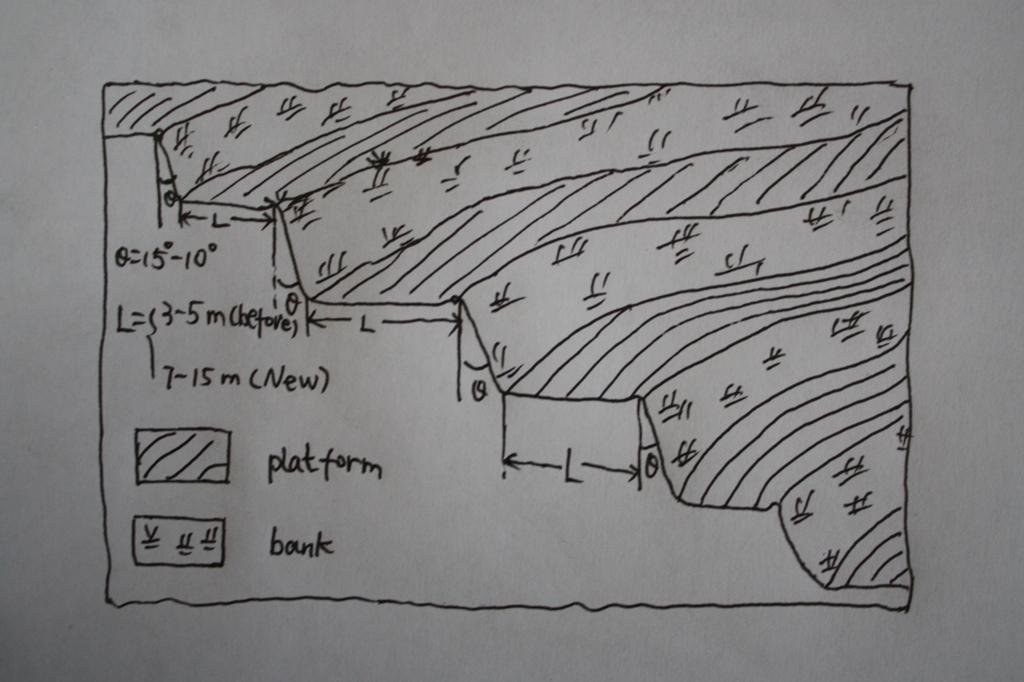
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
The brief structure of terrace in the Yanhe River Basin.
Location: Zhifanggou Watershed. Ansai County, Shaanxi, China
Date: 2008-12-15
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (The location selection and how to build a good terrace need special knowledge on soil engineering.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It is easy to know the benefit for all the local farmers.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 50000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Grass species: Natural grass to protect the bank of terrace.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 1.00%
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.5
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 8
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-100
Construction material (earth): The terrace in the Loess Plateau are used local soil/earth directly.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 30-60%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Wild grassland or range land before mostly. Some time the cropland on the slope.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: The labor is less intensive on the plain platform.
Autor:
Wang Fei, Yangling, Shaanxi, China
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
0,83
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
8.8
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey and design | Before construction |
| 2. | Move the topsoil to other place | 1st step of construction |
| 3. | Built the platform and bank with soil digged | 2nd step of construction |
| 4. | Backcover the topsoil on the surface of platform | 3rd step of construction |
| 5. | Check and accept the terrace | After the terrace finished |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Survey and design | Person/day | 45,0 | 8,8 | 396,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Building terraces (machine price included) | Person/day | 75,0 | 19,0 | 1425,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 1821,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 2193,98 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.5 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reinforce the bank | annually |
| 2. | Fill the erosion hole of the landform | annually |
| 3. | Build the edge in some terraces | annually |
| 4. | Reinforce the bank | annually |
| 5. | Fill the erosion hole of the landform | annually |
| 6. | Build the edge in some terraces | annually |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Keep Terraces in shape | Person/day | 30,0 | 8,8 | 264,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 264,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 318,07 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: Crawl dozer and small traditional hand tool., crawler tractor, spade
In general condition, slope and soil, in the middle reaches of Yan River Basin. The prices of labour-day and Machine-hour are around 2005.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The terrace on the steep slope need more input for more soil and earth should be moved. It is the most important factor.The soil depth is not so important for the deep soil layer here.The cost of labour increases greatly in the last several years and the cost of construction of terrace increased.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The mean annual rainfall in the basin is 515.2 mm in the duration from 1952 to 2000. The rainfall from May to Oct accounts for 446.8 mm, up to 86.7%; and that from Jun to Sep accounts for 367.6 mm, up
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate. The accumulating time that temperature above 0 ℃ about 3800 hours, and that above 10 ℃ is more than 3200 hours.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones convexas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Landforms also: mountain slopes and hill slopes
Slopes on average also very steep
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil texture: There are more than 50% soil particle are fine sand with size between 0.05 and 0.1 mm.
Soil fertility very low: Lack of N, P and SOM.
Topsoil organic matter: The average Top-SOM of cropland is about 0.05%
Soil drainage / infiltration good: The inflitration of Loess is very fast, but it is prone to sealing when flashing.
Soil water storage capacity low: It is easy to evaporation and drainage.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Availability of surface water medium: It is very stable in this region.
Availability of surface water also poor/none: Nearly all the branches of Yanhe are seasonal river.
Ground water table: It depends on the landform. In valley and alluvial land, it is shallow.
Water quality: Good quality for there are few pollution sources.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
It is very stable in this region.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
- comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No clear difference.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
80% of the land users are average wealthy (The terrace are build together in some villages for all the people funded by national subsidy.).
Off-farm income specification: The yield of terrace is much high and stable.
Level of mechanization manual work: The harvesting and other management are by hand, even the tillage on the nerrow terrace
Level of mechanization animal traction: Tillage with animal power mostly in the wider terrace.
Market orientation mixed subsistence/ commercial: Some production for themselves, but most of production is exchanged on the market.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
According to 0.054 ha per capita.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
Comentarios:
Like other rural area in China.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
600
Cantidad luego de MST:
2200
producción animal
producción de madera
riesgo de fracaso de producción
diversidad de producto
área de producción
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
calidad de agua potable
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Cantidad antes de MST:
43.9
Cantidad luego de MST:
120
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
mitigación de conflicto
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Evaporation form the wall of terrace, Especially for the narrow terrace
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
More inflitration of rainfall, but the evaporation near to the wall increases
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
10000t/km^
Cantidad luego de MST:
2000t/km^2
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
Otros impactos ecológicos
Hazards towards adverse events
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
inundaciones río abajo
colmatación río abajo
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
sedimentos transportados por el viento
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | no muy bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no se sabe |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no se sabe |
Comentarios:
Loess is very prone to erosion and extreme storms would destory the bank of terrace. In the study site sesonal rainfall increased and the loess terrace could retain more soil water and reduce the runoff.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
The yield of terrace is stable and relative higher. The income from terrace is high and the maintain cost is low.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
100 households
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
95 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Most land farmers have some terrace. I do not know the exact number of land user families who adopted the technology.
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: the old narrow terraces, now a very small area left, are build voluntarily.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nearly all the people know the benefit of terrace. the benefits of terraces are very good for crops and orchards are high enough in this region.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Increase yield and income. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the terrace is maintained well, the water condition would be better than that on the slope land even in dry year with low precipitation. |
|
Convenient to till and harvest How can they be sustained / enhanced? Tillage and harvesting is much easier on the plain flat land than on the slope. The maintainance of terrace is important. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Reduce soil erosion on the slope. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The loess soil is prone to erosion because of its loose character induced by fine sand content and low soil organic matter. The plain flat makes the dispersion and transportation of soil particls difficult. |
|
Reduce runoff and increase the soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? The runoff generation is smaller on the plain than on the slope. Slow movement of surface water lead to more soil infiltration. |
|
Increase yield. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Water is the limit factor in the loess plateau. The yield would increase if there is enough water available. |
|
Decrease flood risk. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It is a kind of off-site benefits because less runoff generation and gentle process of runoff decrease flooding. Reduction of sediment also diminish flood risk because the drainage capacity of channel and adjusting capacity of reservior increase when sedimentation decrease. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The output is also low in contrast with other industries. | No way to overcome it. The total and net income is too low because the area of terrace per capita is very small. |
| The income is relative compared with other industries. | No way to overcome it. The net income is low because the labour costs are increasing, and the total income because labour cost and very small area of terrace per capita. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| There is possible damage of terraces because the loess is very loosen and prone to collapse. | Keep upmaintaining the bank and land well. |
| Decrease runoff of lower stream. | No way to overcome it, but it also could decrease the risk of floods. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Soil and water conservation records of Shaanxi Province. 2000. Shaanxi People's Press, Xi'an City, China
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Library of ISWC, CAS
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
The soil and agriculture of the Loess Plateau. 1989. Zhu Xianmo, Agriculture Press, Beijing City, China
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Library of ISWC, CAS
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Statistical tearbook of Yan'an. 2003. Compiled by Editorial Board of Statistical tearbook of Yan'an
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Library of ISWC, CAS
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Impact of human activities on runoff and sediment change of Yanhe River based on the periods divided by sediment concentration. 2008. WANG Fei , MU Xing-min ,JIAO Ju-ying, LI Rui. Journal of Sediment Research
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
http://159.226.100.28/asp/Detail.asp
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Changes of soil erosion intensity due to conversion of farmland to forest and grassland in Yanhe River. 2007. BasinWang Bangwen, yang Qinke, Liu Zhihong, Meng Qingxiang, Science of Soil and Water Conservation
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
http://159.226.100.28/asp/Detail.asp
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos