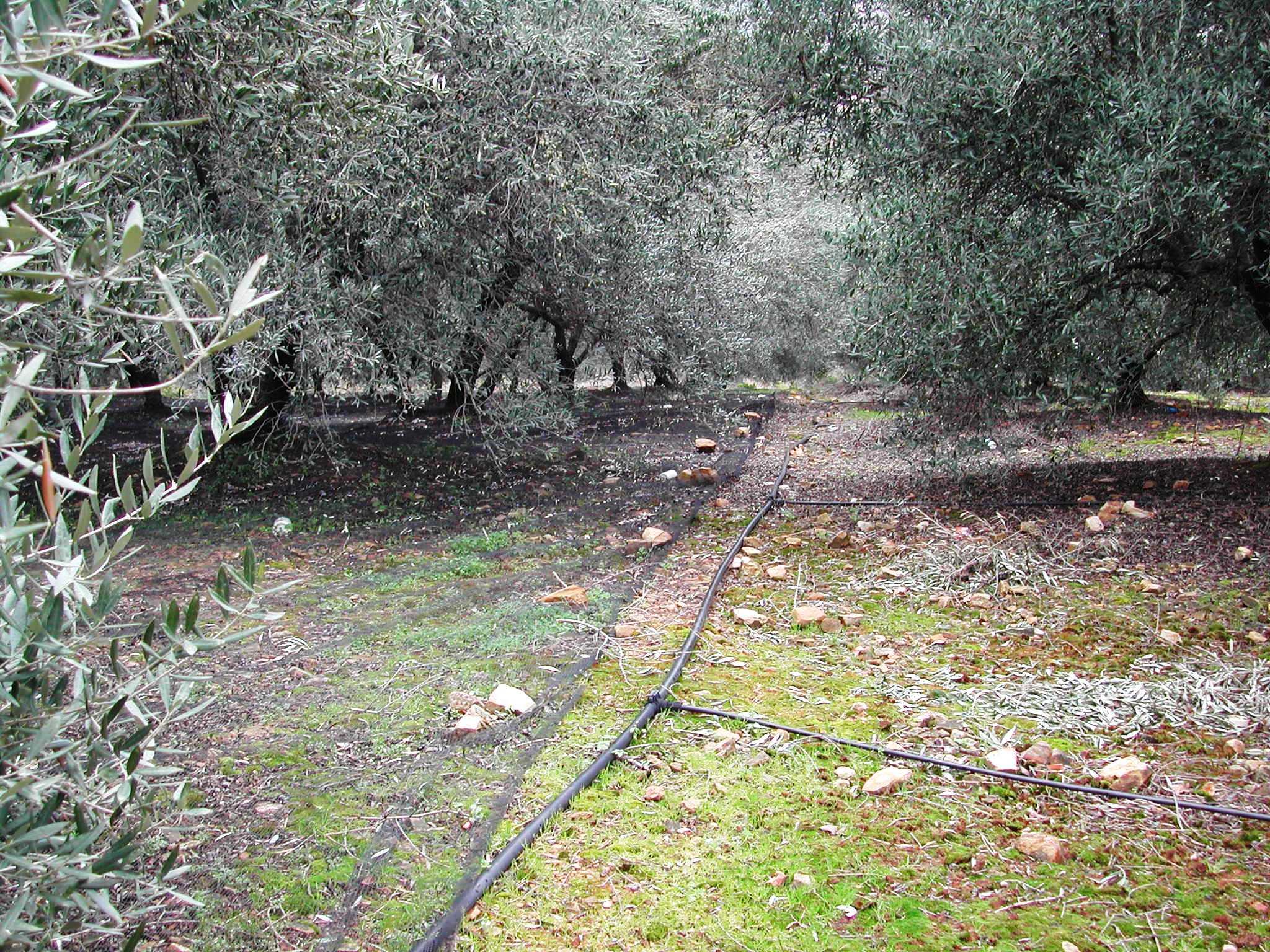
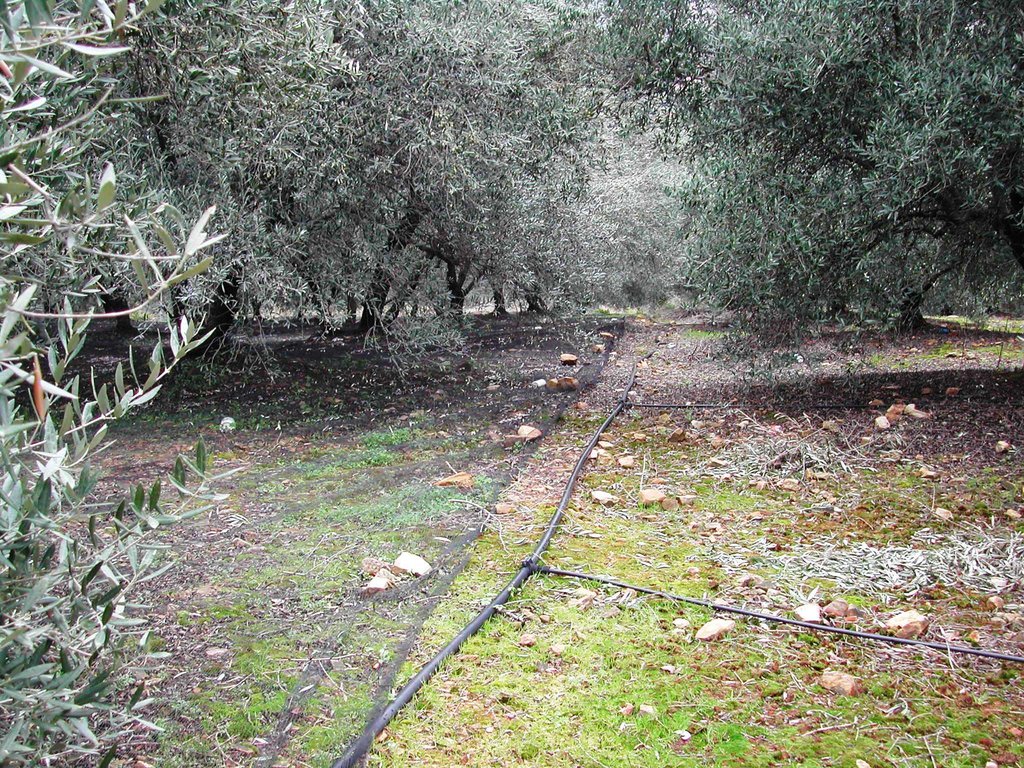
Application of water by drip irrigation [Grecia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Costas Kosmas
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Αρδευση με σταγονες
technologies_1456 - Grecia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Bardoulaki-Spanoudaki G
Organization for the Development of Western Crete OADYK Agia, Chania
Grecia
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Agricultural University of Athens (AUA) - GreciaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Organization for the Development of Western Crete (OADYK) - Grecia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Sustainable use of water [Grecia]
Sustainable use of water
- Compilador: Costas Kosmas
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Drip irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation is a method which minimizes the use of water and fertilizer by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of plants, either onto the soil surface or directly onto the root zone, through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Irrigation is very important for increasing crop yields in arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid climates. The area of irrigated land has increased more than twice in the last decades in the study areas. In recent years, the considerable reduction of winter and autumn rainfall has caused a serious lack of water resources. The production of the various crops is substantially reduced if water is not provided during the summer period.
The high demands for water consumption or other economic activities have increased the price of water, forcing up the cost of agricultural production. In addition, in many cases, low quality (with high electrical conductivity) water is used for irrigation. The need for intensification of agriculture to meet the high cost of production, the use of poor quality of water, the lack of drainage systems are in many cases responsible for soil degradation resulting from water logging, salinization, alkalinization, and soil erosion.
Purpose of the Technology: Drip or trickle irrigation achieves the highest irrigation efficiency since about 90% of the applied water is available to the plants. This SWC technology is especially suitable for watering trees or other large plants keeping strips among trees dry. Application of water by drip irrigation can be considered more as more efficient method using low quality of irrigation water. Irrigation water of high salt content can be applied in higher quantities in spots leaching salts to deeper soil layers. Drip irrigation can be applied in any type of soil from coarse- and fine-textured and without any limitation to slope gradient requiring little labour during installation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In the study area of Chania trickle irrigation system includes mainly three branches from the outlet of main water network transportation system to the application in the trees. The last branch consists of plastic tube 12 to 32 mm in diameter that lies either on or just below the soil surface and applies the water either through small holes in the line or through emitter nozzle.
Natural / human environment: In recent years the increasing awareness of farmers on issues relating to the sustainability of the environment and conservation of water by promoting SWC technologies has led to widespread of use of drip irrigation in the area of Crete and in many other parts of the Country. The categorization of the specific SWC technology according to the WOCAT questionnaire is defined as: CtWtA3.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Grecia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Kidonia
Especifique más el lugar :
Chania Crete
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 480 km2.
Map
×2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- durante experimentos/ investigación
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- aceituna
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: March to JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 150Second longest growing period from month to month: March to June
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): availability of irrigation water, loss of water in the network, conflicts between districts and economic sectors of tourism and agriculure
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): availability of irrigation water, conflicts between districts and economic sectors of tourism and agriculure
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A3: Tratamiento de superficie del suelo

medidas estructurales
- S11: Otros
Comentarios:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (lack of water), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.) (salinization)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
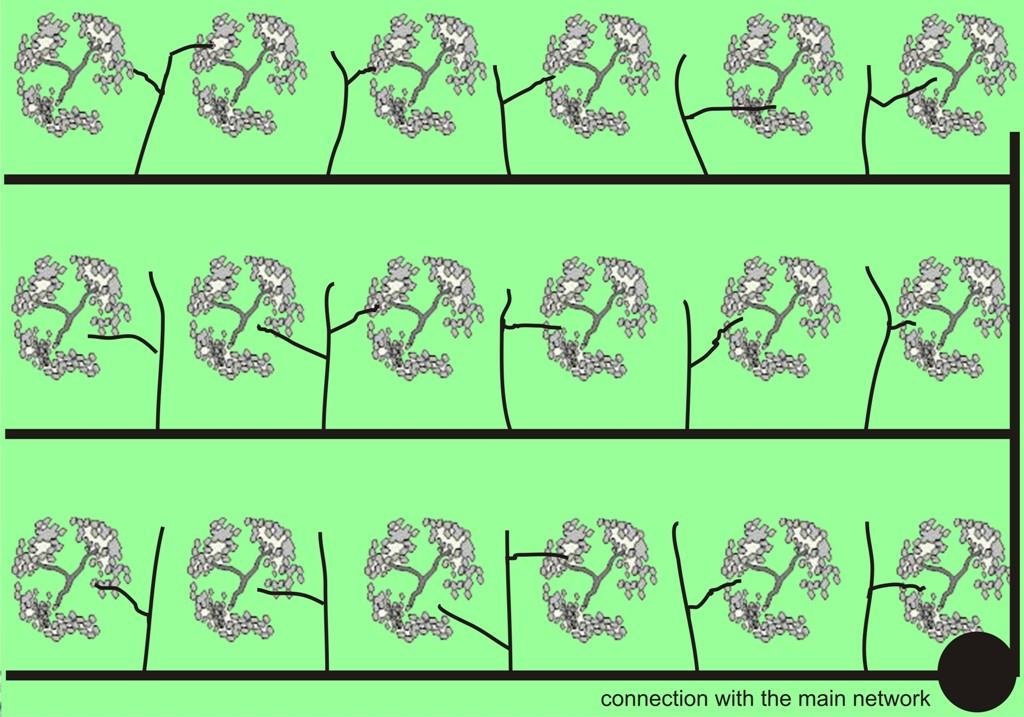
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
In the study area of Chania trickle irrigation system includes mainly three branches from the outlet of main water network transportation system to the application in the trees. The last branch consists of plastic tube 12 to 32 mm in diameter that lies either on or just below the soil surface and applies the water either through small holes in the line or through emitter nozzles.
Location: Kasteli. Chania
Date: March 2007
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (system installation requirements)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity)
In blocks
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 250
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Perennial crops species: olives
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 15.00%
Structural measure: irrigation system
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Construction material (other): plastic, plastic tubes 12-32 mm in diameter
Other type of management: Water distribution among farmers, water is provided under the control of local authorities
Autor:
C. Kosmas
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting the olive trees | 2 days/ha |
| 2. | transporting plastic tubes | once during installation |
| 3. | Whole system of tubes, filters and system of fertilizers application | once during installation |
| 4. | Main network of irrigation system | once per year |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | >Installation | ha | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | |
| Equipo | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 1650,0 | 1650,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 2000,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 2000,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.1 month(s)
Life span of the irrigation network: 20 years
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | cleaning filters and replacing destroyied tubes | 3 hours every year/ha |
| 2. | Checking outlets and conectors | once per year |
| 3. | Control of network for loss of irrigation water | once per year |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipo | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 60,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 60,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: hand tools, System of applying fertilizers through the irrigation water, filters for keeping various solid materials
per hectare of land affected
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
the reguired materials (tubes, filters, etc)
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
With six months of dry period
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is very high-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high-very high
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table: 5-50 m, > 50 m
Water quality (untreated): good drinking water, for agricultural use only (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
- rico
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women in rural areas are involved in other type of work
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are rich (cost for buying materials).
55% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: working in tourist business
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- arrendamiento
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
1500 kg/ha
Cantidad luego de MST:
2000 kg/ha
manejo de tierras
Comentarios/ especifique:
Cultivation of the land is hindered by the irrigation network
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
calidad de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
ingreso agrario
Cantidad antes de MST:
4500 euro/ha
Cantidad luego de MST:
5800 euro/ha
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
oportunidades culturales
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Significant environmental benefit from the rational use of irrigation water
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
humedad del suelo
salinidad
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Otros impactos ecológicos
Waste
Comentarios/ especifique:
environmental pollution due to presence of plastics not easily recycled
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no muy bien |
Comentarios:
Control of flooding by adjusting river bed
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
3850
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 11-50%
Comentarios:
65% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2200 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
35% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1650 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Increase crop production in some cases up to 50% How can they be sustained / enhanced? providing more water |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Technologies on conserving soil and water resources and combating desertification in Crete are mainly related to land management. Olive groves are widely expanded in the island due to the importance of olive oil as one of the essential material for daily human food needs. Furthermore, olive groves can survive under adverse climatic and soil conditions supporting a significant farmer’s income under relatively low labour. Land management practices have been adopted in the area based on tradition and transfer knowledge by the local institutes and specialists. In addition, irrigation of the land by the drip system is considered as a very promising technique for conserving water resources in the area. Land terracing is a human intervention in sloping semi-natural landscapes, which have suffered losses, to some degree, in their sustainability and resilience. How can they be sustained / enhanced? by providing additional water resources in the area (build a water reservoir) |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| High cost for buying materials, better education | subsidizing materials, technology transfer |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| increased cost for the first installation | subsidizing the system |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Sustainable use of water [Grecia]
Sustainable use of water
- Compilador: Costas Kosmas
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos