Maize strip tillage [Suiza]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Streifenfrässaat (German)
technologies_1006 - Suiza
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Wyler Roman
Center for Development and Environment, University of Berne
Suiza
usuario de la tierra:
Wyss Beat
Suiza
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Soil support program for conservation agriculture [Suiza]
Through the soil support program land users get subsidies for applying conservation technologies on their fields during a period of 6 years.
- Compilador: Deborah Niggli

Direktzahlungssystem [Suiza]
Finanzielle Leistungen des Bundes um den Ertragsverlust, den eine Kultur für den Bauern bringt, auszugleichen. Das Direktzahlungssystem führt gewissermassen zu einer 'Vergünstigung des Produkts' für den Konsumenten.
- Compilador: Deborah Niggli

Förderprogramm Boden [Suiza]
Mit dem Förderprogramm Boden des Kantons Bern erhalten beteiligte Landnutzer Direktzahlungen für die Anwendung von bodenkonservierenden Anbauverfahren auf ihren landwirtschaftlichen Feldern. Das Projekt hat eine Dauer von 6 Jahren.
- Compilador: Deborah Niggli
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
A cropping system for maize which reduces the reworking of the soil to the stripes, in which the seeds are planted.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
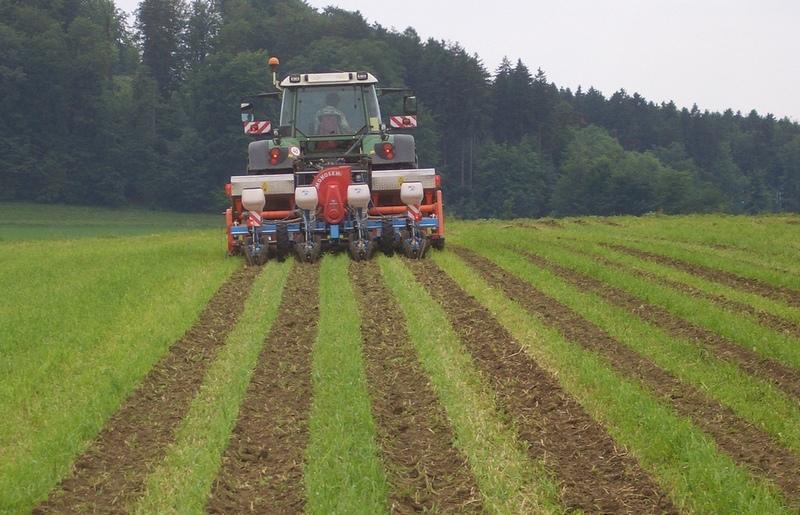
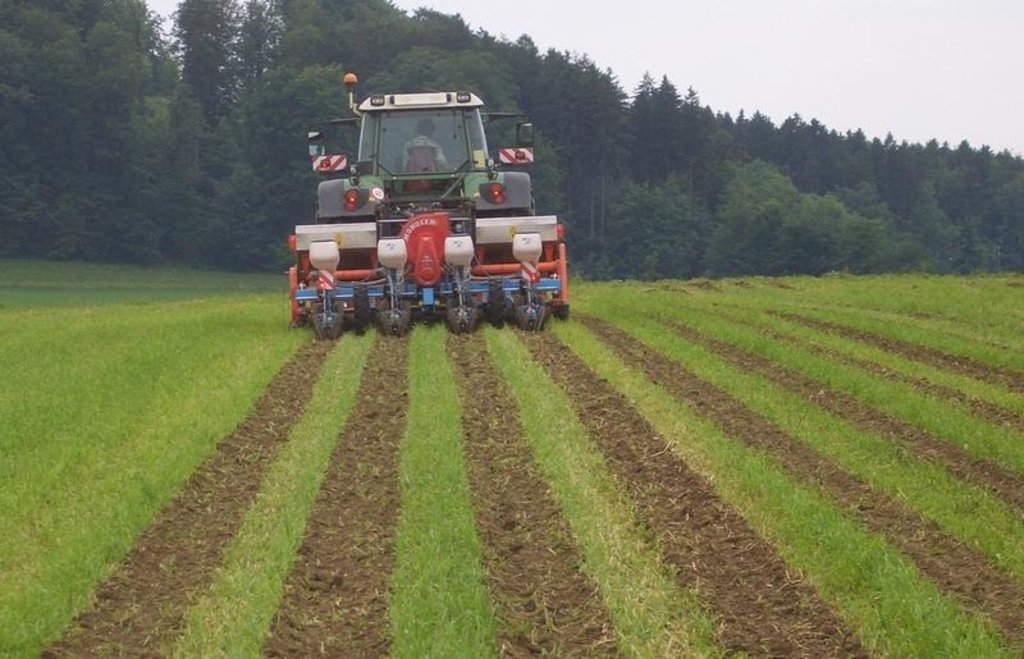
Maize strip tillage is a mixture between no tillage and conventional agriculture. The reworking of the soil greatly reduced. Instead of ploughing and harrowing a special rotary tiller including a grubber is being used. The working depht of the rotary tiller is 10-15cm, the grubber reaches to 20-25cm depht. The machine reworks the soil on stripes of 30cm width. This is where the seeds are planted. In between there are stripes of 45cm width, which are left untouched.
In Switzerland farms usually are small. A major part of the arable land is used to produce fodder. (For example maize, grain, fodder beet)
Usually maize strip tillage is being used to avoid soil erosion or for economical reasons. Compared to conventional agriculture several working steps can be saved. The reworking of the soil, manuring, seeding and applying of herbicides can be done at once.
Since the machine is expensive and a strong tractor is needed, farmers usually don’t buy it on their own. In most cases a contractor will be tasked to do this work. Of course this is not for free. But since several working step are saved, there is more time left to do other work (6.5h/ha).
The reduced reworking of the soil holds remarkable ecological advantages. Occurrence of erosion is very seldom, because the stripes covered by plant residual significantly reduce the speed of surface water. To increase this effect, the stripes are laid along the height countours, if possible. Since the soil structure is not disturbed in the stripes between the seeds, the risk of compaction is reduced there. For that reason maize strip tillage is often used before potatoes in a crop rotation. This is a crop that is very sensitive to soil compaction.
The technique brings along an ecological disadvantage, too. Before sowings the precedent crop needs to be treated with a total herbicide (glyphosat) to avoid unwanted competition. Only in wet areas, where there is enough water available it is possible to not use glyphosat. Also in long time studies, residues of glyphosat could not be detected in the soil. But if ever weeds will develop a resitance against it, that would certainly be a major problem.
The enhanced risk of crop loss is another disadvantage of the technology. In conventional agriculture the soil is left to dry for a few days after ploughing. maize strip tillage does not hold that possibility. If the conditions are wet, risk of crop failure can be a problem. However, if conditions are good (dry enough), both quality and crop yield are similar to conventional agriculture.
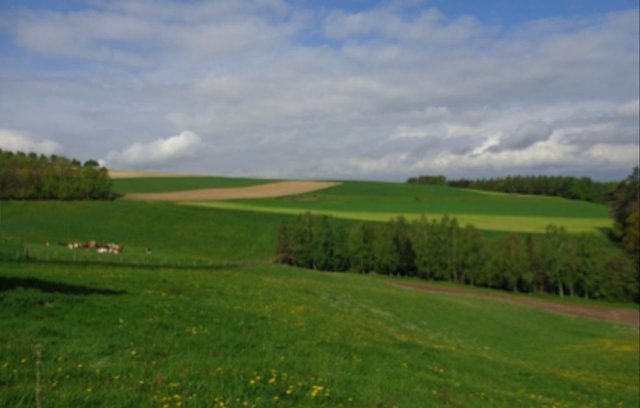
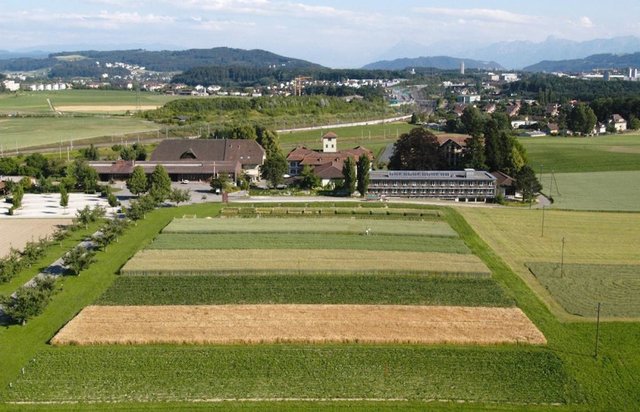
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Suiza
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Kanton Solothurn
Especifique más el lugar :
Oberramsern
Comentarios:
The portraited farmer is working as a contractor and is applying the technology on about 0.8km2. Currently only 1ha of his own land is used for maize.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology was developed some 12years ago by the designer and contractor Walter Witzig supported by researchers from Forschungsanstalt Reckenholz-Tänikon.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- hay
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Oct
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion by water and soil compaction.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- medida de pendiente transversal
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
Comentarios:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: contour planting / strip cropping, minimum tillage
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pc: compaction, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bl: loss of soil life
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (too deep and too intensive reworking of the soil.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), education, access to knowledge and support services (Tradition. Most people do not question tillage.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree / shrub) (too heavy machinery used under wet conditions.)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
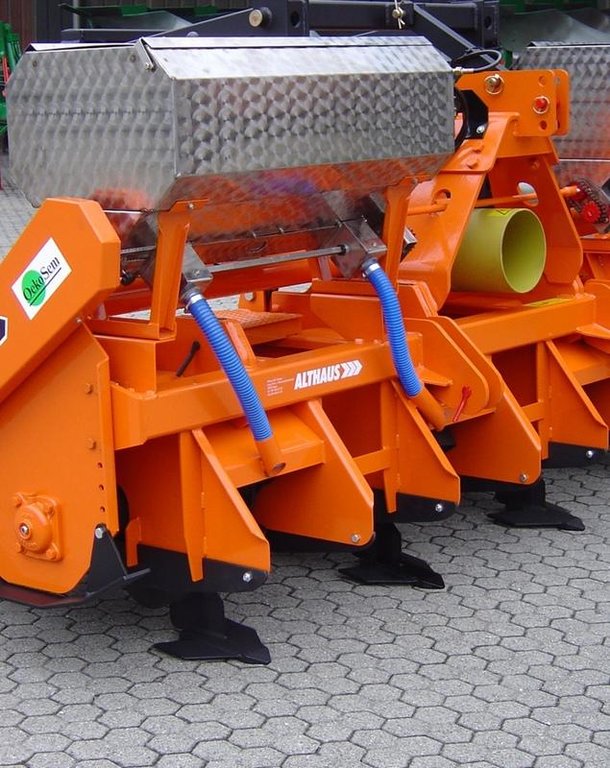
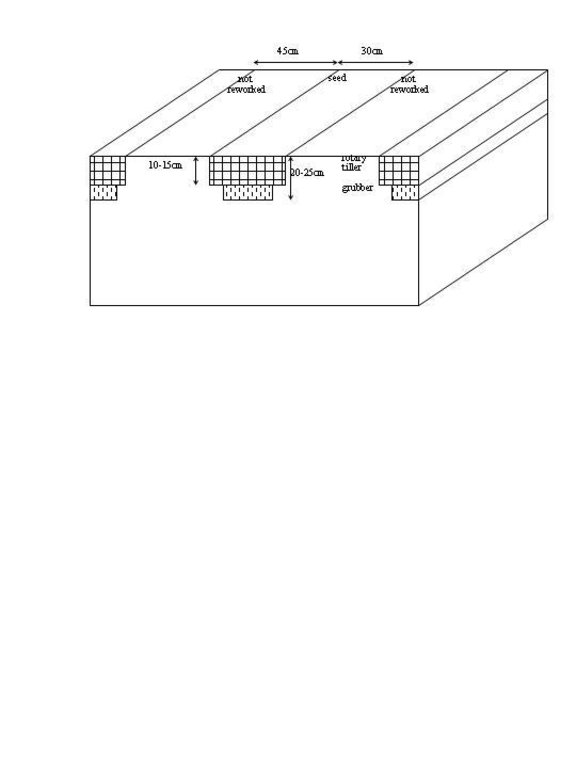
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
The rotary tillers working depth is 10-15cm. The grubber reaches to 20-25cm depth. This is to obtain a loose soil structure. Manure is brought into the soil while tilling.
Immediately after that the seeds are brought into the soil. Finally a selective herbicide can be sprayed. Stripes of 45cm width are not reworked and help to avoid soil erosion and compaction.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Maize
Minimum tillage
Remarks: The stripes are laid along the contours
Autor:
Roman Wyler, Bern, Switzerland
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Swiss Franc
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
1,13
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy a "Streifenfräse" | |
| 2. | Buy a tractor |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipo | Streifenfräse | Machine | 1,0 | 42000,0 | 42000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tractor | Machine | 1,0 | 115000,0 | 115000,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 157000,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 138938,05 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | application of glyphosat (total herbicide) | 1 per growing period |
| 2. | tillage of stripes including seeding, manuring, spraying of herbicide | 1 per growing period |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | tillage of stripes, seeding, | ha | 1,0 | 393,0 | 393,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | appliance of total herbicide | ha | 1,0 | 88,0 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 53,0 | 53,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 534,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 472,57 | |||||
Comentarios:
Crop yield is about the same as in conventional cropping systems. The cost to apply the technology are about $410 per ha. It takes about 2 working hours per ha. In addition the glyphosat needs to be applied, which accounts for $150 or 0.75h of work. The following worksteps are not needed anymore (working hours, costs when tasking a contractor excl. material): Ploughing (1.25h, $260), harrowing (1.25h, $180), conventional seeding (1h, $100), manuring (1h, $50), applying of herbicides (0.75h, $90). In total about $130 and 4 hours of work can be saved per ha. In some cantons Streifenfrässaat is also subsidised. In the canton of bern this accounts for $420 per ha and year for the first 5 years of appliance. The costs for manure, herbicides, seeds are not included since they are the same as in conventional agriculture.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The machine is very expensive. In addition a strong tractor is needed (ca. 150hp). Thats why most farmer task a contractor with the seeding. In this case no initial investment needs to be done. The machine in this case study is used for about 60ha per year. A bigger workload would be possible.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Availability of surface water: good, medium ( precipitation maximum in summer )
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Ist mostly men that get in touch with the technology since it is mostly them who are using the machines. But decisions about which technology should be used are taken at the household level including both women and men.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: The farmer interviewed is working for other farmers, too. In general off-farm income is significantly lower.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comentarios:
The farmer portraited owns not more than 10ha, he is working for others as a contractor
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
steeper hills can be cultivated since the risk for erosion is reduced
calidad de forraje
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
droughts: less water scarcity, intense rain: less erosion but the weather needs to be dryer in spring, since the soil cannot be left to dry between ploughing and seeding
área de producción
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Less worksteps need to be done, income remains the same. But a total herbicide and sometimes a little more manure is needed
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Since the work is usually outsourced to a contractor, the farmer can use his time for other activities
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
less worksteps need to be done
Impactos socioculturales
oportunidades culturales
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced independence if contractors are tasked
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
especies benéficas
Comentarios/ especifique:
more earthworms
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | no se sabe |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | no se sabe |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no se sabe |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no muy bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
The farmer portaited bought a machine on his own. If a contractor were tasked short-returns would be positive too.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 11-50%
Comentarios:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: There is the possibility to get subsidies. But resources are limited and therefore not everybody gets them. (See Approach)
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is not spreading homogenously. Adoption and acceptance varies very much in different regions. Pioneers play an important role.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
The number of worksteps is greatly reduced. Thats why money and time can be saved. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Since less work needs to be done, the farmer can concentrate on other activities to enhance income. |
|
Soil structure is improved. Risk of compaction is reduced. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Still heavy machinery should not be used under wet conditions. |
|
Soil erosion is reduced very much. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology applies for maize only. Other conservation techniques should be used for other crops. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Steeper hills can be cultivated without risking erosion. How can they be sustained / enhanced? the stripes should in general be laid along the contours. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Risk of crop failure is enhanced if seeding under too wet conditions. | The time of seeding is critical and should be chosen carefully. If conditions are too wet, ploughing might be a better choice. |
| The machine is very expensive. Single farmers usually cannot afford it. | Cost can be shared with other parties or a contractor can be tasked. |
| In general a total herbicide must be applied before sowing. | The amount of glyphosat should be adapted to the number of weeds. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Reworking of the soil is still intense. | |
| A powerful tractor is needed. Fuel consumption is still high. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
report on DVD: von Bauern für Bauern
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
www.vonbauernfuerbauern.ch CHF 20.-
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Soil support program for conservation agriculture [Suiza]
Through the soil support program land users get subsidies for applying conservation technologies on their fields during a period of 6 years.
- Compilador: Deborah Niggli

Direktzahlungssystem [Suiza]
Finanzielle Leistungen des Bundes um den Ertragsverlust, den eine Kultur für den Bauern bringt, auszugleichen. Das Direktzahlungssystem führt gewissermassen zu einer 'Vergünstigung des Produkts' für den Konsumenten.
- Compilador: Deborah Niggli

Förderprogramm Boden [Suiza]
Mit dem Förderprogramm Boden des Kantons Bern erhalten beteiligte Landnutzer Direktzahlungen für die Anwendung von bodenkonservierenden Anbauverfahren auf ihren landwirtschaftlichen Feldern. Das Projekt hat eine Dauer von 6 Jahren.
- Compilador: Deborah Niggli
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos