Soil productivity improvement using a combination of technologies [Tanzania, República Unida de]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: ALLAN BUBELWA
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1221 - Tanzania, República Unida de
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Mwasikundima Iddifonce
Ngara District Council Kagera Tanzania
Tanzania, República Unida de
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - Tanzania, República Unida deNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - Tanzania, República Unida deNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Ngara District Council (Ngara District Council) - Tanzania, República Unida de1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
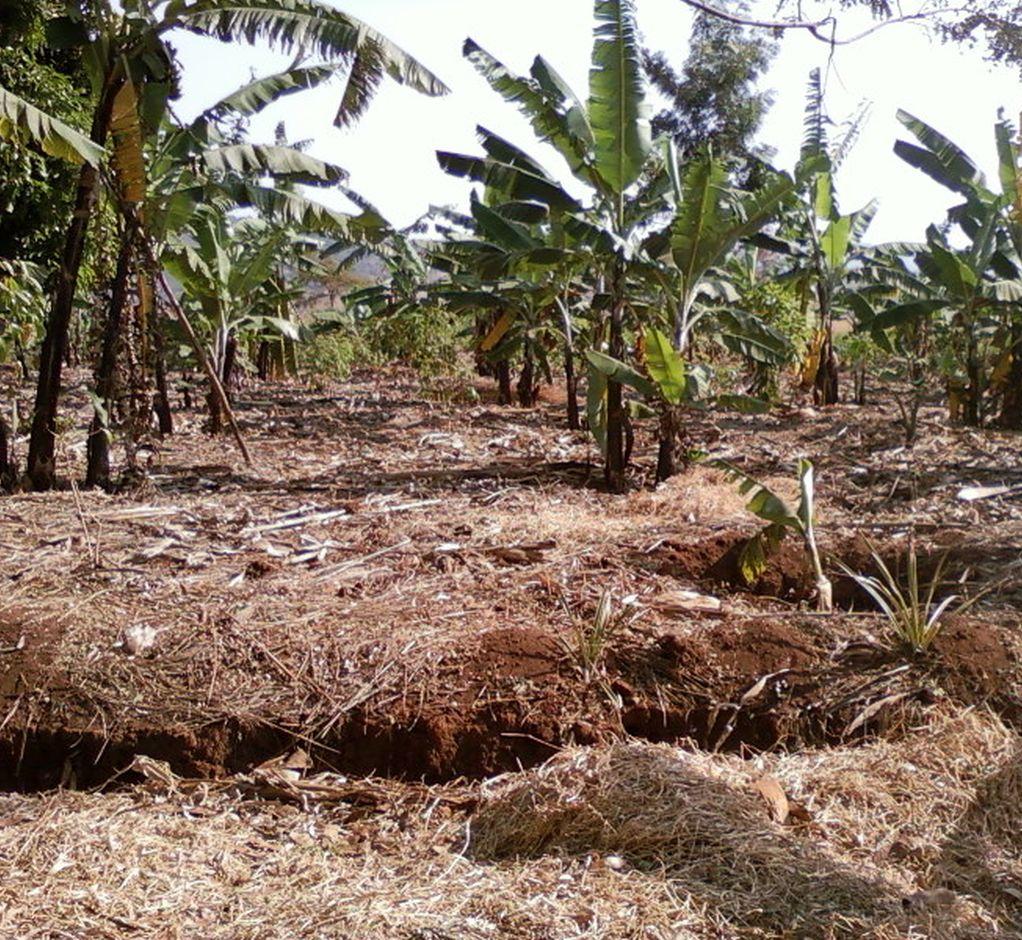
Use of compost basket pits, farm yard manure application, nutrient tapping sub soil agro-forestry, mulching application and productive vegetative stabilized cross slope barriers to improve soil health in Kibanja farming system.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
The technology was documented based on experiences of field SLM specialist and from the perspectives of land users (especially FFS group members) supported by the Trans boundary Agro Ecosystem Management project. The dominant crop in the technology area is banana. In this technology banana is widely spacing to 4m x 4m for the purpose of providing enough space for annual or recurrent soil nutrient feeding using compost ditches or baskets. Compost basket pits of 0.6 m depth and 3x3m width are dug between 4 banana plants. Baskets pits are dug recurrently and filled with farm manure, compost (crop residuals), leguminous green manure (tithonia) and ash and later covered with soil to activate nutrient release though microbial disintegration and avoid volatilization of greenhouse gas through direct sunlight. The size of a hole dug for the purpose of planting banana is 0.6 m depth and 0.6 m height. During digging top soil is separated from subsoil. In initial manure application, 2 tin of manure are mixed with the top soil and the mixture is put in the bottom of the hole. The center of the hole is marked with a stick and waiting is done for 1 or 2 before planting. During planting of banana, only two third 0.24m cubic of the hole is filling with soil and one third 0.12m cubic of the hole is left to form a water retention/harvest pit. Tithonia diversifolia (leguminous shrubs) are planted within the Kibanja farm purposefully for improving soil nutrient recycling though nitrogen fixing and at the same time is incorporate in compost to improve its quality. Infiltration ditches of 0.6 m depth and 0.6 m width and varying lengths are constructed for the purpose of impeding, trapping and harvesting water runoff. Fruit trees are planted in sub soil zone within the water infiltration ditches. The aim is to control nutrient competition between trees and annual/ biennial in the top soil or annual root zone and at the same time fruit tree roots in the subsoil zone is used as nutrient pump i.e. return nutrient lost through leaching to the top soil in form of mulching and litter. Improved banana varieties (FIAH 23) and certified endogenous germ plasma, de-trashing and de-suckering to maintain optimal plant geometry is part and per se of recommended husbandry practice
Purpose of the Technology: Improved food productivity, improved soil moisture content and water holding capacity. Improve nutrient recycling, organic matter content and biomass cycle. Prevent unproductive evaporation of green water and improving soil micro-climate. Combating land degradation through soil erosion caused by water runoff, chemical degradation due to nutrient leaching, biological degradation due the deadly BXW and other diseases and water degradation due to unproductive evaporation of the green water. And also plays significant role in adaptation and mitigation to drought climate. Improved economic returns accrued from surplus food production. Improve year round accessibility of food, shock resistance availability of food and varied food utilization and hence poverty reduction and improved health.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities: land tilling, harrowing, demarcation and spacing of holes for planting banana, digging holes, manure application before banana planting, planting bananas, to demarcate, level and space Fanya chini/infiltration ditches/trenches using A-frame and arm outstretched level, ditch/trench digging, vegetative stabilization of Fanya chini/infiltration ditches, planting of fruit trees within ditches. Maintenance activities: weeding to destroy noxious weeds, in between planting of maize, de-suckering to maintain optimal plant geometry, de-trashing, maintenance and replenishment of banana pits, harvest beans and maize, sediment removal and repairing of infiltration ditches/trenches.
Natural / human environment: Natural (bio-physical) environment: The technology area land use type is cropland with annual crops (maize and beans), perennial crops (banana and pineapples) and fruit tree (avocados and jackfruit “Artocarpus heterophyllus”). The technology involves a combination of the following measures: agronomic, vegetative and structural. Climatic zone is sub-humid with an average of 210 length of growing period (LGP). Average slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. Soil texture classes range from combination of top loam to a red clayey subsoil with medium soil depth categories. Main criteria for a human (socioeconomic) environment: the level of mechanization is hand tools. Production system is mixed (both subsistence and market oriented or commercial). The average costs of inputs required is 1472,62 USD. Land ownership is largely individual not titled and partly communal.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tanzania, República Unida de
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
United Republic of Tanzania, Kagera Region
Especifique más el lugar :
Ngara District council, Kirushya ward, Kirushya Village.
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
The technology is documented from the perspectives of group of land users (SLM FFS) supported by the Trans Boundary Agro-Ecosystem Management Project.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Supported by the Trans Boundary Agro Ecosystem Management Project (Kagera TAMP) in year 2012, a group of 25 members of ENDELEVU Farmer Filed School (FFS) started to learn and test out application of the technology.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- conservar el ecosistema
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agroforestería

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- leguminosas y legumbres - frijoles
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - patatas dulces, ñame, taro/cocoy am, otro
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - mandioca
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- banana/plátano/abacá
- piña
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- avocado
- café, cultivado al aire libre
- mango, mangostán, guayaba
- jack fruits
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

Tierra de pastoreo
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Poor soil moisture (moisture stress), poor soil fertility, loss of vegetative cover and unproductive loss of green water, erosion and washout of the top soil by rainfall runoff.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low banana productivity, unbearable persistence of the deadly BXW and other diseases, drought intolerance, food insecurity and a poverty stricken community.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- agroforestería
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas estructurales
- S2: Taludes, bancos
Comentarios:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues, pits
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Flat cultivation along the slope, no use of slope cross barriers), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Use of unimproved local varieties susceptible to diseases and pests), change of seasonal rainfall (Unforeseen changes in rainfall), droughts (Long dry spell season), population pressure (Exessive use of land without fertility replenishment), poverty / wealth (incapacity to invest in sustainable land canservation measures.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of SLM knoledge.), governance / institutional (Weak institutions with lack of operational capacities)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (The principles governing use of SLM were taught before in colleges to field staff and agricultural advisers and therefore simple retraining courses and learning by doing on the job on the suffice)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Need training on construction of slope cross barriers e.g. on application of A-frame and arm outstretched methods and the principle behind BXW control and use of certified/improved banana varieties.)
Technical knowledge required for Sub national level (Regional and District): moderate (SLM participatory training techniques/skills.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Mulching
Material/ species: Hyparrhenia spps
Quantity/ density: 1500bu/ha
Remarks: Layed accross the slope at e reccommended depth of 15 cm.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farm Yard Manure, banana debris, tithonia
Quantity/ density: 15 ton/ha
Remarks: Applied during planting and in routine fertility replenishment.
Pits
Material/ species: Compost basket pits
Quantity/ density: 156
Remarks: Pits of 5.3m cubic dig between each 4 banana stools used annually for composting the banana field.
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 625
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4m
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: O : other
Trees/ shrubs species: Mangoes
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mangoes
Perennial crops species: Banana
Other species: Pineapples, Cassava and Yarms.
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15
Structural measure: Fanya chini bund
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 15
Structural measure: Banana water infiltration pits
Spacing between structures (m): 4
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Construction material (earth): Soil dug to form trenches is thrown down slope to form embankment of fanya chini bund.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2 - 5%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Tanzanian shillings
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
1700,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
1.18
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land tilling (starting a new banana farm) | March |
| 2. | Harrowing | April |
| 3. | a) Demarcation and spacing of holes for planting banana. b) Digging of holes. | April |
| 4. | Applying manure during banana planting | May |
| 5. | Planting banana | May |
| 6. | Planting fruit trees (jack fruits and avocados) | May |
| 7. | a) Planting pineapples on Fanya chini bund. b) Selective boundary planting of Tithonia | September |
| 8. | a) To demarcate contour line using A-FRAME and arm stretched level method. b) Digging and construction of water retention ditches and fanya chini bund. | September |
| 9. | Tools (hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade, mattock, forked wooden poles and A-frame) |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 713,15 | 713,15 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | tools | ha | 1,0 | 87,65 | 87,65 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 0,29 | 0,29 | |
| Material para plantas | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 65,0 | 65,0 | |
| Material para plantas | mulching materials | ha | 1,0 | 22,06 | 22,06 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 44,12 | 44,12 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 932,27 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 0,55 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 4 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding to control and destroy noxious weeds. | February and October |
| 2. | In between planting of maize and beans. | February and October |
| 3. | De-suckering to maintain mother and two baby plants. | |
| 4. | De-trashing and trimming of unwanted leaves. | |
| 5. | Maintenance and replenishment of banana pits. | |
| 6. | Applying manure using banana compost basket pits | January |
| 7. | Harvesting of beans and maize. | |
| 8. | Mulching application | After harvest of maize and beans |
| 9. | Gap filling and trimming of unwanted leaves/branches (Avocados, Jack fruits and Pineapples) | within rain period |
| 10. | Maintenance by removing soil sediments. | During and after rainfall |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | labour | 1499,72 | 100,0 | |||
| Equipo | Seeds beans (20 kg/ha) | ha | 1,0 | 8,24 | 8,24 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds Maize (2 kg/ha) | ha | 1,0 | 0,77 | 0,77 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Mulching materials (75 bundles) | ha | 1,0 | 22,06 | 22,06 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Compost/manure (325 kg) | ha | 1,0 | 9,56 | 9,56 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 40,63 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 0,02 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: hand hoe, forked hole, machetes and sickles, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes and spade, hand hoe, forked hole, spade, mattock and A-frame
The costs were calculated based on per unity entity of land plot (quarter an acre plot) where the technology was demonstrated/tested .
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Labour is the most determinant factor.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The average annual rainfal is 1300mm. The dry season is from June to August. Rainfall season starts from September to May. There is a dry spell in January/February and June - August is dry season.
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: tropics. Average temperature is 21°C. The area receives bimodal type of rainfall with average lenght of growing period is 210 days
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones convexas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Landforms: Mountain slopes (ranked 1, the area is largely a convex mountanous land slope), plateau/plains (ranked 2) and ridges (ranked 3)
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil texture: Medium (ranked 1, range from combination of top loam to a red clayey subsoil) and coarse/light (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium (due to washout of the top soil by rainfall water runoff and excessive nutrient mining/uptake without replenishment)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (due to washout of the top soil by rainfall water runoff and poor mismanagement of crop residuals)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor (the slope nature of the landscape does not give water enough time to infiltrate instead water is lost downstream through runoff)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (soil textural class range from combination of top loam to a red clayey subsoil)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table: >50m (ranked 1, water can be accessed in down the river valleys streams) and 5-50m (ranked 2)
Availability of surface water: Water is available in natural flowing downstream rivers
Water quality untreated: Poor drinking water (treatment required, water in river stream untreated is poor because is contaminated by runoff pollutants)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Species diversity is reduced by human induced activities e.g. farm opening and expansion, starting of new human settlements, uncontrolled fire burning e.t.c.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land (owning 1-2 ha, moden house, motorcycles).
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land (owning 0.5-1 ha, average house, bicycles).
20% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (owning < 0.5 ha, poor house, no transport).
Off-farm income specification: In general most of the village community are average farmers who largely rely on on farm income.
Market orientation: Mixed (ranked 1, Production is both for domestic food production and commercial use) and subsistence (ranked 2)
Level of mechanization: Manual work (Largely manual by using hand tools)
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha (5% of the land users), 0.5-1 ha (80% 0f the land users) and 1-2 ha (15 % of the land users)
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
Comentarios:
The land is a state property, use right is largely individual not titled. water resources and grazing range lands are owned communally and are free for all.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
25 kg
Cantidad luego de MST:
50 kg
Comentarios/ especifique:
banana bunch
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
pending development and upscalling of value addition technology.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
caused by use of manure and grass mulch.
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to increased production and expected income from fruit tree and pineapples
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
imcome from fruit trees and pineapples
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
caused by increased workload.
Impactos socioculturales
instituciones comunitarias
Cantidad antes de MST:
0 - FFS
Cantidad luego de MST:
1 - FFS
Comentarios/ especifique:
FFS has induced farmer group solidarity and togetherness.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increase in SLM skills and knoledge due training issued through FFS. People visiting the area where the technology is tested or demonstrated
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
Active participation of both men and females
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved crop productivity and the diversification of income sources results to farmer capacity to meet eduction and health services. Production of pineapple and fruit tree (avocados and jack fruit) means increased number of food per table and balanced diet to farmer.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cosecha/ recolección de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
poor
Cantidad luego de MST:
improved
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to the use of water infiltration ditches and fanya chini bund
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
use of closs slope barriers and mulching.
evaporación
Cantidad antes de MST:
poor
Cantidad luego de MST:
improved
Comentarios/ especifique:
educed unproductive loos of green water by use of mulching.
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
poor
Cantidad luego de MST:
improved
Comentarios/ especifique:
reduced unproductive loos of green water by use of mulching.
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
use of mulching rotated by cover crops (beans) and trashline.
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Use of closs slope barriers and mulching
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Comentarios/ especifique:
the use of reguminous plants (beans and tithonia)
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
use of farm yard manure and compost basket feeding
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
biomass due to improved managment of crop debris and residual and use of mulch.
especies benéficas
Comentarios/ especifique:
improved habitat for micro fauna caused by use of manure and compost
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de sequías
Comentarios/ especifique:
reduced hazards towards drought and reduced growing period.
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
reduced volatization of methane gas due to good managment of FYM.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
daño a campos de vecinos
Comentarios/ especifique:
reduced rainfall runoff to down ward stream
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
Comentarios/ especifique:
reduced damage to the nearby road infrastructure
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | no se sabe |
| tormenta de viento | no muy bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
Comentarios:
The technology could be made to be more tolerant to flood by modifying retention ditches to drainage ditches and by introduction of wind breakers.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Heavy investment and recurrent costs at the beginning but costs are surpassed by rewards in the long run.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
46 families and 100% of the area covered
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 51-90%
Comentarios:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: External material support was used on area used for FFS.
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
23 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
4% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support 23 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: 80% farmers have adopted the technology partially without any material support.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: the technology increasingly adopted are mulching, spacing and compost basket feeding
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The technology is easy to learn and understand by a common peasant farmer |
| The technology open a room for availability of improved varieties and diversification of income sources |
| Observable rewards in terms of increased production and environmental conservation. |
| Change of attitudinal and behavioral change (mind set) towards environmental conservation. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The technology has provided options for farmers to blend their vast experience and innovations in managing their often-limited resources with new methods and advice from outside. |
| The promotion of the technology through FFS has strengthened partnership between farmers, extension providers, private sector and researchers. |
| The FFS programme has created unity in the people at grass root level |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| High initial investment capital needed due to high costs of farm inputs. | Farmer support by financial institutions |
| Technology promotion need closeness of extension services but there is no reliable plan for facilitators motivation. | Find reliable means and ways of motivating both field extension officers and grassroots facilitators (paraprofessionals). |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Finances for scaling up technology use in the future is questionable. | Link farmers with rural financial institutions and put more efforts in commercial and market oriented SLM activities. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
02/08/2014
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos