Multiplier fertilization of banana using small ruminants in Kibanja farming system [Tanzania, República Unida de]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: ALLAN BUBELWA
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
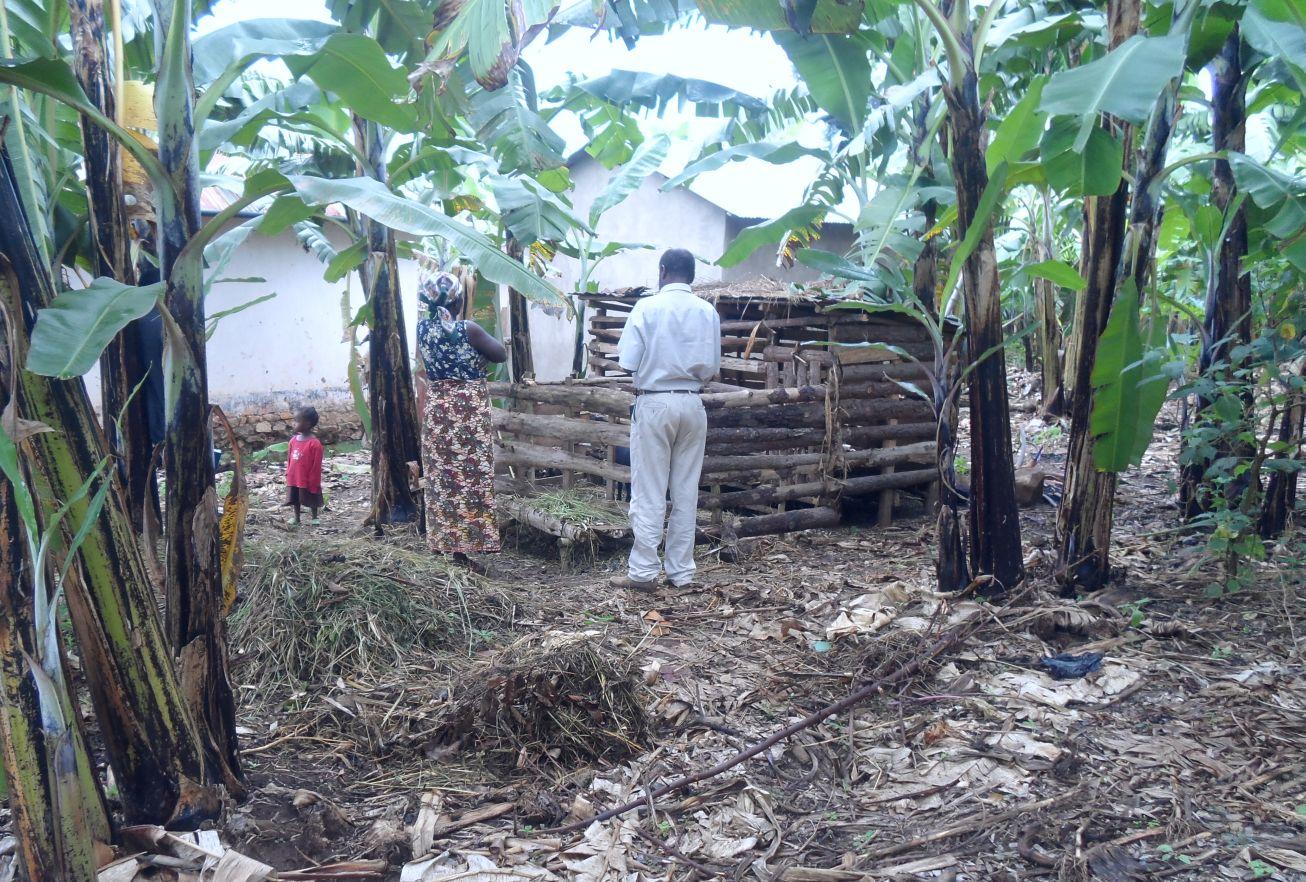
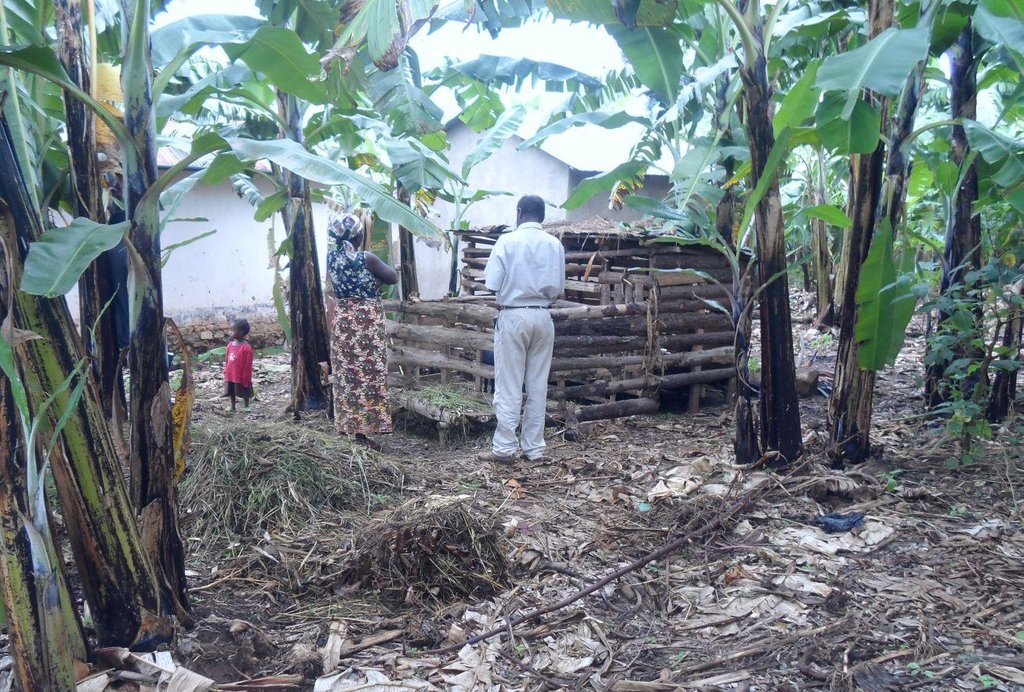
Matumizi ya mifugo katika shamba la kibanja.
technologies_1207 - Tanzania, República Unida de
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Pancras Egidius
Missenyi District
Tanzania, República Unida de
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - Tanzania, República Unida deNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - Tanzania, República Unida de1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Enhancement of sustainable land management by capitalizing on the rapid growth, short gestation nature and multiple benefits of small ruminants kept under zero grazing in a banana based farming system.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Multiplier banana fertilization is a system where rapid growing small ruminants (preferably dairy goats) of low gestation period are kept under zero grazing within a banana based (Kibanja) farming system and their excrement are used in complementing other fertilization of the banana fields. Dairy goats also improve diet of the rural poor and diversify their income. The animals were initially supported by SLM projects as quick win income generating motivation/incentives to farmer who spent their valuable time in SLM activities of long term benefit realization. In multiplier fertilization, a farmer starts only with a few numbers of animals (as kick start). Usually 2 female dairy goats and one improved male goat (buck) suffice. Goat dung collected from the shed is used to perform selective and on spot application of manure to banana plants. Because of their rapid growth and short gestation nature, goats multiplies and increase in number within few years and at the same time in multiplier terms farmers spread and apply manure to more banana plants. Farmers begin with a small animal shed of usually carrying capacity of 4 to 6 goats and can expand it as goat increases. Goats feed on products cut and carried outside or within the kibanja farm. Animals also feed on domestic residuals (e.g. banana peels), food supplements and water for their maximum performance. Goat dung is collected weekly from the shed and is piled in layers, covered with grass and kept shaded under banana canopies to allow microbial action and minimize nutrient loss through volatilization. Depending on the growth stage of banana, dry manure is applied on sport and selectively after every three months of microbial decay. The numbers of animal increases year after year at the same time farmer benefit from the use/sale of animal product (milk in the short term and meat in the long term) and in multiplier manner continue expanding manure application to other banana plants. Manure from goats contributes in improved banana productivity. Benefits accrued from goats also motivate and induce farmers’ patience in terms of their participation in SLM interventions of long term benefit realization.
Purpose of the Technology: Purposes: improved banana productivity, livelihood diversification, income of the rural poor and soil ecosystem through fertility and organic matter replenishment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities includes, kick start support of farmers with goats (two dairy goats and an improved buck), construction of the goat shed (100% borne by land user to inculcate self-initiative and ownership) and purchase of working tools (spade, rake, hand hoe).
Recurrent activities largely includes, fetching fodders and feeding the animals (cut and carry products outside or within the kibanja), weekly cleaning of the goat shed and manure collection, manure heaping and grass covering for microbial decay/reducing nutrient volatilization, spreading/cooling, monthly on spot and selective application of manure to banana plants, milking of the animals, disease control/deworming and providing supplements.
Natural / human environment: Multiplier banana manure application is used in kibanja farming system in sub humid tropical highland plateau/plains of 1000 -1500m a.s.l. with annual rainfall between 1000 – 1500mm, moderate soil depth and medium loam textural class.
Is used by small scale land users both men and women individual households. In Kibanja farm, land ownership is largely individual not titled and is acquired through inheritance. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial).
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tanzania, República Unida de
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Tanzania/Kagera
Especifique más el lugar :
Missenyi Disrict/ Kiziba division/ Kitobo ward/ Kyazi village
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
The technology is implemented in Kibanja cropping land use type by individual farmers who received support of diary goats from the Trans-boundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project (TAMP) as quick win and environmental sound motivation for farmers who spend their valuable time in implementation of SLM intervention of long term benefit realization.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Started in December 2012 as part of environmental sound income generating activities promoted and supported by the Trans-boundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project (KAGERA TAMP).
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - patatas dulces, ñame, taro/cocoy am, otro
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - patatas
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- café, cultivado al aire libre
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Cortar y llevar/ cero pastoreo
Tipo de animal:
- cabras
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Without land conservation there will be inadequate/poor soil fertility and organic matter content, low soil moisture holding capacity, poor health of banana and their increased vulnerability to pest and diseases especially the most devastating Banana Xanthomonas Wilt (BXW).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Banana Xanthomonas Wilt, weak banana plants and low production.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo
- A7: Otros
Comentarios:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, green manure, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

degradación biológica
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Low soil fertilization/manure application), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor banana husbandry practces), population pressure (High land requirement and continuous utilization without fallowing.), poverty / wealth (low investment capacity), education, access to knowledge and support services (Shortage of staff, inadequate extension services and provision of subsidies.), governance / institutional (Low bylaws/law enforcements (e.g. on BXW control))
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
and rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Involve simple retraining of technologies already taught to staff in school/agricultural collages.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (Have some elements of new skills and knowledge. e.g. a farmers must be taught of the principle behind zero grazing and manure preparation (microbial decomposition/control of mineral volatilization))
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Banana, castrol oil, yams
Quantity/ density: various
Remarks: scattered
Mulching
Material/ species: Banana thrashes and stems
Quantity/ density: 100m3/ha
Remarks: thinly pread seasonaly twice per year
Green manure
Material/ species: Various types of weeds
Quantity/ density: various
Remarks: scattered
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: various
Remarks: random
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Goat dung, grass and domestc residues
Quantity/ density: 222 m3/ha
Remarks: Assuming got dung is applied once per hactere
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Tanzanian shillings
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
1700,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
1.20
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase goats (dairy goats) | |
| 2. | Build animal shed | |
| 3. | Purchase tools |
Comentarios:
Lifespan of the goats and tools: 5 years
Lifespan of the shed: 3 years
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipo | Tools | piece | 5,0 | 2,8 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Goat shed | piece§ | 1,0 | 29,0 | 29,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Goats | piece | 3,0 | 70,33333 | 211,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 254,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 0,15 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fetching fodder (cut and carry) and use of domestic residuals. | Daily/annually |
| 2. | Cleaning shed and collecting manure | weekly/annually |
| 3. | Heaping manure and compost | weekly/annually |
| 4. | Tilling on sport and selective application around banana | March, June, Sept and Decemb |
| 5. | Disease control/de-worming | weekly/annally |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Fetching fodder (cut and carry) and use of domestic residuals. | person/days | 120,0 | 1,175 | 141,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Cleaning shed and collecting manure | person/days | 26,0 | 0,8848 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Heaping manure and compost | person/days | 26,0 | 0,8848 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Tilling on sport and selective application around banana | person/days | 16,0 | 1,1875 | 19,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Biocides | litres | 12,0 | 3,91666 | 47,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Labour: Disease control/de-worming | person/days | 26,0 | 1,1925 | 31,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 284,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 0,17 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, rake, hand hoe, machete and bucket.
The costs were calculated per unit of kick start animal flock (three dairy goats) needed annually per individual farmer household.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Labour is the most determinant factor affecting the costs.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
September to December 120 days, March to Maya 90 days = 210 days . Average length of growing period is 210
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: tropics. Average temperature is 20°C
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (about 60cm)
Soil texture: Medium (highly clay loam)
Soil fertility: Low (due to excessive nutrient uptake without replenishment)
Top soil organic matter: Low (low crop remains)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (no water logging)
Soil water storagce capacity: Very high (nature of soil is loamy)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Availability of surface water: Medium (water is available in nearby natural water spring. There is reduction of water flow during the dry season)
Water quality (untreated): Good drinking water as it comes from a natural spring
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Soil microorganisms e.g earthworms and ants.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 1%
6% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
64% of the land users are average wealthy and own 64% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 6% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some have established small kiosk at the village center and most have additional income items of regular support, assistance and cash transference from children or family members who work or have big business in cities, town and in some cases in diaspora.
Market orientation: Mixed (Banana and goats/milk are produced for both sell and home consumption)
Level of mechanization: Manual work (land form and agroecological nature of the kibanja farm cause hand hoe to be the best means of cultivation)
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
< 0.5 ha, Ranked 2, about 30% of household fall in this category
0.5-1 ha: Ranked 1, account for 60 % of the household
1-2 ha: Ranked 3, account for 10% 0f the household
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
Comentarios:
Land is largely acquired by inheritance. Traditionally water is open accessed for public use through customary law.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
15-20kgs/banch
Cantidad luego de MST:
35-40kgs/banch
Comentarios/ especifique:
manure application have contributed in increase of banana yield
producción animal
Cantidad antes de MST:
0 goat per household
Cantidad luego de MST:
3 goats per household
Comentarios/ especifique:
goats introduced through projects.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Cantidad antes de MST:
385 usd
Cantidad luego de MST:
200 usd
Comentarios/ especifique:
manure received from goat overshadow the costs of fodder, concentrates and waters for goats
ingreso agrario
Cantidad antes de MST:
3.5 usd
Cantidad luego de MST:
6.5 usd
Comentarios/ especifique:
net income gain due to use of manure
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Cantidad antes de MST:
1 enterprise
Cantidad luego de MST:
2 enterprises
Comentarios/ especifique:
additional income sources from goat keeping
carga de trabajo
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
237
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased labour needed for goat keeping
Impactos socioculturales
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Farmer use additional income generated from banana production to pay for debts and other commitments like school fee and health expenses. Goats act as moving banks and contributes in farmer income assurance during the sensitive time e.g. sending children to school or wives to maternal/birth services. There is also nutritional improvement to farmers (farmers attain a balanced diet from milk protein).
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Comentarios/ especifique:
improved water holding capacity
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Cantidad antes de MST:
low N
Cantidad luego de MST:
high N
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to application of goat dung
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to goat manure
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
especies benéficas
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased soil micro-organism/insect
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to improved plant health.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | no se sabe |
| tormenta de viento | no se sabe |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no se sabe |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no muy bien |
Comentarios:
Storage of crop remains, hay making for animal to have enough food and produce more meat, milk as well as manure.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
goats give quick win benefits because have short gestation period, usually gives twin kidding twice per year. Their average lactation period is 250 days and a single goat can produce average of 750 litres of milk per year worthy about 441 American dollars.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
317 households and 23% of the area covered
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 11-50%
Comentarios:
4% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
317 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The project supported procurement of goats.
31% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
317 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: goat keeping is part of tradition and culture.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some neighboring farmers have started adoption.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The technology is simple and easy to learn and have a short establishment time due to the short gestation nature of the goats themselves (only two female goats and an improved buck, a goat shed and some concentrates suffice for initial investment). |
| In the long term has synergistic effect and complements other existing land fertilization, moisture conservation and erosion control methods e.g. the quality of compost is improved. |
| Improves livelihood (goats act as moving banks and contributes in farmer income assurance during the sensitive time e.g. sending children to school or wives to maternal/birth services) and nutrition to farmers (farmers attain a balanced diet from milk protein). |
| Increased banana production and continuous returns in multiplier terms. Goats also convert domestic residuals (e.g. banana peels) into useful products . |
| Maintenance activities can be covered by land users and this help in ensuring self-initiative and ownership |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| High workload in looking for fodder | Introduce fodder within kibanja farm |
| Shortage of genetically improved dairy goats | Introduce genetically improved dairy goats. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Shortage in the number of field extension workers needed for effective extension service delivery | Government employ more extension worker |
| Limited reach ability of extension staff due to shortage of transport facilities. | Provision of reliable transport facilities to extension workers. |
| Agro-vert/input dealers services are not available in the rural premises. | Introduce agro-vert/input dealers in rural premises. |
| Goat provision and distribution to farmers done at a small pace | Expand goat provision and distribution to more farmers. |
| Rural urban migration of the youth searching for greener pasture leaving behind the less energetic elders. | Introduce attractive and decent income generating activities for youth in the rural areas. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
04/06/2014
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos