Solar Power Water Lifting and Application to Orchard through Drip Irrigation [Pakistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Madhav Dhakal
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5610 - Pakistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Maqsood Muhammad Mudassar
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Shah Ghulam Muhammad
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Bhatti Ahmad Zeeshan
Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Khan Muhammad Zafar
Karakorum International University
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Khan Babar
World Wide Fund For Nature
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Ali Rehmat
World Wide Fund For Nature
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Ali Amjad
Karakorum International University
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Ali Ajaz
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development
Pakistán
Especialista MST:
Dhakal Madhav
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development
Nepal
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Agricultural Water, Energy, and Hazard Management for Improved Livelihood in the Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan (UIB, Pakistan)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
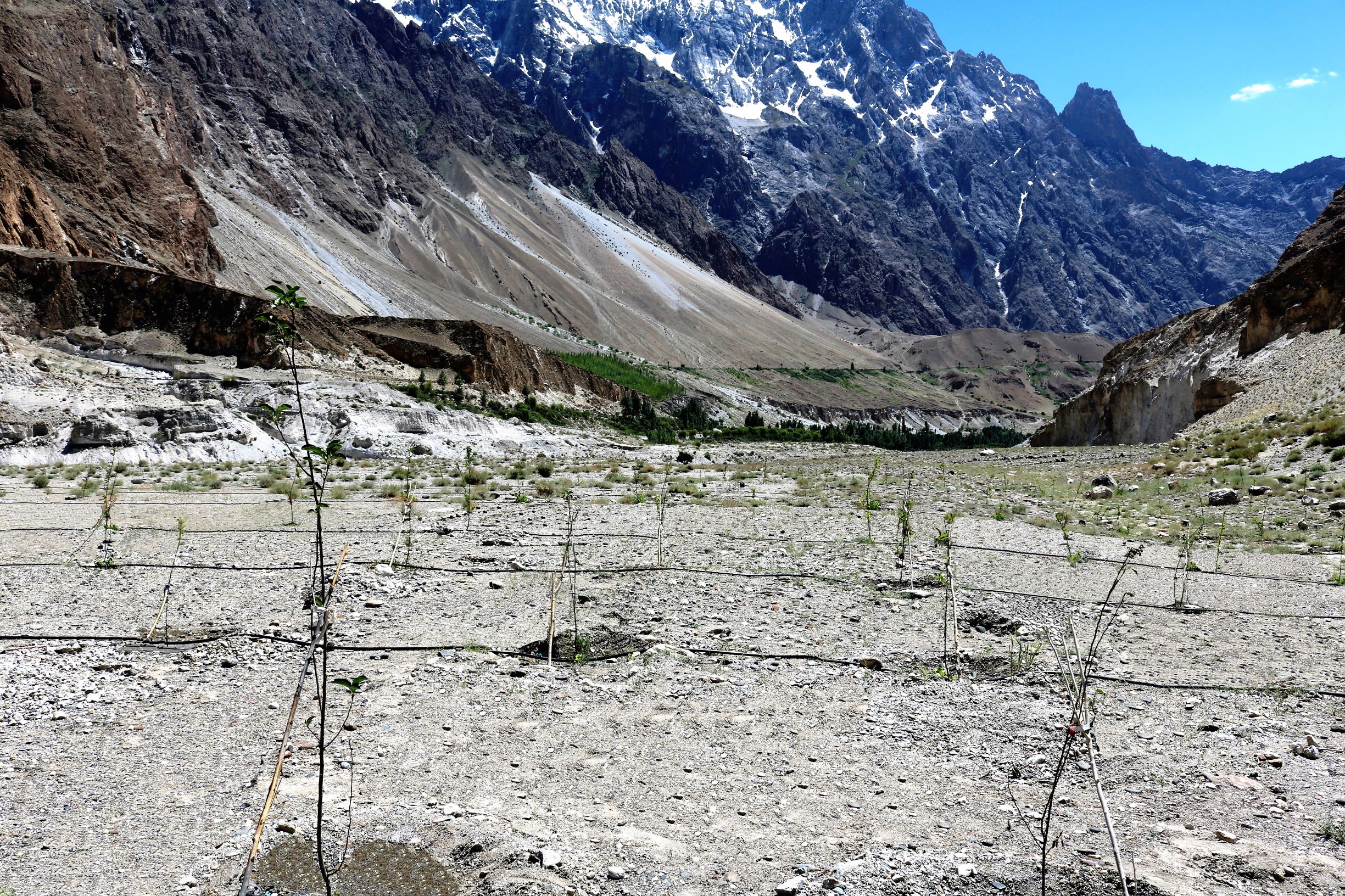
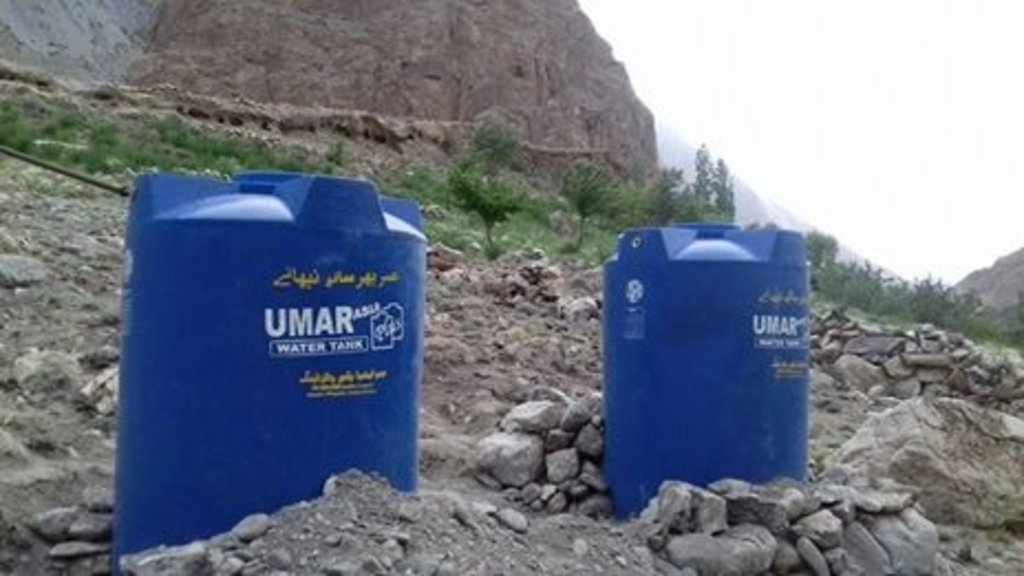
Water from the Hunza river was lifted through solar powered pump, stored above ground plastic tanks and applied to newly planted apple orchards through efficient drip irrigation. Mulch was applied to the plants to conserve soil moisture.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
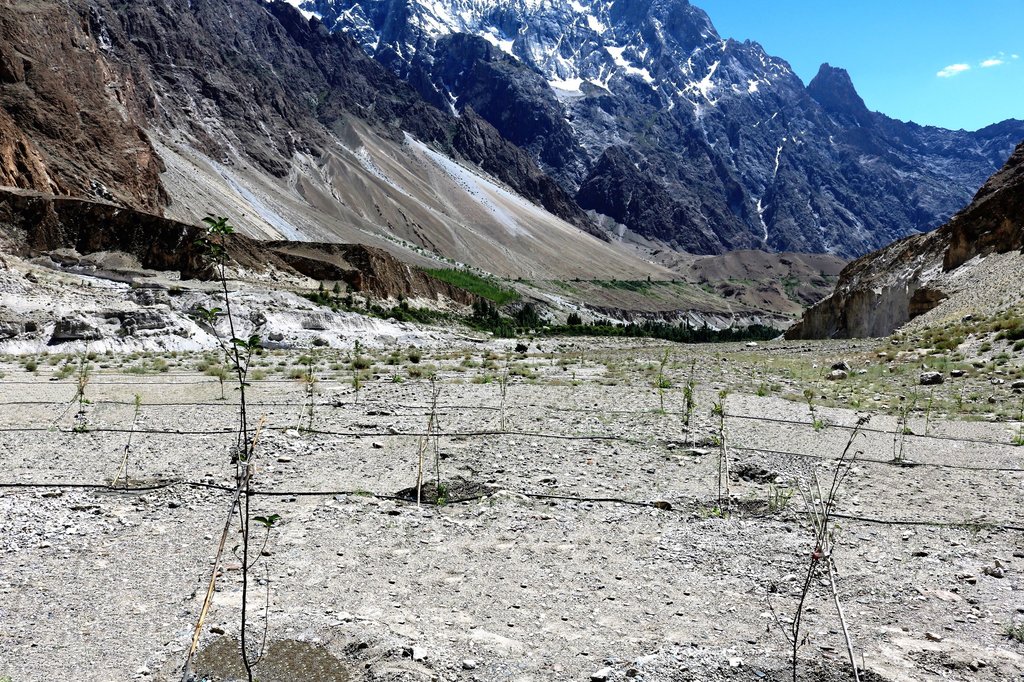
The fragile rouged mountains prone to the effect of climate change makes the mountain com-munities in Gilgit-Baltistan of Pakistan more vulnerable. Agriculture is the major source of their livelihoods and it purely dependents on glacier meltwater which makes the community more susceptible due to the unstable behaviour of the glaciers. Irrigation is practised with traditional irrigation canals, intake of which is located at glacier terminus. On one hand lowering of glacier surface disconnects many irrigation canals. Uncertain glacier behaviour has resulted in the decline of water availability and even forced some communities to abandon their agricultural land. On the other hand, only 2% of land in Gilgit-Baltistan is used for agriculture purposes whereas a huge chunk of barren land lays above the Hunza River, which cannot be cultivated through the traditional irrigation system hence it remains unutilized.
To address both issues, ICIMOD together with a local level partner’s consortia piloted solar water lifting to irrigate barren land for establishing apple orchards along Hunza River at Passu and Morkhun Villages. These two villages are located far from each other. In each village, orchards of 2.5 hectare area were established and the drip irrigation system installed was efficiently used to irrigate apple plants. Similar technological packages (solar pump, drip irrigation and mulch) were applied in both the villages.
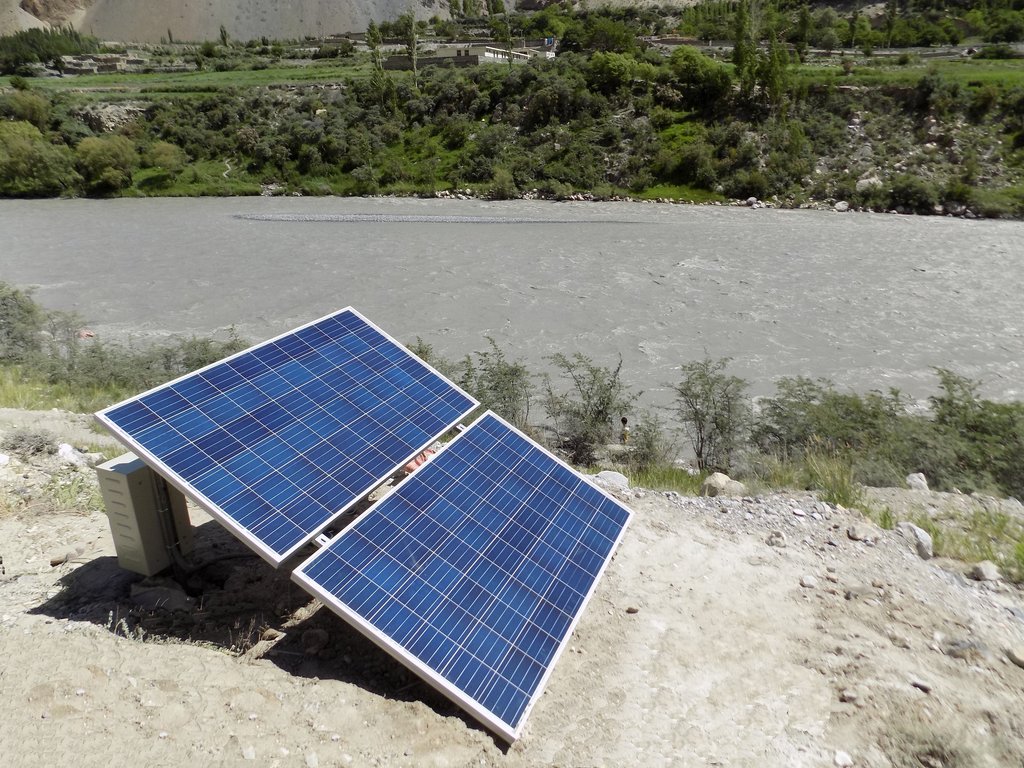
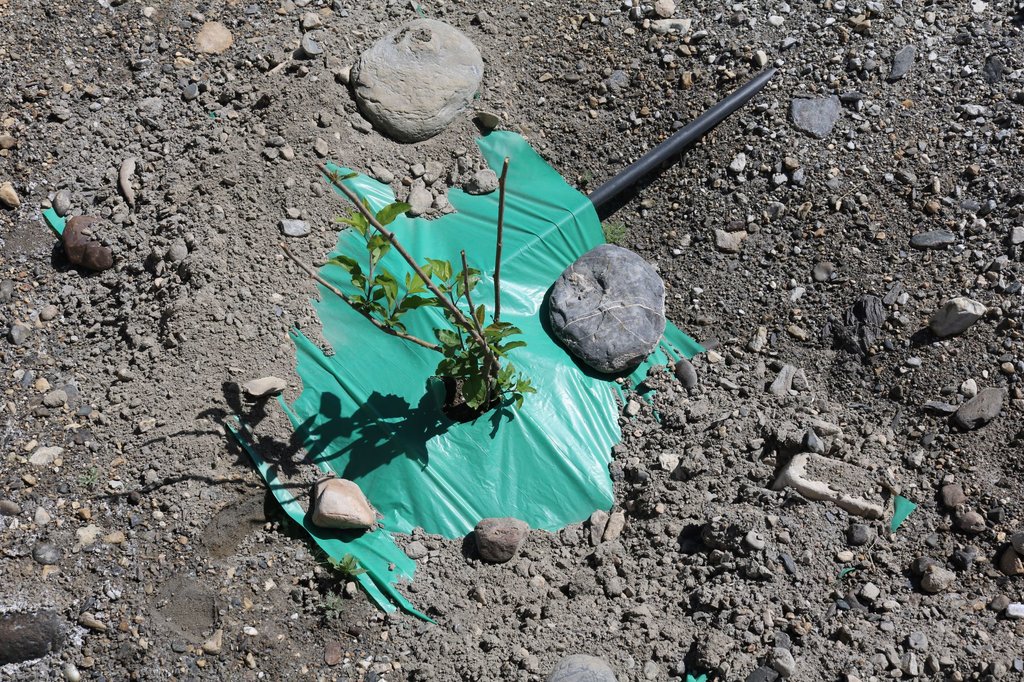
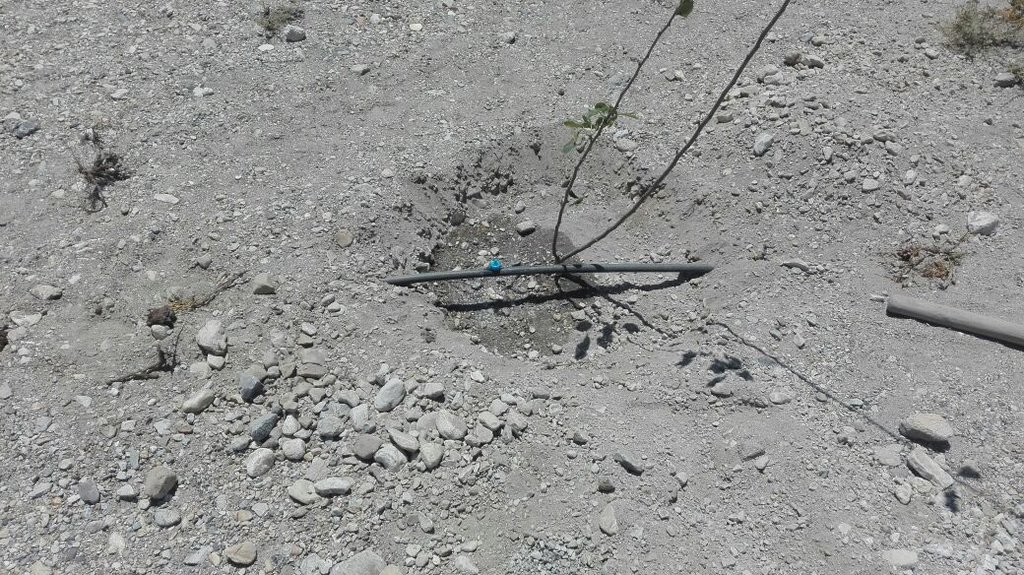
The pumping system comprises a submersible pump (Lorentz, Germany 1 HP) powered by 500 watts solar panels to carry the water to storage tanks (500 litres) made up of plastic that has been placed upslope at 100 feet vertical height from the river. The water from the storage tanks was routed/led to the apple saplings through the surface and pressure compensating drip irrigation system. The pumping capacity of the pump is 7.5 litres/minute, which is irrigating around 3300 apple plants at Passu and Morkhun. The storage tank was kept 60 feet vertical height from the orchard field to be irrigated. Tree to tree distance and row to row distance of apple was maintained at 15 feet in Passu and 10 feet in Morkhun. Drip irrigation (surface and pressure compensating) system was established to irrigate each apple plant, the emitter of the drip system was adjusted according to the plant to plant distance of apple seedlings to be irrigated. Pits were constructed for planting apples and later they also served as water harvesting pits /check basins. Plastic mulch was applied to each apple plants covering a radius around the trunk to minimize soil moisture losses, reduce weed and reduce soil erosion by water and wind.
The cost of an integrated package including solar pumps with accessories, storage tanks, intake and distribution systems (i.e. from river to tank and tank to trees), drip irrigation, apple plants and operational expenses (manpower) for both the sites was US$ 42000 for 5 ha of land. Village Development Organizations (VDO) of both villages take care of maintenance of technological package through a maintenance fund, which is being raised by participating households (HHs). Benefit sharing mechanism has been agreed among the participating HHs. The total income would be divided equally among participating 72 HHs in Morkhun and 135 HHs in Passu.
The technological package was applied in arid climate at an elevation ranging from 2340m to 4877 m above sea level. Passu is located at 36.49o latitude and 74.90o longitude and Morkhun is located at 36.6o N latitudes and 74.86o E longitudes. The area receives 150-200 mm annual rain-fall. The temperature ranges from 11 degree Celsius to 29 degree Celsius. The population of Passu and Morkhun is 1168 and 653 persons respectively. Both villages are semi nomadic and depend mainly on livestock rearing.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Fecha:
09/10/2018
Lugar:
Morkhun and Passu
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Pakistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Gilgit Baltistan Province
Especifique más el lugar :
Morkhun and Passu
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2016
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
This package of practices was jointly implemented by Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR), Worldwide Fund for Nature (WWF) - Pakistan, and ICIMOD
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- crear impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
- Apple
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
April to October, rest months the region is covered with snow
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Unproductive
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- totalmente irrigada
Comentarios:
Water supply with solar pump and distribution to apple with drip irrigation
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
- manejo de agua superficial (manantial, río, lagos, mar):
- tecnologías de eficiencia energética
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación

otros
Especifique:
Damage and dysfunction of irrigation canal .
Comentarios:
Damage and dysfunction of irrigation canal intake by shifting nature of glacier as intakes are located at the glacier terminus.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
due to water access cultivation was possible and vegetation cover improved.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
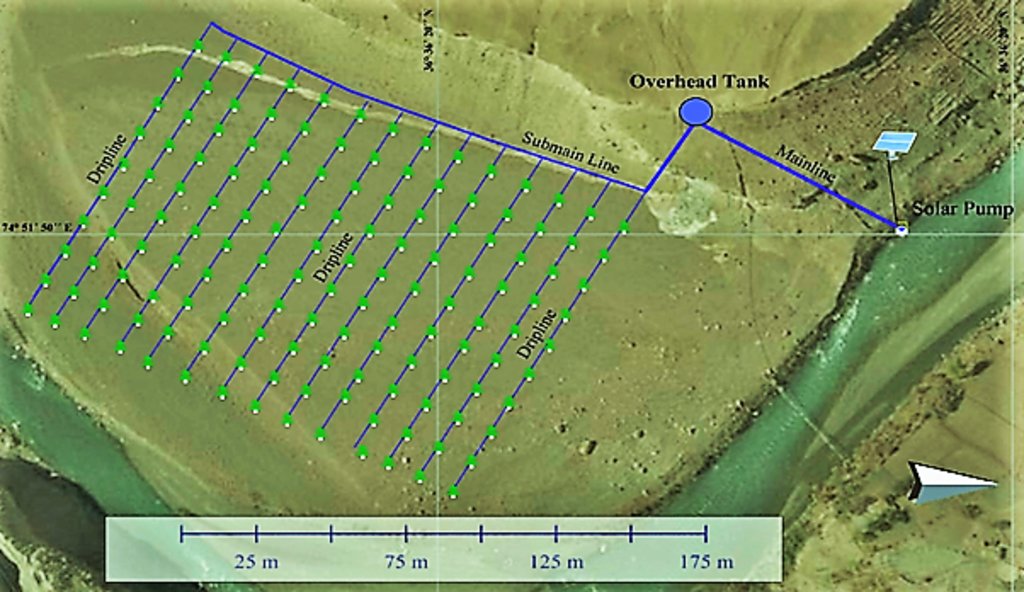
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Solar Pump: DC submersible (Lorentz, Germany 1 HP), the capacity of Panels: 500 watts, and pumping capacity of the pump: 7.5 litres/minute.
The capacity of storage tank: 500 litres, location of storage tank: 100 feet height (vertical) from the river and 60 feet height (vertical) from the orchard field.
Drip Irrigation: Surface and pressure compensating. The spacing of dripping points: 10 feet in Morkhun and 15 feet in Passu. Water application per plant by drip irrigation is 2 litres per day.
Plant to plant and row to row distance of apple 10 feet in Morkhun and 15 feet ( both plant to plant and row to row) in Passu coinciding with the dripping holes.
Pits: Constructed for planting apples, later they served as water harvesting pits /check basins.
Plastic mulch: In each plant. Shape of the plastic mulch is rectangular and dimension is variable, average about 5 ft long and 3 feet wide. It is an opaque plastic sheet.
Autor:
Muhammad Mudassar Maqsood)
Fecha:
09/10/2018
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
Technological package at two sites ( solar system, water storage tank, drip, orchard establishment, and mulch) , same package is applied in two sites separately. Total area of two sites is 5 ha
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
US$ 14.5 for skilled person and US$ 7.5 for unskilled person
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site identification in consultation with the communities | Pre Monsson (March) |
| 2. | Detailed engineering surveys, design formulation, tendering and work orders etc | Pre Monsson (March ) |
| 3. | Implementation agreement with the community | Pre Monsson (March) |
| 4. | Installation of solar-powered pumping units with four poly-crystalline solar panels. | Pre Monsson (April) |
| 5. | Installation of storage (plastic tank) with a line filter attached to it for the operation of the drip system and avoid sediment entry into the tank | Pre Monsson (April) |
| 6. | Digging of pits for plantation of the apple orchard at the plant to plant and row distance of 10 feet (Morkhun) and 15 feet (Passu)) | Pre Monsson (April) |
| 7. | Constructed pits for each plant used for application of compost | Pre Monsson (April) |
| 8. | Laying of drip irrigation systems | Pre Monsson (May) |
| 9. | Laying down plastic mulch | Pre Monsson (May) |
| 10. | Plantation of tubed apple (Kala Kolu variety) it is bought from the local nursery | Pre Monsson (May) |
| 11. | Training to selected farmers as caretakers of the technologies for its days to day repair and maintenance | Pre Monsson ( May) |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Skilled | Person days | 136,0 | 14,43 | 1962,48 | |
| Mano de obra | Unskilled | Person days | 745,0 | 7,7 | 5736,5 | |
| Equipo | Spade | Number | 20,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Shovel | Number | 20,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Plumbing tool kit | Kit box | 1,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Apple Plants | Number | 3300,0 | 0,087 | 287,1 | |
| Material de construcción | Solar panel, pump with all accessories | sites | 2,0 | 6490,0 | 12980,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Water storage, intake, distribution pipes and mulch | sites | 2,0 | 6861,0 | 13722,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Drip irrigation | sites | 2,0 | 4173,0 | 8346,0 | |
| Material de construcción | -Check basin (pits) | number | 3300,0 | 0,466 | 1537,8 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 44571,88 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 44571,88 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The technological package was designed and implemented by ICIMOD's Indus Basin Initiative with partners and contributes to the sustainable Development Investment Portfolio and is supported by the Australian Aid program.
Comentarios:
Establishment costs and inputs for a solar pump –drip irrigation - mulch system was estimated for apple orchards piloted on a 5 hectares of total land in two villages.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring of water pumping, storage, and drip system by a regular visit to the site. | Regular (annually) |
| 2. | Repair and maintenance of solar pump panel and drip irrigation: fixing clogged drip lines and replacement of broken solar panel and cleaning of impellers of the solar pump. | Regular (annually) |
| 3. | Replacement of dead apple plants | As and when required |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Unskilled | Number | 26,0 | 7,7 | 200,2 | |
| Equipo | Spade | Number | 10,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Plumbing tool kit | Kit box | 1,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Apple ( replacement of dead plants) | number | 330,0 | 0,087 | 28,71 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 228,91 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 228,91 | |||||
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Equipment and labor
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
150,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
it varies from 150 mm to 200 mm
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Passu ghar
Zona agroclimática
- árida
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Water is available in the river but fields are higher up than river
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Semi-nómada
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Relative level of wealth: Poor 35 %, average 65%
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
Most of the uncultivated land is communal, community decides uses of the land
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
área de producción
Cantidad luego de MST:
5 ha
Comentarios/ especifique:
Production area increased as uncultivated land brought under cultivation, but crop production has not increased yet because orchard just established.
generación de energía
Comentarios/ especifique:
Use of renewable solar energy for fruit cultivation
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
Irrigation water availability increased with innovative technological packages.
Impactos socioculturales
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
Community institution (village development organizations) strengthened due to the approach of farming in a group.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Land management skills of community enhanced due to various training such as crop cultivation, operation and maintenance of water conservation and management technologies.
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved soil moisture as a result of water harvesting pits, mulching and efficient drip irrigation.
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
improved soil cover due to mulch.
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced soil loss ( from wind and water erosion) due to application of mulch and also due to vegetation cover and above-ground biomass.
Otros impactos ecológicos
Comentarios/ especifique:
The technological package is climate change resilient as compared to the melt water dependant surface flood irrigation. Melt water of glacier and snow is very sensitive to climate change. Glaciers are dynamic, their depth and volume fluctuation happens each year.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced risk of downstream flooding though the amount is very less.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| condiciones extremas de invierno | bien |
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación repentina | moderadamente |
Otros extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
| otros (especifique) | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? |
|---|---|
| Heavy load of suspended river sediment | bien |
Comentarios:
Drip is sensitive to temperature increase; but tolerant to wind storms/dust storms and floods. Solar panel is tolerant to temperature increase.
The solar panel is sensitive to wind storm. The pump is sensitive to flood and sediment load in the river, emitters of drip clog due to sediment. Mulch is sensitive to windstorm. Apple plants at an earlier stage are sensitive to wind storm, plants are sensitive to extreme winter conditions (low temp and snowfall)
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
The initial cost of investment would be fully recovered in 10.9 years, hence the payback period of the project is around 11 years, and the repayment of the investment would start from the eight years. Benefit-Cost Ratio is found to be 4.96.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
45 Households
Comentarios:
None
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
Si fuera así, indique a qué condiciones cambiantes se adaptó:
- cambios climáticos / extremos
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
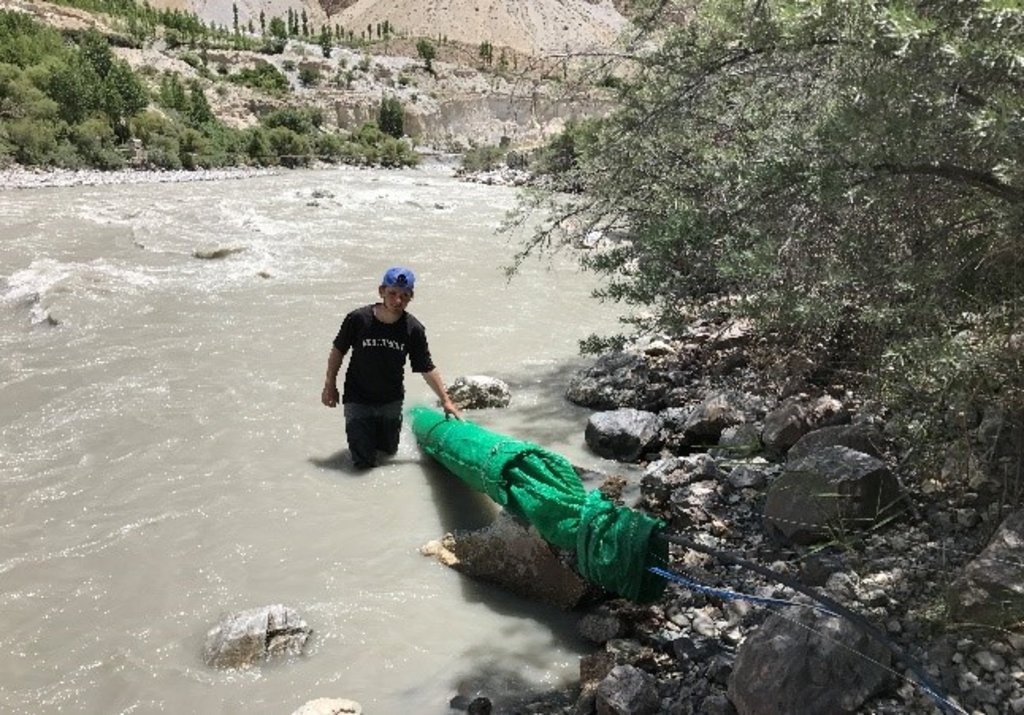
Due to heavy load of suspended sediment flowing in the Hunza River, impellers of the solar pump couldn’t function properly. Site-specific customiza-tion of the pump was carried out to make the system functional and to sustain it in the long run.
For that, an outer filter was developed for the pump to avoid sediment entry into the pump. The outer filter is UPVC pipe (of 10-inch diameter and 13 ft long) wrapped with a finely-meshed green net. The out filter was tightly bound together with the pump. The filter with the pump was placed in the river, transverse to the direction of flow. The farmers are also trained to open the clogged drip to release the sediments from time to time.
Damaged solar panel sometimes was replaced. A portion of mulch was buried under the soil. Apple plants were tied together with support stakes. Application of mulch helped to protect apple plants from low winter temperature.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The solar powered water lifting and drip irrigation is the first of its kind in the upper Indus basin. The system is simple and anyone once trained can operate it. It will contribute to nearly 50% of the additional income of the Passu community. |
| The technological package is environmentally friendly and are effective adaptation measures in the context of climate change. |
| Women are often most involved in agricultural activities and this intervention has provided them relief by making it possible for them to work nearer to their valley. More over, once the trees bear fruit, women will be able to sell them to generate income. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The first innovative technological package in GB that is climate-resilient as compare to meltwater-dependent flood irrigation is operated by renewable solar energy. |
| Water application through drip irrigation is very efficient as compared to flood irrigation, per plant water applied trough drip is 2 litres/day as compared to 30 litres/day through flood irrigation. Integration of mulch enhances soil moisture. |
| The technological package can last more than 20 years. Maintenance cost is nominal, it is US$ 100 at the initial stage and later stage it is US$ 300. |
| As women are predominantly responsible for farming activities, im-proved water access and application through drip reduces their work-load and frees up time for other activities |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Frequent maintenance operation and maintenance of the solar pump due to high sediment concentration of the river from where water is pumped. | Include capacity building activities as an integral part of the technology implementation process. |
| Drip irrigation and parts of solar panel may not available locally | A spare parts should be made available locally for immediate replacement as and when required. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The investment cost is high . | Explain cost-benefit analysis to aware farmers that the benefit is high in the long run. |
| Techniques of multiple cropping were not practised to get short term benefits from the orchard field. | Engage the agricultural department to demonstrate and train farmers on multiple cropping in the dry land. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Field visits was done several times as this was a part of the project activity. Cost benefit analysis was done in 2019.
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Frequently with beneficiaries of the SLM technological packages (around 50 households) .
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
ICIMOD 2017. An Innovative Approach to Agricultural Water Management in the Upper Indus basin: the Water_Energy-Food Nexus at the Local Level
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
http://lib.icimod.org/record/32794/files/Innovative%20Approach.pdf
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Kifayat, U., Khan, F. A., & Ejaz, A. (2014). Determinants of poverty in the mountain region of Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. Developing Country Studies, 4(7), 10-19.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Google scholar
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Amjad Ali 2019. Unpublished report on cost-benefit analysis of UIB phase 1 intervention in Upper Hunza
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
ICIMOD
7.4 Comentarios generales
It has been improved a lot as compared to past 10 years .
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos