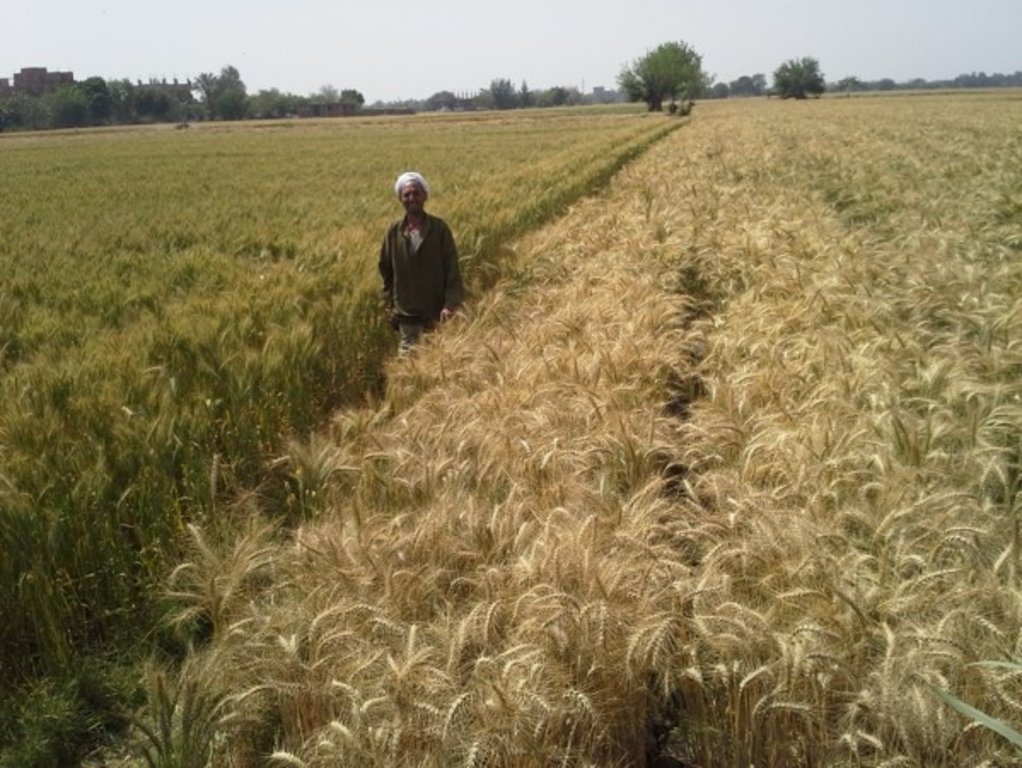
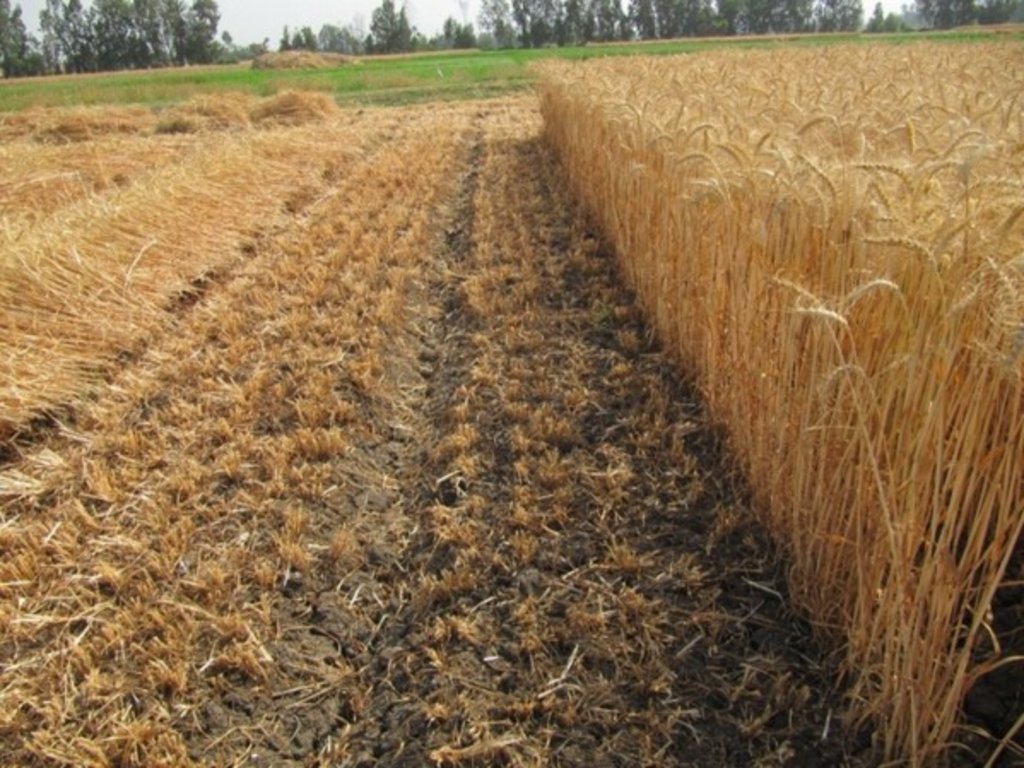
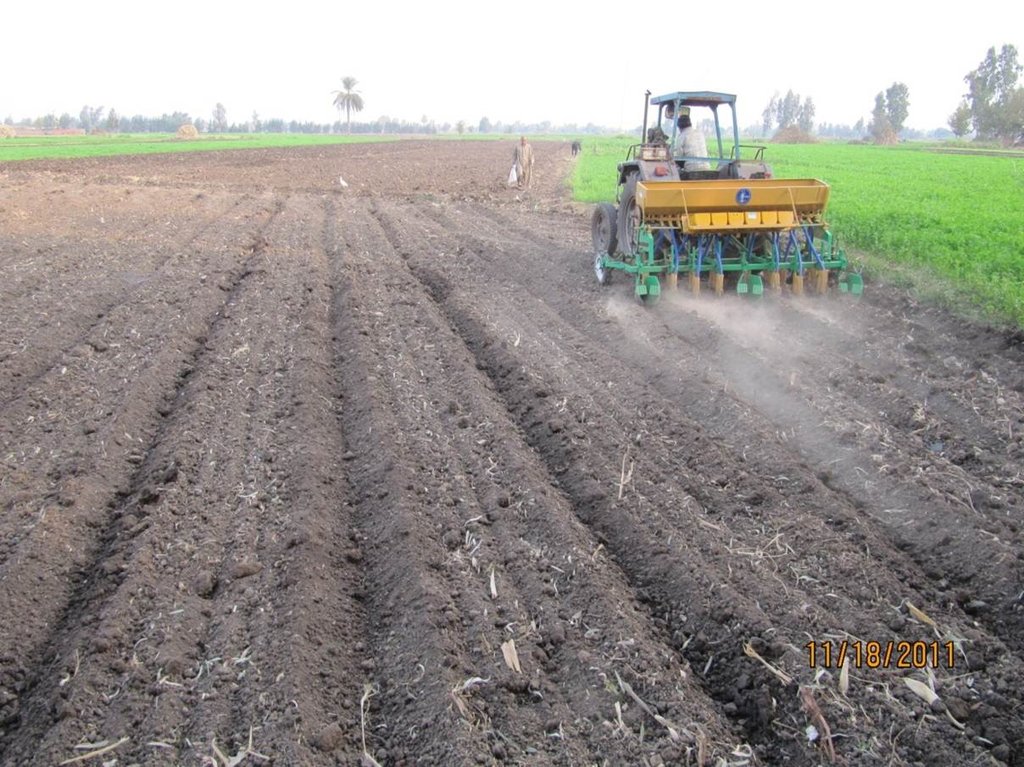
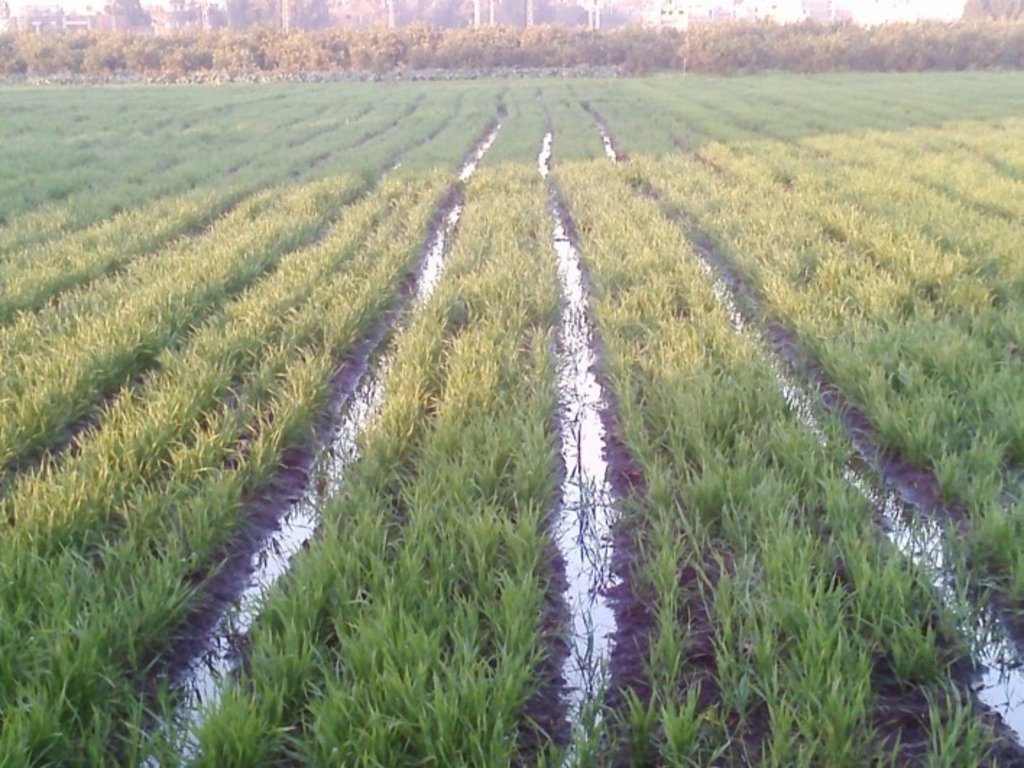
Mechanized Raised Bed (MRB) Technology in a wheat based production system. [Egipto]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Joren Verbist
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5804 - Egipto
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Senior Scientist, Irrigation Water Management:
Swelam Atef
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Egipto
Social Sciences Specialist (Water Land and Ecosystem Program):
Dessalegn Bezaiet
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Jordania
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management InitiativeNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - Líbano1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Mechanized Raised Beds (MRB)-technology improves livelihoods because raised beds lead to significantly reduced costs (30% less water, 20-40% less nitrogen fertilizer) and higher wheat yields increased by 20-30%. MRB-technology helps to do more with less.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Mechanized Raised Beds (MRB)-technology has been applied by the International Centre of Agriculture Research in Dryland Areas (ICARDA) and national partners in Egypt. Egypt is a water scarce country and 95% of its water comes from beyond its borders. In addition, Egypt is highly dependent on the import of wheat, 50% of the wheat demand is met by import.
In Egypt, water scarcity and mediocre yield are two issues that keep the majority of people working in the agricultural sector in poverty. Water is scarce as the annual precipitation is less than 250mm leading to most farming to be irrigated. The water comes from the Nile river. However, available irrigation water per farmer is rather low due to population growth. Thus, due to clay soil and the use of flood irrigation, water logging and uneven water distribution over the field lead to salinization of the soil, harming the farmer's yields. Furthermore, the latter is caused by the lack of water, insufficient use of fertilizers and the use of relatively low-quality seeds. In particular, fertilizers are expensive leading to an insufficient and poor application of fertilizers.
In effect, the core objective of MRB-technology package is to fit within this context and realize more output with less input, consequently improving involved livelihoods. Indeed, MRB improves farmers' resilience with increased water and nutrient efficiency. The adopters of MRB receive benefits from direct effects such as improvement in their livelihoods, a decreased workload, increased yields and more efficient use of resources (water, fertilizer and seeds).
The first stage research and designing of MRB-technology was done in 2003. Introductions and pilots of the technology were designed together with regular farmers in the Nile Delta-area, from 2010 until 2013. In 2015, MRB-technology was proven beneficial permitting out-scaling. Thanks to the shown potential of MRB-technology and Egypt's reliance on foreign countries for water and wheat, that MRB-technology has become a strong component of Egypt's national wheat campaign. The Egyptian Government aims to cultivate 2 million acres of wheat under MRB-technology, by 2022.
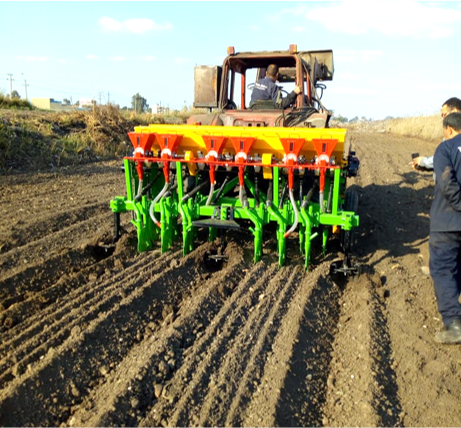
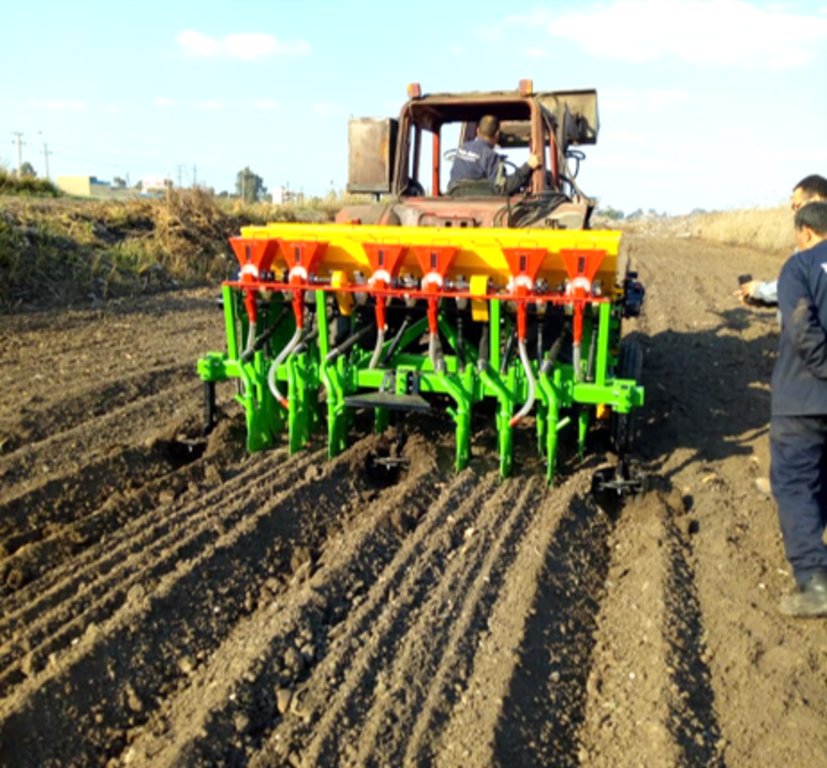
MRB-technology raises the seedbed simultaneously seeding wheat, consequently creating furrows, of which the length depend on the dimensions of the farm- field. The inter- furrow spacing and the width depends on the type of crop planted and on the soil type. The field/terrain may not exceed a slope of 5%. This allows water to infiltrate, reach the end of the furrow and for safe run-off, preventing water-logging. So, to implement MRB-technology, the field might be levelled prior to implementation, but this is often not the case as MRB is designed to local conditions, and most fields already have a slope of less than 5%. The practice of the machine requires a loose soil, so it is required that the field is ploughed prior to seeding, and therefore MRB is not seen as a type of ploughing. If the field preparation is done, a MRB-machine can start seeding and raising the seedbed. Specific characteristics for MRB-technology with respect to conventional seeding, is that seeding and raising seedbeds are done simultaneously. Raising seedbeds mechanically saves 80% of the workload with respect to manually raising seedbeds. The after-harvest practice depends on the farmer preference, as some farmers prefer letting the stubble grazed, while others clear the field. The after-harvest practices are thus independent with respect to MRB.
In addition, to complement the Mechanized Raised Bed, High Quality Seeds are offered. These are beneficial as they yield higher than the regular wheat seeds. Nevertheless, the machine can also be practiced with regular wheat seeds, if the high-quality seeds are found too expensive by the farmer. The High Quality Sees are hybrid, and need to be replaced after three years to ensure high quality.
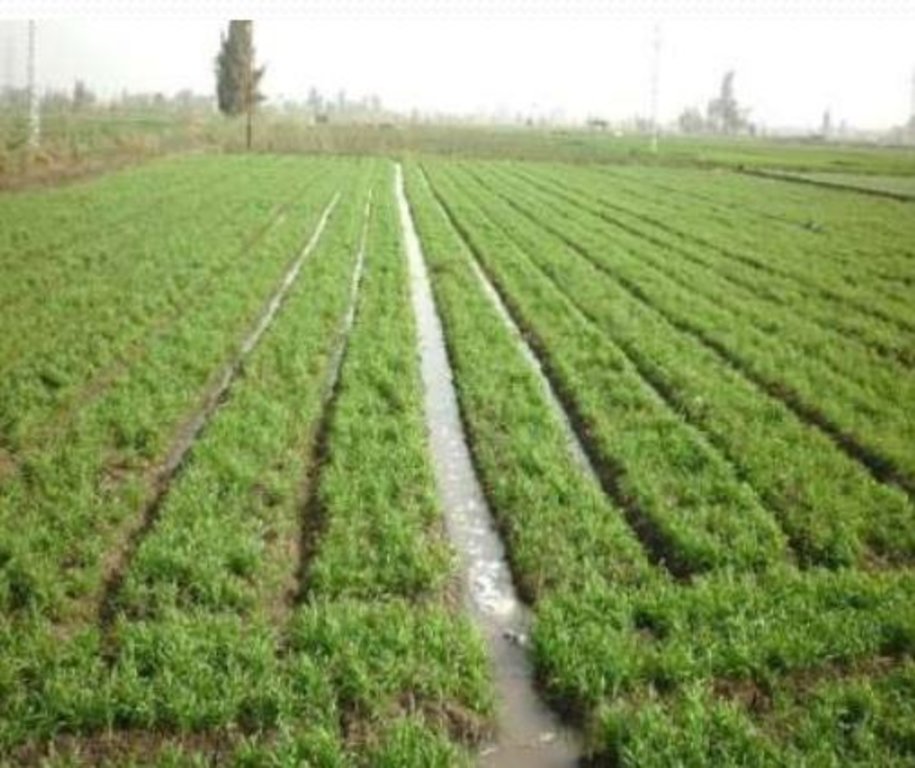
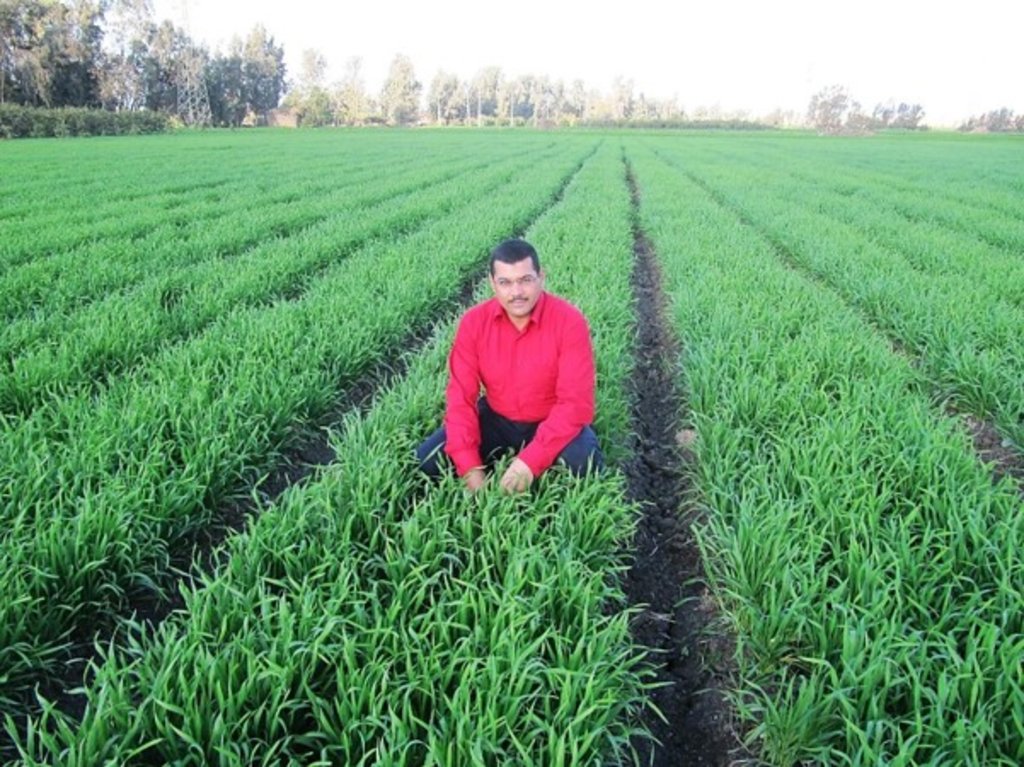
The technology has significant positive impacts for local farmers as applied water is saved by 25%, water pumping costs decreased by 25%, seed rate reduced by 50%, farming costs decreased by 30%, fertilizer use efficiency increased by 30%, and crop yield increased by 15-30% with respect to conventional farming. On overall, it is estimated that farming under MRB is about 1/3 of the cost with respect to conventional farming. Manually raising seedbeds was considered too expensive due to the required amount of labour. Thus, regular flood irrigation was practiced. Practically, this results in full surface flooding of the field. This has significantly higher evaporation hence increasing salinization, as opposed to furrow irrigation through raised seedbeds. Also, because water is well distributed over the field due to the furrows (reducing water stress and water logging), there is less leaching of the nutrient hence increased nutrient-efficiency. The raised seedbeds allow excess water, in case of a heavy rainfall event or over-irrigating, to safely run-off. These features of better water disposal and reduced evaporation makes MRB-technology well suited with respect to climate change, which leads to more concentrated rainfall events and increased temperature hence increased evaporation. In addition, as MRB prevents e.g. waterlogging it prevents land degradation (e.g. salinization).
Therefore, livelihoods of farmers who have adopted this technology have been greatly improved. Farmers who have adopted MRB, agree that MRB is affordable, easy to apply, improves production and is cost saving. Furthermore, since this technology increases irrigation efficiency , it can mitigate existing upstream-downstream issues in terms of availability, as there is more available irrigation water. Also, as MRB-technology is currently out scaled, it creates employment opportunities since MRB-machines are locally produced from scratch.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Comentarios, descripción breve:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5SW_Hf5AM3Y
Nombre del videógrafo:
ICARDA
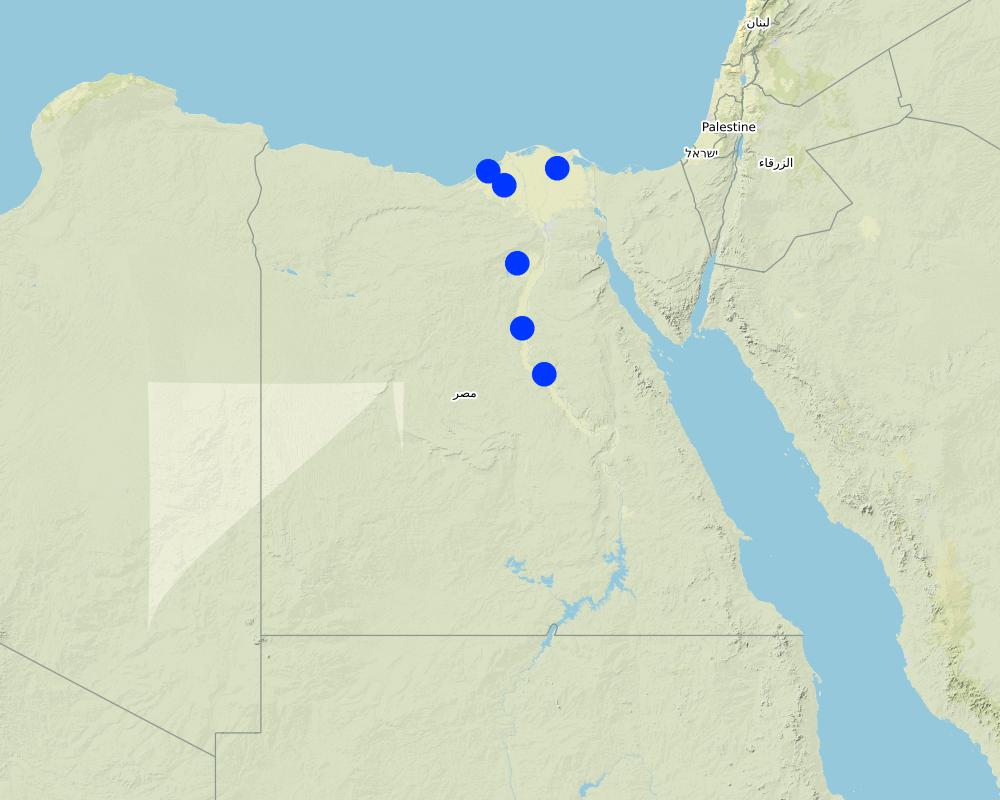
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Egipto
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Sharkia, Dakahlia, Beheira, Fayoum, Minya and Asuit
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- 1-10 km2
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2003
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- durante experimentos/ investigación
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- crear impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - trigo (invierno)
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- No (Continúe con la pregunta 3.4)
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- totalmente irrigada
Comentarios:
The farms are irrigated from water that comes from the Nile river.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- variedades vegetales/ razas animales mejoradas
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A3: Tratamiento de superficie del suelo
- A5: Manejo de semillas, variedades mejoradas

medidas estructurales
- S3: Acequias graduadas, canales, vías fluviales
Comentarios:
Ploughing is required to allow for raising seedbeds mechanically. Nevertheless, ploughing was also done in conventional farming. As seedbeds are raised whenever wheat is sown, this is recurrent so ploughing is as well.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cs: salinización/ alcalinización

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pw: encharcamiento

degradación biológica
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
Comentarios:
Due to degradation the biomass production decrease. MRB-technology increase safe water disposal and decreased evaporation. This results in the prevention of water logging and a decrease in the rate of salinization and aridfication.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
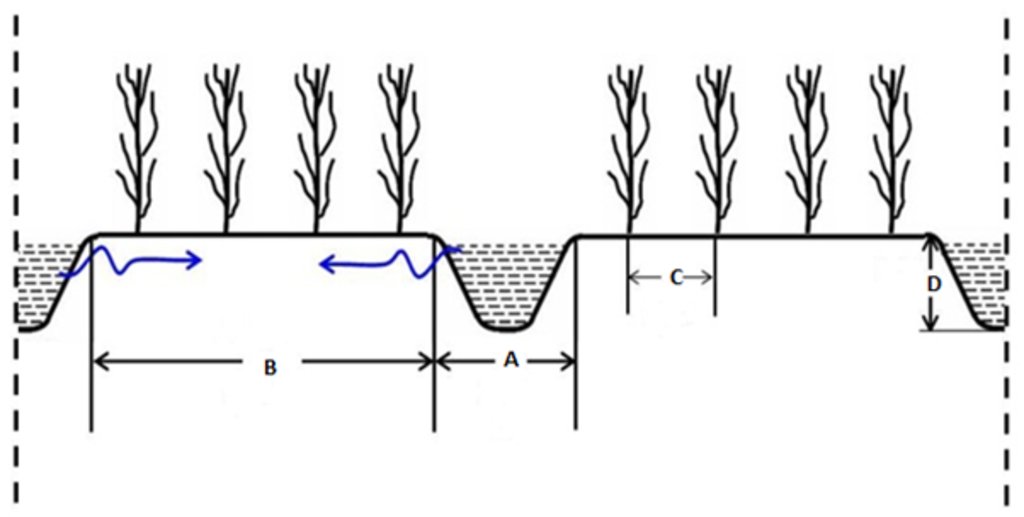
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Firstly, prior to Mechanized Raised Seedbed (MRB)-implementation the field is prepared. This consist of two-way ploughing. This makes the soil sufficiently loose, to enable the practice of MRB i.e. construction of the raised seedbeds. Also, for successful implementation of the MRB, the field should have a slope of less than 5%.
Secondly, the raised bed seeder is pulled by a tractor and raises the seed bed while seeding wheat, hence Mechanized Raised Seedbed technology. The width of the furrow (A) is 35 -45 cm, this is affected by the related soil texture. The width of the raised seedbed (B) is 100-130 cm, also dependent on the soil texture. Between
seed rows (C) there is a space of 14 cm.This inter-row spacing of the crops relates to the type of crop seeded. The furrow has a depth (D) of 35-45 cm. However, after the first irrigation event the depth could be reduced to 25 cm, due to the influx of loose soil. This is not a problem for the current growing season.
This technical drawing is based on the most common conditions where MRB is implemented. These are that the crop is winter wheat, the soil texture is mostly clay and the system is watered through irrigation coming from the Nile river, rather than rain-fed. If MRB is used under different circumstances, the dimension would change as well.
Lastly, once these above-mentioned steps are successfully done, the agricultural practices do not differ from the previous/traditional method. After harvest, prior to the new season, the raised seedbed structures are still well in shape. This means that after some small reshaping, the raised seedbeds can be used for cultivation again, without using MRB and/or the previously mentioned field preparation. This reshaping is done by cleaning/digging out the furrows. Additionally, this reduces the consequences of compaction by heavy machinery, such as the tractor. As these heavy machinery are used less frequently.
Autor:
Joren Verbist (Drawing: Atef Swelam)
Fecha:
30/09/2020
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
1 acre
Si usa una unidad de área local, indique el factor de conversión a una hectárea (ej. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
2.47 acres
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
6.31
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase MRB |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipo | MRB-Machine | Machine | 1,0 | 6000,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 6000,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 6000,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
The total costs per acre are estimated to be 44 USD to 64 USD for solely a MRB-machine, so the costs of the High Yield Seeds are excluded.
The purchase of a MRB-machine is commonly done by a community (such as a village). Therefore the realistic costs per farmer of the machine are rather low, as well as the cost per area. The tractor which is used to pull a MRB-machine is the same as has been used before the adoption of a MRB, so this is not an additional cost
The High Yield Seeds are offered with a MRB-machine, but a MRB-machine is build that it can use other seeds as well.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing | Prior to seeding |
| 2. | Levelling (if needed) | Prior to seeding |
| 3. | Seeding/Raising seedbeds (i.e. use of MRB) | November |
| 4. | Irrigation Event (300-400m3) | Once in every 25-30 days |
| 5. | Fertilizer Application | Establishment Stage (November) |
| 6. | Fertilizer Application | Flowering Stage (March-May) |
| 7. | Fertilizer Application | Grain Filling Stage (June-July) |
| 8. | Harvesting | April |
| 9. | Purchase new High Yield Seeds | Once in the 3 years |
Comentarios:
MRB-machines are produced by local manufactures. This means that repairs could be done relatively cheap and on time.
The cleaning of the furrows can be done by the farmers self. Therefore, it is not a significant cost.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Pesticide and herbicide application | Person-Day | 2,0 | 6,0 | 12,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Field Preparation and Raising Seedbeds | Person-Day | 2,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Mano de obra | Fertilizer Application | Person-Day | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Irrigation Management | Person-Day | 5,0 | 7,0 | 35,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Combine (harvesting) | Machine Day | 1,0 | 64,0 | 64,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | MRB | Machine-Day | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tractor (Raising Seedbed) | Machine-Day | 1,0 | 17,0 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Sprayer | Machine-Day | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Plough | Machine-Day | 1,0 | 32,0 | 32,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tractor (Field Preparation) | Machine-Day | 1,0 | 32,0 | 32,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | High Yield Seeds | Kilogram | 45,0 | 0,6 | 27,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Fertilizer | Kilogram | 150,0 | 0,26 | 39,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Herbicide | Kilogram | 1,0 | 9,5 | 9,5 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Pesticide | Kilogram | 2,0 | 7,0 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Water (Irrigation Event) | 350m^3 | 20,0 | 8,0 | 160,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Harvesting | Person-Day | 5,0 | 7,0 | 35,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Maintenance Raised Seedbed | Person-Day | 8,0 | 7,0 | 56,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 569,5 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 569,5 | |||||
Comentarios:
The pumping cost is 25% less with respect to the conventional flood irrigation.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The most impacting cost factor is the purchase of a MRB-machine. Whereas, the High Yield Seeds are also significant, but the increased yield justifies this. In addition, farmers could also choose to use different seeds. Additionally, the High Yield Seeds are hybrid and can be reproduced for three years on the farm.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The annual rainfall varies between 20mm and 200mm
Egypt is characterized as a hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification BWh). The hot season is from May to October. While the cool season is opposite, from October to May.
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
- árida
Egypt is characterized as a hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification BWh). The hot season is from May to October. While the cool season is oppesite, from October to May.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones convexas
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
- baja (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
< 5 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
Sí
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
- ancianos
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
However, it is hard to generalize, since the MRB has been used on such a scale, including many different farms and sizes.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- individual
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
Land use right are formed by Islamic influences as well as colonial influences. The are different status such as private ownership and open acces.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Comentarios:
In the Nile Delta, the MRB-technology is used on very large area with many different farmers, therefore it is hard to generalize the aspects of the Health and Education since these are highly related to the income of a farm.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad luego de MST:
+20%-30%
Comentarios/ especifique:
The yield is increased due to reduced water stress and because of the use of improved wheat varieties.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The quality of the crops is increased due to reduced water stress.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
This decrease as the impact of intense rainfall events is reduced as consequence of safe disposal through furrows.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
demanda de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
The demand of irrigation water is reduced because the efficiency of it is increased i.e. water is applied more effectively.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
50% less seed rate. 20% higher fertilizer efficiency.
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Because of higher yield and less input
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The workload was reduced by 80% for mechanized seedbed raising (MRB) compared to manual seedbed raising.
Impactos socioculturales
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Because the irrigation efficiency is increased, there is relatively more available irrigation water. This leads to a mitigating effect on upstream/downstream tensions
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Run-off occurs more easily with respect to traditional practices. This is positive, since this prevent water-logging.
drenaje de agua en exceso
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Compared to previous border/field irrigation, the water infiltrates easier, and is concentrated more. This leads to a decrease in evaporation.
Suelo
humedad del suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to better infiltration, the fertilizers are used more efficient.
salinidad
Comentarios/ especifique:
Salinity is decreased because evaporation and water logging is reduced.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
Comentarios/ especifique:
The impact of a flood is reduced because the excess water is able to safely run-off through the established furrows.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to the increased irrigation water efficiency, there is relatively more water available to desirably flood (border/surface irrigation/ MRB) farm fields downstream
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | moderadamente | |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
| inundación repentina | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
In the short-term investments are weighing relatively more than in the long term with respect to the benefits. However, on the overall, the MRB-technology offers more efficient use of resources, coming down to achieving more output with less input. Thus, highly improving the involved livelihoods.
In the long term the benefits are less positive with respect to maintenance. This is due to the aging of machinery. MRB-machines are estimated to have a life span of 12 years.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- > 50%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
otros (especifique):
Local Conditions
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
These adaptations are initiated because of the successes of the MRB, so currently MRB-technology is modified to be used with other crops (e.g. Faba Bean), other soil textures and for rain-fed areas.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| MRB significantly contributes to the prosperity of the farmers who have adopted this technology. For farmers, the major advantage of MRB (High Quality Seeds plus the raised seedbeds) is the increased yield. |
| The adoption of the technology leads eventually to less leaching hence higher fertilizer efficiency. This is also highly valued by the farmers as this translates into less expenses. This advantage of the MRB combined to the increased yield, results in the realization of more income with less expenses, and thus a higher net income. |
| In Egypt climate change is visibly present and water does not seem to be abundant anymore, the farmers do have increasingly attention for the value of water. MRB increases the irrigation efficiency, therefore this is also observed as a great advantage of MRB. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The increased yield is of great advantage not only for the improved situation of the involved livelihood, but also on national level. Namely, because more yield means less import of food from other countries. This makes Egypt more self-sufficient, and less dependent on other countries. This is particularly relevant with respect to the significant population growth of Egypt. |
| The increased water availability, because of higher irrigation efficiency is important on a national level. This is certainly important, with respect to trend of increasing the power generation by water (hydraulic power plants), in upstream areas of Egypt. |
| MRB-technology has led to a local industry. This industry is the manufacturing of MRB-machines. This is on broader level beneficial, because it creates local employment, efficient supply chain, easy and fast access to technical knowledge and gives Egypt an independent position. |
| MRB improves soil health because salinization is reduced as water is less evaporated and logged. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| A current risk of MRB is that many farmers are convinced of the beneficial application of the MRB, which means that there is higher demand. Therefore, there is currently not a sufficient number of MRB-machines. In practice this means that some farmers are not able to use MRB-machine during the essential seeding period. This is possibly followed by tensions between users since the technology is often purchased as communities. Land users found this a weakness of the technology. | This is to overcome if public and private sectors invest in the manufacturing of MRB. This would lead to an increased supply of machine, thus eliminating the deficit of machines. |
| The cost of the High Yield Seeds is a weakness of MRB-technology. This is because the costs of the seeds are quite high and they contribute significantly to the increased yields. So without the seeds, MRB-technology does not reach its full potential. Farmers dislike the costs of these seeds and the yearly purchasing. | There are investments needed and plans to improve the production of these seeds. The increased supply would lead to reduced costs. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The risk of tensions that are a consequence of the limited availability of the MRB's. | This could be overcome by increasing the production. However, better social cooperation could reduce the tensions between and within communities as well. |
| The costs of the High Yield Seeds. This is a weakness, because MRB-technology is significantly improved by these seeds, realizing its full potential. | There are investments needed and plans to improve the production of these seeds. This would lead to reduced costs. However, alternatively, other seeds can be used. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Atef Swelam and Y. Atta, (2012) Improve Water Saving and Water Productivity by New Approach of Farm Management under Surface Irrigation. Mi. J. Ag. Eng., 29 (2):745-762.
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Jeffrey Alwang, Samy Sabry, Kamel Shideed, Atef Swelam and Habib Halila (2017) Economic and food security benefits associated with raised-bed wheat production in Egypt, Journal of Food Security, FOSE-D-17-00372)
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/8228
Título/ descripción:
Atef Swelam (2016) Science Impact: Raised-bed planting in Egypt: an affordable technology to rationalize water use and enhance water productivity, Issue: 6-FEB 2016, ICARDA.
URL:
http://www.icarda.org/sites/default/files/u158/Science Impact Raised-Bed_final.pdf
Título/ descripción:
National Wheat Campaign Report (2020), Agricultural Research Center, Ministry of Agriculture and Land Reclamation, Cairo, Egypt
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/8228
Título/ descripción:
Karrou, M., T. Oweis, B. Benli and A. Swelam (2012). Improving Water and Land Productivities in Irrigated Systems, ICARDA, ISBN:92-9127-259-0.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/8825
Título/ descripción:
Atef Swelam. (16/11/2016). Egypt farmers save water with new irrigation method. New York, United States: The Associated Press (Executive Producer)
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/5757
Título/ descripción:
Atef Swelam. (31/7/2020). On-farm irigation improvement Infographic Map. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/11823
Título/ descripción:
Secretariat FAO. (1/4/2018). Mechanized raised-bed irrigation: Production package. Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/11114
Título/ descripción:
Swelam, A. ICARDA. (2019, 1 juli). Improve on Farm Irrigation [Presentation]. Slideshare.
URL:
https://www.slideshare.net/ICARDA/improve-onfarm-irrigation-management
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos