Rock catchment [Kenia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Fredrick Ochieng
- Editores: Boris Orlowsky, Nicole Stolz
- Revisores: Renate Fleiner, Boris Orlowsky
Rock catchment
technologies_580 - Kenia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Fredrick Ochieng:
Kenia
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
21/09/2016
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
The technology has instead addressed the perennial water shortage among the beneficiary households
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
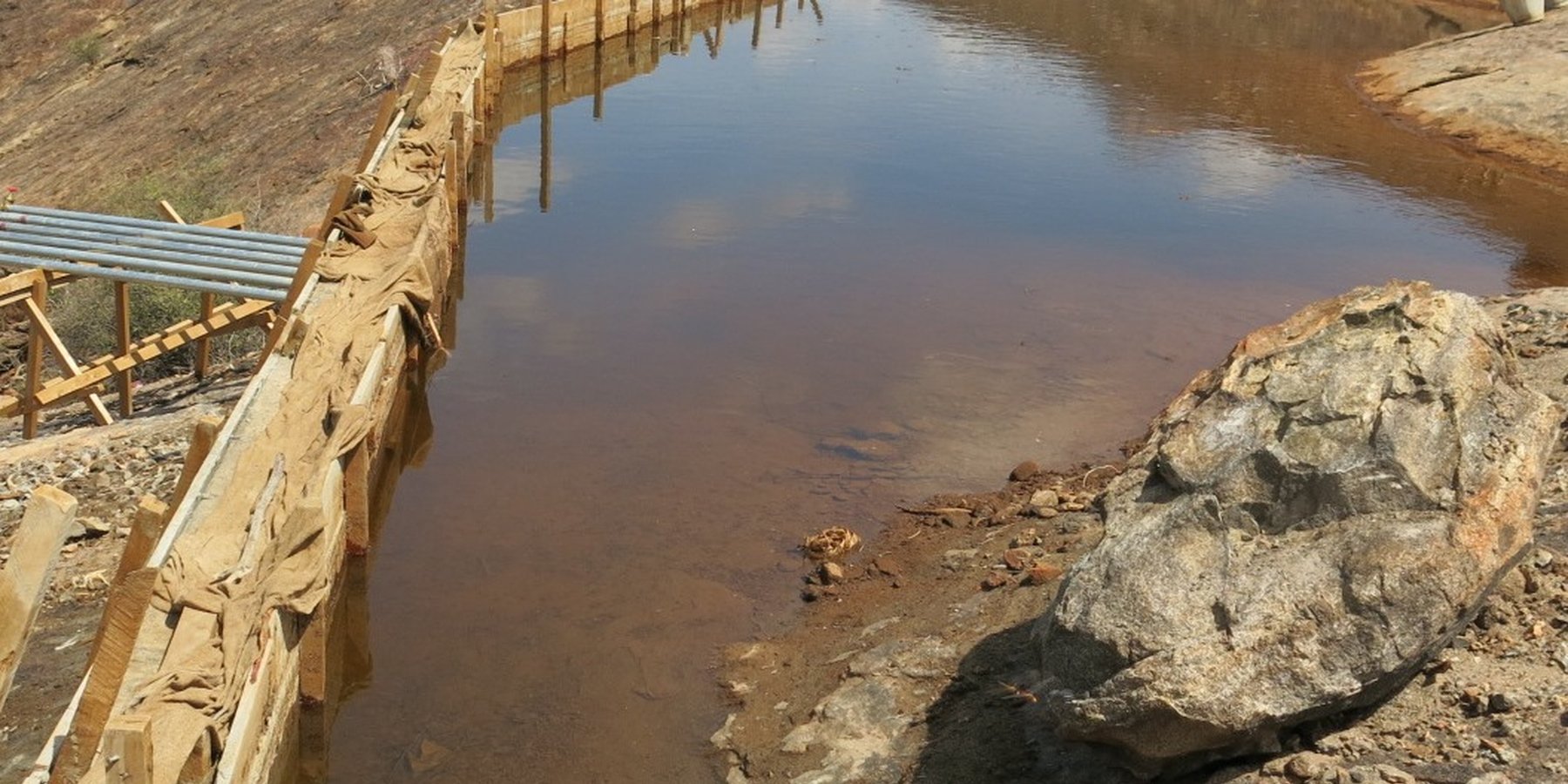
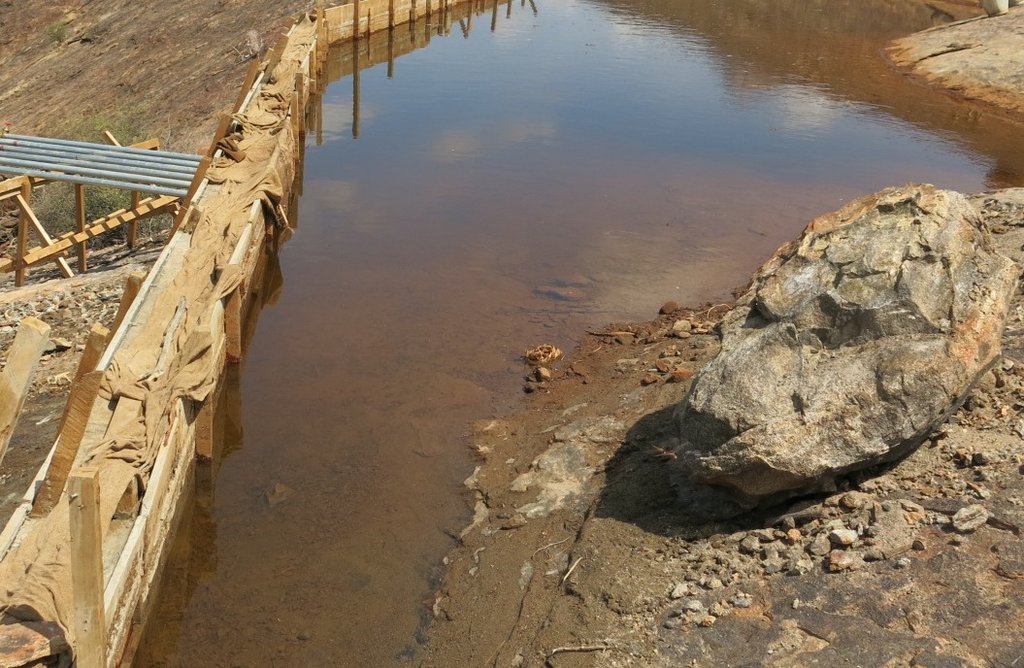
A rock catchment system is a water harvesting structure comprising a bare slopping rock surface (catchment area), a built concrete wall at a strategic point (weir), pipeline from the weir to the storage tank(s), storage tanks and water kiosk(s) connected to the water tanks by pipelines.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
A rock catchment system is a water harvesting structure comprising a bare slopping rock surface (catchment area), a built concrete wall at a strategic point (weir); a pipeline system running from the weir to the storage tanks; storage tanks and water kiosk(s). The Technology is built on an a gently sloping outcrop of a continuous rock on the hillside. The bare rock is the catchment surface from which rainwater is harvested. The weir is constructed at a strategic point for maximum collection at the lower end towards the foot of the hill. The weir dams the harvested water and channels the water through a piping system to the reservoirs, mostly masonry tanks, located at the foot of the hill. A weir is usually a concrete wall constructed and reinforced with iron bars to give it adequate strength that can withstand the weight of the dammed water. The length, height and thickness of a weir vary with the size and the slope of the rock catchment area. On average a weir will be 10 meters long, 2 meters high and 0.5 meters thick. At the base of the weir, an infiltration box of approximately 1 square meter is constructed and filled from the bottom with fine sand, coarse sand and gravel in that order for the purpose of sieving off impurities before the water is directed into the tanks. Metallic piping is recommended for connecting the weir to the storage tanks downhill due to high pressure exerted by flowing water. The piping distance would range from 15 to 300 meters from the weir to the storage tanks. Provision is usually provided for additional pipelines in case there is need for expansion of the system. At the bottom of the hill, masonry tanks are constructed ranging from 100 cubic meters and above depending on the catchment area, population, and available resources. The pipes join the tanks through a control chamber box meant for regulating water flow into the tanks. Adjacent to the tanks are a water kiosks room, where the community draws water. To gauge how much water is issued, a water meter is fitted inside the kiosk. Metering the water is a structural measure for accountability and control.
Construction of a rock catchment system needs heavy investment of materials - cement, quarry stones, ballast, iron bars, sand, hard-core stones, water, metallic (GI) pipes and fittings for plumbing. Construction of the system is labour intensive for both skilled and non-skilled. The main purpose of the rock catchment system is to harness, harvest, and store rainwater for domestic and a limited number of livestock use. For the case of the documented project, the benefiting communities are pastoralists who live in northern Kenya, a region characterised by chronic droughts, seasonal floods and acute water shortages.The communities have chronic and seasonal acute water shortages. The water situation is aggravated by increasing drought frequency and severity. On the other hand, the little rain received has often been destructive downstream, usually cutting off roads and causing massive soil erosion due to high water velocity flowing downhill. During the dry periods when the open water sources such as earth pans dry up, women travel long distances to search for water from hand dug shallow wells along the dry seasonal riverbeds. These wells are hazards to both livestock and the locals.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
The weir which dams rock surface runoff when it rains channelling the water into the piping system which takes the water into masonry storage tanks.
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Comentarios, descripción breve:
https://youtu.be/_5-a7badNdw
Rock catchment showing how the system harvests water and channelled down to water storage tanks
Fecha:
08/12/2014
Lugar:
Ndikir village, Marsabit County, Kenya
Nombre del videógrafo:
Fredrick Ochieng
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Kenia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Laisamis sub county, Marsabit County, Kenya
Especifique más el lugar :
Implemented with three different communities in three locations, Ndikir, Manyatta Lengima and Mpagas
Comentarios:
The Technology was implemented with three different communities in three locations, Ndikir, Manyatta Lengima and Mpagas
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2015
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology was introduced after technical assessments which looked at areas that had rock catchment potential with willing communities to participate in their construction
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- conservar el ecosistema
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- crear impacto social benéfico
- The common hazard in the region where the Technology has been implemented is drought. The Technology aims at reducing the drought impacts among the pastoralists
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierra de pastoreo
Tierras de pastoreo extensivo:
- Semi-nomadismo/ pastoralismo
Especies y productos animales principales:
Camels, cattle, donkeys, goats, sheep
Comentarios:
The pastoralists practice sedentary to semi-nomadism way of living. However, even for those who are sedentary, they do not cultivate land. They entirely rely on livestock and relief assistance.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Especifique:
Do not apply as the communities to not grow crops. However, there is a bi-modal rainfall season with more rains received between October to December.
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
The livestock owners constantly move with their livestock from one location to another.
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
- medida de pendiente transversal
- cosecha de agua
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques
- S7: Equipo para cosechar agua / provisión de agua/ irrigación
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de subterráneas
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
A Rock catchment consists of the following main components:
Catchment area - vary between more or less than 100 square meters
Infiltration box - concrete box with approximately one square meter and 0.5 meters deep
Weir - a wall approximately 20 meters length, approx. 0.3-0.5 meters width, and 1.5 meters height; depending on the site the catchment can store between 150 and 700 cubic meter above the weir
Pipes - Galvanised steel pipes of varying diameters and length depending on catchment size and storage location and capacity
Tanks - tanks with varying capacities, of the same order of magnitude as the catchment storage capacity above the weir. Together, tanks and catchment can store some 10-20% of the annual precipitation falling over the rock catchment, which is enough to sustain water use during a normal year, but not during a year of exceptional water scarcity.
Here is a link where you can see a sketch of typical rock catchment: http://www.climatetechwiki.org/sites/climatetechwiki.org/files/images/extra/media_image_3_22.png
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
A unit comprises the key component of the Technology. The rock catchment technology has four components - the weir, piping, tanks and water kiosk
Especifique volumen, largo, etc. (si fuera relevante):
N/A
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
15 dollars per day for skilled labour and 3 dollars per day for unskilled labour.
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Surveys - topographical, environmental impact assessment | Otras medidas | no specific time |
| 2. | Drawings and bill of quantities | Otras medidas | no specific time |
| 3. | Procurement of materials | Manejo | advisable should be done during the dry season when roads are passable without difficuities |
| 4. | Recruitment of artisans | Manejo | no specific time |
| 5. | Start of construction works | Estructurales | no specific time |
| 6. | Continuous technical supervision and completion | Estructurales | Continuous throughout the year |
Comentarios:
The key activities are not generally affected by the seasonality or any other type of timing with exception of procurement, for which it is advisable to do it when roads are passable.
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
Si fuera posible, desglose los costos de establecimiento de acuerdo a la siguiente tabla, especificando insumos y costos por insumo. Si usted no pudiese desglosar los costos, proporcione un estimado de los costos totales para establecer la Tecnología:
1,0
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Skilled labour | Days | 607,7 | 15,0 | 9115,5 | |
| Mano de obra | Unskilled labour | Days | 1973,0 | 3,0 | 5919,0 | 40,0 |
| Material de construcción | Construction materials for all the four components together | 1 catchment system | 1,0 | 75407,0 | 75407,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 90441,5 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Caritas Switzerland
Comentarios:
The project was implemented with funding support from Caritas Switzerland to assist the community recover from the 2011 devastating drought experienced in Kenya and the entire Horn of Africa
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Periodic washing of tanks and scooping out of sand and silt at the weir | Estructurales | Twice a year |
| 2. | Repairs of broken parts - valves, pipes, taps etc.. | Estructurales | Through the year |
Comentarios:
Rock catchment systems generally have minimal maintenance and repairs
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Si fuera posible, desglose los costos de mantenimiento de acuerdo a la siguiente tabla, especificando insumos y costos por insumo. Si usted no pudiese desglosar los costos, proporcione un estimado de los costos totales que se necesitan para el mantenimiento de la Tecnología:
1,0
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otros | Seasonal scooping of sand and silt from the weir | seasons/year | 2,0 | 100,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Broken parts and repairs | lumpsum | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 500,0 | |||||
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
1. Availability of parts, whether they can be bought locally or from far
2. Quality of parts
3. Extent of the system exposed to vandalism and/or destructive weather events
4. Early detection of broken/spoilt parts
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The are two rainy seasons annually. The long rainy season start in March to May and short rainy season begins in October and ends in December. There has been however variations in the recent years mostly seen on rainfall variability in distribution, amounts and seasonality.
Zona agroclimática
- árida
Amount of rainfall received annually coupled with high rates of evapotranspiration cannot sustain crop farming.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
The Technology applies where there is adequate gradient of a rock surface.
5.3 Suelos
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
The technology is implemented on a rock surface.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
Sí
Especifique:
The community currently benefiting from the rock catchment have reported health problems (kidney stones) due to use of salty borehole water. The water is saline.
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
The borehole which has been the main source of water is strongly saline and the community only use it when they can no longer find water from nearest (approximately 5 kilometres away) shallow wells. In addition, the borehole is run by diesel generator attracting high operations and maintenance costs. Earlier, breakdowns would necessitate water relief from NGOs and the government.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
The area is covered with arid and semi arid type of vegetation mostly characterised by acacia trees and other thorny shrubs. There is limited variety of wild animals, insects and birds. This could be due to harsh climatic conditions.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
- Semi-nómada
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- muy pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- niños
- personas de mediana edad
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comentarios:
Not applicable. The land use system is communal and without clear demarcations from one community to another. The herders constantly move from one area and region to another in search of pasture and water resources.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- comunitarios (organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Cantidad antes de MST:
600 cubic meters
Cantidad luego de MST:
3800 cubic meters
Comentarios/ especifique:
The community almost every year would need emergency water trucking. This is not so anymore.
calidad de agua potable
Cantidad antes de MST:
Borehole water was the only alternative source during dry season
Cantidad luego de MST:
Water free of salt is now available and adequate for domestic use
Comentarios/ especifique:
They no longer use the the highly saline water which has been reported to have adverse negative health effects. The harvested water is easy to treat for microbial contamination at the household level.
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
Cantidad antes de MST:
N/A
Cantidad luego de MST:
N/A
Comentarios/ especifique:
The harvested water from the rock catchment is mostly for household use.
calidad de agua para ganado
Cantidad antes de MST:
N/A
Cantidad luego de MST:
N/A
Comentarios/ especifique:
The harvested water from the rock catchment is mostly for household use.
Ingreso y costos
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
The time women used to spend in search of water has drastically reduced. They are now freer to engage and participating in social local networks and small businesses.
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Women have benefited hugely from this Technology. Before the intervention, they would walk up to 5 kilometres in search of water for domestic use. This was particularly worse during drought or an extended dry spell as they also had to queue for many hours a day to get the water from available water points.
Otros impactos socioeconómicos
Reduced conflicts over scarce water resources
Cantidad antes de MST:
N/A
Cantidad luego de MST:
N/A
Comentarios/ especifique:
The pastoralist communities have in the recent decades experienced resources-based conflicts. These conflicts happen at regional, communal and family scales. The communities and families benefiting from this intervention no longer have to fight over the resource because it is adequate.
Impactos socioculturales
situación de salud
Cantidad antes de MST:
Little water available for hygiene practices such as handwashing
Cantidad luego de MST:
Additional of 30 litres per day now available for good hygiene practices
Comentarios/ especifique:
The availability of water have drastically improved hygiene practices.
instituciones comunitarias
Cantidad antes de MST:
No properly functioning water managment committee
Cantidad luego de MST:
There is a vibrant and dedicated water management committee
Comentarios/ especifique:
The implementation of the Technology has invigorated the community members and they have shown better organisation to prudently manage the water system. The management committee was existing before the technology was implemented when they managed other water sources. However, the motivation then was low coupled with low capacity to operate and maintain the water sources they had.
mitigación de conflicto
Cantidad antes de MST:
Several occurences of conflict over water
Cantidad luego de MST:
No more reason for conflict
Comentarios/ especifique:
The pastoral communities have in the recent decades experienced resources-based conflicts. These conflicts happen at regional, communal and family scales. The communities and families benefiting from this intervention no longer have to fight over the resource because it is adequate.
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Cantidad antes de MST:
About 6 hours spent a day in search of water especially during the dry season
Cantidad luego de MST:
A maximum of 30 minutes spent by a woman to fetch water
Comentarios/ especifique:
The Technology benefits women most who traditionally are socially and economically disadvantaged. Now they have more time to engage in other profitable activities. The Technology has also taken away the burden of proving water for the households, freeing them for greater social engagement
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cosecha/ recolección de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Water that would normally be lost almost after it has rained is now stored and kept for future use.
escurrimiento superficial
Cantidad antes de MST:
All rainwater from the developed catchment was lost each time it rained.
Cantidad luego de MST:
About 3500 cubic meters of water is retained within the locality of the community
Comentarios/ especifique:
There is increased control of surface runoff reducing its damaging effects on soil, vegetation and infrstrature. However, the the scale to which this is realised is low.
nivel freático/ acuífero
Cantidad antes de MST:
N/A
Cantidad luego de MST:
N/A
Comentarios/ especifique:
The rock catchment do not in any way lead to increased groundwater recharge.
Suelo
pérdida de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
N/A
Cantidad luego de MST:
N/A
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to reduced amount of water flowing from the hillside downstream, the ability of water to erode soil downstream is reduced though at very low scale.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de sequías
Cantidad antes de MST:
Water emergency supply at least two a year during the two dry spells.
Cantidad luego de MST:
No single water trucking done in the last two years
Comentarios/ especifique:
Water has been the most affected livelihood commodity during drought events among the benefiting community. The impact had been acute water shortage leading to external emergency interventions. It was also happened that sometimes when food aid was provided, the community would have no water to cook. There is no longer need for water emergency in these communities.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
Comentarios/ especifique:
The high velocity water from the hills have been a constant menace in cutting or blocking roads downstream with debris. The harvesting of water has reduced the impact of this water at some sections of the hilly landscape.
Comentarios acerca de la evaluación del impacto:
Some aspects of information are difficult to establish and could be best evaluated by a household survey.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura estacional | estación seca | incrementó | muy bien |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | moderadamente | |
| lluvia estacional | estación seca | incrementó | muy bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | muy bien |
| tormenta local | muy bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | muy bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
The benefits are instantaneous as soon as the structure is completed and especially if it is during a rainy season. The technology has minimum to near zero maintenance costs which remains relatively the same in the long term. The main tasks for maintenance is seasonal removal of silt at the weir and the washing of the tanks.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- más de 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
This is a one Technology which is benefiting the entire community. At the time of project implementation the estimated total population was 1000 people.
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 90-100%
Comentarios:
N/A
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
1. Relatively low cost of operation and maintenance. 2. The technology does not require specialised technical skills for the day to day operations |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| 1. Relatively high initial investment cost that is unlikely to be raised by communities themselves. Without external financial support it is therefore unlikely that the system can be expanded when water needs increase. |
1. A long term plan that includes savings from fees from water sales. 2. Funds could also potentially be acquired from the county government or NGOs |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
A field visit was done by the data compiler to meet with the land users
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
One meeting (Focused group discussion) was done with the beneficiaries of the Technology
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Filling in some sections for the questionnaire required input from technical/specialist personnel who implemented the project. These are technical staff of Caritas Switzerland.
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
reference was made on technical documents of the project - proposals, technical reports (narrative, photos, videos).
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
A Handbook of gravity-flow water systems for small communities; Thomas D. Jordan Junior; 1980; 978 0 94668 850 0
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
CACH office library, Nairobi
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Rock Catchments for Community Water Supply in Eastern Equatoria State, South Sudan
URL:
http://waterconsortium.ch/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Poster_Rock_Catchments_Caritas_South_Sudan_2016.pdf
Título/ descripción:
Adopting locally appropriate WASH solutions: a case study of rock catchment systems in South Sudan
URL:
http://wedc.lboro.ac.uk/resources/conference/37/Leclert-1935.pdf
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos