Multistorey agroforestry [Etiopía]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: GERBA LETA
- Editores: Julia Doldt, Noel Templer, Kidist Yilma
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Mitikarsamino Ersha
technologies_6621 - Etiopía
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
Gabiba Afra
A farmer
Etiopía
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Kenia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
Agroforestry is the best technology/practice to sustainably manage the land. It has multiple economic, environmental and social benefits.
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Multistorey agroforestry is the intentional mixing of trees/shrubs with crops, pastures, and livestock. The practice creates environmental, economic, and social benefits for the end users.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
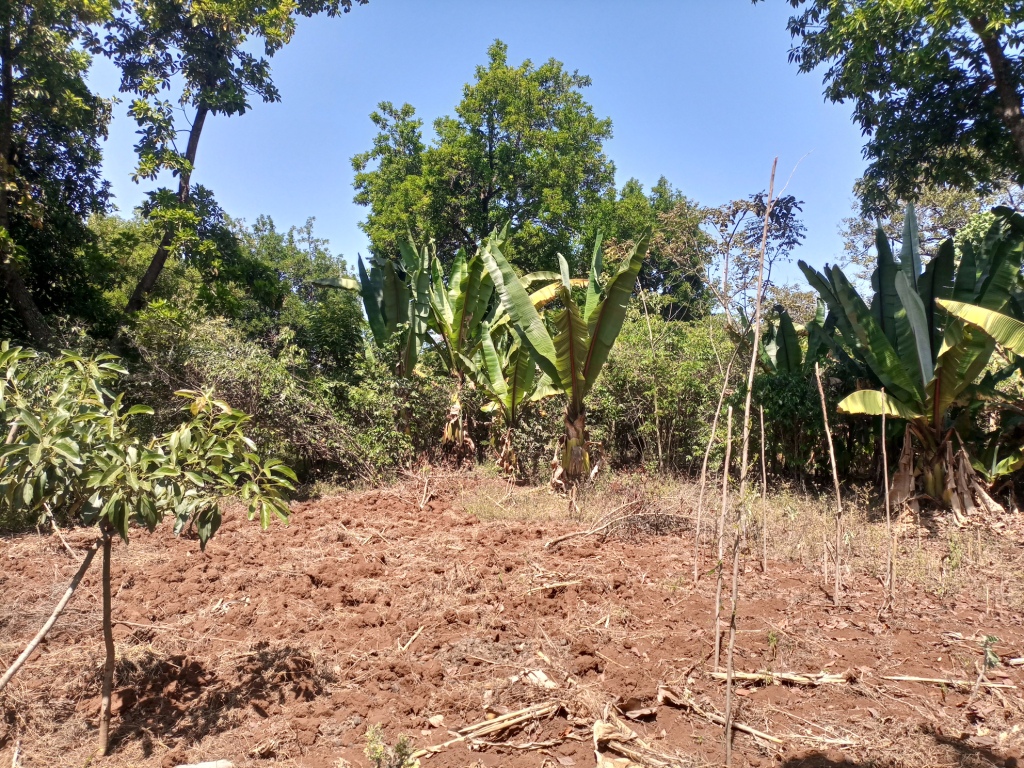
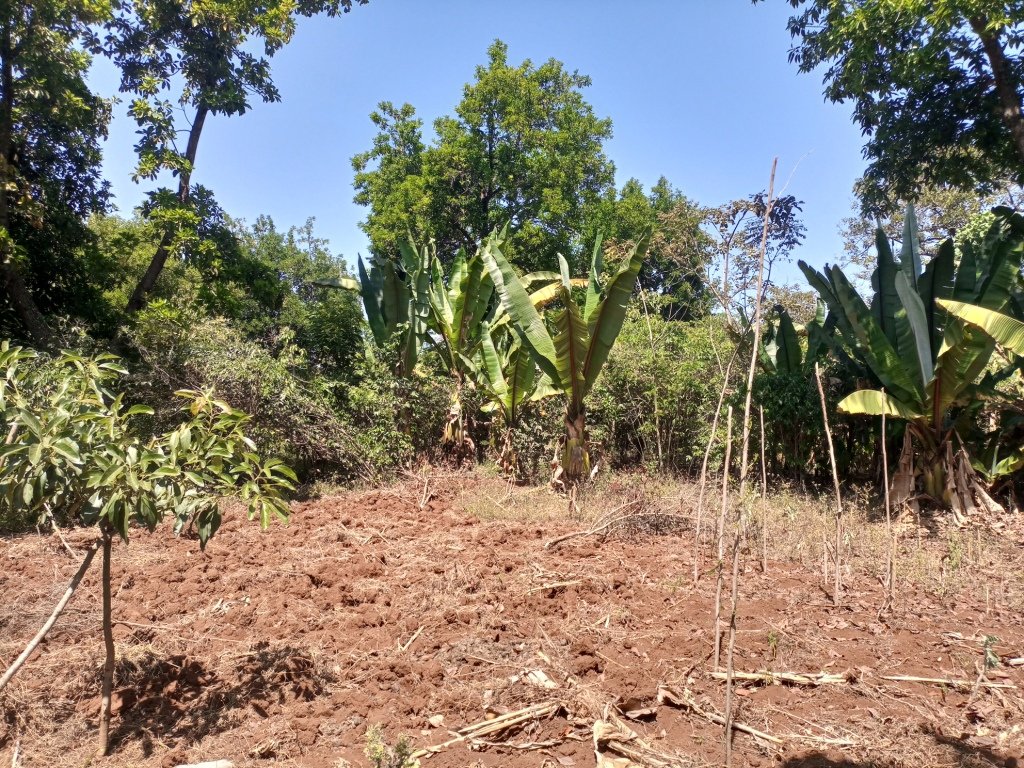
Multistorey agroforestry is the intentional mixing of trees/shrubs with crops and pasture at different levels ("storeys" or heights) and the livestock. The practice creates environmental, economic, and social benefits for the end users. Agroforestry practices provide opportunities to integrate productivity and profitability with environmental stewardship resulting in healthy and sustainable agricultural systems that can be passed on to future generations. Tree litter increases soil organic matter and reduces soil chemical and biological degradation. Tree cover can reduce soil erosion and evaporation from the soil surface. The technology is applied close to the homestead as it demands close follow-up and steady management practices, and that is where tree-crop-livestock integration can be best applied. The farmer whose practice is described here used to be very poor four decades ago. He has planted coffee gradually over the years under shade trees. As a staple perennial food crop, enset was planted also in the mixture. Livestock were also integrated. Eventually, numerous multipurpose tree species, food and fodder crops, and physical structures with productive barriers were integrated into the farming system. As a consequence, a multistorey agroforestry system has been established over years.
The purpose of the technology is to ensure ecological, economic, and social benefits. The rolling landscape of the area necessitates permanent ground cover to reduce the effect of erosive rainfall that degrades the soil. Once established, the technology needs management practices including pruning/stumping of coffee trees, managing other trees, weed control, enrichment planting with coffee and enset, and fertilization of annual and perennial crops. The livelihood of the respondent farmer has been completely changed. He has made a significant accumulation of wealth from producing and sale of tons of unprocessed coffee, avocado fruits and some indigenous bananas. This form of agroforestry creates year-round employment opportunities for proactive farmers. However, subsistence farmers with small parcels give priority entirely to the mono-cropping of cereals and other fast-maturing crops to meet their urgent demand for food. Shortage of land, capital, and a general lack of awareness about the sustainable benefits of the technology are reasons for lack of adoption of the technology.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
The farmer has integrated several crops and tree species. Over years, he noted some tree species are not the best fit for the multi-storey system. He tends to remove some of them. The high-yielding avocado fruit per se was found as an inappropriate mix for the agroforestry system as it has a complete shading effect over the undergrowth. Several other tree species such as Podocarpus species, Olea, Euphorbia, Misana (Croton macrostachyus), Doqima (Syzygium guineense), Tiqur enchet (Pygeum africanum), Pulm tree (Phonex species), Birbira (Millettia ferruginea), Wanza (Cordia africana), Sesa (Albizia species), Sesbania species, Girawa (Vernonia amygdlina) and some fodder grass species such as Napier and Guatemala grass…are all part of the system but the farmer’s choices are the latter five to seven species. Despite his views of the characteristic feature of the different trees in relation to the undergrowth such as coffee, enset, beans, pumpkins and so on, they have immense ecological benefits as well as supply food, bee forages and construction materials.
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Comentarios, descripción breve:
The video of this technology is not documented.
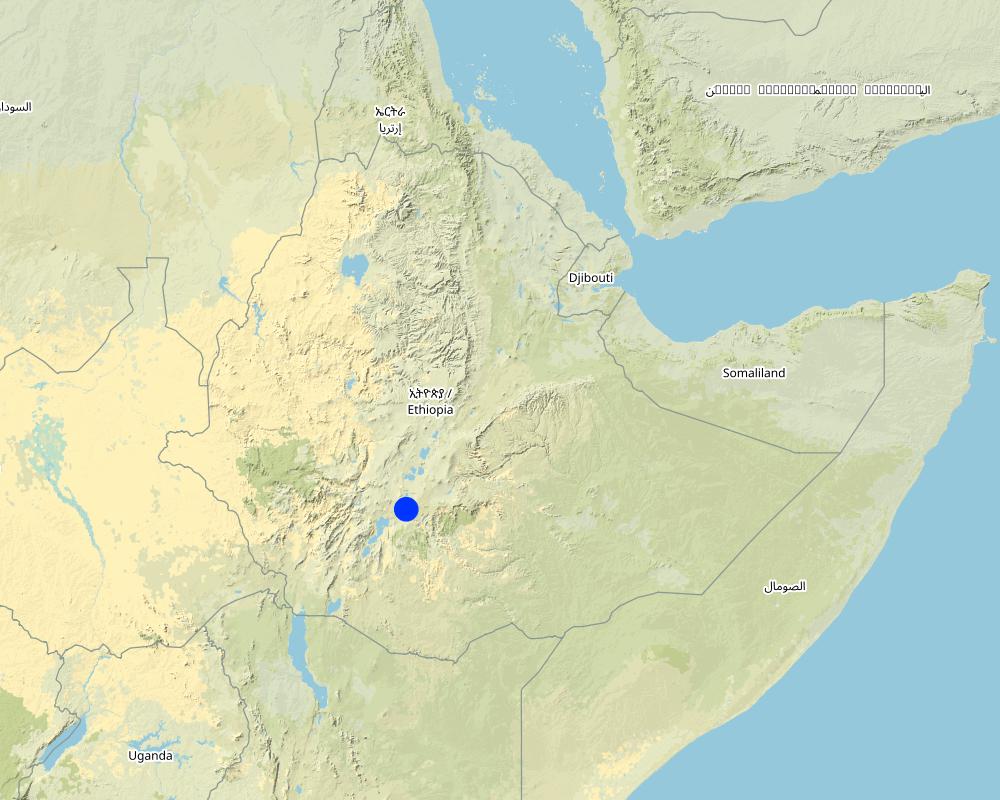
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Etiopía
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Sidama
Especifique más el lugar :
Shoye kebele (Kebele - lower administrative level)
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
It is located on farm around the resident area or in homegarden.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
1980
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
- durante experimentos/ investigación
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The farmer started to implement the technology by himself but gradually managed to access support and inputs such as coffee and tree seedling, training, and visits from the agriculture and coffee development office through the extension workers. Farm visit and mentoring services from the district experts were also commendable to inspire the farmer. The visit to the farm by researchers, local development and other actors add knowledge and motivation to the farmer.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agroforestería

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- Legumes - Haricot beans and other climbing species, Pumpkin and root crops/tuber potato and yam.
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- banana/plátano/abacá
- cultivos para forraje - pastos
- herbs, chili, capsicum
- Enset/false banana
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- avocado
- café, cultivado en sombra
- mango, mangostán, guayaba
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Belg, short rain (March to April) and Meher, long rain (June to September).
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
Sí
Si respondió que sí, especifique qué cultivos son intercultivados:
Haricot beans intercropped within maize and under coffee. Actually, maize grow in the buffer zone of the agroforestry farm.
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Cereal maize farm rotate to legume such as haricot beans.
Comentarios:
Adjacent small plots of land are used to grow maize to complement Enset/false banana - a staple crop for the household. Also, beans and vegetables such as local kale are integrated into the farming system.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agroforestería

Tierra de pastoreo
- Open/free grazing
Tipo de animal:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- cabras
- mulas y asnos
- aves de corral
¿Se practica el manejo integrado de cultivos - ganado?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
In an integrated crop-livestock system, crops and livestock interact to create a synergy, with recycling allowing the maximum use of available resources. Crop residues can be used for animal feed, while livestock and livestock by-product production and processing can enhance agricultural productivity by intensifying the use of nutrients that improve soil fertility and reduce the use of chemical fertilizers. Apparently, crop residues are a valuable, low-cost feed resource for animal production, and are consequently the major source of nutrients for livestock.
Productos y servicios:
- manure as fertilizer/ energy production
Especies:
ganado - lechero
Conteo:
10
Especies:
cabras
Conteo:
4
Especies:
aves de corral
Conteo:
3
Especies:
mulas y asnos
Conteo:
1
Comentarios:
Four decades back or before the conversion of the land into the agroforestry, it was partly wetland and the grazing land used by free roaming animals.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Agriculture is entirely rainfed that rely on bimodal rainfall intercepted twice a year.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- agroforestería
- manejo de agricultura—ganadería integrada
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas estructurales
- S2: Taludes, bancos

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
Comentarios:
Diverse SLM practices are integrated over the farmland.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
- Wm: movimiento de masas / deslizamientos de tierra

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)
- Ca: acidificación

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación
- Pw: encharcamiento
- Ps: hundimiento de suelos orgánicos, asentamiento del suelo

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bh: pérdida de hábitats
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores
Comentarios:
The bare land that was subjected to soil erosion is arrested and reversed. Frequent cultivation, a threat to degradation has been entirely changed. Diverse types of degradation to the farmland have been mitigated.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Agroforestry practice helps to conserve soil and water as a barrier and via covering the ground. Tree species also serve as wind break to reduce wind velocity and wind erosion. Integrating tree species with grasses/forage not only reduces soil and water loss but also supply feed to the livestock. It also maintain soil organic matter and improve physical properties, fix nitrogen and promote efficient nutrient cycling. Furthermore, the twigs and leaves serve as mulch, green manure, etc. Integration of diverse trees/shrubs also break the impermeable layer and facilitate nutrient cycling from deep layer in certain soils, and reduce the development of soil acidity.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
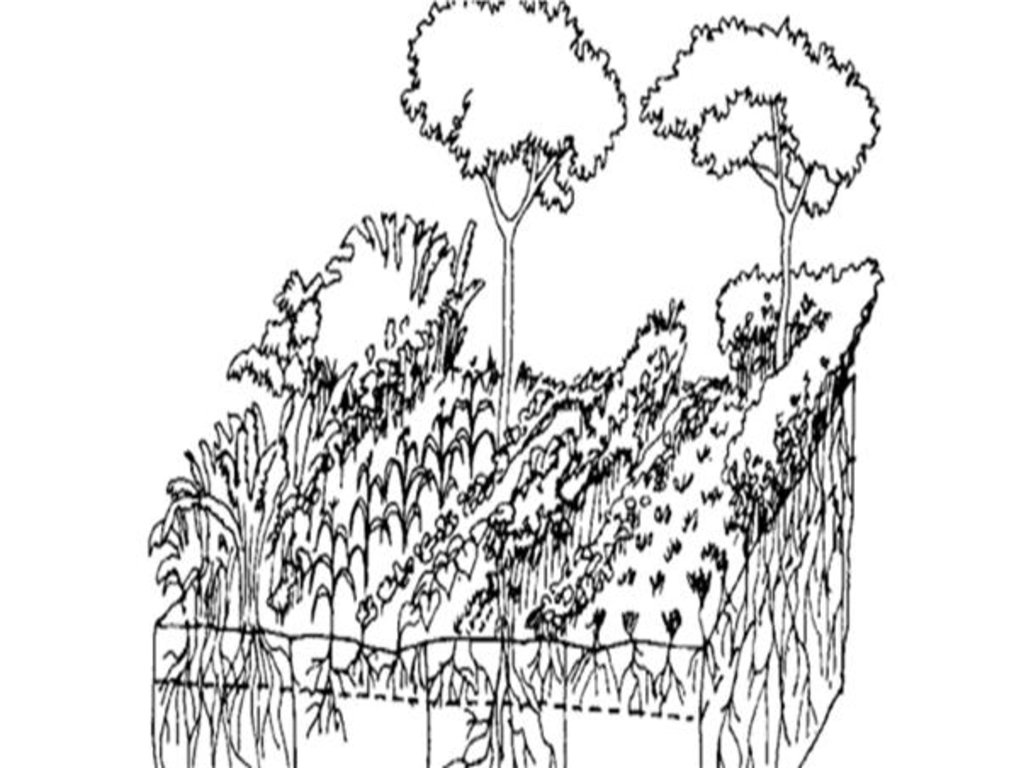
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
An adopted technical drawing/specification of the classification of tree-crop arrangement in the multistorey agroforestry system.
Autor:
Xu J, Mercado A, He J., Dawson I (eds.) (2013); ISBN 978-92-9059-333-1
Fecha:
20/01/2023
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
4Timad
Si usa una unidad de área local, indique el factor de conversión a una hectárea (ej. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
4 Timad = 1 ha
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Ethiopian Birr
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
53,12
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
In rural area wage rate vary by type of work: coffee harvest-80 ETB/day, weeding 60 ETB/day. About 70 birr/day, on average.
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | Before and during Belg (short rain) and Meher (long rain) season. |
| 2. | Enset and Coffee planting | In Belg and Meher season, respectively. |
| 3. | Planting beans (annual crops) | In Belg season |
| 4. | Fodder and other Multipurpose trees planting | In Meher (main rainy season). |
Comentarios:
Farmer start small and keep on enriching and managing the farm with inputs and technology components. This is for a single year but two seasons with short and long rain. Actually, perennial crops such as coffee and enset are not planted every year.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Land preparation | Oxen plow | 16,0 | 200,0 | 3200,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Planting annual crops | Oxen plow | 4,0 | 200,0 | 800,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Planting perennial crops | PDs | 20,0 | 70,0 | 1400,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Planting fodder crops and trees | PDs | 5,0 | 70,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Spade | Number | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Hoe | Number | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Digging fork | Number | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Coffee seedling | number | 2500,0 | 10,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Enset seedling | number | 6000,0 | 5,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Tree seedling | number | 1500,0 | 2,0 | 3000,0 | 50,0 |
| Material para plantas | Beans seed | kg | 50,0 | 42,0 | 2100,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | NSP fertilizer | kg | 100,0 | 44,0 | 4400,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Urea fertilizer | kg | 50,0 | 44,0 | 2200,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 73950,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 1392,13 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
In the past, coffee seedling was freely supplied to the farmer by the Ministry of Agriculture. The trend has changed recently. Apart from some tree seedlings that are freely supplied through government nurseries, virtually all costs for the establishment of Agroforestry are covered by the farmer themselves.
Comentarios:
Commodity price in Ethiopia is frequently changing because of inflation and economic crisis. Therefore, it is impossible to confidently estimate the price of inputs, farm tools, and labor costs.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Inputs | Before the onset of short/long rain. |
| 2. | Management | Throughout the year depending on the management types. |
| 3. | Farm tools | During off-season. |
Comentarios:
A farmer estimate maintenance costs of about 40,000 ETB per hectare of land. However, my calculation in the following section reduces it a bit lower by excluding the cost of plant protection, and by boosting the contribution of family labor in the household. Apart for the general calculation, as the average land holding in Sidama region is less than 0.25 ha, a farmer may not go for adopting the technology on 1 ha.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Enrichment/replacement planting | PDs | 5,0 | 70,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Fertilization | PDs | 40,0 | 70,0 | 2800,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Weeding | PDs | 40,0 | 70,0 | 2800,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Hoes | number | 4,0 | 600,0 | 2400,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Digging fork | number | 4,0 | 500,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Spade | number | 4,0 | 400,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Coffee seedling for replacement | number | 250,0 | 10,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | NSP | kg | 100,0 | 44,0 | 4400,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Urea | kg | 50,0 | 44,0 | 2200,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 21050,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 396,27 | |||||
Comentarios:
Frequently changing prices of inputs, labor, and farm tools disable someone to give an estimate for the establishment and maintenance costs in the future. Essentially, maintenance cost demands lower investment than the establishment cost. Unlike in the past years, agroforestry doesn't start from scratch but can be built up on the existing initiative. Therefore, it would be rather an intensification of agroforestry than just establishing.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Economic crisis and the prevailing inflation in the country, and global changes in price of petroleum and other commodities such as chemical fertilizers.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The area receive adequate rainfall.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Awassa Meteorology center
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
The climate is virtually consistent except during the season of El Nino and cyclical shortage that happens once in years.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
The topography feature is changing from moderate to bit slopy. However, the steepness of the farmland is not more than 15%.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Not available.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Surface water is available year-round with fluctuation of the volume with the season. Besides, pollution is high during the rainy season because of soil erosion from the upstream.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
The applied technology/practices comprise diverse species of tree crops. It can be characterized as a practice highly rich in agrobiodiversity.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- muy rico
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- ancianos
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
He is also engaged in fuel wood business. Of course, the business does not focus on indigenous tree species but the most commonly marketable trees for construction and fuel wood in Ethiopia i.e. eucalyptus species.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
Comentarios:
He possesses 4.5 hectares of land. However, it is much higher than the regional average, and could be still less than a few farmers.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
No
Especifique:
Land use right is issued by the state. Of course, the land is inherited in the parent line. He also accessed more parcel during land redistribution of the Derg regime. As a rule, the land belongs to the state but the user has usufructs.
Comentarios:
Farmers are certified based on the usufructs right issued by the government via the land administration policy enshrined in the country's constitution.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Comentarios:
Tap water is accessible some distance away. The deep well the farmer has is not clean for drinking by the household but for cattle and cleaning goods and clothes.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
It is difficult to guess the increment by weight of perennial crops such as Enset. Of course, the performance is much better in the agroforestry system with intensive management and application of organic fertilizers. The integration also ameliorates the microclimate of the area and makes the situation ideal for the crops.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
In the agroforestry system, a combination of livestock manure, tree litter, and a mixed cropping system contributes to soil fertility and soil health which improves crop quality.
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased with improved soil fertility and soil healthy.
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Livestock access to feed during the dry spell when communal grazing land is denuded of grass. Furthermore, agroforestry promotes a cut-and-carry feeding system that strengthens reliance on one's feed reserves at disposal. This goes with the intensification of livestock production.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
The practices rather improve the resilience of the crop as it creates an ambient environment.
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
The integration increase product diversity.
área de producción
manejo de tierras
generación de energía
Comentarios/ especifique:
Cattle manure is used for the production of heat and light energy through the application of biogas technology.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
Comentarios/ especifique:
Agroforestry's contribution to drinking water availability and water quality was not measured and was beyond the scope of respondents to comprehend and address the questions except the merely conceptual reflection. Of course, the technology reduces runoff and recharges the ground water which directly contributes to the availability of surface water for livestock.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Fertilizer supply changed more to organic than chemical fertilizer. The foliage of tree litter and in situ decomposition of organic matter added substantial value to the restoration of soil fertility.
ingreso agrario
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased management demand with gradual increase of the integration of tree crops and the overall size of the land is remarked by the farmer.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Land users generate reasonable income from the integration of different perennial and annual crops as well as livestock.
situación de salud
derechos de uso de la tierra/ agua
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
The technology immensely contributed to SLM by covering the farmland with perennial trees and crops and by incorporating the physical structure into the practice.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
drenaje de agua en exceso
nivel freático/ acuífero
Comentarios/ especifique:
The groundwater table is estimated to increase as the ground cover promotes the infiltration and vertical movement of the intercepted rain on a gradual basis.
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
As some tree species such as avocados consume large amounts of water for transpiration needs, the degree of evaporation reduction of the practices is counterbalanced by the integration of the high-consumers with low-consumer species. Overall, agroforestry has a positive impact on evaporation reduction.
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
acumulación de suelo
compactación de suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Comentarios/ especifique:
Nutrient cycling is highly improved because different tree species may penetrate the impervious soil layer and bring the nutrient to the surface via tree litter, fix atmospheric nitrogen, and add to the soil.
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Highly increase, though not measured for this particular farm.
acidez
Comentarios/ especifique:
The cause of soil acidity can be diverse including the soil parent materials. However, agroforestry has positive acidity-reducing factors by improving soil fertility and soil health.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Highly increased because of the combination of trees/shrubs with food crops and fodder crops.
especies invasoras extrañas
diversidad animal
especies benéficas
diversidad de hábitats
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
Agroforestry hosts the predators and prey and creates balanced food chains that reduce the degrees of pest development.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de sequías
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
It is a climate-smart agriculture by its virtue that increase carbon sequestration as a regenerative agriculture.
velocidad de viento
micro-clima
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
The practices ameliorate the prevailing adverse climatic conditions and land degradation.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
inundaciones río abajo
colmatación río abajo
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
Comentarios/ especifique:
Even if the impact of agroforestry plays a positive reduction role in pollution, the overall impact is compromised by the total farmland covered by a combination of tree crops.
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios/ especifique:
Agroforestry has a filtering capacity of polluted air with dust and adverse temperature such as during dry and hot days.
sedimentos transportados por el viento
Comentarios/ especifique:
Intercepted by leaves of trees and shrubs.
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
impacto de gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
It highly contributes to carbon absorption and storage above and below the ground.
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
Agroforestry has beneficial ecological and economic functions.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | muy bien | |
| temperatura estacional | estación seca | incrementó | muy bien |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | bien | |
| lluvia estacional | estación húmeda/ de lluvias | disminuyó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | moderadamente |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 11-50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
About 30% of resident farmers have adopted the technology. The prevailing farming system necessitate change in the approach, and outshined farmers motivated the others to follow suit.
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 11-50%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
Si fuera así, indique a qué condiciones cambiantes se adaptó:
- mercados cambiantes
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
Raising coffee prices motivated farmers to refocus on the crop which years back discouraged to shift of the coffee farm to eucalyptus plantation.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Increase production per unit of land and improve livelihoods of family farmers. |
| Reduce land/soil degradation because of permanent soil cover. |
| Ensure sustainable production, reduce risks and improve the biodiversity. Also, increase the family farmers income and their status in the society. It enables them to feel as valuable elite in the community. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Agroforestry improves total production earned from a farmland and improve the wellbeing of the adopted farmers. Implies, it has substantial economic benefits. |
| It reduces soil erosion and land degradation. Also has immense ecological benefits and improves the microclimate of the surrounding. |
| It reduces risks of crop failure owing to climate variability. Also, boost the biodiversity of trees, crops, and habitat diversity that host various living creature in the biosphere as well pedosphere. This is related to carbon sequestration, emission reduction, proper ecosystem function, and overall ecological contribution. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Demand intensive management, and there is shortage of labor. | Identify and established trees and crops that requires minimum labor for planting, maintenance & propagation. |
| Incompatible tree species to the essence of proper integration in Agroforestry. | Select and adopt trees and crops with desirable characteristics to be integrated in the technology and responsive to management practices. |
| Inconsistent product prices for the farm products such as coffee beans and avocado fruits on the local market. | Link farmers to free and fair market which is consistent and sustainable. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Failure to select tree species with desirable characteristics |
Trees/shrubs with the following desirable characteristics need to be considered: - Deep root system to draw water & nutrients. - Easy to propagate, & high biomass producers, palatable, provide more green manure, & high survival percentage. - Adaptable to close spacing like in hedgerows. - Good sprouting & positive response to pruning. - High coppicing and pollarding capacity. |
| Highly dense in some areas and slightly sparse in some part of the farm. | Try to maintain the spacing and distribution of suitable species composition. |
| Trees and shrubs less used as livestock feed except during the shortage period | Promote feeding the diverse fodder trees to the livestock to ensure their access and benefited from trees/shrubs as well than rely only on grass family. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
An intensified agroforestry system visited.
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Only one farmer interviewed.
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Land users, regional bureau of agriculture natural resource management expert and GIZ regional advisor consulted.
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
13/01/2023
Comentarios:
Extensive field visits and interviews were conducted with Land users, Regional NRM expert, and ISFM + regional advisor.
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
World Agroforestry Centre. 2008. Annual Report 2007-2008: Agroforestry for food security and healthy ecosystems. Nairobi, Kenya: World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF). ISSN 1995-6851
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
www.worldagroforestry.org
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Agroforestry System for Ecological Restoration: How to reconcile conservation and production options for Brazil's Cerrado and Caatinga Biomes. Miccolis, Peneiveirok Marques et al. 2016. ISBN: 978-85-63288-18-9
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
http://apps.worldagroforestry.org/downloads/Publications/PDFS/B19034.pdf
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Indigenous Agroforestry Practices and their Implications on Sustainable Land Use and Natural Resources Management: The Case of Wonago Woreda. Sustainable Land Use Forum (SURF), 2006. Research Report No 1, Addis Ababa
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
www. devinet.org/sluf
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
The Center for Subtropical Agroforestry (CSTAF)
URL:
http://www. cstaf.ifas.ufl.edu/
Título/ descripción:
World Agroforestry (ICRAF)
URL:
https://www.worldagroforestry.org; https://www.cgiar.org/research/center/world-agroforestry-centre/
7.4 Comentarios generales
The questionnaire is comprehensive and give the opportunity to add additional techniques/approaches via the "other" options. However, it is demanding as it requires for videography and sketching skills for every technology.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos