Water Spreading Weirs [Etiopía]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: GERBA LETA
- Editores: Torben Helbig, Noel Templer
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Biye Baahiwe
technologies_6715 - Etiopía
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Mohamed Badal
Natural Resource Development Protection and Utilization Department of Somali Region Bureau of Agriculture.
Etiopía
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Kenia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
It is soil and water conservation and degraded land rehabilitation technology. Furthermore, the water harvested can be used for spate irrigation and growing food crops and livestock feed.
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Water Spreading Weirs are designed to protect the degradation of agricultural fields and rangelands. They contribute to soil and water conservation and enhance the productive use of dry valleys for food crops and livestock fodder production via the harvest and spread of runoff water and fertile soils.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
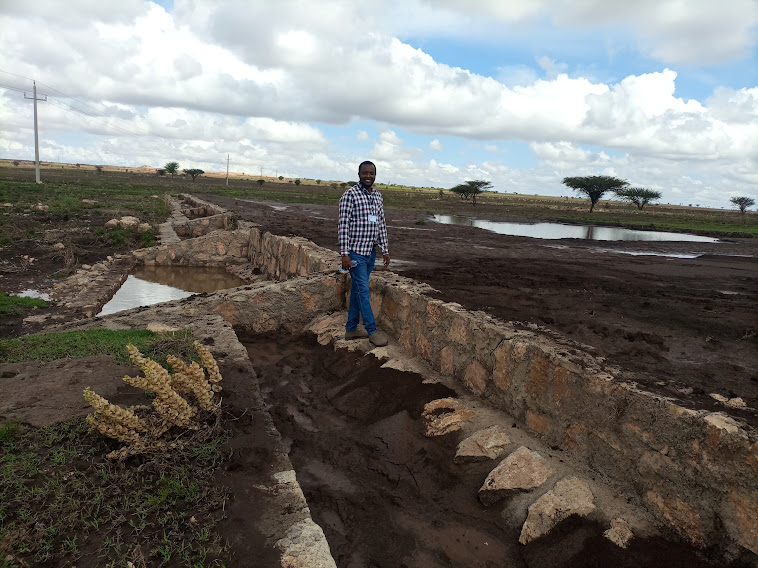
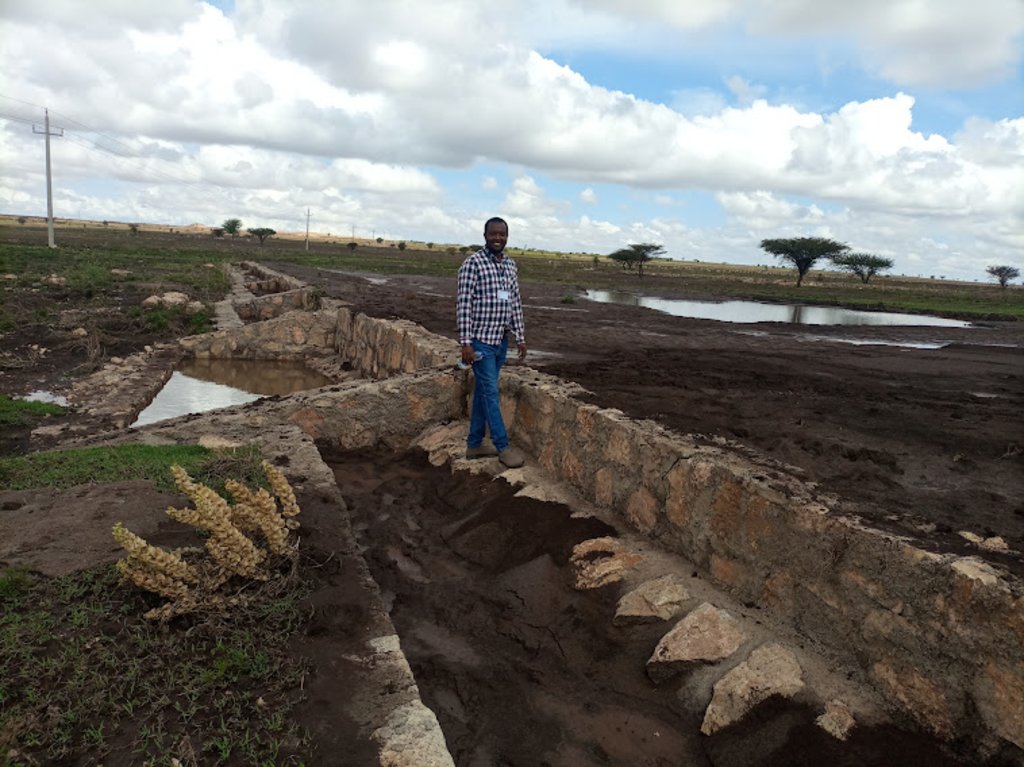
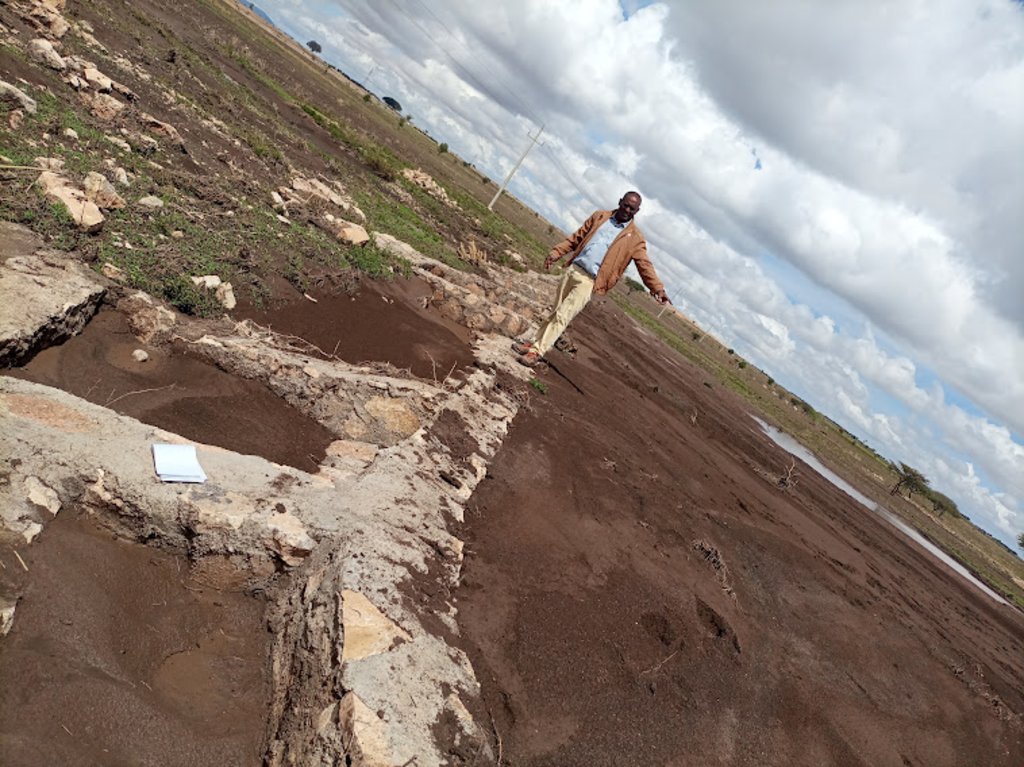
Water Spreading Weirs (WSWs) spread runoff water to the tips of the structure's wings, slowing down the speed of runoff and arresting the sediment pouring downstream. WSWs are applicable both on farmland and rangelands to improve the productive use of the land’s resources. They protect soil erosion and control gully development as well as increasing surface and sub-surface water availability. Activities such as mobilization of the community through awareness creation are among the numerous tasks implemented to put the technology in place. The community participates in site selection and participatory planning. Other stakeholders assist in area delineation, profiling the implementation area, and design. Labour and inputs such as surveying and construction materials, notably stone, sand, water, and cement, and equipment such as line levels, theodolites, spades, hoes, forks, string and measuring tapes etc. are required. On top of these, implementing the technology is supported by satellite images and ground validation exercises.
The main purpose of the technology is to reduce land degradation, harvest and use runoff water for spate irrigation and household uses, improve environmental resilience to the risks of drought, increase the depth and fertility of land behind the structure by capturing sediment washed away, allow infiltration of water and increase overall production of food and fodder crops. Also, the contribution to groundwater recharge is immense. Furthermore, it allows the agropastoral community to grow both cash and food crops which helps to ensure food security. Above all, the water harvested means people can remain in the area and that their livestock have access to drinking water for about three months after interception of rainfall. However, the agropastoralists may be discouraged by the size of the WSWs which can be from one hundred to over two hundred meters across. Care also must be taken that the structures do not cross livestock migration routes.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
The photo is trying to portray the water and soil harvested/stopped from running downstream. The detachment and removal of the topsoil without cover and fragile soil types are easily removed and transported to a long distance beyond the regional territory. The trends denied the productive use of land resources. In contradiction, the structure mitigates the loss of water and soil.
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Comentarios, descripción breve:
Video for this technology was not captured.
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Etiopía
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Somali
Especifique más el lugar :
Amadle kebele, South Jijiga district
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
It is located on the farmland used by the extended family and beyond.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2022
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology was put in place in partnership with the government bureau of agriculture and line office with the Capacity Development and Strengthening Drought Resilience (CDSDR) Project of the GIZ in the Somali Region.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agropastoralismo (incluyendo cultivo-ganado integrados)

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- cereales - sorgo
- leguminosas y legumbres - soya
- vegetales - otros
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
The legume crop is chickpea. Whereas, the vegetables are tomato and onion.
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
Sí
Si respondió que sí, especifique qué cultivos son intercultivados:
Maize is intercropped with chickpeas.
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Cereal crop sorghum rotates with maize and chickpeas. Essentially, crop production suffers from a lack of adequate rainfall. For example, during the last two to three years the area experienced drought. Mainly livestock supports the livelihoods of the inhabitants.

Tierra de pastoreo
- Agro-pastoralist
Tipo de animal:
- camellos
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- cabras
- ovejas
¿Se practica el manejo integrado de cultivos - ganado?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Essentially, the farming operation is practiced by oxen-plow in which case the animals provide traction force whereas crop residue supply feed to the animals.
Productos y servicios:
- manure as fertilizer/ energy production
- carne
- leche
- transporte/ de tiro
Comentarios:
Agro-pastoralism is the common practices in Amadle kebele of south Jijiga district.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- No (Continúe con la pregunta 3.4)
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
The rainfall distribution is erratic with violent erosive feature flooding the plain with severe damage when flowing downstream.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo de agricultura—ganadería integrada
- medida de pendiente transversal
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S6: Muros, barreras, vallas, cercas
Comentarios:
The technology is Water Spreading Weirs, stop the run-off and distribute the water across the farmland.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
- Wm: movimiento de masas / deslizamientos de tierra

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable
- Ed; deflación y deposición
- Eo; efectos de degradación fuera del sitio:

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pi: sellado de suelo

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hg: cambio en nivel de aguas subterráneas/ nivel de acuífero
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de subterráneas
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de aguas subterráneas
Comentarios:
The technology/structure contributes strongly to soil and water management. The tremendous loss of both resources is immensely reduced by the application of water spreading weirs.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
The technology reduces the speed of runoff, stores the sediments, and distributes the water across the structure which creates an opportunity for spate irrigation and the use of residual moisture as supplemental sources of irrigation for growing early maturing crops.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
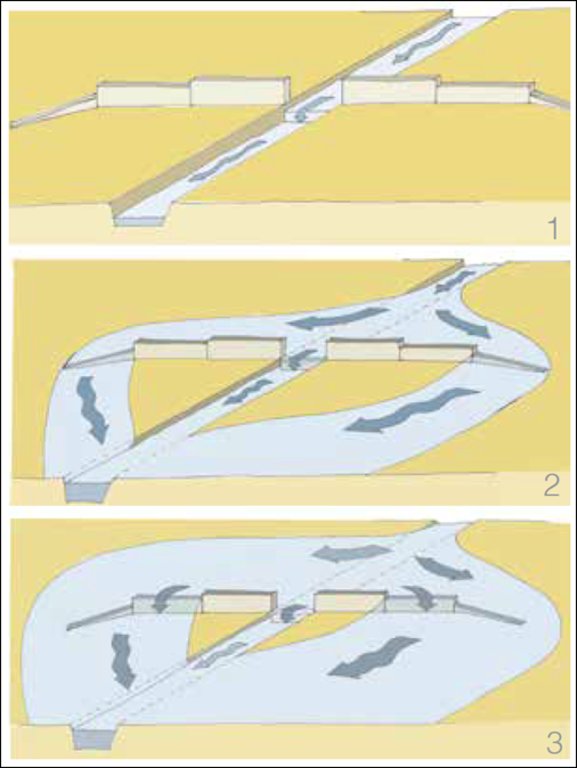
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Spate schemes depending on the increase supply flow:
Part i: The flow of small flood rested channel in the river bed
Part ii: A small or medium flood and overflows pours on the lower wings, &
Part iii: A large flood also pours on high wings.
Autor:
Anonymous consultant
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
1 WSW
Especifique las dimensiones de la unidad (si fuera relevante):
Variable ( could be from 100m to over 200m depending on the steepness and width of the farmland.
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
8.414 USD
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Assessing the field (observation) | |
| 2. | Consult the local community along with agricultural partners at different levels | |
| 3. | Surveying and profile data collection | |
| 4. | Develop design and get approval | |
| 5. | Outsource the engineering/masonry works | |
| 6. | Train the masonry workers | |
| 7. | Supply materials | |
| 8. | Implement (execute the excavation and the masonry work) | |
| 9. | Monitor the development (construction supervision) |
Comentarios:
Note: 1 USD = 53.481 Ethiopian birr (ETB) when this data is collected.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
Si no puede desglosar los costos especificados en la tabla anterior, proporcione un estimado de los cálculos totales en los que se incurrió para establecer la Tecnología:
27490,0
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
So far, the project entirely cover the investment and maintenance costs.
Comentarios:
According to the project and regional bureau of agriculture experts, a single structure costs 27, 490 USD. However, in one cascade (dry valley treatment unit) about 8-10 structures are necessary to successfully address the objective of the technology (Soil and Water Management) and ensure productive use of the land from soil arrest and residue of moisture captured in the area. It also enables the use of runoff for spate irrigation.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Assess and identify the damage | During the off-season for ease of access to the sites |
| 2. | Estimate the level and cost of damage | During the off-season |
| 3. | Supply materials | |
| 4. | Employ the masonry worker | |
| 5. | Construct /maintain the damaged parts | Before the short/long rainy season. |
Comentarios:
Maintenance costs are largely associated with the degree of damage and cost of materials and masonry worker or labor costs that consistently changing in current Ethiopia.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Si no puede desglosar los costos especificados en la tabla anterior, proporcione un estimado de los cálculos totales en los que se incurrió para mantener la Tecnología:
12154,0
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The cost is borne by the project.
Comentarios:
The technical experts give only an estimate of both initial investment and maintenance costs. Variations in materials and labor costs are frequent beyond the imagination. However, maintenance depends on the degree of damage. It seems that maintenance cost estimation takes the highest sides which may dishearten the adoption of the technology in the absence of projects.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Economic crisis and frequently escalating material costs along with rising financial inflation.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
750,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Rainfall is erratic and erosive. The project site receives rainfall twice a year (Belg- short rain from March to April and Meher- long rain from June to September). However, the number of days on which rain is intercepted is fewer than the ranges stated over here.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Jijiga Meteorology station
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
South Jigjiga district is characterized by hot weather.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones cóncavas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
The topography where WSW technology/structures are put in place is mostly on gentle slopes across the dry valley drainage line.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
The soil ranges from black silty loam to brown silty and fragile soils that are highly vulnerable to flood. It easily detached and moved away with runoff.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
Sí
Especifique:
As the weather of the area is often too hot salinity is not uncommon in the aquifer.
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Rainfall is characterized by erratic and erosive nature. Therefore, flooding is common when heavy rain is intercepted.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Less biodiversity of plant species. Acacias are the common trees, and opuntia and euphorbia species are also common plants in the area. A wild species that may be considered invasive is common in the area. The lower growing weed (wild species) locally known as Weylowed is suggested introduced from Yemen to the Somali part with onion.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Semi-nómada
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
It is the community who are benefiting from the technology. Furthermore, this respondent is a regional SLM specialist. Therefore, specific information on age and gender is not given here though the community was also consulted.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Extended family groups of four households are using the land where the WSW is put in place.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
Land use right is based on clan and extended family.
Comentarios:
The land is also owned by individuals. However, there is no land measurement and certification in this region.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
It is the expert's conviction that crop production in the area increased with water harvest and spread over the farm for use as spate or supplementary irrigation to the seasonal rainfall.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the moisture harvested by the structure is believed to add grain filling period, the crop quality is also expected to increase.
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Fodder production also increases with the availability of good soil and moisture conserved in the farm behind the structure.
calidad de forraje
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increases with increasing availability of feed or fodder from either crop residue, natural grass or browse.
producción de madera
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
It rather improves crop resilience because of improved soil moisture.
diversidad de producto
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Opportunities can be created to increase the size of land under farming with increasing availability of moisture and fertile soils.
manejo de tierras
Comentarios/ especifique:
Moisture availability eases the management operation.
generación de energía
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
calidad de agua potable
Comentarios/ especifique:
Basically, quality is not a priority issue for agro pastoralists in dry valley areas.
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
calidad de agua para ganado
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
calidad de agua para irrigar
demanda de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the structure reduces the degree of degradation, expense on agricultural inputs is believed to be reduced.
ingreso agrario
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
derechos de uso de la tierra/ agua
oportunidades culturales
oportunidades recreativas
instituciones comunitarias
instituciones nacionales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
It promotes land users' understanding of SLM through training and exposure to the actual structure and soil and water harvested behind the structure.
mitigación de conflicto
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
They may manage to access water for livestock drink and/or household consumption.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
calidad de agua
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
drenaje de agua en exceso
nivel freático/ acuífero
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The structure harvests soil moisture on the farm. It reduces the speed of runoff, stops, and spread over the farm.
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased through production of more biomass.
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The physical barriers stops the soil and water loss.
acumulación de suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
salinidad
Comentarios/ especifique:
It is related to a warm climate that triggers evaporation and salinity development in the long run.
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
acidez
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
especies invasoras extrañas
diversidad animal
especies benéficas
diversidad de hábitats
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
deslizamientos/ fluyos de escombros
impactos de sequías
impactos de ciclones, tormentas de lluvia
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
velocidad de viento
micro-clima
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
As the intervention is in its early phase, it is difficult to give an assumption before and after the application of SLM (technology or physical structure). However, a 40 years old woman known as Run Muhamed gave us her insight into the productivity of the land by comparing the hindsight vs the current harvest under highly erratic and erosive rainfall distribution. Accordingly, over the years the harvest per hectare diminished from 0.75 ton/ha to 0.1 ton/ha. This signals the effect of climate change/climate variability and land degradation on crop production. Her household is one of the owners of the land among the other four members of the extended family where the WSW was put in place.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the structure is recently constructed, it is dire to envisage the off-site impacts of the technology at this juncture. However, it has a positive contribution to the availability of groundwater in the adjacent farms.
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
Comentarios/ especifique:
Streams are less common in the dry valley.
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
It reduces the speed and volume of downstream flooding.
colmatación río abajo
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
Comentarios/ especifique:
Need an investigation of its impact on the groundwater.
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
sedimentos transportados por el viento
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
impacto de gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Believed to reduce it in the long run.
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
The intervention believed to improve the existing negative consequences of degradation through promoting soil and water management and reducing risks of crop failure.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | moderadamente | |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | moderadamente |
| tormenta de arena/ de polvo local | no muy bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | moderadamente |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación repentina | moderadamente |
Comentarios:
After an extended dry year, like this season, the technology is overloaded with a flash flood. The soil was frequently exposed to the sun and the prevailing heat waves in the area were easily detached by torrential rain. Then the soil and water were partly arrested whereas an immense amount washed away. It seldom could topple the structure if not the cascade comprises eight to ten structures with relatively short intervals to support one another. Furthermore, the dry valley soil is very fragile let alone exposed to a long-term drought that is associated with a heavy shower at the beginning of a short season like this season.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Comentarios:
It is a technology implemented at the community or extended family level. It is too early to evaluate the adoption trend at this particular time.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The technology/structure reduce soil and water erosion. |
| Harvest water and make the people and livestock beneficiaries from the still water for crop production, drinking, and household uses. |
| Increase soil moisture and risks of crop failure because of shortage of rainfall. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Rehabilitate both degraded agricultural and grazing lands. |
| Improve agropastoralist access to livestock feed and benefit from the positive impact caused by the technology. |
| Eventually, contributes to the improvement of ecology and overall ecosystem functioning. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| High initial investment cost. | Enhance the in-kind contribution of the land users, and increase matching funds from the government as cost-sharing with other projects. |
| Agropastoralist complains about the space it occupies in their farmland regardless of the benefit they accrue over a long period. | Increase the awareness of the community on the productive uses of the degrading land based on the evidence. |
| The structure may fall over the livestock migration/travel routes that are not acknowledged by some members of the community. | During masonry work, precaution is essential to calm down the possible complaints that could emerge because of the raised structure by leveling the crossover roads/paths. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| An inadequate number of structures in a cascade subjected to ineffective soil and water management and distribution of rainwater to support as supplementary sources of moisture for crop production. | Increase the number of structures per conceptual statement and standardize the intervals between the structures. |
| Excessive land users' desire that is unassociated with a tangible contribution to the development of the technology from their side. | Further building land users understanding of SLM technologies and their benefits so that they can build a sense of ownership and accountability to contribute and complement the external efforts. |
| Land users give emphasis mainly on the immediate benefits of the technology (harvesting water for livestock drinking and household use) than the objectives of rehabilitating the dry valley for productive use of it such as crop and livestock feed production. | Acknowledging the immediate benefits, and the mainstreaming work regarding the pillar objectives of the project intervention. |
| The initial investment, as well as maintenance costs, are either expensive or overestimated by local actors. Such a higher cost may discourage land users in the absence of projects or SLM funds. | It would be good to be pragmatic in cost estimation. Furthermore, adapting the technology using local materials may promote the adoption and sustainability of the structure for widespread use. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Three individuals.
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
One person.
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Four individuals.
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
23/03/2023
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Mekdaschi & Linger, 2013. Freie Universitat Berlin
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
https://www.geo.fu-berlin.de/en/v/iwrm/Introduction/Principles/index.html
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Water-spreading weirs
URL:
https://www.unccd.int/best-practice/water-spreading-weirs
Título/ descripción:
Water Spreading Weir - NATURAL RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
URL:
https://nrmdblog.wordpress.com/2016/12/12/water-spreading-weir/
7.4 Comentarios generales
The questionnaire is inclusive and more relevant to evaluate such physical structures as a technology. However, successive drought seasons experienced in the area subject the fragile soil to be easily detached and immensely moved by the early rains past the structure. This may affect the valuation of the efficiency of the technology since dry areas are also characterized by a flash flood that could certainly mask the benefits of such a good technology.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos