Double Basin Masonry Check Dam [Etiopía]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: GERBA LETA
- Editores: Torben Helbig, Noel Templer
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
NA
technologies_6716 - Etiopía
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Abdi Amir
Dry valley Rehabilitation and Productive Use (DVRPU) project of the GIZ
Etiopía
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Kenia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
The Check Dam helps to arrest the runoff of flood and rehabilitate the gully development.
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
A double basin masonry check dam is a physical structure that helps to stop gully formation or further development of gullies in dry valleys. It rehabilitates small to a medium-sized deep gullies that are eating into the heart of adjacent land.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
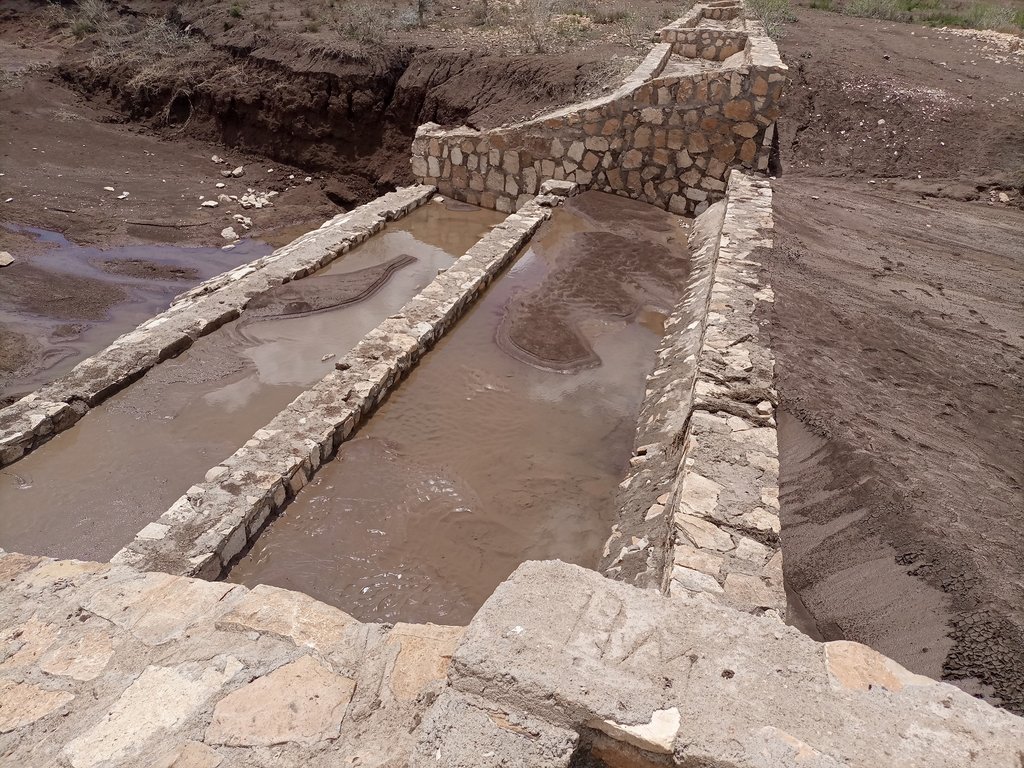
A “double basin masonry check dam” is a structure built in a narrow gully or depression to stop further gully formation. It is made of stone, concrete, gabions and wooden bars and serves as a permanent barrier. In this particular site stone is used as the structure is masonry. The technology is applied in areas where there are concentrated flows of water or runoff. The double basin masonry check dam is sited across a slope or a deep gully to slow water flow and capture sediment from upstream in the basins and behind the structure, thereby preventing expansion of the gully. The width of a check dam is variable. This particular structure is 14 meter wide, three meters deep and about 52 meters long. By helping to fill up the gully with sediment, it leads to rehabilitation and makes productive use of the area for growing trees, forage, and other plants. Apart from reducing the speed of surface runoff, the structure also promotes water infiltration, and recharges the groundwater reserves in the aquifer.
The main inputs necessary to build the check dams are financial resources, technical skills, skilled and unskilled labour, and construction materials including sand, stone, cement, water and other materials. Furthermore, construction tools such as a theodolite, line level, string, hammers, spades, hoes, and other tools are essential for design & construction. Technical skills for designing and profiling, and further capacity-building training are essential also. Application of the technology is also supported by satellite image and ground truthing to ensure the precision of siting.
The agropastoralists in the dry basin areas are pleased to see a huge movement of the soil arrested by the structure. The reduced expansion of the gully into the heart of the farm and grazing lands raises hopes of their land become productive and remaining so for generations to come. This hope and expectation have motivated them to welcome the intervention and develop an understanding of the actual benefits accrued from it. This leads to their support for the construction efforts. The disadvantages are that the technology is labour and resource-intensive which can be unaffordable for resource-poor agropastoralist communities living in food-insecure areas where rainfall is unreliable. This may make the adoption of the technology difficult to establish and nurture on their own without outside support.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
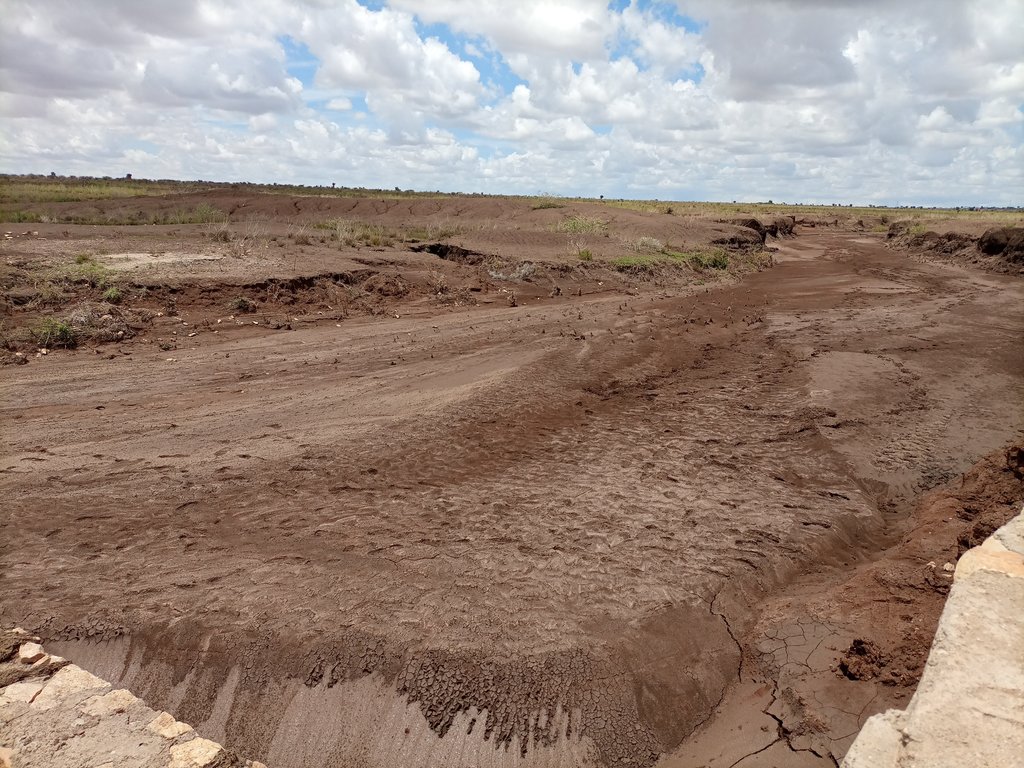
The photos display a large amount of sediment captured by a few days' shower post recurrent droughts experienced in the area over the last two to three years.
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Comentarios, descripción breve:
Video of the technology was not taken by this particular documentation exercise.
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Etiopía
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Somali
Especifique más el lugar :
Hadow kebele of south Jigjiga district
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
Locating the check dam closer to each other may help to stop the damage of heavy and concentrated flood moving in the drainage basin.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2021
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Capacity Development and Strengthening Drought Resilience (CDSDR) project of the GIZ in Somali Region.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- conservar el ecosistema
- proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- No (Continúe con la pregunta 3.4)
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Rainfed is the type of water supply that often experiences erratic distribution characterized by the reception of lower amounts. Mostly characterized by erratic and erosive feature.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
- medida de pendiente transversal
- cosecha de agua
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S6: Muros, barreras, vallas, cercas
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
- Wm: movimiento de masas / deslizamientos de tierra
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
The technology stops the mass movement of soil and water. As a result, it reduces land degradation, rehabilitates the degraded dry valley, and makes the land available for productive uses.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
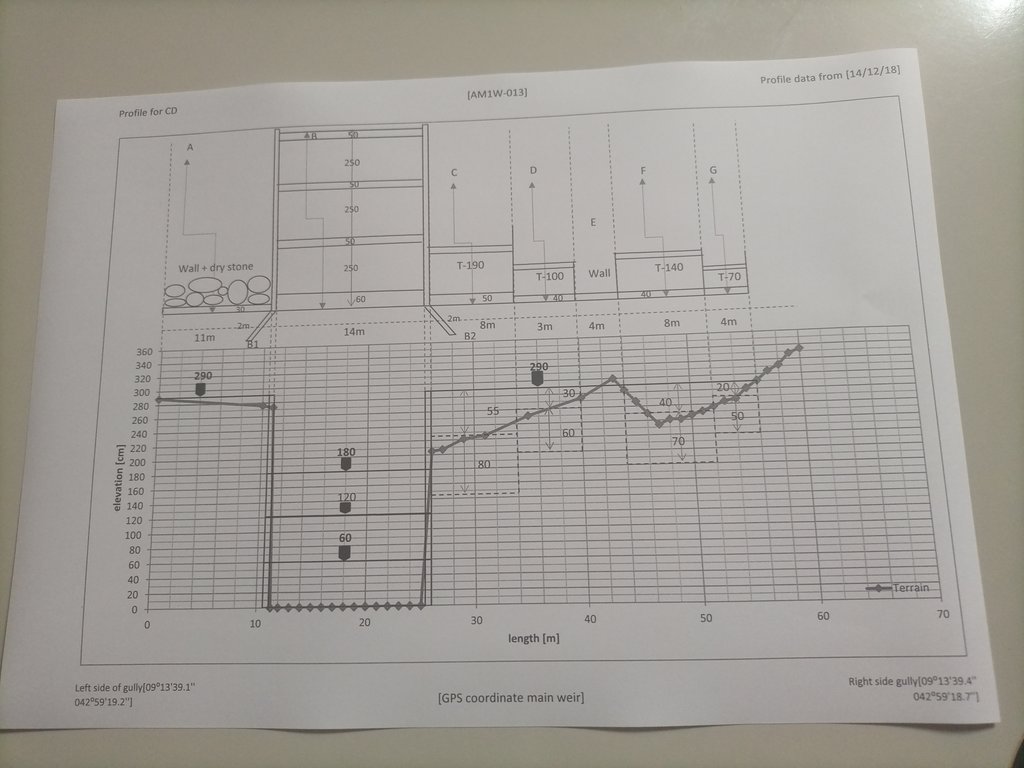
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
The design (layout - top view) and profile (lower view) of the technology is presented with universal units to clearly read and understand by the SLM experts or engineers. In addition, there are section drawings of the main weir and Bill of Quantity (BOQ).
Autor:
Amir Abdi
Fecha:
14/12/2018
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
check dam
Especifique las dimensiones de la unidad (si fuera relevante):
14m*3m*52m =2184m3
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
8.5 - 16 USD based on their skills
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Conduct rapid assessment and Surveillance of intervention site | During the off-season |
| 2. | Finalize site selection | ditto |
| 3. | Layout, Design and profiling works | |
| 4. | Identify and train masonry workers | During off-season |
| 5. | Material supply | |
| 6. | Start actual layout and excavation work | |
| 7. | Supervision... |
Comentarios:
Once intended to put the technology or the structure in place, a series of activities are conducted involving experts and contract workers until the activities are effectively finalized.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
Si no puede desglosar los costos especificados en la tabla anterior, proporcione un estimado de los cálculos totales en los que se incurrió para establecer la Tecnología:
9200,0
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The project is responsible to cover the cost.
Comentarios:
The cost for an unskilled casual laborer a day is 8.5 USD whereas the daily cost of a skilled Masonry worker is 16 USD per day.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Oversee and identify damage | During and after rainy season |
| 2. | Measure the degrees of damage | ditto |
| 3. | Quantify cost and materials needed | |
| 4. | Schedule the maintenance work | Right before the off-season |
| 5. | Employ the workers and reconstruct the damaged parts or upgrade it. | During off-season |
Comentarios:
As some of the technology implementation sites are inaccessible during the rainy season, implementing the activities during the off-season is commendable.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Si no puede desglosar los costos especificados en la tabla anterior, proporcione un estimado de los cálculos totales en los que se incurrió para mantener la Tecnología:
3244,0
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The project is expected to cover the entire maintenance cost. However, maintenance cost is attributed to various factors including the degree of damage, material costs at the time, etc. The figure merely represents an estimation of the cost, on average.
Comentarios:
As the dry land receive erratic and erosive rain, damage to the structure is not uncommon. Combining fast-growing trees and deep-rooted perennial fodder grass stabilizes the sediment and reduces the speed of run-off on top of the structure. Therefore, associating the structure with biological barriers right after the first season of rain is a mandatory action that assists to reduce the damage and maintenance cost that is not affordable by resource-poor communities.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Inflation and increasingly changing material prices, labor and transportation costs.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Rainfall distribution is erratic and erosive.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Jijiga Meteorology station
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
There are bimodal rainfall patterns but the distribution in each respective season is not uniform. Particularly, the past consecutive seasons have been characterized by drought.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones cóncavas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
The technology is implemented in the gully or depression to reduce the speed of runoff and hold back the sediment and running water itself.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
Sí
Especifique:
Land users communicated the presence of a medium level of water salinity.
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
The water quality is a relative description as it is not supported by facts. Both livestock and human beings are using ponds and still water for drinking after rainfall.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
A few tree and shrub species are common in the area. Acacia, opentia (Euphorbia species), and some invasive weed species are common.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Semi-nómada
otros (especifique):
Agro-pastoralist
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
The agro-pastoralist settlement pattern is stable except their mobility with their livestock looking for water and feed. Land users of various age groups are benefiting from the technology.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
Land use is largely communal and individual inherit it from their lineage.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Comentarios:
Not much service is available in the pastoralist area except that the road paths through the area also create access to the market and other service centers.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
With the development of the sediments trapped by the structure by fodder crops of multipurpose tree species, it is possible to boost production and ensure the sustainability of the structure.
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the sediment brings in fertile topsoil from the upstream catchments, the likelihood of producing quality fodder in the rehabilitated area is so high.
producción de madera
Comentarios/ especifique:
The multipurpose tree species assumed to be planted in the rehabilitated area are expected to increase wood production.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the rehabilitated valley reduces runoff and increases the groundwater reserves, it caters to the opportunity to access drinking water.
calidad de agua potable
Comentarios/ especifique:
Succeeding vegetation covers enables to filter of the water and improves the quality of surface and subsurface water.
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
Comentarios/ especifique:
Slightly increases as the structure and rehabilitated areas improves water infiltration and formation of still water or micro ponds behind the structure.
calidad de agua para ganado
Comentarios/ especifique:
Simultaneously increases with the availability of surface and subsurface water.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduction of gully formations that consume the rangeland allows accessing relatively more rangeland areas for the livestock to graze over. This inevitably improves the food security of the pastoralist community.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
The technology and its function along the mainstreaming work with local development actors certainly improve the understanding and evidence-based knowledge of the land users.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
The technology is believed to increase both surface and groundwater quantity in the intervention valley.
calidad de agua
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Surface runoff speed and volume are gradually decreased with the rehabilitation of the gully and the development of the area behind the structure.
drenaje de agua en exceso
nivel freático/ acuífero
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Soil moisture in the rehabilitated area positively increased.
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the structure on the upstream side reduces the speed of runoff, soil, and water loss decrease, and soil accumulation is increasing over time.
acumulación de suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
It increases with the deposition of sediments. Seeds of different trees and vegetation can emerge as succession species.
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increases!
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
Comentarios/ especifique:
The structure and rehabilitated areas reduces the speed and impacts of the flood.
deslizamientos/ fluyos de escombros
impactos de sequías
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Overtime, tree cover reduces emission of carbon and green gases.
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
Assessment of on-site impacts desires long-term follow-up, data collection, and analysis.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the technology put in place in recent times, off-site impacts need assessment based on facts.
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The structure and rehabilitated areas inevitably reduces downstream flooding and siltation in the future.
colmatación río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
There is visible siltation held back by the structure. However, quantifying demands empirical analysis.
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
impacto de gases de invernadero
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
The facts regarding the off-site impacts will certainly be assessed as a long-term impact.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | moderadamente | |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no se sabe |
| inundación repentina | muy bien |
| deslizamiento | bien |
Comentarios:
Similar to on-site impacts, the off-site impact assessment needs, facts, and long-term follow-up.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
Adoption rate is yet to be evaluated. The technology put in communal land.
Comentarios:
No community so far adopted and implemented the technology on its own.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Rehabilitate the gully, and stop and reverse the gully formation. |
| It creates the opportunity for productive use of the degraded environment. |
| Recharge the groundwater aquifer and supply still water for temporary use by local people and livestock. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Promote regeneration of the lost species through resilience building. |
| Improve the landscape feature. |
| Improve the ecosystem and its overall services. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| High investment cost to implement the technology. | Promote government awareness and emphasis on the benefit and investment in developing the technology. |
| Lack of implementation skills. | Develop the skills and motivation of the community and other stakeholders. |
| Conflict of interest on the use of the rehabilitated land in the intersection of neighboring kebeles. | Awareness creation and promote behavioral change on the joint benefit of the technology. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Inability to put micro check dams along the drainage line before it cuts deep into the soil. | Improve surveillance and promote early intervention. |
| Lower level of participation from the land users. | Develop the capacity, awareness and motivation of the land users. |
| Stakeholders and land users lower level of environmental education, improper land management and the consequent climate change and other associated adversities. | Promote environmental education, emerging climate change and climate variability in adult and vocational education. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Four individuals
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Two individuals.
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
23/03/2023
Comentarios:
The flash flood post three years of drought is so damaging. The fragile soil that has been exposed to the sun is easily detached and moved away by the flood. Substantial tons of soil stopped by the check dam signals the positive effects of the structure in changing the trends.
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Criteria for optimizing check dam location and maintenance requirements. Hassanli, A. M. & Beecham. 2013; ISBN: 971-1-60876-146-3
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287636490_Criteria_for_optimizing_check_dam_location_and_maintenance_requirements
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Different Types of Check Dams & Design Procedures
URL:
https://forestrybloq.com/different-types-of-check-dams/
7.4 Comentarios generales
The questionnaire is comprehensive. However, to answer every question, there must be a tradition of long-term data collection and documentation exercises by either the project or the partners government organizations. In that way, it is possible to fully address the multifaceted demands included in the questionnaires such as " the before and after SLM intervention" which is dire to address them for those projects at their early stages of implementation.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos