Panicum coloratum for irrigated fodder [Etiopía]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: GERBA LETA
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Panicum
technologies_6563 - Etiopía
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
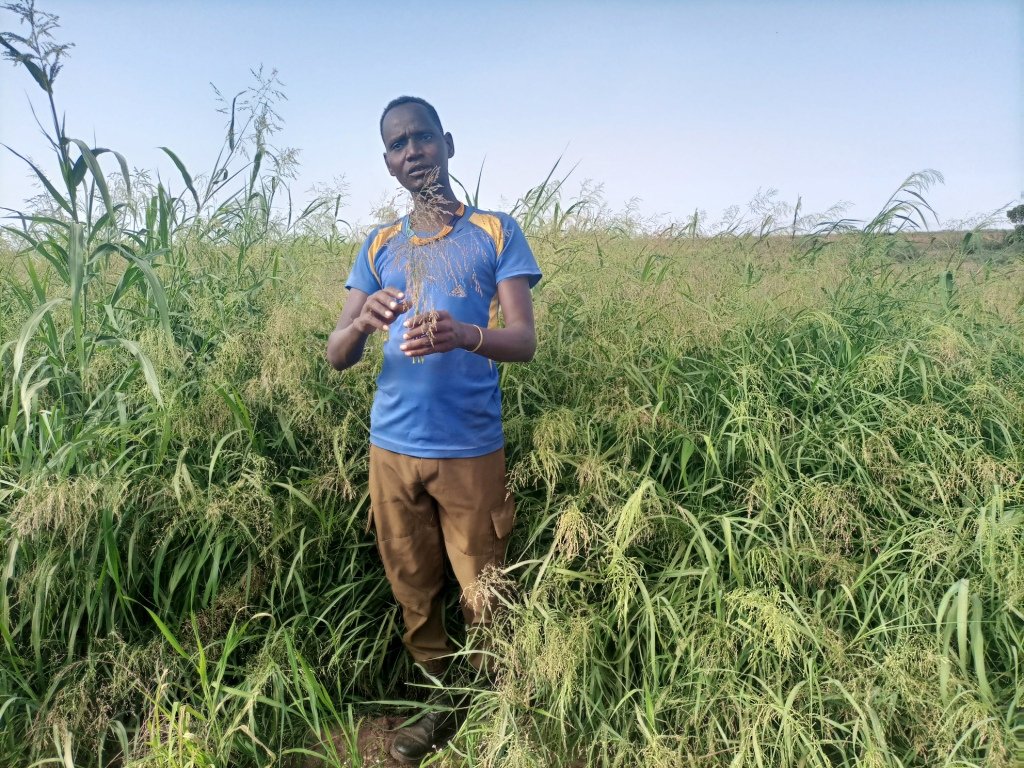
Lutulya Abebe
Agro-pastoralist (fodder producers group leader)
Etiopía
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Resilient in Pastoralist Areas (RIPA)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
International Development Enterprises - Ethiopia (iDE-Ethiopia) - Estados Unidos1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
The technology is a regenerative practice friendly to the environment.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
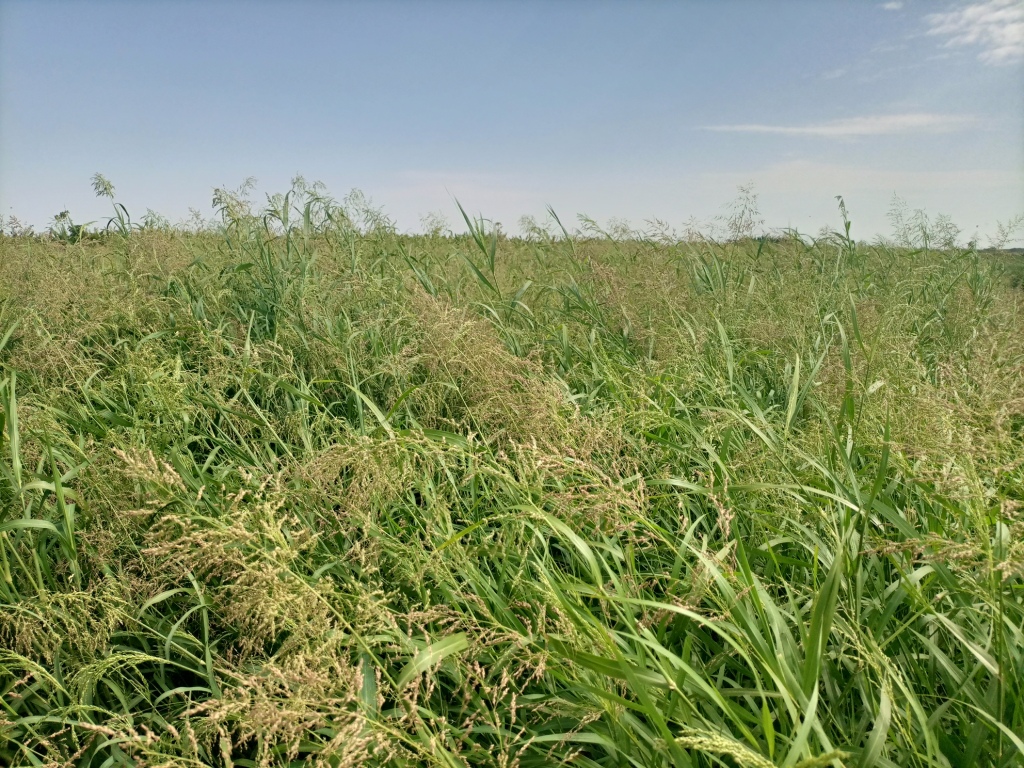
Panicum coloratum is a palatable tropical grass with high biomass production potential. It is grown in the irrigated fodder development areas of Dassenech district. Panicum is a fast-growing perennial which can be repeatedly harvested once it reaches maturity. It mitigates the issues of recurrent livestock feed shortage in dry periods – which are becoming worse with climate change.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Irrigated fodder production is carried out by pastoralist groups in arid areas of South Omo. Among a number of fodder grasses, Panicum coloratum is a fast-growing species. Panicum is grown as livestock fodder, particularly for the dry season when feed availability is in short supply. It mitigates the issues of recurrent livestock feed shortages which are becoming worse with climate change. Also, growing fodder grass allows resource-poor pastoralist communities to generate income from the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. Irrigating at least twice a week, good weed management, and fertilization ensure sustained production.
In Dassenech district of Southwest Ethiopia, Panicum’s annual fresh biomass and dry matter production potential is over 63 and 18 tons/ha, respectively. It can reach its first harvest after about 60 days and subsequently can be harvested every 45 days. Panicum germinates and establishes readily on any soil type under both irrigated and rainfed conditions. It is also drought tolerant and resilient to climate variability, and does particularly well on alluvial soils with high fertility. Panicum is mainly used for grazing, but it is also suitable for cut-and-carry feeding systems. Each member of the pastoralist group grows panicum on 0.04 ha of land. In the flood lowlands of the Omo River basin, panicum is known for tolerating periodic flooding, salinity, & disease.
Previously, the land users were unfamiliar with this particular grass and its associated management practices. Also, irrigating on a regular schedule and keeping the grass free from roaming animals adds a work burden to the pastoralist community. However, the Resilience in Pastoral Areas (RIPA) project has introduced and familiarized the community with fodder production and management practices. The project also assists in linking the output to sustainable market. In this regard, the contribution of the RIPA project of the International Development Enterprises (iDE) is immense. The pastoralists appreciate their livestock’s access to year-round feed, as well as the generation of income from the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. Fodder production also creates year-round employment opportunity. However, the community's reliance on government and civic organization support for land preparation and access to irrigation water (conveyance services) might be considered a threat to ensuring sustainability of fodder development by the pastoralist groups.
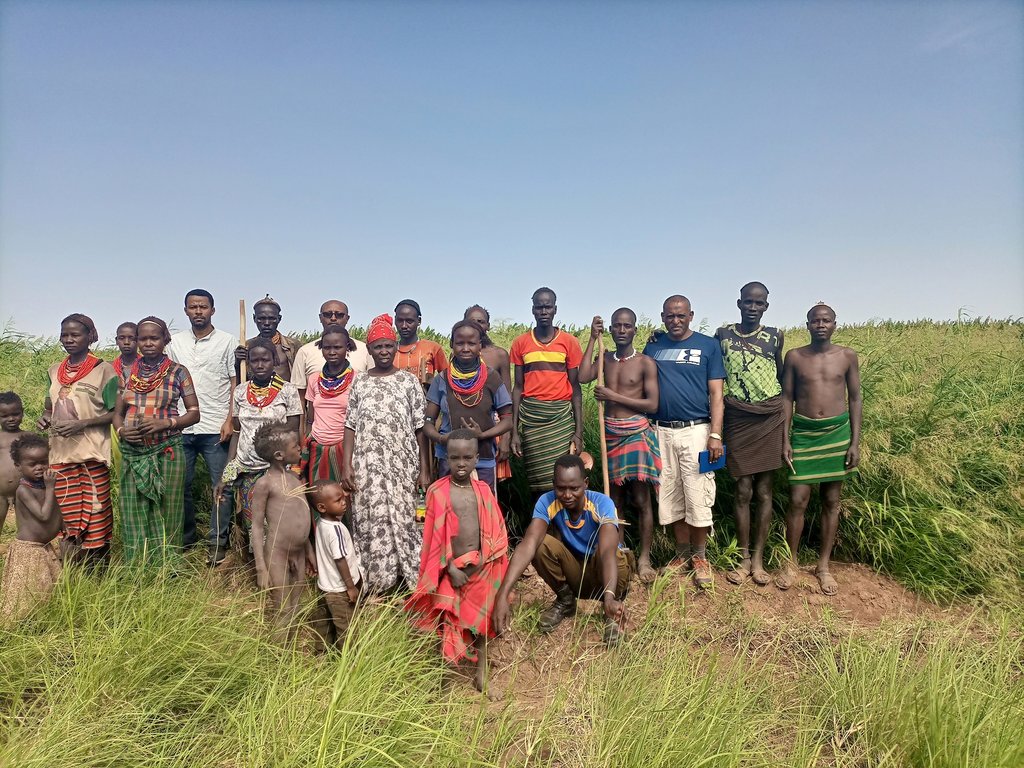
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
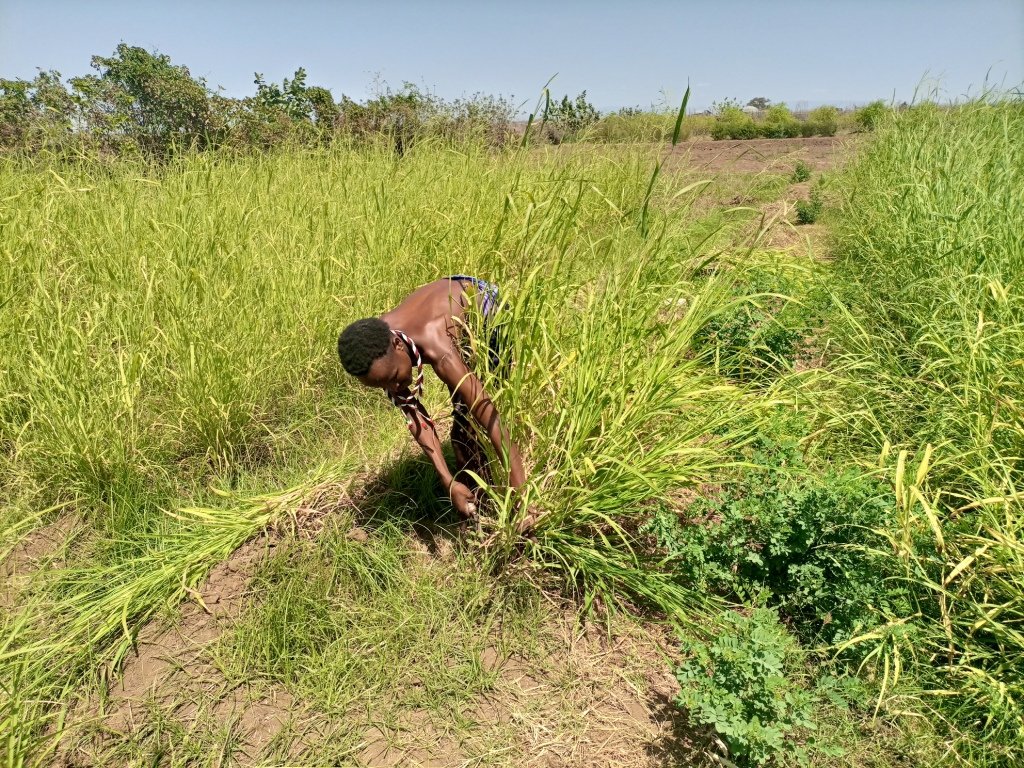
The photos display panicum seed and feed harvesting.
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Comentarios, descripción breve:
Videos of the technology is not documented.
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Etiopía
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Southern Nations, Nationalities and People Region (SNNPR).
Especifique más el lugar :
Omorate, Dassenech.
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
Panicum production site is closer to the mouth of the Omo river. The technology is piloted in two sites and scaling up sites have been increasing around the irrigable areas.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2021
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Resilient Initiatives in Pastoralist Areas project of the International Development Enterprises has implemented fodder development along with other perennial crops such as banana as part of promoting resilient agriculture in the dry areas of South Omo Zone of SNNPRS.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- banana/plátano/abacá
- herbs, chili, capsicum
- natural grasses
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
The area receive bimodal rainfall but not reliable to grow crops.
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo extenso:
- Pastoralismo semi-nómada
Tipo de animal:
- camellos
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- cabras
- ovejas
¿Se practica el manejo integrado de cultivos - ganado?
No
Productos y servicios:
- economic security, investment prestige
- leche
- cueros/ pieles
Especies:
cabras
Conteo:
12
Especies:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Conteo:
8
Especies:
camellos
Conteo:
1
Especies:
ovejas
Conteo:
9
Comentarios:
The site is pastoralist area who used to rely on flood retreat agriculture in the past. However, due to the construction of Gibe III hydroelectric power dam, the spill over during plenty of rain remain still as artificial lake over thousands of hectare for long period of time. As a result, the conventional agriculture practices abandoned. Thus, a shift to irrigation agriculture is in the process at least to produce fodder crops and other perennial crops such as banana for consumption and market.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- banana/plátano/abacá
- herbs, chili, capsicum
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Cortar y llevar/ cero pastoreo
- Pastoreo mejorado
Comentarios:
The area used to receive short rain twice a year. However, rainfall distribution is unreliable. So, the introduced perennial fodder and banana production persist throughout the year using irrigation.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- totalmente irrigada
Comentarios:
Fodder and tropical fruit crop production is entirely practiced using full irrigation from Omo river.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- perturbación mínima del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes
Comentarios:
Perennial fodder production contributes to SLM through permanent soil cover.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por viento
- Ed; deflación y deposición

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cs: salinización/ alcalinización

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
Comentarios:
As a perennial crop, the grass covers the ground permanently and reduces moisture loss to excessive evaporation in the dry areas.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
This is the photo of the pastoralist group. There is no specific sketching that portrays the technology but the following points provide tips for adopters of the technology:
- The land is tilled and harrowed by a tractor for two to three rounds.
- On the third-round ridge and furrow are formed using tractor or hand tools.
- The seeds or splits are planted in rows along the ridge.
- Spacing between ridges varies with the purpose: for haymaking 25 -30 cm and for seed production 50-60 cm to simplify the application of intensive management practice for the latter one.
- The farm/crop should be irrigated twice a week for better production.
- Need Fertilization to ensure good production/harvest.
Autor:
Gerba Leta
Fecha:
19/08/2022
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
1 timad
Si usa una unidad de área local, indique el factor de conversión a una hectárea (ej. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
4 timad
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Ethiopian Birr (ETB)
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
53,438
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
It is variable based on the types of work (from 50 birr to 100) for half day before the sun gets too hot. That is equivalent to one day in dry lowland areas.
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing and land preparation | Any season for irrigated fodder production, |
| 2. | Planting/sowing | During the start of season for irrigation fodder production. |
| 3. | Fertilizing | At planting and at boot height. |
| 4. | Irrigating the farm | Twice a week. |
| 5. | Weeding | Twice starting 3- 4 weeks post planting. |
| 6. | Harvesting the grass (fodder) | During harvest maturity. |
| 7. | Hay making (bailing) | Post harvest. |
| 8. | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | Harvesting season and post harvest. |
Comentarios:
As fodder development is based on irrigation, it can be started any time/season of the year.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Clearing and land preparation | PDs | 12,0 | 200,0 | 2400,0 | 50,0 |
| Mano de obra | Planting/sowing | PDs | 5,0 | 100,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Irrigating the farm | PDs | 14,0 | 200,0 | 2800,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Weeding (twice a season) | PDs | 10,0 | 100,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Spade | Pcs | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | |
| Equipo | Hoes | Pcs | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Seed | kg | 4,0 | 300,0 | 1200,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | NSP | kg | 50,0 | 50,0 | 2500,0 | |
| Otros | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Harvesting and hay making | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 15200,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 284,44 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Other than cost of labor, some inputs and material costs are covered by the RIPA project of the iDE.
Comentarios:
Irrigation-based fodder development is in the pilot phase. There is growing interest among the government organization (Woreda Office of Agriculture) to adopt and scale up the promising development. Please note, the cost is estimated only for a season or one round of production. Once reaches its first harvest, Panicum can be harvested every other 45 days onward. Of course, it needs the application of necessary management practices, every season.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning irrigation ditch | During off-season or before the start of next growing season. |
| 2. | Fertilizer (NSP) | Twice: at the beginning of the season & when the fodder reaches boots height. |
| 3. | Irrigating the farm | Twice a week. |
| 4. | Weeding (2x) | Based on the density or prevalence of weeds. |
| 5. | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | When the seed reaches harvest maturity. |
| 6. | Harvesting and hay making | At harvest and post harvest. |
Comentarios:
As there is no structure such as fodder banks, maintenance cost is not documented.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Cleaning irrigation ditch | PDs | 5,0 | 200,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Irrigating the farm | PDs | 12,0 | 200,0 | 2400,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Weeding (at least twice during the growing season) | PDs | 10,0 | 100,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Harvesting and hay making | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | NSP Fertilizers | kg | 50,0 | 50,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 10900,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 203,97 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
NA
Comentarios:
The cost estimation is only for one irrigation season that may range from 45 days to 60 days or some more including the harvesting and drying of the outputs. Once established, the cost of production is gradually declining.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Economic crisis and increasing Inflation rate affect the establishment as well as maintenance costs. Particularly, fuel, fertilizer, and labor costs are consistently changing.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Erratic and unpredictable.
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Rainfall distribution is unreliable to produce crops under rainfed conditions.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
The site is in the lowland around the mouth of Omo River basin.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil pH is over 7 and the soil is slightly saline alluvial.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Diversion/river water is used for irrigation. There is ample water provide that there is pump to convey the water to the nearby farm. In the rainy season, the river is turbid and full of eroded soil from the upstream catchments. However, the depth of the water table is variable based on the distance of the farm from the edge of the river. Around the main river basin, the water table is shallow but too deep as one go away from the river basin.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Around the farmland, diversity of crops and vegetation is limited. Away from the farmland, there are a few lowland shrub species and faunas common to the dryland.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Semi-nómada
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
The water pump is used to convey water and the tractor for land preparation. Therefore, a mix of mechanization and manual systems are employed in the area. Irrigation land was allocated to the group but they partitioned and distributed to each member of the group.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
As their animal is freely roaming, only small size of land is permantantly owned around the river side and homestead.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- grupal
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
The pastoralist, still freely move and settle where they think appropriate and shift after certain years.
Comentarios:
Apart from the irrigable land which are located around the river basin, land is openly accessible to the pastoralist community.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Comentarios:
Access to facility and the services is mainly to those pastoralist community who are residing closer to the Omorate, the woreda capital.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Access to irrigation water increase the fodder production throughout the year.
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the alluvial soil around the river bank is suitable for Panicum, it increases the quality of fodder.
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increase in livestock production is related to the availability of feed/fodder.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Access to irrigation water highly reduced risk of production failure.
área de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
-1
Cantidad luego de MST:
2
Comentarios/ especifique:
The land that used to be ideal is now converted to farming.
manejo de tierras
Comentarios/ especifique:
Panicum as perennial fodder increases ground cover throughout the year and contributes to land management from wind erosion in the dry land areas.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Cantidad antes de MST:
-3
Cantidad luego de MST:
1
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
calidad de agua para ganado
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
calidad de agua para irrigar
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
demanda de agua para irrigar
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
-1
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
As Panicum is harvested at least six times a year post reaching the first maturity, farm income is significantly increases.
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Income can be generated from the sale of fresh fodder, hay and seeds.
disparidades económicas
Cantidad antes de MST:
-2
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Irrigated fodder production needs intensive management practices. Panicum is perennial fodder that remain on the field all year round. So, irrigating, weeding and looking after the farm... increases the workload.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Cantidad antes de MST:
-1
Cantidad luego de MST:
2
situación de salud
Cantidad antes de MST:
-1
Cantidad luego de MST:
1
derechos de uso de la tierra/ agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
oportunidades culturales
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
1
oportunidades recreativas
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
instituciones comunitarias
Cantidad antes de MST:
-2
Cantidad luego de MST:
2
instituciones nacionales
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Cantidad antes de MST:
-2
Cantidad luego de MST:
2
mitigación de conflicto
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
2
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Cantidad antes de MST:
-2
Cantidad luego de MST:
1
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
As it permanently covers the ground, it has high likelihoods of reducing surface runoff.
drenaje de agua en exceso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improve water drainage.
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Decreases surface evaporation but not transpiration.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
The farm remains covered by perennial grass. Irrigating the farm also favor the regrowth of other wild species.
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Above ground biomass is highly increased as described in the description section.
diversidad vegetal
especies invasoras extrañas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced with increased management practices. Invasive alien species such as Prosopis juliflora is less common in this part of the River basin.
diversidad animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Animal diversity correlates with fodder availability.
especies benéficas
diversidad de hábitats
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
impactos de sequías
Comentarios/ especifique:
It reduces the impacts of drought on livestock by providing access to adequate feeds throughout the year.
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
As Panicum increase ground cover and store the carbon above and below the soil surface, it reduces the emission of the carbon.
velocidad de viento
Comentarios/ especifique:
It breaks the velocity of wind in the lowland, one of the main issues.
micro-clima
Comentarios/ especifique:
Slightly ameliorate the micro-climate of the area.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
It is expected that downstream flooding is reduced as the perennial fodder crop cover the ground throughout the year.
colmatación río abajo
Cantidad antes de MST:
-3
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
Cantidad antes de MST:
-1
Cantidad luego de MST:
0
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios/ especifique:
Permanent ground cover expected to increase the filtering capacity.
sedimentos transportados por el viento
Comentarios/ especifique:
It has expected positive effects of reducing wind transportation.
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
impacto de gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
As perennial crops cover the ground and absorb the carbon, it has an inevitable positive effects on reducing carbon emission.
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
The fodder development is a pilot practice. Its up scaling will have a positive off-site effects to the surrounding areas.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | moderadamente | |
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de viento | moderadamente |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| ola de calor | moderadamente |
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | muy bien |
| inundación repentina | bien |
Desastres biológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| enfermedades epidémicas | bien |
| insectos/ infestación de gusanos | bien |
Comentarios:
Panicum has drought, flood and disease tolerating feature.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
The technology was piloted two years ago. The cost of establishing it is partly supported by the RIPA project. Land preparation and conveying irrigation water covered by the local government.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Comentarios:
So far, the pastoralist piloted the technology through government and NGO support.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Supply year round feed for the land users' livestock. |
| Allow pastoralists/agro-pastoralists to generate income from the collection and sale of fresh fodder, hay and seed. |
| The technology supplies feed that can be reserved for the emergency time through hay making. |
| Introduction of fodder production technology enables the pastoralist group access usufructs to irrigable land that promotes the changing in farming practices from entirely pastoralist to agro-pastoralist on a gradual basis. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The technology considered as one of the regenerative agricultural practices that have positive contribution to carbon sequestration. |
| It reduces risks of feed shortage during the extended dry season. |
| A prompt sources of income for the pastoralist community via the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. |
| Feeding livestock on grass reduces methane production as compared to feeding them on processed feeds. |
| The onsite shattering of the seed increases the density of grass every other season. Thus, it improves the ground cover and production of huge biomass per unit of land. |
| Panicum harvested 15 cm high that simplify regrowth/tillering and propagation of the grass from the ratoon. The practice stimulates prompt ground cover and year-round sequestration of carbon. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Access to irrigation facility and service is via government and project support. | Try to secure multiple sources of finance, and encourage market oriented production to enhance the pastoralist groups develop reliance on their own. |
| Smaller size of land is accessible to irrigation. | Increase intensification of fodder development and diversify sources of income via production and marketing of fresh fodder, hay, and the seed. |
| Shortage of baling machine to fasten the hay for simplicity of storage and transportation | Improve pastoralist access to the facility and services so that their resilience to feed shortage and associated issues are promptly increases. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Shortage of storage structure or fodder bank to store/ reserve the harvest for market and/or later uses. | To promote the establishment of storage or fodder bank by the land users group themselves, and try to find sources of finance to support them in this regard. |
| Lack of sustainable market links for Panicum seed. | Establish reliable market value chain with private suppliers/distributors to the other part of the country. |
| Lack of legume fodder species to improve the dietary value of the grass family. | Introduces important legume species with high biomass production potential or other leguminous tree species with multiple uses such as windbreak or as buffer plants around the periphery of the fodder farm. |
| Panicum needs longer time to reach harvest if intended for seed production that may dishearten the pastoralist to wait longer time. | Allocate separate plots for seed production, or else, make the right choice for the types of outputs that suits the pastoralist's urgent needs. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Over 20 members of the pastoralists group are met.
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
One knowledgeable land user who is representative of the pastoralists group.
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Three
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
Published articles and locally developed guideline for growing Panicum.
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
20/08/2022
Comentarios:
Field visit was made from 17 August to 19, 2022.
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
ILRI. 2013. Colored Guinea grass (Panicum coloratum) for livestock feed on small-scale farm. ILRI Forage Factsheet.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Free online
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Hidosa, D., Hitiso, W. & Guyo, M. 2017. Biomass Production of different grass species available at irrigated lowland of Dassench woreda in Southwestern Ethiopia. Bangladesh Journal of Animal Science, 46 (3): 188-191.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Free online
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Hidosa, D., Adicha, A., Sultan, M., 2022. Production and Commercialization Status of Improved Panicum Grass Cultivation in the Lowland Livestock Production System of South Omo South-Western Ethiopia. Research on World Agricultural Economy, 3 (4): 694. DOI:10.36956/rwae.v3i4.694
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Free online
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Tropical Forage. 2020. Panicum coloratum
URL:
https://www.tropicalforages.info/text/entities/panicum_coloratum.htm
7.4 Comentarios generales
The questionnaire is very comprehensive and inclusive to socio-economic and environmental benefits, and the effects of a specific SLM technology.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos