Contour Stone Bunds [Bután]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Nima Dolma Tamang
- Editor: Kuenzang Nima
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Dhoyi Gaytshig (རྡོའི་གད་ཚིགས།)
technologies_6891 - Bután
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
Yangzom Pema
NA
Bután
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - Bután1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
The technology reduces soil erosion and conserves soil moisture
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Community Mobilization for SLM Interventions [Bután]
Community mobilization in implementing sustainable land management technologies is indispensable in engaging the community to identify their priorities, resources, needs and solutions. It ultimately promotes bottom-up participation and fosters accountability.
- Compilador: Nima Dolma Tamang
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Contour stone bunding on sloping agricultural lands reduces soil erosion and conserves soil moisture in order to retain soil productivity. It is promoted /recommended on slopes where there is adequate surface stone.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
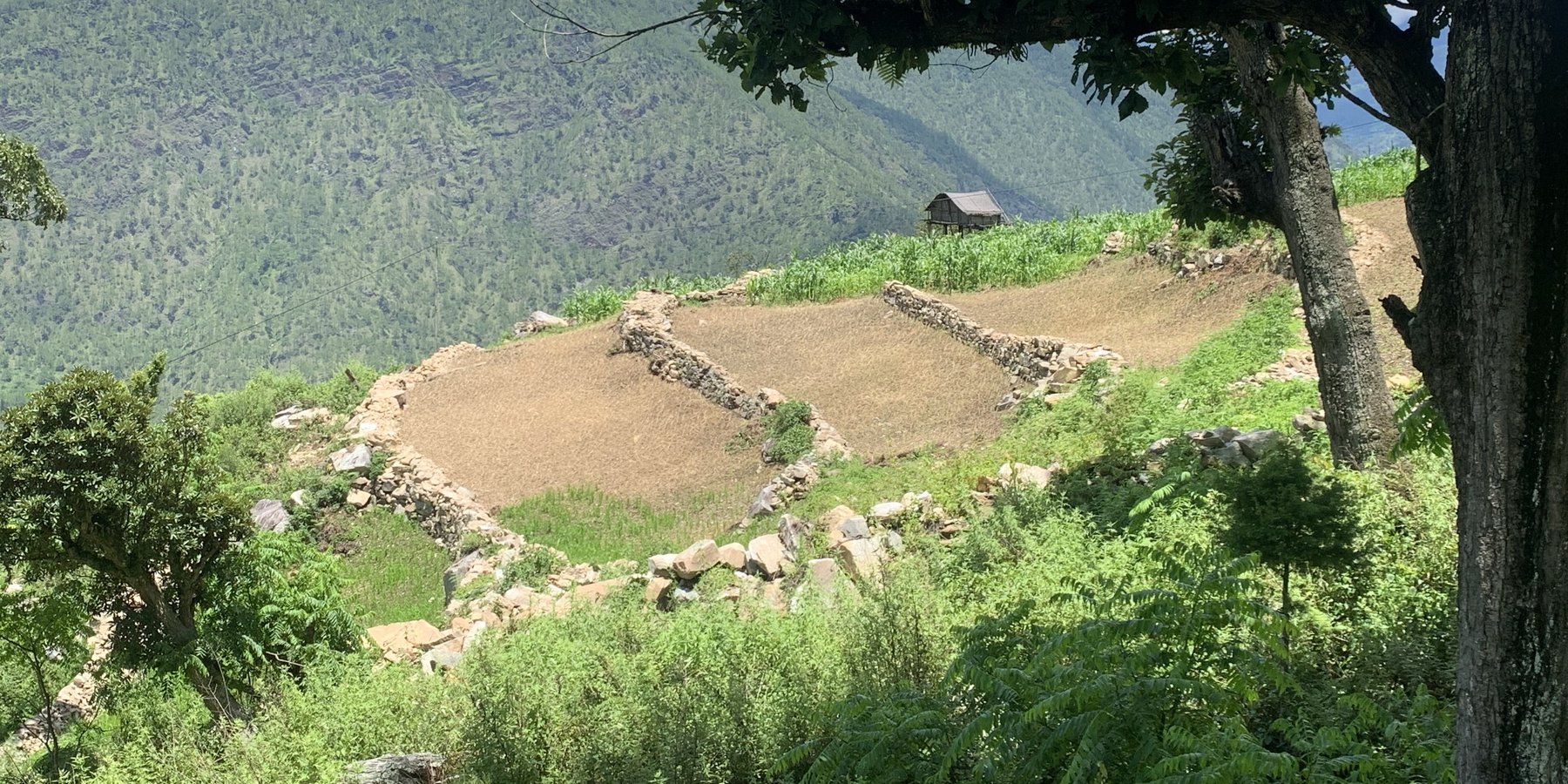
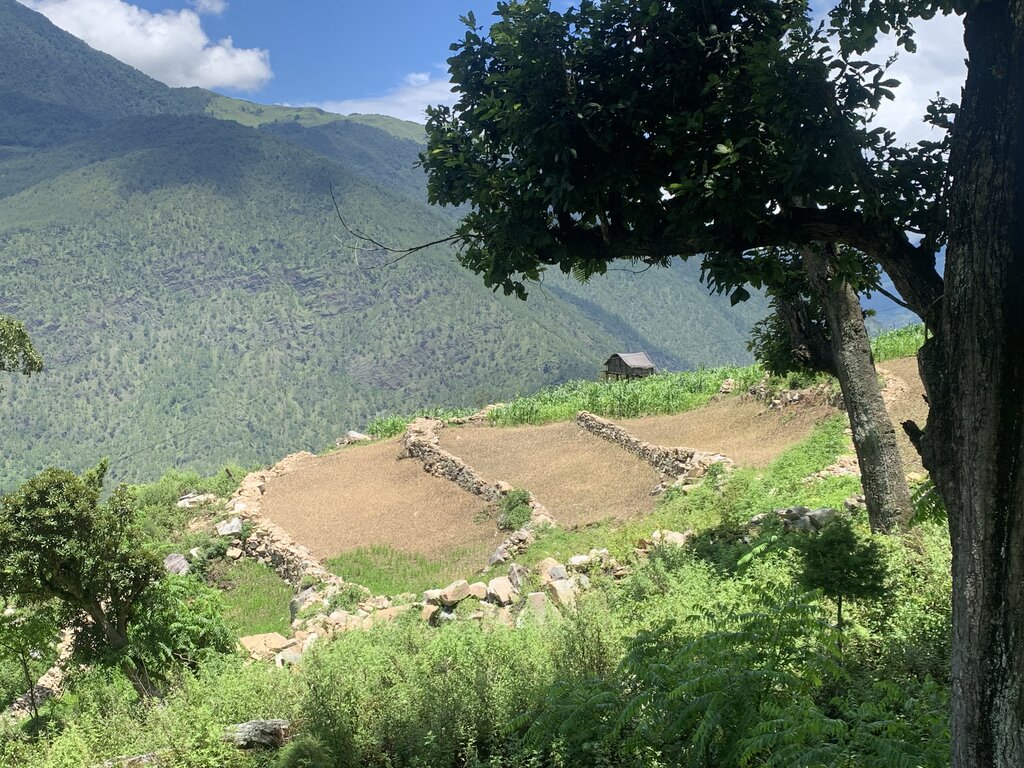
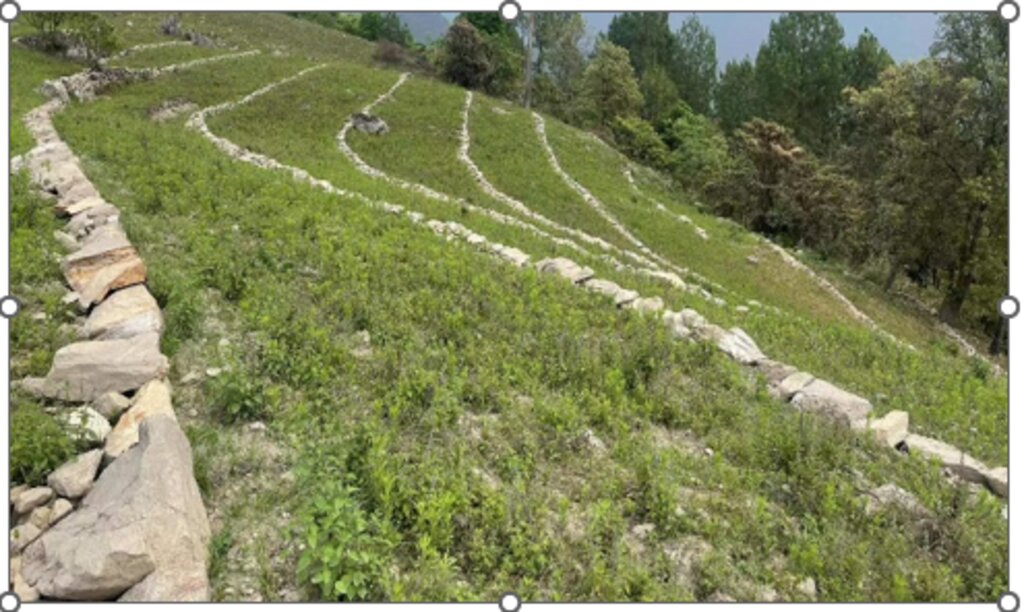
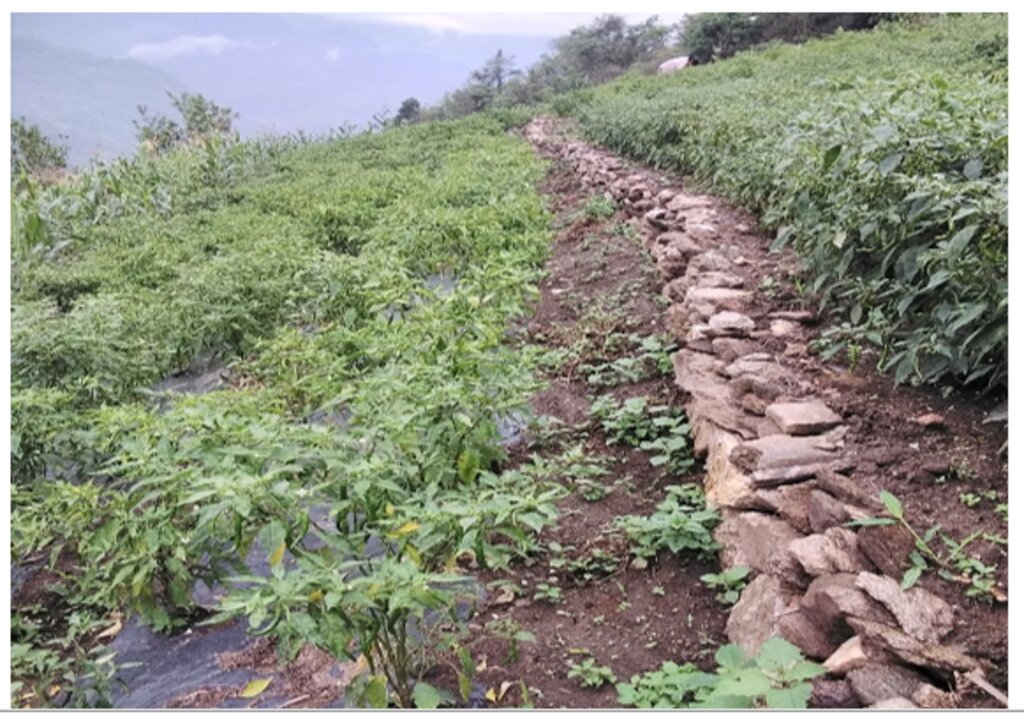
Contour stone bunds are small walls of stone that are laid out along the contour line to help reduce soil erosion, conserve soil moisture, increase soil fertility, to ease workability, increase cropping area, and ultimately ensure sustainable use of lands for enhanced food and nutrition security. This practice is recommended in fields that have plenty of surface stones (> 20%). Construction of contour stone bunds not only helps to get rid of the excess surface stones and gravel but also reduces the slope gradient through formation of partial terraces over a few years.
The stone bund is not new to Bhutan, being a mountainous country, forefathers used the technique to remove stones from the field and stabilise the land for agricultural purposes. Therefore, there were some traditional stone lines constructed in the study area.
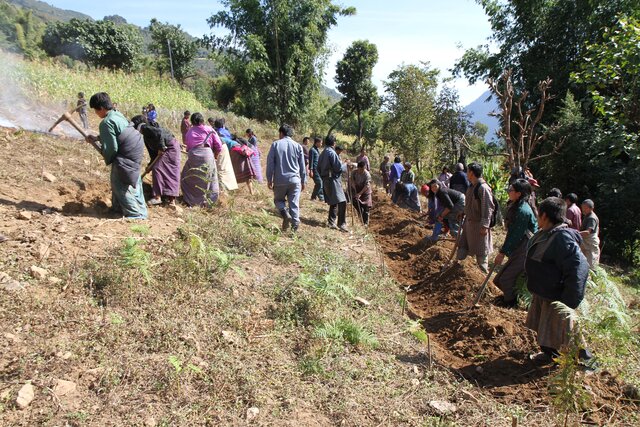
Constructing stone bund is labour intensive, therefore land users resort to a labour sharing approach where all the land users from the community come together and work on a rotational basis until every household in the community has established stone bunds.
The major activities and inputs required to establish the contour stone bund includes sensitization of beneficiaries, followed by SLM action planning, and hands-on-training. Field implementation follows this sequence: (a) determination of intervals between stone bunds, (b) demarcation of contour lines using an ‘A’ frame, (c) digging a trench of 0.1 - 0.2 m deep and 0.5 m wide to establish a foundation along the contour lines, and (d) constructing stone lines along the trenches with the larger stones at the base to set a sound foundation. A typical stone wall is 0.3 m high (1 ft) and 0.3 - 0.5 m wide, but this depends on the slope and availability of stones in the field. Contour stone bunds are commonly spaced 6 metres apart on slopes of 60%. In some cases, the fodder grass slips are also planted at the base of the stone bund for better stabilization of the bunds and fodder availability.
The major drawbacks of this SLM technology according to respondents are (a) labour demanding, (b) no immediate return, and (c) the space between piled stones harbours rodents leading to crop damage.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Bután
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Lhuentse Dzongkhag
Especifique más el lugar :
Zangkhar Village, Yabi-Zangkhar Chiwog, Jaray Gewog
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- 0.1-1 km2
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
The region where this SLM technology was implemented falls under Phrumsengla National Temperate Park. Phrumsengla National Park is a temperate park with large tracts of old-growth fir forests, its altitudes ranging from 700 metres (2,300 ft) to 4,400 metres (14,400 ft). Phrumsengla has scenic views, including forests ranging with elevations from alpine to sub-tropical. Because the soil of Phrumsengla's biomes is particularly fragile, the land is unsuitable for logging or other development
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2015
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The National Soil Service Center (NSSC), Semtokha, Thimphu initiated this activity as part of three-year (2015 to 2017) SLM project funded by Bhutan Trust Fund for Environmental Conservation (BTFEC).
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- conservar el ecosistema
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agroforestería

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - patatas
- vegetales - verdura de hojas verdes (ensaladas, repollo, espinaca, otros)
- Chili, cauliflower, cabbage, onion, brinjal and garlic.
- Peach, pear, fig, chayote
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Maize in summer is followed by cole crops in winter.
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
Sí
Si respondió que sí, especifique qué cultivos son intercultivados:
Brinjal, beans, onion and chayote.
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Maize cultivation followed by vegetables (cabbage)

asentamientos, infraestructura
- Asentamientos, edificios
- Tráfico: caminos, rieles
- Energía: gasoductos, líneas eléctricas
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- No (Continúe con la pregunta 3.4)
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- medida de pendiente transversal
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas estructurales
- S2: Taludes, bancos
Comentarios:
The technology also incudes vegetative measures where some land users plant fodder grass slips at the base of the stone bunds for better stabilization and fodder availability.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
- Wo: efectos de degradación fuera del sitio

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores

degradación del agua
- Ha: aridificación
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- adaptarse a la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
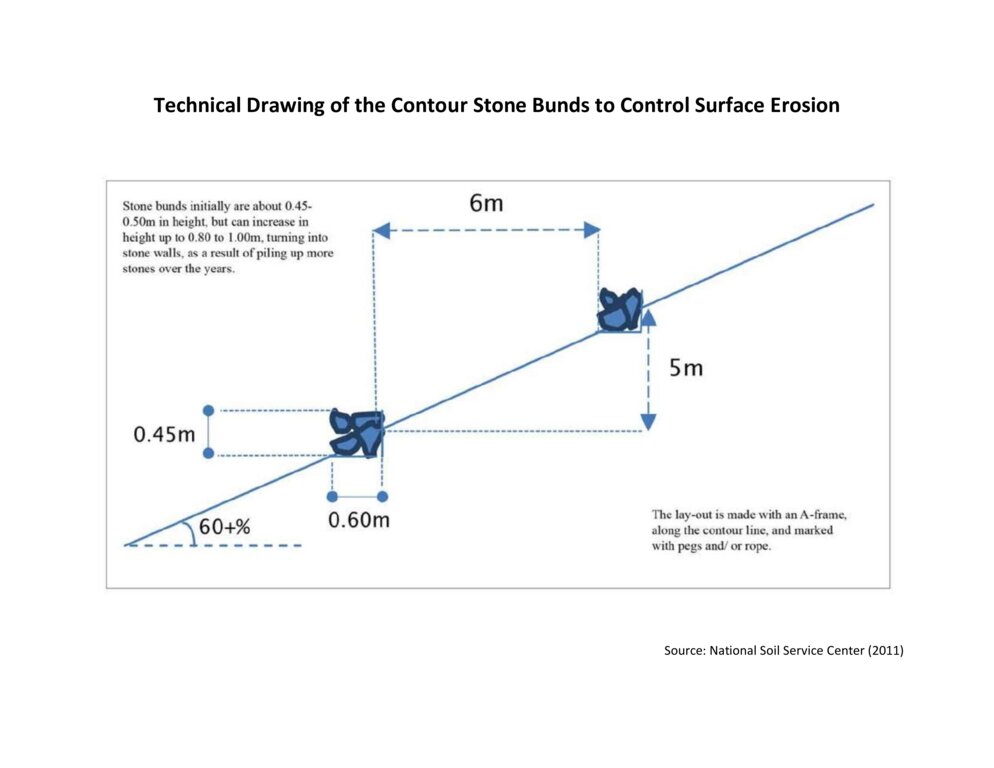
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
The specifications provided in the technical drawing (NSSC, 2011) may vary based on the field situation and slope of the land. Variations may be in the width of the terrace (3 m to 6 m), the height of the stone bund (0.45 m to 1m), and minimal variations are observed in the width of the stone bund (0.6 m).
Autor:
National Soil Service Centre
Fecha:
2011
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
3 acres
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Nu
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
80,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
400
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Traditional stone bund construction | 50 years earlier |
| 2. | Sensitization, SLM action planning, and Hands-on-training | 2015 |
| 3. | Field implementation of the activity | 2015 |
| 4. | Provision of incentives (Nu. 3000 per acre) | 2015 |
| 5. | Project phase-off | 2017 |
| 6. | Scaling up of this technology through GEF-LDCF | 2022 |
Comentarios:
Traditionally stone bunds were constructed by forefathers during land preparation on the slopes. The stones were piled at the contour lines to make the soil workable and improve the gradient of the land.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | Person/day | 49,0 | 400,0 | 19600,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Project incentive | Per hectare | 1,0 | 6420,0 | 6420,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 26020,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 325,25 | |||||
Comentarios:
The costs and inputs needed for stone bund establishment are calculated for 1 hectare of land.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The most important factor affecting the cost is labor.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1250,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The rainfall received in the region may vary from 1000 to 1500 mm.
The rainfall data of the Gewog is not available. The area shares a border with the Medtsho Gewog and has similar agroecological zones. The data provided is for Medtsho Gewog.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Website, Lhuentse Dzongkhag Administration
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
The Gewog falls under dry sub-tropical to warm temperate region (1500 to 2400 meters above sea level) from the six agroecological zones of Bhutan. It is characterized by extreme cold in winter and moderate in summer, humid and foggy.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones convexas
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Moisture content 3.10%, organic matter 7.15%, Organic carbon 4.15%, pH 6.79, electrical conductivity 209.20 µs/cm, nitrogen 0.21%, phosphorus 1.00 ppm, Potassium 121.40 mg/100ml, texture loamy sand.
The soil analysis was conducted at the Science Laboratory of College of Natural Resources, Royal University of Bhutan, Lobesa, Punakha.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Diversidad de hábitats:
- elevada
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
The area is rich in species diversity as it has pockets of microclimate ensuring habitat diversity.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
There are 11 Household members of which only the land user and her mother (86 years old) stay at home. Nine household members have migrated to the city for better opportunities.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- gran escala
Comentarios:
The land user has 4 acres of land of which the technology is applied in 3 acres. The average land holding in Bhutan is 3.4 acres per household in 2021. Therefore, more than 3.4 acres are characterized as large-scale in the Bhutanese context.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
- Family
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The cultivation of potatoes increased due to an increase in the cultivable area as the stones are removed.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Crops appear greener and healthier due prevention of soil erosion as the topsoil is retained. Maize leaves were dark green and potatoes were bigger.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to the removal of stones from the soil, it is suitable for diverse crop growth (deep-rooted and shallow). Therefore, the land user can cultivate diverse crops throughout the year. Crop diversity and increased growing season will ensure land user with stable household income even if one crop fails.
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
The technology reduces workload (mechanization) and increases cultivable area leading to the cultivation of diverse crops for market purposes.
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased due to the removal of stones from the land.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Expenses on agriculture input are reduced. For example, with the use of a power tiller which costs Nu. 1500 per day, it takes 2 days to complete ploughing. If it is done by oxen then it takes 8 days and Nu. 400 is paid as a labour charge per day. The total amount required using the power tiller is Nu. 3000 and using oxen is Nu. 3200 with an additional cost of food for the labourers.
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Previously the land user was not able to meet the demand for maize as a feed for the cattle. With the introduction of stone bunding and increased production, the land user can meet her domestic demand for maize and additionally sell processed maize alcohol as a source of farm income.
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
There is an increased diversity of income sources as the land user can grow different crops throughout the year and also sell some processed products.
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced work load due to farm mechanization. The removal of stone from field had eased workability, lesser wear and tear of farm tools.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
With the increase in cultivable areas, technology has ensured food self-sufficiency and generated income to meet other household demands for food.
oportunidades recreativas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced workload is directly related to an increase in the available time for recreational opportunities.
instituciones nacionales
Comentarios/ especifique:
Support provided by the NSSC and land users' active participation in the implementation of the technology enabled the national agency to have a better understanding of the land users. Labour sharing enabled the community to work together to achieve a common goal which improved collaboration among the community members.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Awareness was created during the introduction of the technology by SLM specialists. Further, the field observation on the neighbours' fields who have already established stone bunds has led to 90% of the population knowing about the stone bunding in the locality.
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Human-wildlife conflict was reduced as wild boars were not able to climb the stone bund. Although other wild animal such as procupine continued to cause harm to the crop.
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
The technology improved soil quality leading to improved production and increased household income.
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The stone bund holds irrigation water preventing surface runoff. Further, the gradual labelling of the land increases soil moisture retention capacity.
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased due to crop diversification and year-round cultivation.
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Soil erosion and surface runoff is reduced leading to decreased soil loss.
acumulación de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Eroded soil is accumulated at bunds.
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Soil organic matter is decreased at the upper part of the terrace and increased at the lower part of the terrace due to runoff from the slopes.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased with the practice of year-round cultivation.
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
The technology increased suitability of the soil for diverse crops increasing plant diversity.
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
The better crop stand resists pest and diseases attacks on crops. To some extend, the stone bunds keep the wild boars away.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
deslizamientos/ fluyos de escombros
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced surface runoff leads to decreased landslides or debris flow.
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
The impact percentage given in this section is a mixture of farmer and professional estimates.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
No off-site impact of the technology is expected or measurable on this small scattered scale.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lluvia anual | incrementó | no muy bien |
Comentarios:
The technology does not cope well with increased annual rainfall as it loosens the foundation soil on which the stone wall is built leading to the collapsing of the stone wall.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
The benefits compared with the establishment costs for the short term are positive due to the subsidy provided.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- > 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
Total of 33 households adopted stone bunds technology.
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
All the households received incentive in the form of cash and machinery.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Sloping land is challenged by soil erosion and it has a poor ability to retain water. This challenge was alleviated by stone bunding as it significantly reduced soil degradation. |
| The land user shared that there is an increased cultivable area after the implementation of the technology. Bigger stones were excavated and piled as stone bunds increasing the total area for cultivation. |
| The technology eased farming, as agronomic practices such as tilling became efficient due to the use of power tillers. Soil depth was increased leading to ease in weeding, bed making and other management practices. |
| Stone walls prevented wild boar from entering the field reducing crop loss. Therefore, the farmers need not guard the field from wild boar. |
| Increased cultivable area and easy working conditions of the soil lead to increased production, and improved livelihood of the farm household. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The technology contributed to reducing rural-urban migration and generated employment. Stone bunding indirectly helped the farming community to engage in agricultural activities and stay back in the village rather than going out to the city in search of employment. |
| Prevent natural disasters. The Gewog is located in the steep slopes and there is a risk of landslides leading to loss of agricultural land, property, and life. Stone bunding prevents surface runoff which could aggravate and lead to land slides. |
| Once the stone and boulders are removed and piled along contour line, it improves workability on the farm. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Construction of stone bunds is a laboursome and has no direct benefit to the land users. | Practice labour sharing working modality. |
| If stone bunds were not constructed properly, it could be easily damaged by cattle, washed or collapsed by heavy rainfall. | Proper piling of stones during the stone bund construction. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Some sort of incentives is required to scale out the adoption of technology as its requires huge labour and time with no immediate benefits. | Incentive of Nu 3000 tied with construction of 1 ac of stone bunds |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Three field visits was conducted
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Randomly picked land user from the community for documentation. One land user was interviewed.
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
22/07/2023
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
NSSC. (2011). Bhutan catalogue of soil and water conservation approaches and technologies. National Soil Service Center (NSSC), Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Forests, Royal Government of Bhutan, Thimphu
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Book and soft copy from https://www.wocat.net/documents/140/Bhutan_catalogue_of_SLM_Technologies_and_Approaches.pdf
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Sustainable Land Management for improved land productivity & community livelihood in Thangrong
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-XS-qFv2dYQ
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Community Mobilization for SLM Interventions [Bután]
Community mobilization in implementing sustainable land management technologies is indispensable in engaging the community to identify their priorities, resources, needs and solutions. It ultimately promotes bottom-up participation and fosters accountability.
- Compilador: Nima Dolma Tamang
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos