Integrated Technologies for Household Plots [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Habib Kamolidinov
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_1057 - Tayikistán
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Integrated Technologies for Household Plots: 20 de marzo de 2017 (inactive)
- Integrated Technologies for Household Plots: 22 de julio de 2017 (inactive)
- Integrated Technologies for Household Plots: 14 de agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Integrated Technologies for Household Plots: 2 de noviembre de 2021 (public)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
GITEC/ADB/DMC Rural Development Project Land Management Institute - Tayikistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
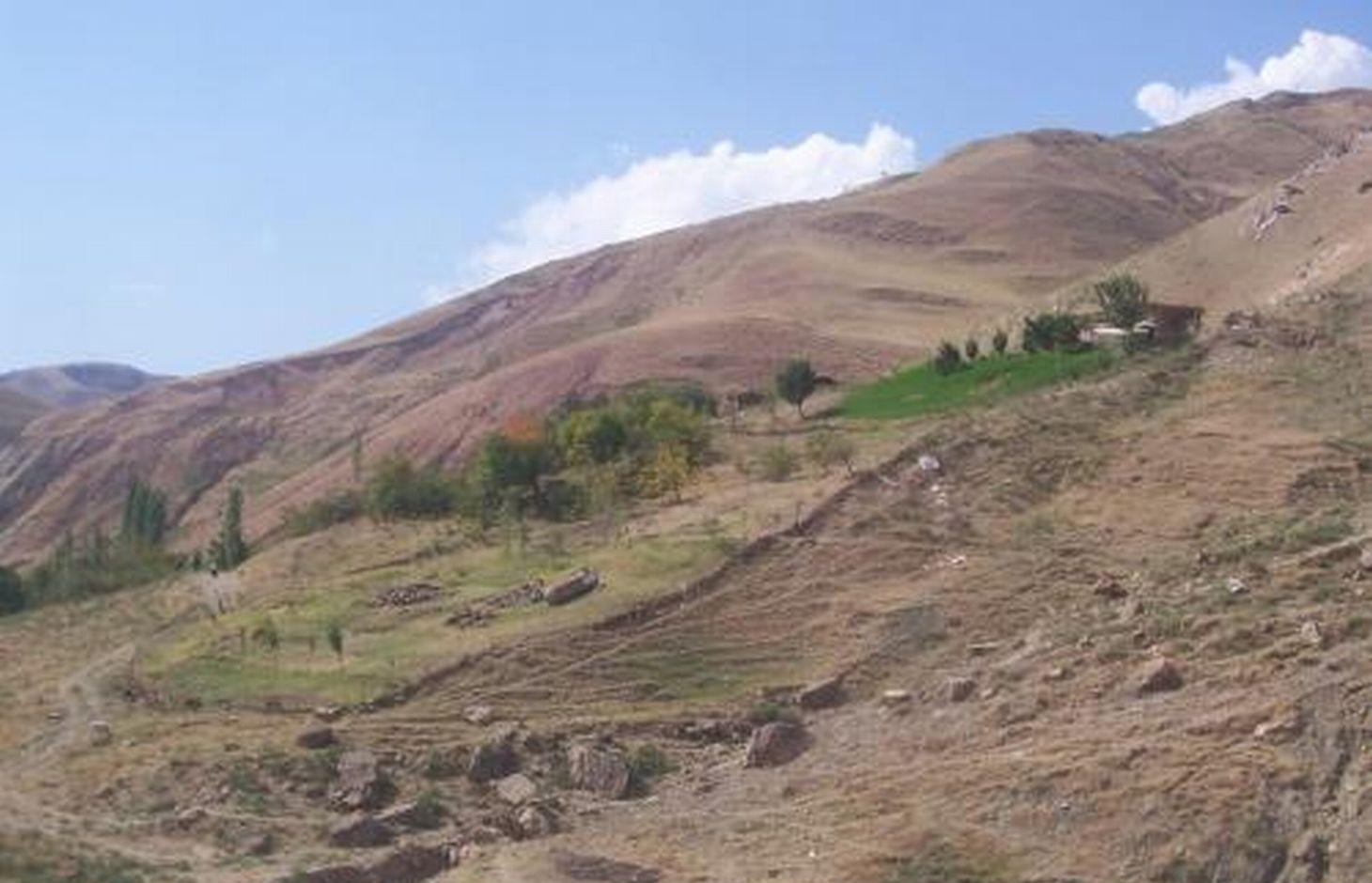
A fenced enclosure transformed with stone clearing and a small scale irrigation system, to grow a wide range of perennial, annual and orchard crops, beekeeping and small scale animal production.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
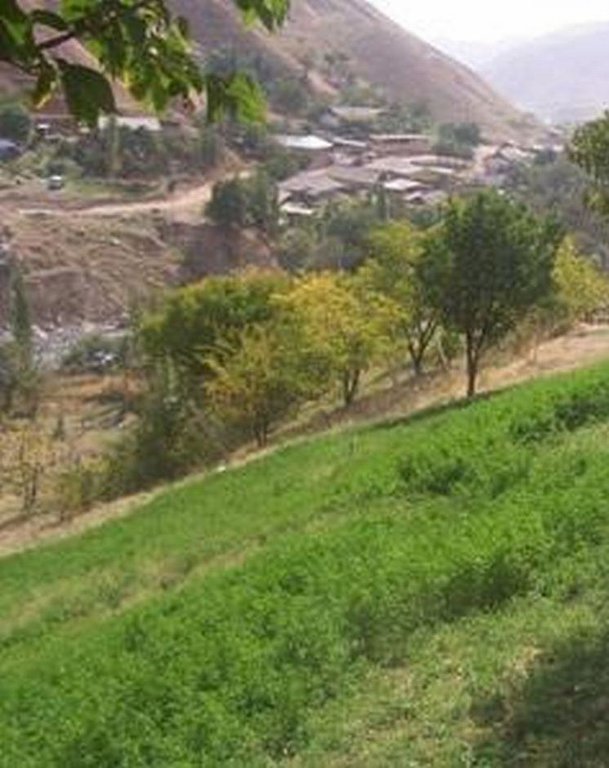
A small area of previously severely eroded and almost devoid of vegetation area of land that was transformed through the building a perimeter fence, supplying a simple irrigation system and the planting of a diverse range of crops to provide a rich, integrated farming system. Activities then completed on this area included: orchard planting, perennial fodder crops (lucerne), garden vegetables, bee keeping for honey production and small scale animal rearing.
Purpose of the Technology: The farmer clearly stated that his prime, initial purpose in taking over this “ruined and abandoned land” was to improve and better guarantee the quality of his family’s lifestyle through enhanced and assured food and fodder production. He also recognised the potential for future profit through sale of his excess produce to market. Currently, the family has almost no need to buy food (and fodder) from nearby markets, apart from flour for bread making. This is a large cost saving. In hindsight, the farmer sees that he has dramatically improved land quality within the enclosure through mitigating erosion and increasing year-round vegetation cover.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The family (Enomali is the family name) first occupied this land in 1984. The first task was tree planting – a variety of orchard trees – on 0.1 ha of the current enclosure. This was fenced using abandoned wire and metal supports from old Russian factories. After nine family members left (to work in Dushanbe) the land user expanded the fence to the current 0.2 ha and continued to plant trees. He continued the stone removal through the 1990s and even up until the present day. Lucerne and vegetable gardens were initiated in the 1990s and continue to be enriched as required. Fodder, tree and vegetable production includes an ongoing set of tasks, as does the animal feeding with the home-grown fodder. Bee keeping is seasonal and the honey kept for home consumption. The land user continues to plant orchard trees every year and currently has more than 100. He gained a “certificate” of ownership” in 2008.
Natural / human environment: Before the family occupied this land, the land user stated that it was “totally ruined and abandoned”. That is why it was unoccupied. The family were prepared to work extremely hard to convert this ruined land to the green and productive “island” that it now is. The people in the area are dependent upon the produce of the land, however suitable land is in short supply and subject to population pressures.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Central District of Tajikistan
Especifique más el lugar :
Varzob
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
The small area was all that the family could manage as there was an initial large workload, clearing stones and fence building, etc
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The land user developed the integrated approach to implentation of the technology.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- rehabilitate severely degraded land
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agroforestería

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cultivos para forraje - otros
- vegetables, orchard fruits, lucerne
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April to September

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Cortar y llevar/ cero pastoreo

Bosques
Productos y servicios:
- Frutos y nueces
Comentarios:
Livestock density (if relevant):
< 1 LU/km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Massive water erosion causing gullies, sheet washing and landslides. This leads to land denudation of the soil and vegetation. Almost total lack of soil organic matter and above/below ground biodiversity. No water holding capacity of the land – combination of steep slopes and no vegetation causes all rainwater to immediately runoff.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Same – the above words were used by the farmer in the on-farm interview.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Other type of forest: orchard species
Forest products and services: fruits and nuts
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agroforestería

Tierra de pastoreo
Comentarios:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- agroforestería
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- variedades vegetales/ razas animales mejoradas
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas estructurales
- S6: Muros, barreras, vallas, cercas

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping, cover cropping, retaining more vegetation cover, furrows (drainage, irrigation)
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
- Wm: movimiento de masas / deslizamientos de tierra

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bh: pérdida de hábitats
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bl: loss of soil life
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Post Soviet era – massive forest clearing for firewood), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Exploitation of fire wood.), overgrazing (massive overgrazing of an already depleted land resource), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Loess landscape – highly susceptible to water erosion – massively exacerbated by vegetation clearing (tree chopping and animal grazing))
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure, poverty / wealth, war and conflicts (increased natural resource pressure during the civil war.)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
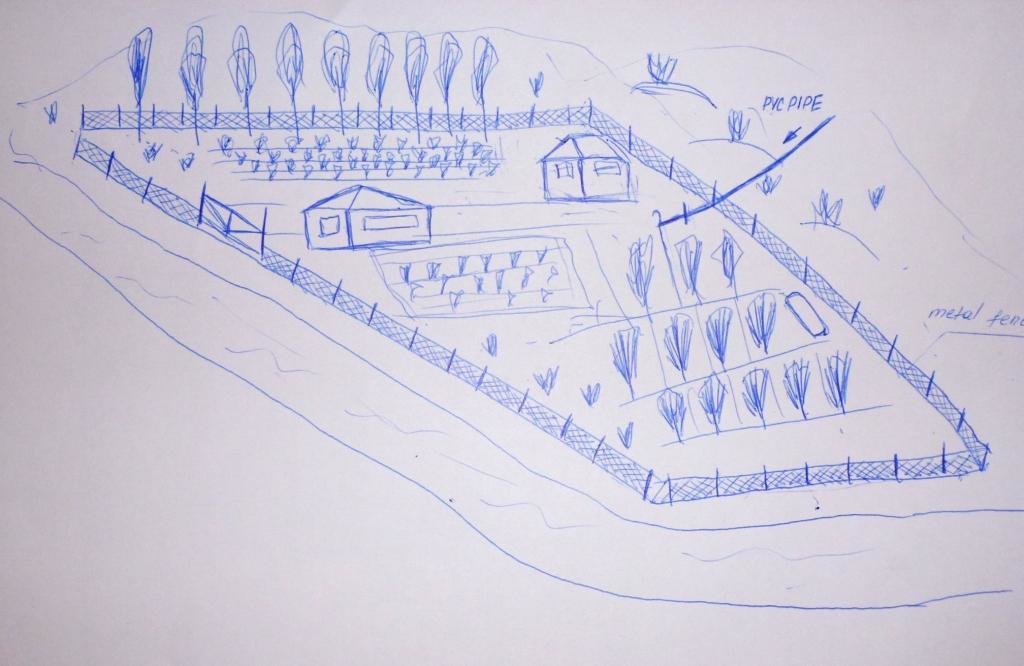
The drawing shows an enclosed area, a fence line consisting of wire fencing, brush and scrap metal materials. At the top of the slope a row of fast growing poplars was planted to protect the enclosure and the adjacent vegetable plot from the wind and rain. Perenials are intercropped with fruit trees further below the dwelling and the area is fed by an irrigation pipe originating from a local spring.
Location: Tajikistan. Varzob, Luchob
Date: 28 April 2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (If training was provided to replicate the technology.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Perennial lucerne for fodder
Quantity/ density: 100% cover
Remarks: 0.1 ha
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Lucerne is a cover crop
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: Land previously bare
Agronomic measure: other
Material/ species: Perennial legume pasture species - lucerne
Quantity/ density: 0.1 ha
Furrows (drainage, irrigation)
Material/ species: Irrigation via hand cut 20cm cube ditches and poly pipe
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
In blocks
Number of plants per (ha): 100%
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): about 0.1 ha planted
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Apple, cherry, apricot, pear
Perennial crops species: lucerne
Other species: Vegetable garden
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 38.30%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 5.24%
Wall/ barrier
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1000
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 21 degrees – measured with cli%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 3 degrees%
Autor:
Habib Kamolidinov, Land Management Institute, Giprozem 15, Dushanbe, Tajikistan
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
somoni
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
4,5
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
5.50
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fence building | At the start |
| 2. | Irrigation pipes | At the start |
| 3. | Tree planting | At the start |
| 4. | Cover cropping (lucerne replanting) | annually |
| 5. | Small vegetable beds | annually |
| 6. | Vegetable garden | annually |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Fence building | Persons/day | 100,0 | 25,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Tree planting | Persons/day | 10,0 | 25,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Cover cropping | Persons/day | 5,0 | 25,0 | 125,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Vegetable garden | Persons/day | 50,0 | 25,0 | 1250,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Trees | Pieces | 50,0 | 10,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Plants | Pieces | 3000,0 | 0,33333333 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Fence | meter | 200,0 | 2,25 | 450,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Irrigation pipe | meter | 1500,0 | 1,5 | 2250,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Labour: Small vegetable beds | Persons/day | 20,0 | 25,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 8825,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 1961,11 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 48 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Better crop cover and cover cropping | Annually |
| 2. | Stone clearing | Annually |
| 3. | Vegetable garden | Annually |
| 4. | Animal husbandry (and bee keeping) | Annual |
| 5. | Fertilising (garden vegetables) | Annual |
| 6. | Tree planting | Annually |
| 7. | Lucerne reseeding | Annually |
| 8. | Vegetable planting | Annually |
| 9. | Small vegetable beds | Annual |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Better crop cover and cover cropping | Persons/day | 10,0 | 25,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Stone clearing | Persons/day | 10,0 | 25,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Vegetable garden incl. fertilizing | Persons/day | 15,0 | 25,0 | 375,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Animal husbandry (and bee keeping) | Persons/day | 40,0 | 25,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Labour: Tree planting | Persons/day | 10,0 | 25,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Labour: Lucerne reseeding | Persons/day | 10,0 | 25,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Labour: Vegetable planting | Persons/day | 50,0 | 25,0 | 1250,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Labour: Preparing small vegetable beds | Persons/day | 20,0 | 25,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 4125,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 916,67 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: All work is done manually. There is one mule available to aid with carrying fodder and rocks., All works done manually. Mule assists with heavy lifting and carrying.
The area is approximately one hectare in total, however the costs are spread over a period of time up to 2010.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The human labour costs (I believe) are most misleading. The farmer and his family happily and willingly committed their time and effort over a period of 27 years to improving this piece of land – as they knew that their family lifestyle would vastly improve and be greatly assured through their efforts. As the farmer said during the interview: “What else would I be doing?” Meaning – this is his life and he thoroughly enjoyed the inputs, realising the richness of the outputs.
Fence costs were minimal (a few hundred dollars) as on departure of the Russians after the Soviet period, the factories were ransacked by locals for metals of all types, not a sustainable practice, but at this time gave locals access to free materials to use. In this case for fencing.
Trees – there was an initial set up cost and the farmer said he tries to plant at least 20 new trees each year to maintain and enhance productivity.
Lucerne – there was a set up cost (farmer forgets how much – but approx. $50) for seed. But now the lucerne is almost self-regenerating (from it's own seeds) as the last cut each year is for seed production that the farmer spreads in the lucerne field.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Dominate in Spring (March-May) The period June to September is very hot and dry (almost no rainfall)
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones convexas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zone: The site is exactly at 1,180 meters a.s.l.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil texture: Loess soil – silty loam
Soil fertility is high with proper management (as in intervention) these soils are very fertile. Before the intervention –extremely low fertility
Topsoil organic matter was before intervention <1%
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Availability of surface water was medium before the intervention.
Water quality (untreated) is good because the spring water is almost pure water.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
But it will have improved with intervention through dramatically increased vegetation cover
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: There is not a great difference. The farmer’s wife shares the workload but tends to focus more on the garden, fruit production, household duties and bee keeping. The farmer generally conducts hay cutting and gathering, stone removal, fence upkeep and animal tending (feeding and slaughtering when required).
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
80% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The issue is that it tends to be the older and very young family members (ie Mr Enomali and his wife are in their late 50s, and their pre-school age grandchildren stay with them) stay on the farm. The others (18 to 50 yrs old) have paid employment in Dushanbe and Russia – and only visit the farm occasionally. However, it is believed they part-finance (contribute) to the upkeep of the family farm.
Market orientation of production system: All of the farm produce stays on the farm for home consumption, but they do eat well and very healthy (fresh and organic) food.
Level of mechanization: Normally manual but with one mule to help with heavy work.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Comentarios:
Not yet an issue – as he is the only one with access to the spring water.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Comentarios/ especifique:
Prior to the technology this land was “ruined, denuded wasteland” that had almost no carrying capacity, no productivity and no water supply, so the % increase as a result of the technology is from a starting point of zero.
producción de forraje
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
calidad de forraje
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
producción animal
Cantidad antes de MST:
2
producción de madera
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
diversidad de producto
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
área de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
manejo de tierras
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
calidad de agua para ganado
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
calidad de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
ingreso agrario
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
oportunidades culturales
oportunidades recreativas
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
The primary aim of the farmer in introducing the Technology was to improve the family’s lifestyle and well being. He has easily achieved this and it seems to be getting better, year on year. The family have improved their food security and quality.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
calidad de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
cosecha/ recolección de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
escurrimiento superficial
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
drenaje de agua en exceso
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
evaporación
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
cubierta del suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
pérdida de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
compactación de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
diversidad vegetal
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
Otros impactos ecológicos
Hazard towards adverse events
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
0
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the Technology has so revolutionised the productive capacity and sustainability of the site, there are no obvious disadvantages.
colmatación río abajo
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
daño a campos de vecinos
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no se sabe |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
The establishment and ongoing costs are very small in comparison to the long and short term benefits. If natural materials cannot be used for fencing materials, then the initial establishment costs will be higher.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
1 household
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 91-100%
Comentarios:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There are (seemingly) quite a few enclosures already in this area – but these have not been reviewed.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
The land provided food security and a small income for my family. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To replicate it, maybe small grants and loans could be awarded. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
The fence building started and underpins the whole SLM initiative. That it was achieved by only 2-3 people, in a one year period and at low cost (using mainly scrap materials) adds to the strengths. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The farmer wishes to expand his fenced area so the enclosure is 1 ha in size |
|
Bringing water to the site (at his own cost) by poly pipe was a critical part to the technology. The land in the enclosure would probably have improved anyway, due to animal exclusion, but this was greatly improved by the provison of irrigation water. This is relatively a small volume of water, but it is available all year round which is key to the plants being able to survive through the hot summer months. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The farmer wishes to source a 2nd spring to water the extended (1 ha) site |
|
The rich mix of vegetation on the site (trees, perennial fodder legume and vegetable production) not only ensures the intervention remains viable but also ensures a continuous, rich, healthy food supply to the family all year round How can they be sustained / enhanced? The farmer has already started to plant new fruit trees outside the fence area, in readiness for moving the fence to encompass a 1 ha site |
|
Clearing stones was an important technological input, to greatly increase the available “growth area” for the introduced plants and trees as well as maintain soil depth. Linked to the irrigation system, the increased soil depth has greatly aided the vitality of this SLM approach – especially in the hot summer months. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Stone clearing will be a critical phase of the expansion of the enclosure to 1 ha. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| It is a lengthy process to secure land certificates. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Enclosing the land is important, however the cost of the wire fence becomes an issue. | There may be access to finance through the bank or from relatives. |
| The success of the project is dependent upon the supply of irrigated water to supplement the rainfed supply. | Areas for replication need to be assessed for water supply. There is also potential that drip irrigation schemes could help support the implementation of the technology. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos