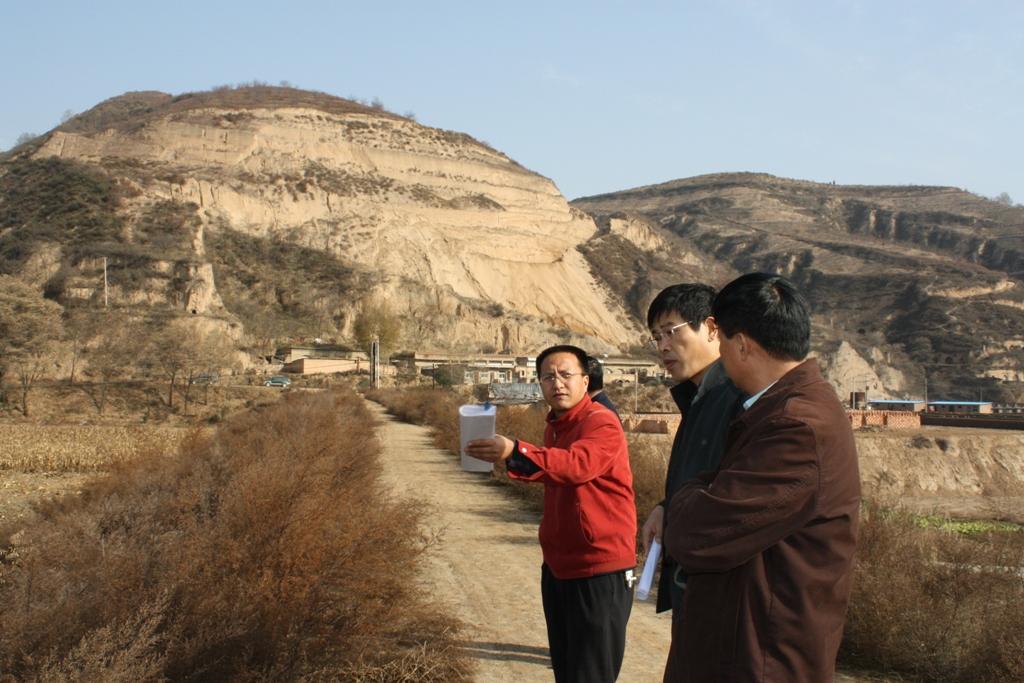
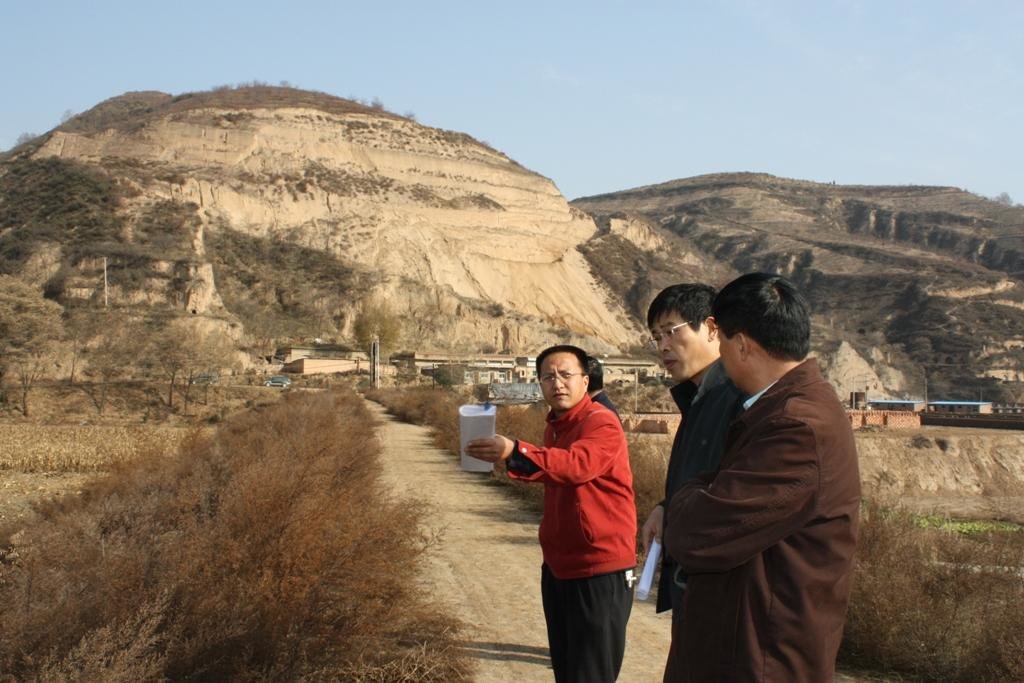
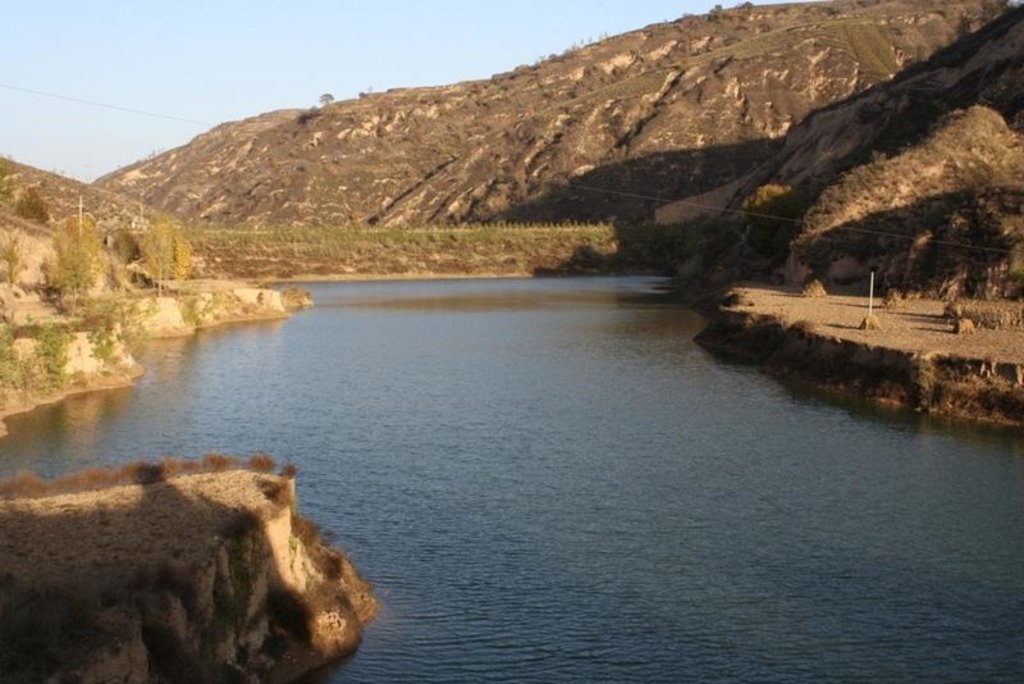
Check dam for land [China]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Fei WANG
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
淤地坝,谷坊
technologies_1455 - China
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Mu Xingming
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
China
Especialista MST:
Wen Zhongmin
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
China
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Chen Yun-ming
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
China
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Northwest A&F University (NWAFU) - China1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)
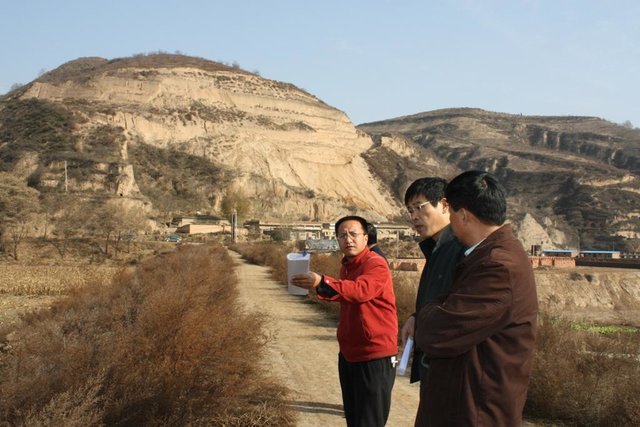

Project of check-dam for land [China]
Approach of check dam for land is a kind of soil and water conservation activity to reduce the sediment discharge and improve the agricultural condition through building a dam across the valley in order to silt the sediment from upstream untill it convert to land with few soil erosion and …
- Compilador: Fei WANG
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Check dam for land is a structural SLM practice that is constructed in the valley of a watershed in order to slow down the runoff and increase sedimentation. After this, the land quality of the controlling area will increase because soil and water conditions in this place are improved.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
The check dam is a small dam designed to reduce flow velocity, control soil erosion, and allow to settle on the bed of the valley. The whole system includes main body of dam, spillway, overflow and supporting measures. The check dam for land is a small dam mainly for land after it is filled up by the sediment from upstream area, from several years to 20 years in common, it could be flat land in the valley, not mainly for water collection (different from reservior).
Purpose of the Technology: Check dams in the Loess Plateau are very common. There are many advantages. The check dam could not only reduce the erosion of the gullies, furthermore it retain the sediment in the flow and this decreases the sediment of the Yellow River. The check dam is good quality land for the soils because of the sedimentation of organic matter and other nutrients from topsoil . In this region soils are deep and very fertile because most soil is from the top soil upstream. The soil moisture of check dam is also much better than in any other places in the watershed because the flood should go away from its surface and the water inflitration is great in raining seasons.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment needs enough money because it has to be safe enough, and the maintenance cost is not so high. The catchment with great soil erosion is better when we considered the formation time of land.
Natural / human environment: The controlling area of check dam for land varies greatly from 30 square km or more. Since the "Grain for Green" Project of China in 1999, the soil erosion on the slope decreased. The time from reservoir to land need more time because there is less and less sediment from upstream and the sedimentation changed slowly.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
China
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Shaanxi Province
Especifique más el lugar :
Yanhe River Basin
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
Comentarios:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Only one check-dam for land is listed here.
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 19.4 km2.
The total area with different measures is almost 2000 km2 . Yanhe River is a first class branch of Yellow River, China. The average channel slope is 3.26‰, and the area of whole basin is 7,687 km2. It is situated in the semi-arid North Temperate Zone with an average annual precipitation varying from 500 to 550 mm, and an average annual air temperature ranging from 8.5 to 11.4℃. It is in hilly gully area of the Loess Plateau covered by loess. The landform is broken seriously. The gully density (the length of channel in one km2) is amount to 2.1 to 4.6 km•km-2. The soil loss is severe all along.
The Ganguyi Hydrology Station (109°48′E, 36°42′N) located in the Ganguyi Town, Baota Country, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province. The area up Ganguyi Hydrology Station is 5,891 km2, including of Jingbian County(256km2), Zhidan County(708km2), Ansai County(2,699km2) and Baota County(2,228km2). The average annual runoff is 0.22 billion m3, and the runoff modulus accounting for 4,776.36 m3•km-2•yr-1. The average annual sediment flow is 4.776 million tons, and the sediment flow modulus accounting for 8,100 t•km-2•yr-1. The coarse sediment (sediment particle diameter not less than 0.05 mm) flow modulus is 2,430 t•km-2•yr-1 on the Ganguyi Hydrology Station.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- durante experimentos/ investigación
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
It is an old methodology in the Loess Plateau. Since 2003, the check dam had been determined as "Highlight Project " of the Ministry of Water Resources in order to expand in the whole area of the Yellow River Basin.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación del suelo
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agro-silvopastoralismo

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- cereales - mijo
- cultivos florales
- cultivos para forraje - alfalfa
- leguminosas y legumbres - frijoles
- cultivos de semillas oleaginosas - girasol, colza, otros
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - patatas
- buckwheat
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- dátiles
- frutas de pepita (manzanas, peras, membrillo, etc.)
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 300Longest growing period from month to month: March to NovemberSecond longest growing period in days: 200Second longest growing period from month to month: April to October

vías fluviales, masas de agua, humedales
- Estanques, diques
Comentarios:
major crop: beans, sunflower, apple, Chinese date, alfalfa, potato, millets, maize, buckwheat
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Normally, the bed of valley is V-shaped and is covered by grass and trees. For the seasonal torrent or flash, it is very difficult to plant crops. The gully also cuts down by runoff and extends because of erosion's gravity .
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): It can not be used as agricultural purpose, especially to get more food.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- medida de pendiente transversal
- manejo de agua superficial (manantial, río, lagos, mar):
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques
- S11: Otros
Comentarios:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
- Wo: efectos de degradación fuera del sitio
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (It is the reason of erosion that influence the valley.)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación del suelo
- reducir la degradación del suelo
Comentarios:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
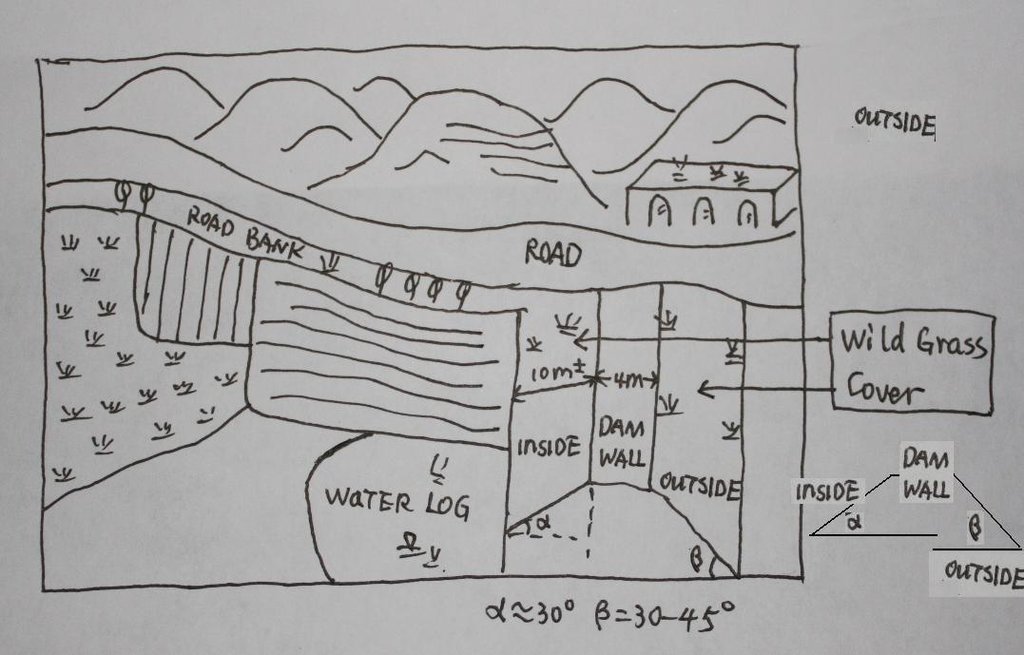
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
The check dam land.
Location: Mazhuang Watershed. Baota County, Yan'an City, Shaanxi China
Date: 2008-10-20
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The design and construction need professional knowledge.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (it is easy to use, like alluvial land or wide terrace.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Spillway
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 10
Spacing between structures (m): 100
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-100
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 300-1000
Construction material (earth): The earth-bank dam is built in Yanhe River Basin.
Construction material (stone): to build the spillways
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2-5%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 180000m3
Catchment area: 58.3km2m2
Slope of dam wall inside: 30%;
Slope of dam wall outside: 60%
Dimensions of spillways: 3m
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Autor:
Wang Fei, Yangling, Shaanxi Province, China
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
-2,17
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
8.80
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Field survey and location selection | Before design |
| 2. | Design | before construction |
| 3. | Build the dam wall | |
| 4. | Check and accept | After the construction |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Building the wall/ field survey and planning | Person/day | 180,0 | 8,8 | 1584,0 | 90,0 |
| Mano de obra | Building the wall/ field survey | Machine/hrs | 75,0 | 43,8 | 3285,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Stone | m^3 | 40,0 | 26,35 | 1054,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 5923,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | -2729,49 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | check the dam wall | annually |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | check annualy the dam wall | Person/day | 15,0 | 8,8 | 132,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 132,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | -60,83 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: crawler type bulldozer, giant jet, tractor, traditional tools, ruler,
The grass on both sides of check wall is natural grass.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The wide of dam wall affects the cost greatly, the wider, more expensive.The labour cost and the distance of rock quarry are also important.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The mean annual rainfall in the basin is 515.2 mm in the duration from 1952 to 2000. The rainfall from May to Oct accounts for 446.8 mm, up to 86.7%; and that from Jun to Sep accounts for 367.6 mm, up
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate. The accumulating time that temperature above 0 ℃ about 3800 hours, and that above 10 ℃ is more than 3200 hours
It is based on the classification sysytem only based on the rainfall.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones cóncavas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zone: All check dam and check dam liand here is in such altitudinal zonation.
Slopes on average: Based on 1:100 thousand scale landform map
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: The depth of Loess varies from nearly 30 m to more than 100 m in Yanhe River Basin. The depth of soil is less than this but it could be nearly 10 meters in commom.
Soil texture: There are more than 50% soil particle which are fine sand with size between 0.05 and 0.1 mm
Soil fertility very low: Lack of N, P and SOM
Topsoil organic matter: <0.5%
Soil drainage / infiltration good: The inflitration in Loess is very fast, but it prones to sealing when flashing
Soil water storage capacity low: Evaporation and drainage are easy
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Availability of surface water also poor/ none and: Nearly all the branches of Yanhe are seasonal rivers
Availability of surface water medium: It is very stable in this region
Water quality (untreated): Good quality for there are few pollution sources
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
It is very stable in this region
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
- comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- tracción animal
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No clear difference
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
(The Check dam for land are build together in some villages for all the people funded by national sub).
Level of mechanization also manual work: The harvesting and other management are by hand
Level of mechanization animal traction: Tillage with animal power mostly
Level of mechanization mechanized/motorized: Tillage with machine in large area check-dam land.
Market orientation of production system mixed: Some production for themselves, but most of production is exchanged on the market.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
According to 0.054 ha per capita
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
Comentarios:
Like other rural areas in China
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
600
Cantidad luego de MST:
6000
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
4500kg/ha
Cantidad luego de MST:
2500kg/ha
Comentarios/ especifique:
In extreme year with great rainfall, low yield of check dam land
diversidad de producto
área de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
950
Cantidad luego de MST:
59
Impactos socioculturales
instituciones nacionales
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Cantidad antes de MST:
200 kg
Cantidad luego de MST:
350 kg
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
drenaje de agua en exceso
nivel freático/ acuífero
Cantidad antes de MST:
8 m
Cantidad luego de MST:
4-6m
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
12-16%
Cantidad luego de MST:
16-22%
pérdida de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
60t/ha/yr
Cantidad luego de MST:
5t/ha/yr
Otros impactos ecológicos
long time period to form land
Comentarios/ especifique:
Sediment from slope decelerate the process of building arable land. In other words the economic function can not appear soon.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
inundaciones río abajo
Cantidad antes de MST:
2events/yr
Cantidad luego de MST:
nearly no
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no se sabe |
Comentarios:
The better condition of soil and water of check dam land improves the capacity of land tp cope with the changing climate.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
In the first stage, there is no economic output but the check dam is going to fill up with sediments. Afterwards the check dam forms land and with it benefit which would keep up a long time.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 11-50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
675 households in an area of 19.4 km^2 (11 percent of the area)
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
675 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: All the lands (cropland on the slope or check dam land and forest et al, ) are shared evenly by people. Of course, the work like to build check dam should be finished by all the families.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: No single farmer or family can finish this work because the land right and great investment.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: More and more local farmers want to get more check dam land for its long-term benefits.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
The yield of check dam land is much higher than that on the slope land. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ask the local people to do more work without payment because they would get more benefits from this land as such. |
|
The yield is stable because the soil moisture is good even in dry year How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use the land efficient and mainten it. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
It could reduce the soil erosion originated from the gully. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The local people know this benefit that make them try to find chance to build check dam. |
|
The dam can retain the flow and sediment and reduces the sediment delivery of the downstream. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ask the people or government of the lower reaches to combat soil erosion through the building of check dams. |
|
The check dam land is fertile and productive How can they be sustained / enhanced? When we make the plan or design the construction, we should better take this into account. |
|
Land is fertile and productive How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the awareness of local people to use this technology. |
|
The ceck dam can be used as rural road. How can they be sustained / enhanced? When we make the plan or design the construction, we should better take this into account. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| It is too expensive to build the check dam. | Ask the government or other organization and person to invest in check dams.The local people can work together without payment. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The land in a check dam with less and less soil erosion on the slope, needs longer time to form | It is difficult to overcome this because the control of erosion on slope has higher priority. We can find how to use the water or the temporary wetland. |
| The input of check dam is quite high. | Ask the government or other organization and person to invest in check dams. The local people can work together without payment. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Soil and water conservation records of Shaanxi Province. 2000. Shaanxi People's Press, Xi'an City, China
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Library of ISWC, CAS
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Project of check-dam for land [China]
Approach of check dam for land is a kind of soil and water conservation activity to reduce the sediment discharge and improve the agricultural condition through building a dam across the valley in order to silt the sediment from upstream untill it convert to land with few soil erosion and …
- Compilador: Fei WANG
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos