Plastic-lined conservation pond to store irrigation water [Nepal]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Madhav Dhakal
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Plastic bichchhayeko Samrakshan pokhari - Nepali
technologies_1462 - Nepal
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
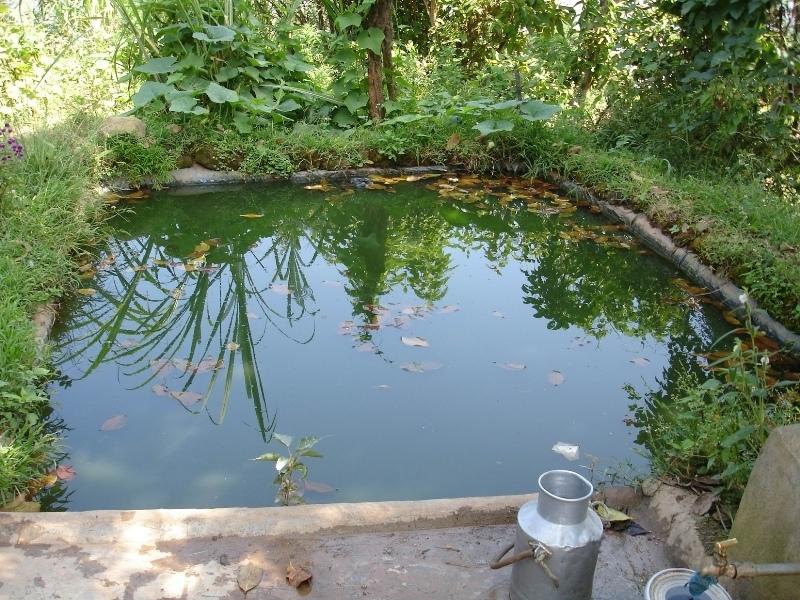
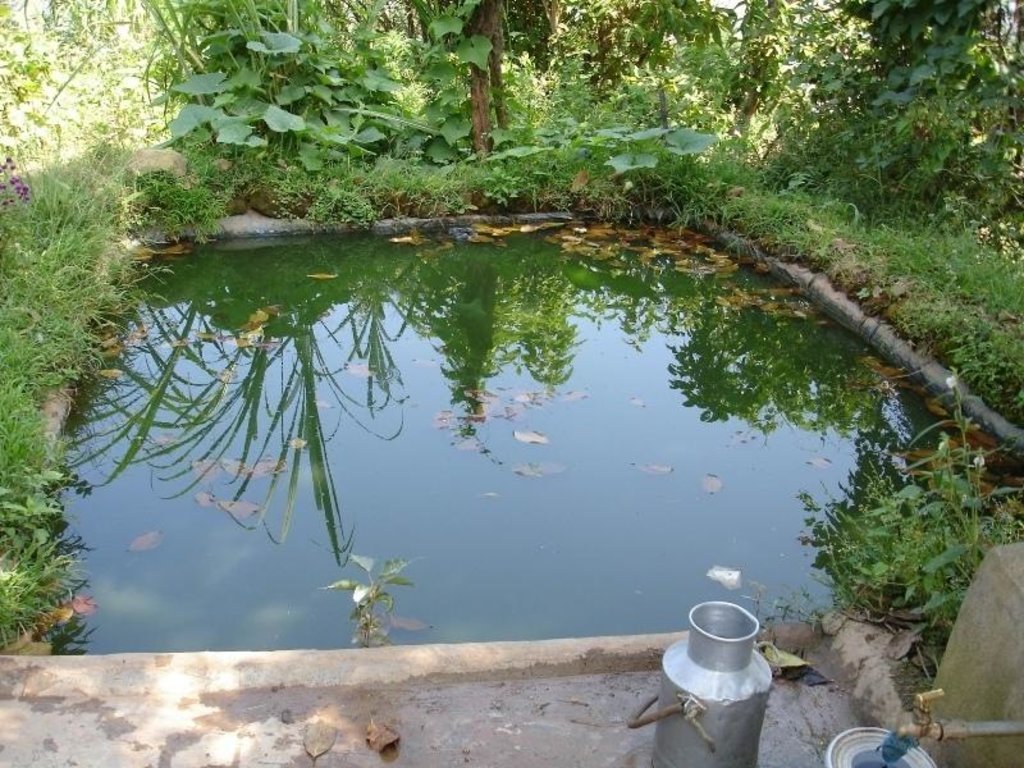
A plastic-lined dugout pond to store runoff and household wastewater for irrigation purposes during dry periods
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Water harvesting technology is very useful in areas where there is limited rainfall for long periods of the year. These dry periods severely limit the growing of crops across Nepal’s middle mountains especially on steep slopes where conventional irrigation can be difficult to arrange. Plastic-lined conservation ponds store water for irrigation more efficiently than the traditional earthen ponds which lose much water to seepage.
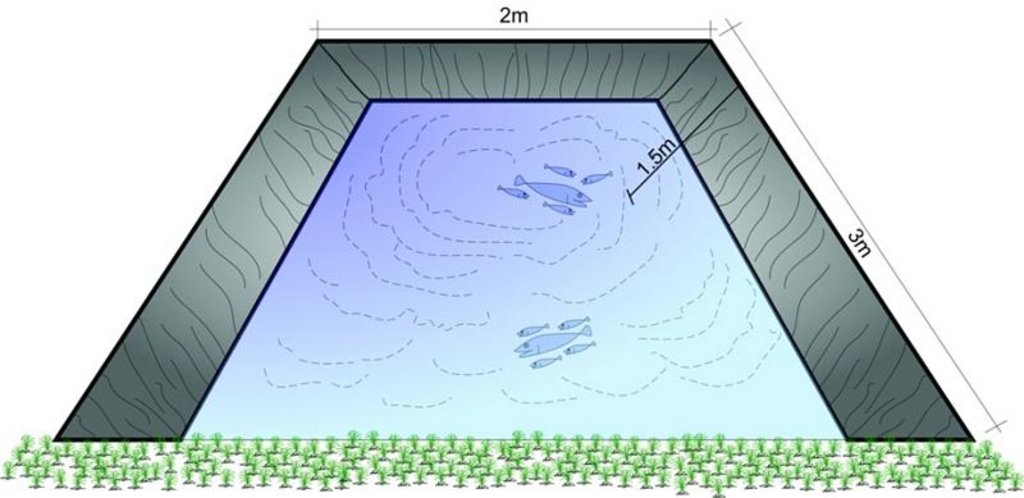
The ponds are dug out and the earthen walls lined with high density polyethylene (HDPE) sheet or SILPAULIN (multi-layered, cross laminated, UV stabilised) heavy duty plastic sheeting. The size of the pond will vary depending on the area available and the soil characteristics. The PARDYP project tested and demonstrated plastic-lined ponds with a capacity of 8,000-10,000 litres. These ponds were about 3m long, 2m wide and 1.5m deep and were located at shady sites to minimise evaporation losses. The conservation ponds tested and demonstrated by the PARDYP project were used for irrigating high value off-season horticultural crops (vegetables, fruit, and spices). These crops were irrigated with drip irrigation and micro sprinklers (see sheets QT NEP6 and QT NEP21). The ponds were fed from rainwater, upland springs and taps, and household wastewater. The ponds were established during the dry season in three days. They were prepared by selecting a suitable site with a sufficient catchment; mapping out the area and depth of the pond; digging out the soil; removing protruding stones and roots; and compacting and smoothing the sides and bottom of the pond. Then the sides and bottom of the pond were lined with sieved soil followed by plastic sheet, which was anchored by stones and soil.
The main maintenance activity is to prevent livestock and people from entering the pond to avoid damaging the sheet. The pond should not be allowed to dry up as this would let rats damage the sheet. The sediment that accumulates in the pond should be removed once a year carefully by hand only as the use of agricultural tools could puncture the sheet.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Nepal
Especifique más el lugar :
Kavrepalanchowk district/ Lamdihi, Patalekhet, Chiuribot, villages of Jhikhu Khola watershed
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
It is an ancient water management technique, later adapted according to the local condition.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- Improve water availability
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- leguminosas y legumbres - otros
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - patatas
- cultivos de semillas - sésamo, amapola, mostaza, otros
- rice, wheat, tomato
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 3
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
Comentarios:
major cash crop: Tomato and potato
major food crop: Rice and wheat
other: Mustard and legumes
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. Small landholdings which are mostly rainfed for cropping.
2. Low soil fertility status and high susceptibility to erosion.
3. Limited supplies of irrigation water and poor irrigation infrastructure.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The farmers experience serious constraints in terms of adopting better farming options, e.g., cash crops due to soil fertility and soil moisture problems.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Maize- wheat/ vegetables
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cosecha de agua
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S4: Acequias niveladas, fosas
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Plastic- linined conservation pond
Location: Patalekhet, Lamdihi and Chiurobot.. Kavrepalanchowk
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Structural measure: pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Construction material (earth): It is a earth excavated pit with earthen side walls
Construction material (other): plasitc sheet - Lining of a HDPE sheet or SILPAULIN (Multi-layered, cross laminated, UV stabilized p
Autor:
A.K. Thaku, Madhav Dhakal
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
Pond
Especifique las dimensiones de la unidad (si fuera relevante):
3m long, 2m wide and 1.5m deep
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
2.10
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a preferably fl at site with a suffi cient catchment area | dry months |
| 2. | Measure the area to be irrigated and estimate the size of the pond | dry months |
| 3. | Measure and mark out the pond | 1st day |
| 4. | Dig out the soil to the pre-determined depth | 1st day |
| 5. | Remove protruding stones and roots | 2nd day |
| 6. | Compacting and smooting the sides and bottom of the pond. | 2nd day |
| 7. | Line the sides and bottom of the pond with sieved soil (preferably a clay | 2nd day |
| 8. | Lay out the plastic sheets without any folds over the pond with | 3rd day |
| 9. | Overlay thick fine soil on the plastic sheet | 3rd day |
| 10. | Anchor the edges of the sheet at the rim of the pond with stones and soil. | 3rd day |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Dig out pond | persons/unit | 3,0 | 2,1 | 6,3 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Plastic | unit | 1,0 | 29,2 | 29,2 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 35,5 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 35,5 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prevent livestock and humans from entering the pond | daily/regularly |
| 2. | Ensure that the pond is not allowed to dry out completely as this could | dry months./regularly, |
| 3. | Removing accumulated sediment once a year carefully by hand (using | dry months./once in a year. |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Clean and maitaining the pond | persons/unit | 3,0 | 2,1 | 6,3 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 6,3 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 6,3 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: measuring tape, spade, shovel, knife, hoe, hammer, trowel, and pan
The cost given above is for unit technology having 9000 litre capacity as in 2006.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Cost of plastic, members of a household contributed as labour in all sites.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1070,00
Zona agroclimática
- húmeda
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Water quality (untreated): Also good. More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May; source: spring
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 90% of the land (ranked by land users).
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and
increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are
working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Market orientation of production system: Vegetables- commercial
Level of mechanization: Manual labour consists of planting, irrigation , harvesting, while field field preparation is carried out by animals, also machines but just in valley bottom.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- comunitarios (organizado)
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
área de producción
manejo de tierras
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to availability of more water for irrigation
Impactos socioculturales
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to informal network of farmers with ponds
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
farmers discuss and share experiences
livelihood and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
increased vegetable production, more income from vegetables.
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
fallow land is turned into cropped land
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to trapped runoff
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | no se sabe |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Perception of land users who accepted the technology by getting
incentives from the PARDYP project. If incentives are not available the short-term costs and benefits would be equal.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- > 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
5 households in an area of 10 ha
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: because of the expense of the plastic sheet and it not being locally available
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Water is sufficient to irrigate 2-3 ropani( 1 ropani = 508 sq.m.)land in one season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Advantages of the technology should be shared with large number of people. |
| Plastic pond lasted more than 5 years and it is leak proof. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Good income from sales of vegetables in the dry season can be achieved even from a small piece of land How can they be sustained / enhanced? Advantages of the technology should be more widely shared |
|
The source of water for these ponds was not only rainwater but also other sources like springs and taps, These ponds are fed with rainwater and household wastewater and from springs and taps. The ponded water was mainly used for micro irrigation including drip irrigation and micro-sprinklers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote the use of other water conserving techniques like mulching when using the harvested water |
|
Reduced the dependence on large scale water supply schemes How can they be sustained / enhanced? Harvest all possible sources of water |
|
No seepage loss observed fi ve years after building the ponds meaning that the plastic lasts at least five years How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue trials |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Plastic pond is expensive for poor farmers. | subsidised cost for poors |
| unsafe for small childrens | Protection structures should be constructed. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| SILPAULIN (multi-layered, cross laminated, UV stabilized) heavy duty plastic is not available in local markets and is expensive for poor farmers | Make it available in the local market at a subsidised cost for poor farmers. |
| The ponds attract insects, mainly mosquitoes, that cause disease; and the ponds are unsafe for small children | Regularly clean the pond and fence them in |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
ICIMOD
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
SCWMC (2004) Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Measures and Low Cost Techniques. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Component - Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
DSCWM, Kathmandu
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Shafi q, M.; Ikram, M.Z.; Nasir, A. (1995) Water Harvesting Techniques for Sustainable Agriculture in Dry and Cold Mountain Areas. Paperpresented at the Workshop on Sustainable Agriculture in Dry and Cold Mountain Areas, Pakistan Agricultural Research Council, 25-27 September1995, Queta, Pakistan
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
ICIMOD
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos