Mulch-till [Eslovenia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Gregor Kramberger
- Editor: Matjaz Glavan
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Konzervirajoča obdelava tal (mulch-till)
technologies_6241 - Eslovenia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Curk Miha
Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
Eslovenia
Especialista MST:
Cvejic Rozalija
Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
Eslovenia
usuario de la tierra:
Ropič Andrej
Farmer
Eslovenia
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor (KGZS) - Eslovenia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Mulch-till is a method of farming that does not utilise a plough, and thus the soil is not turned over. Furthermore, at least 30% of the cultivated area remains covered with organic residues left over from the previous crop. There are multiple benefits to the soil and carbon dioxide emissions are reduced.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
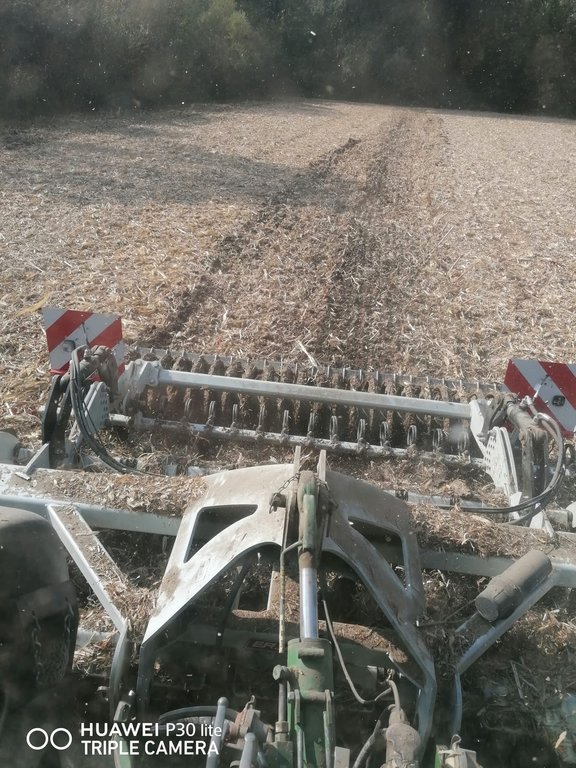
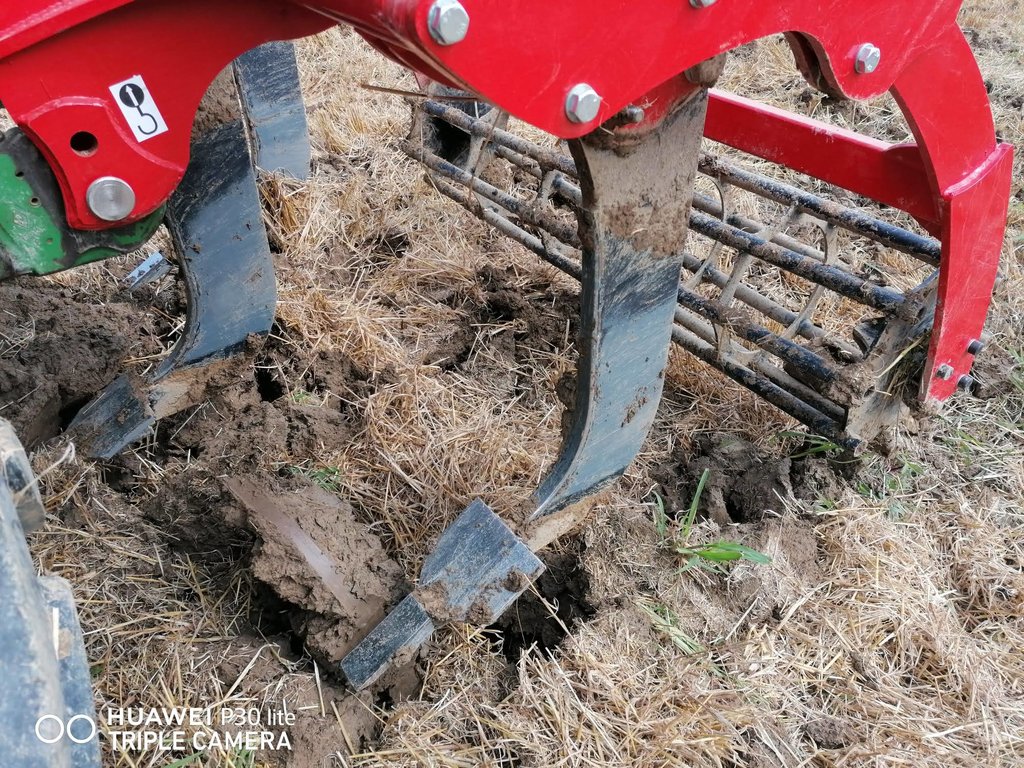
Mulch-till (also called “conservation agriculture” or “minimum tillage”) is a method of land management with modified, less intensive tillage, where land is covered with plant residues year-round (at least 30% cover) or grass, energy consumption is reduced, and there is less trampling/ compaction of the soil because of fewer machine passes and the protected surface. Under mulch-till, special agricultural machinery and attachments are required. Disc harrows and chisel ploughs are used to loosen the soil, and direct drills are employed for seeding. Ploughs are not used and the soil is not inverted. This method of tillage is intended to maintain soil structure, build up humus, improve nutrient supply and soil moisture, increase soil microbiological activity and also to prevent soil erosion. Mulch-till reduces the number of work operations on the cultivated area. Because the soil is disturbed less, this minimises the exposure of soil organic matter to the air, and therefore decreases the formation and release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
The debate over whether ploughing is still necessary has been going on for quite some time. Both mulch-till and ploughing have their advantages as well as disadvantages. Research shows that mulch-till reduces soil erosion and compaction, and this has a significant impact on soil fertility. On the other hand, ploughing better inhibits the spread of weeds and certain types of diseases and pests.
Mulch-till requires complete replacement of machines/tools, and this is a considerable initial investment. Regular annual maintenance of the equipment is needed also. Mulch-till provides full benefits after a number of years, through making sure that minimal soil inversion and organic soil coverage is guaranteed. It also requires good planning of crop rotation, the use of a special seed drill and employment of herbicides after emergence (or surface hoeing). Users mention one advantage being the low costs for tillage, which is less expensive than ploughing, and the reduction of soil erosion on sloping terrain. However, they do not like the high investment for equipment, possible lost of yields and increase in weeds: all tend to arise at the beginning of implementation. Knowledge and experience are required, as the technology is quite demanding, so there are chances of failure.
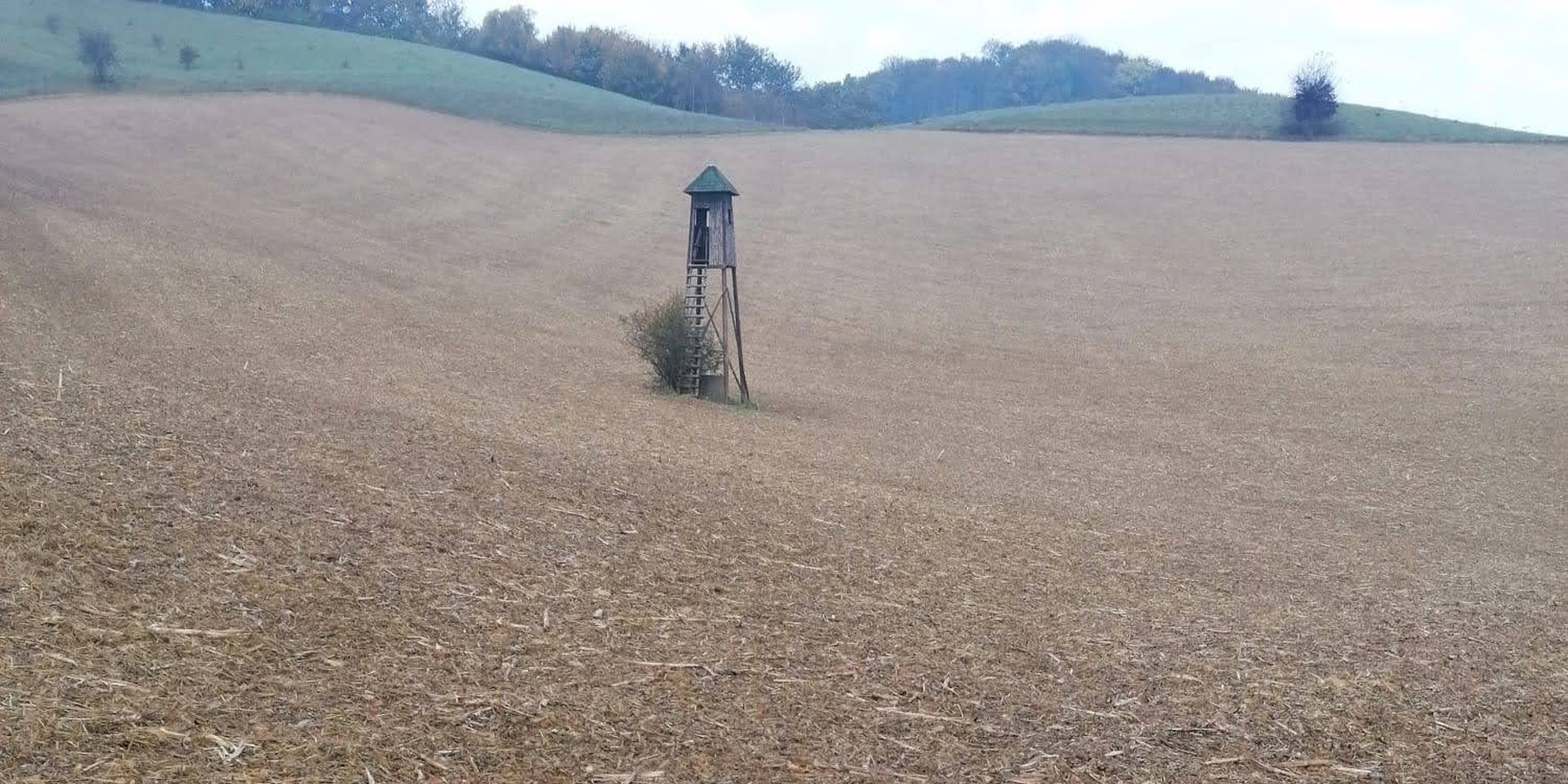
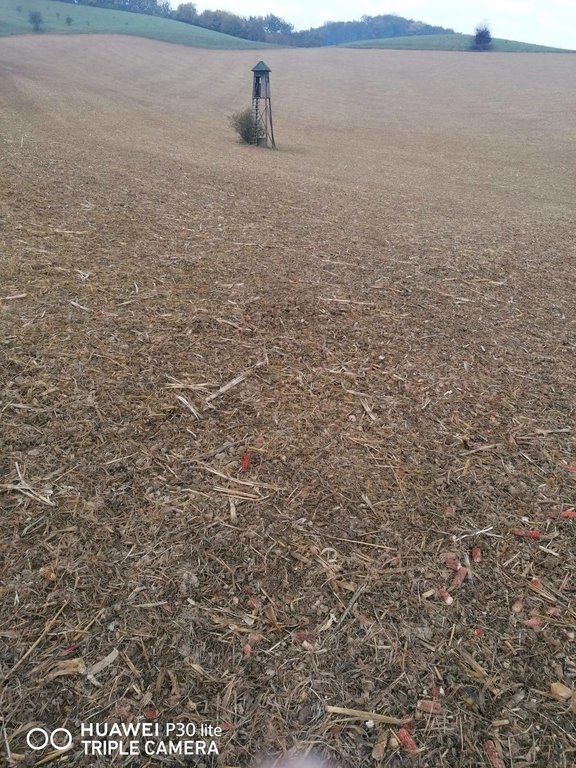
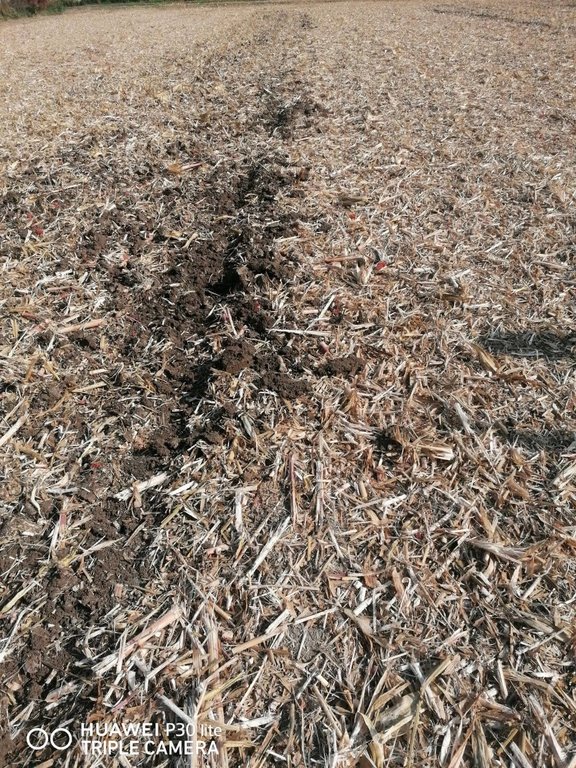
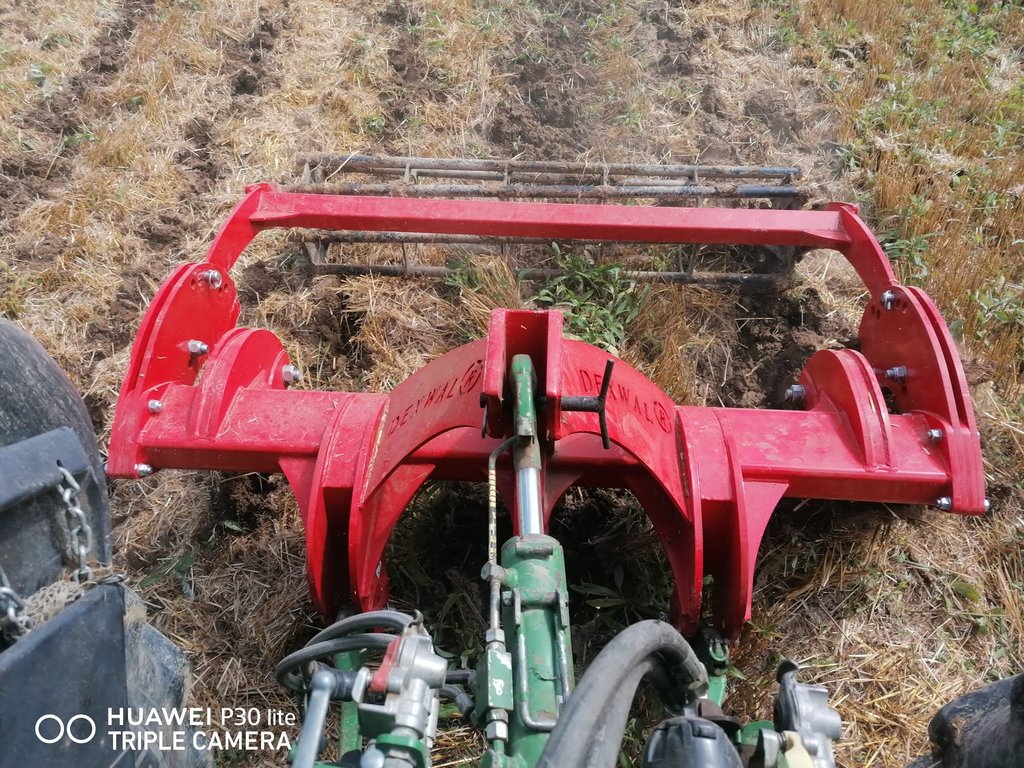
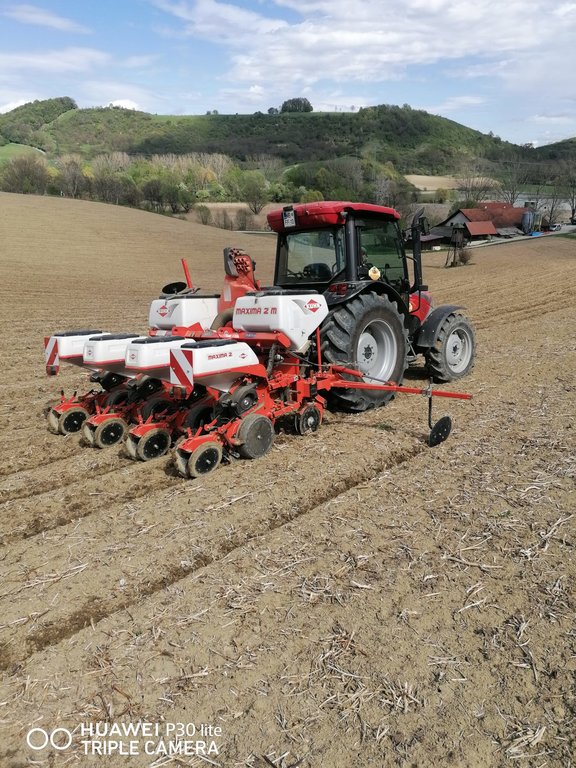
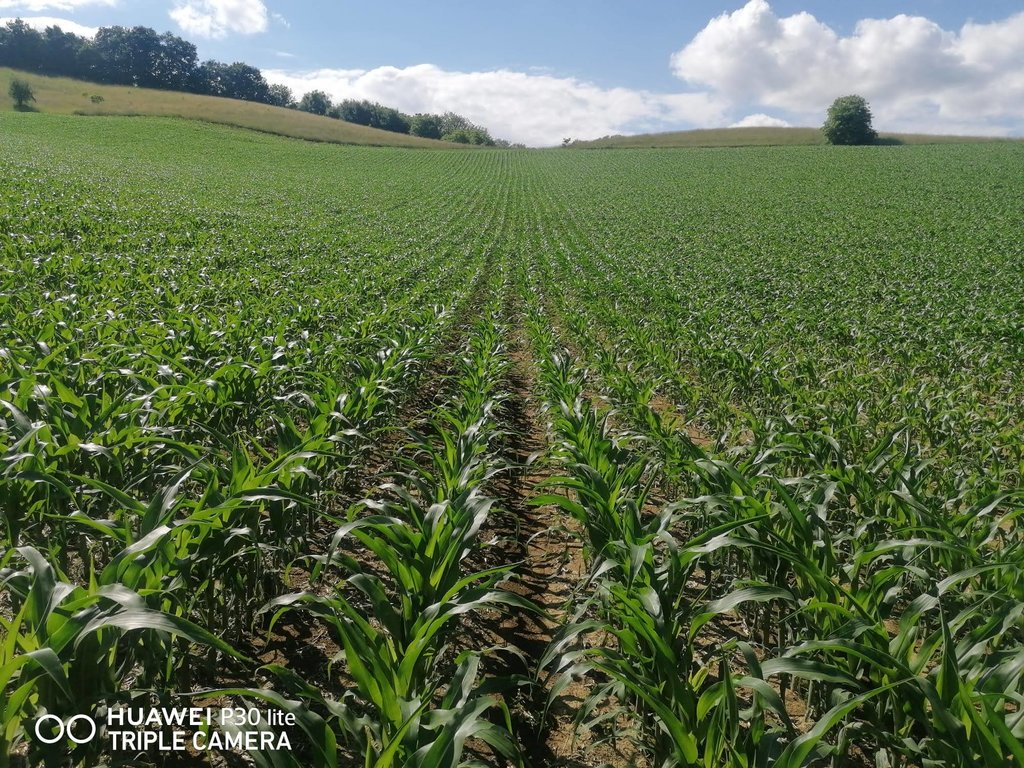
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
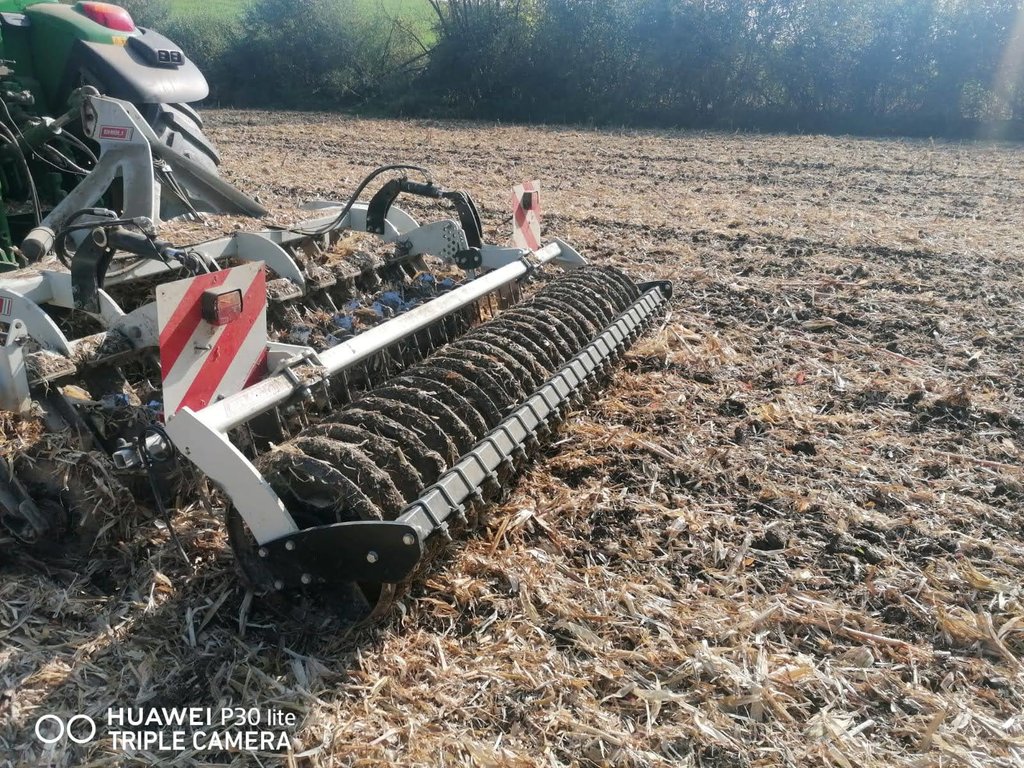
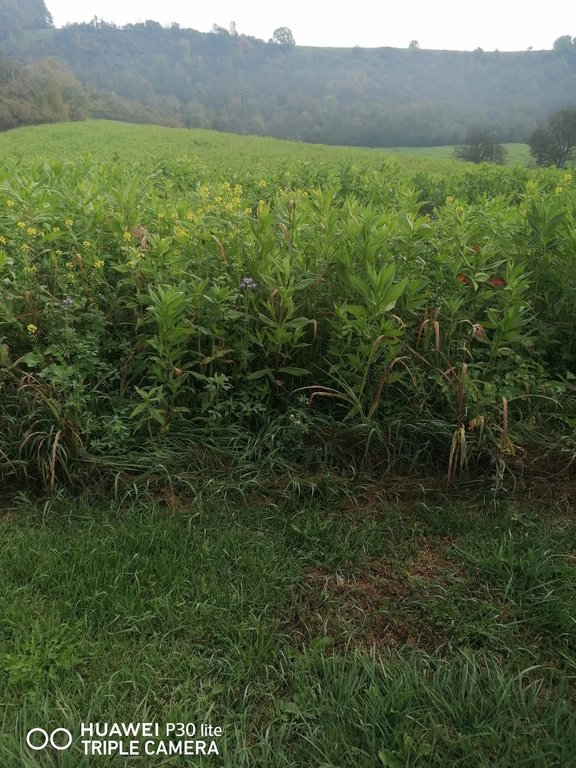
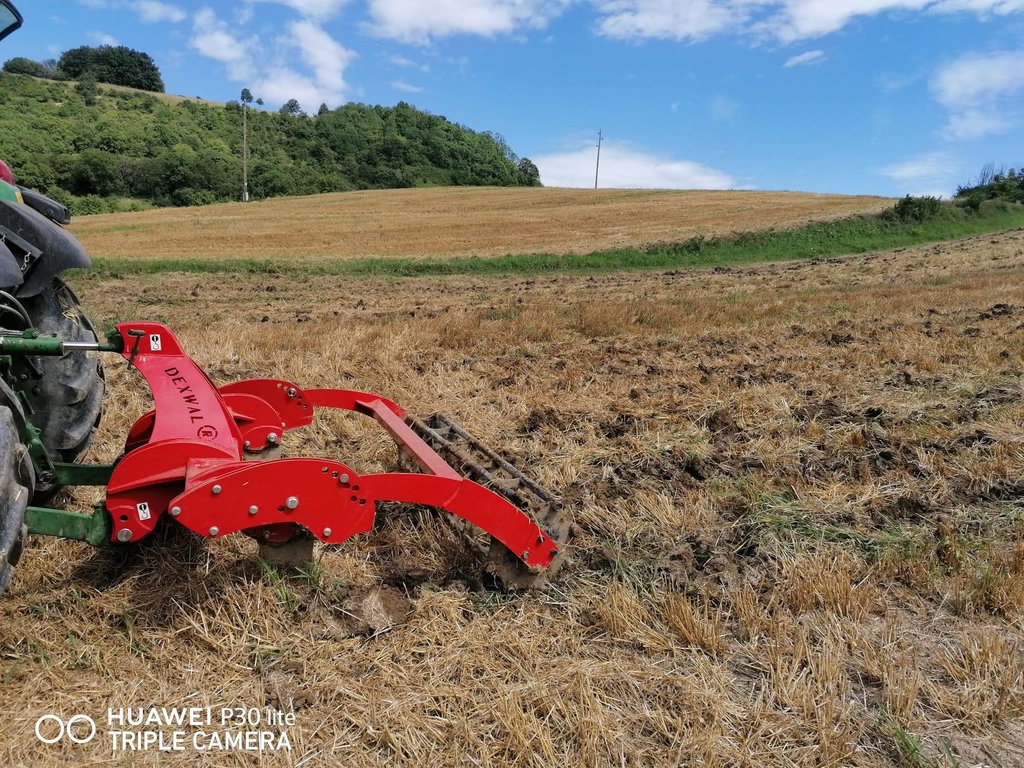
Mulch tillage technique and sowing of maize at the Ropič farm.
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Eslovenia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Jareninski dol, Pernica
Especifique más el lugar :
Vosek
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2020
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
- durante experimentos/ investigación
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
A few years ago, the farmer transitioned from traditional plowing to a mulch-tillage technique and has been using this method since 2020. In 2021, the farmer sought assistance from a consulting service to connect with the Biotechnical faculty in Ljubljana. Tests were conducted to assess the impact of conservation tillage. Following the positive results, the farmer has continued collaborating with the Biotechnical faculty and the public advisory service, further experimenting with the technology and maintaining the new cultivation approach. Today, he is one of the prominent advocates of conservation tillage.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- mitigar cambio climático y sus impactos
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - cebada
- cereales - maíz
- cereales - trigo (invierno)
- cultivos para forraje - trébol
- cultivos para forraje - otros
- leguminosas y legumbres - otros
- leguminosas y legumbres - soya
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Continuously 1 main crop: maize, wheat (winter) or barely (winter) and fodder peas or soy. After the main crop, the rotation includes cover crops (greening) which consist of mixtures of plants such as phacelia, clover, mung bean, etc.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- No (Continúe con la pregunta 3.4)
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- perturbación mínima del suelo
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo
- A3: Tratamiento de superficie del suelo
- A6: Manejo de residuos
A3: Diferencie sistemas de labranza:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
A6: Especifique manejo de residuos:
A 6.4: retenido
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Whether it is low-till or conventional tillage depends on the tool use during soil tillage and how we use it. There are many implementation variants of conservation tillage that go by different professional names and definitions. Low-till is defined according to the depth of tillage, the intensity of soil layer mixing, the coverage of soil surface with harvest (organic) residues or intermediate tillage residues, according to the way tools move on the soil and the number of machine operations that are performed individually or combined (basic tillage, soil loosening seedbed preparation, pre-sowing tillage, sowing, ...). We focus on one version of low-till that we estimate has the greatest chances of being established in a short time in the case study area, which is so called »mulch-till«. We will concentrate on the term »mulch-till« which we define as a medium deep (10 cm) conservation tillage technique using chisel plow in combination with disk harrow. The coverage of the soil surface with residues must be at least 30% or higher. In addition, a special seeder is required to carry out "mulch" sowing (with moving parts). The success of mulch-till also depends on the combination with other implemented measures like crop rotation, cover crops, etc.
Autor:
Bodenbear beitung und Bestellung
Fecha:
2015
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
1 ha
Si usa una unidad de área local, indique el factor de conversión a una hectárea (ej. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 ha = 10,000 m2
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
EUR
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
0,97
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
90.90
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of 2-row disc harrow | 1st year |
| 2. | Purchase deep chisel plow | 1st year |
| 3. | Purchase pneumatic seed drill combined with rotary harrow | 1st year |
| 4. | Purchase pneumatic precision planter with rotating elements | 1st year |
| 5. | Purchase cover crop seed drill | 1st year |
Comentarios:
Tractor should also be considered as part of the investment in implementing the mulch-till technology. The required tractor for operating Mulch-till is at least 110 HP. Let's assume a tractor with four-wheel drive, 95–125 kW (129–170 HP), with an investment cost of 66,400 €. Its usage should be economically justified for the entire farm (used for all farm tasks).
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipo | Purchase of 2-row disc harrow | piece | 29,7 | 404,0404 | 12000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Purchase deep chisel plow | piece | 29,7 | 101,0101 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Pneumatic seed drill combined with rotary harrow | piece | 29,7 | 909,0909 | 27000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Pneumatic precision planter with rotating elements | piece | 29,7 | 572,3905 | 17000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Cover crop seed drill | piece | 29,7 | 151,5151 | 4500,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 63500,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 65463,92 | |||||
Comentarios:
The estimated lifespan of the equipment represents only an illustrative measure in terms of total hours, hectares, or machine work until its obsolescence. This data is not considered in the cost calculation. It is generally not economically viable to use a machine until its complete obsolescence, as it may become technologically outdated or require excessive investment for restoration compared to its economic usage. It is more sensible to use the machine's depreciation period. The average depreciation value is determined based on the average annual usage of the machine. The depreciation period for attachments is 12 years.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tractor operation and maintanance | It is used for all operations related to the technology (without cover crop seed drill operation).. |
| 2. | Deep chisel plow operation and maintanance | 1 time per 5 years, on all cultivated field surfaces (29,7 ha), 1.0 h/ha. |
| 3. | 2-row disc harrow operation and maintanance | 2 time per year, on all cultivated field surfaces (29,7 ha), 0.8 h/ha. |
| 4. | Pneumatic precision planter with rotating elements operation and maintanance | 1 times per year, on 50 % of all cultivated field surfaces (14.85 ha), 1.3 h/ha. |
| 5. | Cover crop seed drill operation and maintanance | 1 time per year, on all cultivated field surfaces (29,7 ha), 0.8 h/ha (combined with harrow). |
| 6. | Pneumatic seed drill combined with rotary harrow operation and maintanance | 1 times per year, on 50 % of all cultivated field surfaces (14,85 ha), 1.4 h/ha. |
| 7. | Purchase cover crop seed mixture Fruh | 1 time per year, on all cultivated field surfaces (29,7 ha). |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Tractor operation | EUR/ha | 29,7 | 18,144 | 538,88 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Machine maintenance | EUR/ha | 29,7 | 2,88 | 85,54 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Machine avarage total costs of tractor operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 29,7 | 122,598 | 3641,16 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Machine avarage total costs of deep chisel plow operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 29,7 | 4,36 | 129,49 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Machine avarage total costs of 2-row disc harrow operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 29,7 | 30,432 | 903,83 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Machine avarage total costs of pneumatic precision planter with rotating elements operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 14,85 | 29,744 | 441,7 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Machine avarage total costs of cover crop seed drill operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 29,7 | 2,872 | 85,3 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Machine avarage total costs of Pneumatic seed drill combined with rotary harrow operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 14,85 | 52,416 | 778,38 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Cover crop mixture Fruh | EUR/ha | 29,7 | 66,768 | 1983,01 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 8587,29 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 8852,88 | |||||
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
It very much depends on the type of soil, what is the structure of the soil. In addition, the planning of the crop rotation and cover crops also affect the costs. As a result, weed development and subsequent herbicide use may be different.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1015,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
The most precipitation falls in summer, the months with the highest average precipitation are June and August, the least precipitation falls in winter, in January and February at least, and in principle more precipitation falls in autumn than in spring.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Jareninski vrh (1981 – 2010)
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Mean annual temperature in year 2014 Jareninski vrh is 11,9°C.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones cóncavas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
There are depressions, settlements are in the valley, concave type.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Hydromelioration was carried out in the area, a drainage system and water retention systems (e.g. ponds and basins) were arranged.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- arrendamiento
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
No
Especifique:
based on national legal system
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Some farmers report a slight drop in yield in first years after the implementation of the measure, but the farmer in the case study location didn't notice any difference in yield.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced risk, but with the wrong approach it can increase. For example, reduced risk due to unfavorable weather conditions, increased risk due to the possibility of weed development.
manejo de tierras
Comentarios/ especifique:
Simplified soil tillage technology.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced costs due to lower energy (fuel) consumption.
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Fewer hours dedicated for tillage.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Facilitated production with lower costs, motivation to do business in agriculture.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
With positive effects more interest of the farmer in sustainable production.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
acumulación de suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
especies invasoras extrañas
diversidad animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Cover crops act as hiding places for various animals.
especies benéficas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Plants attract pollinators.
diversidad de hábitats
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de sequías
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios/ especifique:
Surface cover with plants.
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
Comentarios/ especifique:
The soil is not carried into ditches and ponds.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lluvia anual | disminuyó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | muy bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| ola de calor | bien |
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| deslizamiento | muy bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
The initial establishment and investment costs for implementing the technology are high, and in the short term, the benefits may not be very noticeable or even negative compared to conservative technology. However, the long-term benefits are more significant and positive. While there are recurring costs involved, such as maintenance expenses, they are considerably lower compared to the initial investment costs. The technology requires substantial upfront investment in equipment, which can initially outweigh the immediate returns. It takes time for the technology to mature and for the full benefits to be realized. As the system becomes established and optimized, the positive outcomes become more apparent over the long run. Additionally, the lower costs mentioned refer to the ongoing maintenance and operational expenses required to sustain the technology (machines), which are generally lower than the initial investment costs. These costs are often outweighed by the benefits gained from improved efficiency, reduced resource consumption, and other long-term advantages. Therefore, while the short-term returns may not be overwhelmingly positive, the investment in the technology pays off over time, with greater benefits and lower operational costs.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
otros (especifique):
added equipment/mechanization attachments to facilitate technology implementation, improved technology implementation with knowledge and experience
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
Added cover crop seed drill. more emphasis on cover crop.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Less depression, erosion and soil leaching. |
| Cost and time (fewer passes, machine hours, less machine power required). |
| Care for nature, sustain natural resources. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| In the long term it enables the achievement of better soil conditions, in terms of appropriate ratios of water, air, nutrients, organic matter, microbial activity, pH, microbial activity, pH and other factors of soil fertility. |
| Compaction and drying of the top layer of the soil is significantly less frequent and as a result losses of young plants are therefore smaller. |
| It reduces the potential for soil erosion. A major threat to soil fertility is erosion processes (wind, water and other erosion), where the most fertile surface layers of the soil are carried away to other parts of the ecosystem that are not intended for food production. |
| It brings advantages in terms of energy consumption and the possibility of carrying out production tasks in a shorter time and in difficult weather conditions. Conservation tillage tools typically operate in a shallower soil layer and mix less soil mass, it enables the use of tools with larger working widths and thus less unproductive driving in the field. |
| Benefits in terms of reduced transfer of phytopharmaceuticals and nutrients excess from the cultivation area to water and other ecosystems. |
| Reduced tillage improves soil quality, reduces nutrient leaching and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Benefits in terms of bioavailability and nutrient uptake efficiency. |
| Benefits in terms of greater adaptability of crops to extreme weather events. |
| Benefits in terms of maintaining the overall biological diversity of the agricultural landscape and soil. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| A big investment in machinery. | It is possible to start gradually with cheaper and simpler machines (also home-made). |
| Adaptation of crop protection. | Implementing integrated pest management (IPM). |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| An increase in the occurrence of certain types of weeds and a high dependence on certain types of herbicides. Some studies show that the introduction of conservation tillage slightly increases losses from certain diseases and pests. | For successful weed control, it is important to have a varied crop rotation, frequent sowing of cover crops and intercrops, and that the weeds never leave uncontrolled development on the stubble. The variegated crop rotation is meant as an obstacle that interrupts the development cycle of diseases and pests. How we handle harvest residues is also important. The more finely they are chopped by combines, mulchers or tools for vertical tillage before sowing, the faster they decompose and the worse the chances of harmful organisms developing on them. An evenly distributed mulch of harvest residues should remain, which prevents the emergence of new waves of weeds. These additional measures, together with mechanical weed control with new types of tools, allow limiting the weed population to a level that can be controlled with a limited range of herbicides. |
| Investment costs in machines designed for the method of soil cultivation can be very high. An important obstacle in the introduction of conservation tillage is the large investments in new machinery... The value of purchasing these tools can well exceed the amount of 100,000 euros for an individual farm, which is a practically unfeasible investment for small farms. | Small farms can take the transition to conservation farming only with the help of hired machinery services from neighbouring large farms that have been able to invest in new equipment. The subsidization of the purchase of machinery and also the economic legal status of the farm in terms of VAT calculation play an important role. |
| It is necessary to replace all the tools used by farmers according to the old methods of tillage. It is necessary to purchase adapted cultivators, harrows, looseners and especially seeder drills. | Increase in the supply of relatively inexpensive machines from manufacturers from Eastern Europe and Turkey, which can increase the availability of this equipment to smaller farms. |
| In the first years of the transition period, there may be a significant reduction in yields and poor financial results. There is a yield reduction and financial stress during the transition period to the new system. The transition from conventional cultivation to conservation tillage is usually difficult and risky. | Growers must be financially strong in order to make the transition, and the areas under alternative cultivation systems must increase gradually when they really master the new cultivation technique. Good financial support during the transition period is very important for small farms with weak investment assets. Targeted education and training is necessary, as technological errors due to lack of knowledge regarding the implementation of conservation cultivation in different soil types can be economically very fatal. |
| A small increase in the seeding rate (10 to 15 %) is often recommended to compensate for losses caused by diseases and pests at the time of plant emergence. | A necessary cost that must be accepted (higher sowing rate for the main crops and additional crops – cover crops) for the successful implementation of the measure. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
1 farmer (Andrej Ropič)
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
3 (Biotechnical Faculty; Matjaž Glavan, Miha Curk, and Rozalija Cvejič)
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
2 (we utilized the following documents: "ANALYSIS OF ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY OF ALTERNATIVE AGRONOMIC PRACTICE (AAP) ON VVO" by Črtomir Rozman, Karmen Pažek, Mario Lešnik, and "Bodenbearbeitung und Bestellung Definition von Bodenbearbeitungs- und Bestellsystemen" (translated to English as "Tillage and cultivation Definition of tillage and cultivation systems") by Dr. Joachim Bischoff et al.)
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
17/01/2023
Comentarios:
Visit to the farm and farmer interview. A working group was established, where we met 2 times to review and respond to the questionnaire.
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
TJ Townsend, SJ Ramsden, P Wilson. Analysing reduced tillage practices within a bio-economic modelling framework. Agricultural Systems 146 (2016) 91–102.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
ScienceDirect
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
E Houshyar, MJ SheikhDavoodi, M Almassi, H Bahrami, H Azadi, M Omidi, G Sayyad, F Witlox. Silage corn production in conventional and conservation tillage systems. Part I: Sustainability analysis using combination of GIS/AHP and multi-fuzzy modeling. Ecological Indicators 39 (2014) 102–114.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
ScienceDirect
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
C Rozman, K Pažek, M Lešnik. Analiza ekonomske ucinkovitosti alternativne agronomske prakse (AAP) na VVO. Univerza v Mariboru, Fakulteta za kmetijstvo in biosistemske vede, 2018.
URL:
https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjNtpH7peD8AhWFzaQKHdPXBM4QFnoECAYQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.kgzs-ms.si%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2018%2F07%2FD.T3.3.1-Study-final-May-2018.pdf&usg=AOvVaw3qni6nXmwUM25mhI0FwPln
Título/ descripción:
Mimalna obdelava tal – praktični primeri na naših kmetijah (žipo, ropic, horvat)
URL:
https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwiZ6smRpuD8AhWrsaQKHcRSBoMQFnoECAkQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.kmetijski-zavod.si%2FPortals%2F0%2Flombergarjevi%2FMinimalna%2520obdelava%2520tal%2520%25E2%2580%2593%2520prakti%25C4%258Dni%2520primeri%2520na%2520na%25C5%25A1ih%2520kmetijah%2520%5BSamodejno%2520shranjeno%5D.pdf%3Fver%3D2021-12-13-094249-623&usg=AOvVaw1jtWGuL4ovgrvC0rvqm1iS
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos