Retention ditches for soil and water conservation [Kenia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: William Akwanyi
- Editores: Innocent Faith, JARED AYIENA, Noel Templer, George Onyango, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger, Sally Bunning
Mitaro ya kuhifadhi maji (Kiswahili)
technologies_6675 - Kenia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
Odongo Rosemary Ogola
Welthungerhilfe
Kenia
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Kenia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
Farmers who have implemented the technology have been able to control surface runoff at their farms.
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Community Resource Persons (CRP) in agricultural extension [Kenia]
Community Resource Persons (CRP) form a farmer-to-farmer learning approach that bridges the gap in agricultural extension, increases farmers' access to agricultural information (SLM knowledge), and increases the adoption of SLM practices.
- Compilador: William Akwanyi
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
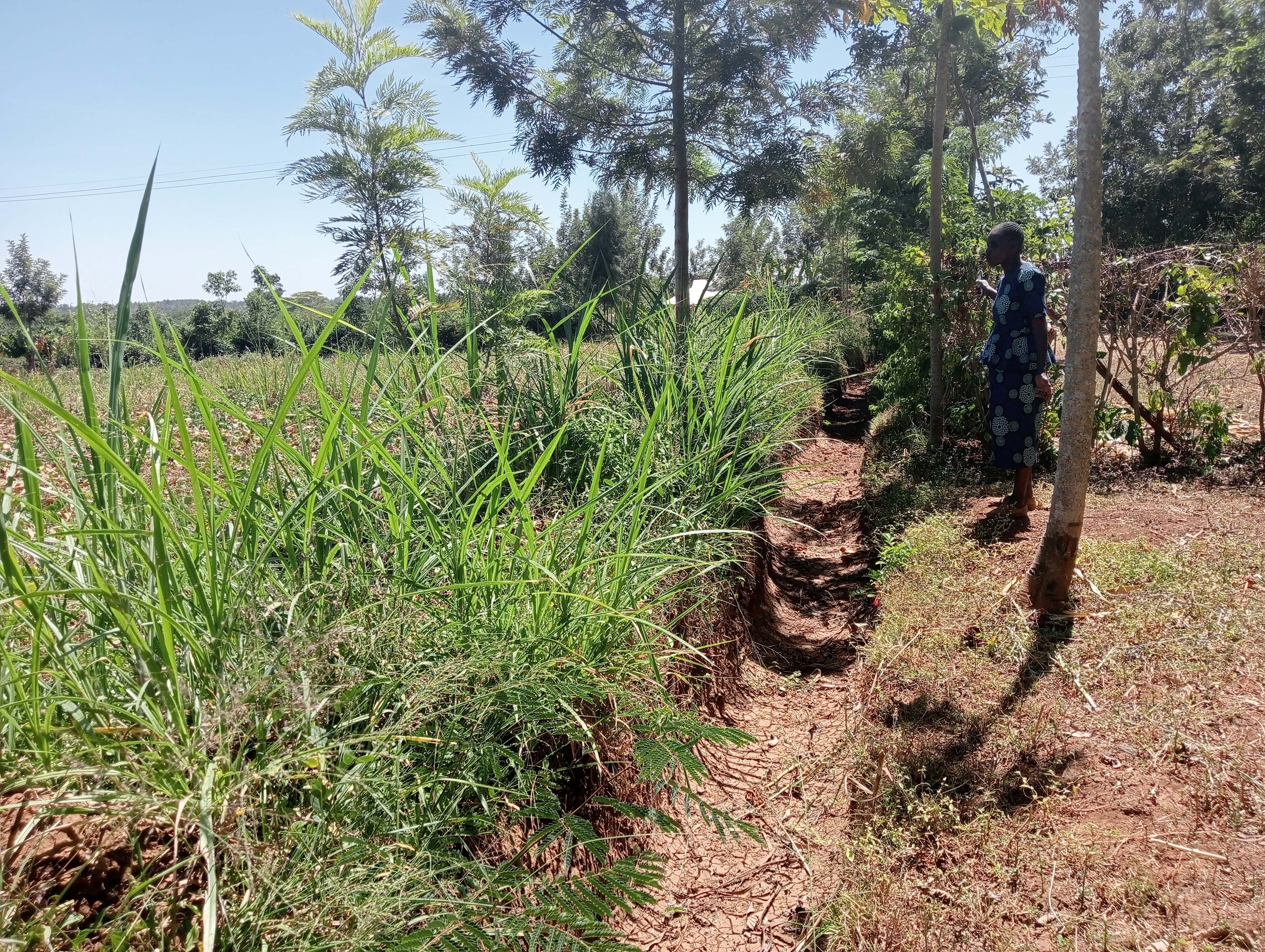
Retention ditches are channels aligned along the contour which are designed for surface runoff management. They improve water infiltration into the ground and prevent soil erosion.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Retention ditches are soil and water conservation practices. They are channels dug along contours (i.e., across the slope), especially at the uppermost part of the farm to retain stormwater/ surface runoff. They typically comprise two components: (a) vegetational-biological and (b) mechanical-structural components which are integrated to collect surface runoff, allowing for sediment carried by runoff to settle as water infiltrates into the ground. The mechanical-structural component consists of channels dug in such a way that they follow the contour and run perpendicular to the flow of water in areas where runoff naturally flows or collects. The soil excavated from the ditch forms a bund below the ditch. Retention ditches prevent surface runoff from outside the farm from flowing into or through the farm. The vegetational-biological component consists of plants grown on the bunds. The plant roots bind the soil thus increasing the slope stability, especially of the bunds; thus, preventing soil from collapsing and falling back into the channel. Retention ditches thus harvest and retain water (especially in low rainfall areas) preventing fertile soil from being washed away by surface runoff and increasing water availability for plants. In high-rainfall areas, they play the role of discharging excessive runoff into waterways.
Retention ditches are dug to about 60 cm deep and about 50 cm wide. To ensure stability, especially in areas with unstable soils, the top width is made wider than the bottom width allowing for slanting walls that are more stable than vertical walls. An understanding of the slope angle is an important factor in the designing and construction of retention ditches. A line-level (a spirit level attached to a string suspended between two poles) can be used to determine the measure slope. The slope angle determines the size of the ditch (depth and width) and the spacing between successive ditches on the same piece of land. In low-rainfall areas (such as Siaya), retention ditches are spaced at about 50 – 70 m while in high-rainfall areas the space between the ditches are closer (about 20 m). Similarly, the size of the retention ditches increases with increasing slope.
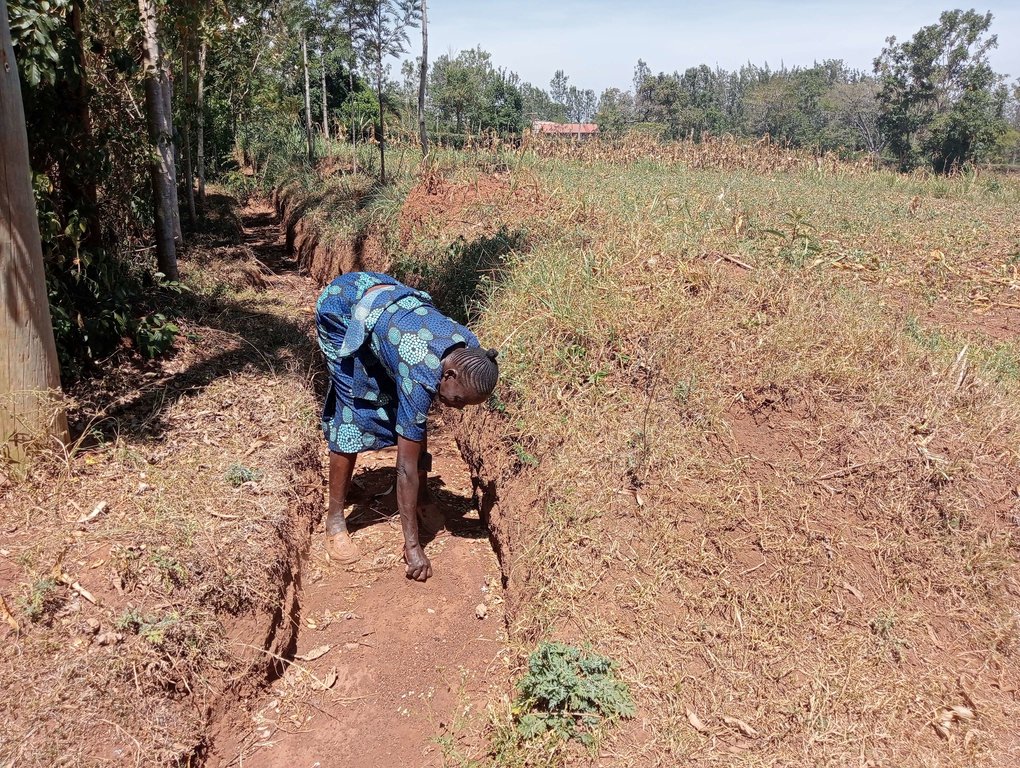
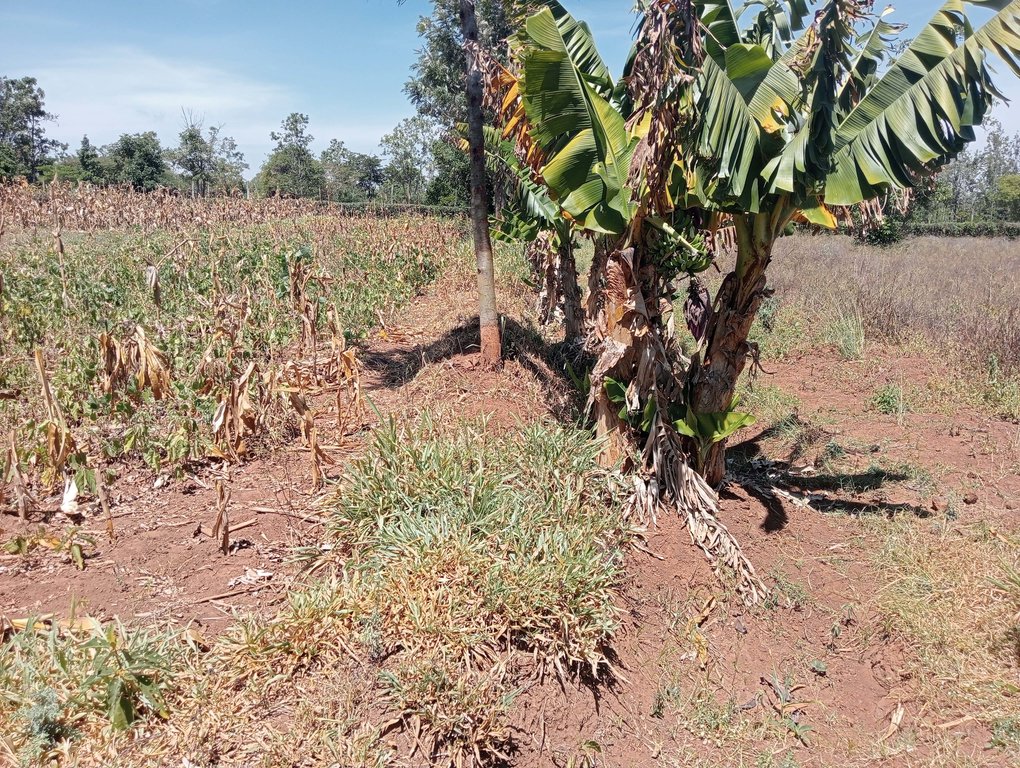
Some crops, especially bananas, arrowroot, etc. that demand a lot of water can be established in the ditches. Maintenance of retention ditches involves regular desilting, whenever the ditch is about 1/3 filled with silt. Hoes, shovels/ spades, and a panga (machete) are some of the tools used in digging and maintaining retention ditches. Farmers like retention ditches because they help in controlling soil erosion.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Kenia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Siaya County, Nyanza Region
Especifique más el lugar :
Uloma Village, Bondo Municipality, Bondo Sub-county
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
The farm where the technology is implemented is not in a protected area.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2018
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Soil Protection and Rehabilitation of Degraded Soil for Food Security (ProSoil) project
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agro-silvopastoralismo

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cultivos para forraje - otros
- cultivos para forraje - pastos
- cereales - maíz
- vegetales - otros
- leguminosas y legumbres - otros
- leguminosas y legumbres - frijoles
Sistema anual de cultivo:
Barbecho - maíz/sorgo/mijo en intercultivo con legumbre
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- banana/plátano/abacá
- cultivos para forraje - pastos
- fodder crops - legumes, clover
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- árboles para forraje (Calliandra, Leucaena leucocephala, Prosopis, etc.)
- avocado
- frutas, otros
- mango, mangostán, guayaba
- papaya
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Long and short rain seasons
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
Sí
Si respondió que sí, especifique qué cultivos son intercultivados:
Maize and legumes e.g., beans
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Some sections of the farm are left fallow during the short rains to allow for soil regeneration.

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Cortar y llevar/ cero pastoreo
- Pastoreo mejorado
Tipo de animal:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- aves de corral
¿Se practica el manejo integrado de cultivos - ganado?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Fodder (nappier grass) planted on the berms is fed to the cattle. The manure from the cattle and droppings from the chicken is used as manure for the crops.
Productos y servicios:
- leche
- huevos
- carne
Especies:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Conteo:
3
Especies:
aves de corral
Conteo:
100
Comentarios:
There are assorted trees on the farm, including fruit trees. Some of the trees are planted on the berm of the retention ditches.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- No (Continúe con la pregunta 3.4)
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Crops are planted only during the rainy seasons since there is no irrigation.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- medida de pendiente transversal
- diversión y drenaje de agua
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas estructurales
- S4: Acequias niveladas, fosas
Comentarios:
Trees and grasses are planted on the berms of the retention ditches.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
Comentarios:
The retention ditches, especially when applied at the top of a plot and the design is to heap the soil below the channel ('fanya chini') has helped control gully erosion. Gullies were common in the farm before the digging of the retention ditches.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
The retention ditches saved the land from gullies, and are still controlling soil erosion.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Ditch dimensions: length = 70m, width = 50cm, depth = 60cm
Slope of the field = 4%
Plants on the berm: nappier grass
Autor:
William Akwanyi
Fecha:
01/07/2023
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
0.4 ha
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
KES
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
122,95
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
300
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slope measurement and determination of position for the retention ditch | During the dry season |
| 2. | Digging the ditches | Before onset of rains |
Comentarios:
The ditches should be constructed during the dry season or before the rains start when the soil is light and easy to remove from the ditches.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Digging the ditches | Man days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Hoe | No. | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Panga (broad blade) | No. | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Wheelbarrow | No. | 1,0 | 800,0 | 800,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Spade | No. | 1,0 | 90,0 | 90,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Planting rope | No. | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Spirit level | No. | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | |
| Otros | Slope measurement and determination of position for the retention ditch (professional service) | Professional service | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 6690,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 54,41 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
ProSoil project
Comentarios:
The costs of the implements are KES 400/- for a hoe, KES 4,000/- for a wheelbarrow, KES 300/- for a planting rope and broad blade, KES 3,000/- for a spirit level, and KES 450/- for a spade. It is assumed that the farmer will be able to use the hoe, planting rope, broad blade, and spade over a period of 5 years, and a wheelbarrow over a period of 10 years before these implements will have depreciated to a point where they will not be useable. The cost is thus spread over the years when the farmer will be able to use the implement.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desilting | Whenever the ditch is about 1/3 filled with silt |
Comentarios:
Maintenance activities do not happen at regular intervals but depend on volume of runoff and amount of silt carried by surface runoff for desilting the ditch, rate of growth of weeds for weeding, and factors that lead to lead of plants for plant re-establishment.
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Si no puede desglosar los costos especificados en la tabla anterior, proporcione un estimado de los cálculos totales en los que se incurrió para mantener la Tecnología:
2000,0
Comentarios:
the above cost is based on the farmer's estimate.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Rate of man-days vary from one place to another and also depend on the kind of work.
Exchange rate for January 2023, source: European Commission/ InfoEuro online at https://commission.europa.eu/funding-tenders/procedures-guidelines-tenders/information-contractors-and-beneficiaries/exchange-rate-inforeuro_en
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Rainfall pattern is bimodal. Monthly rainfall variability is high with some months such as January recording less than 5 mm of total rainfall.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Bondo Meteorological Station
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
The area is found near Lake Victoria which influences the climate.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones convexas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Retention ditches divert the flow of surface runoff. The slope of the farmer's field is 4%.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
N/A
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea y superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
There are several boreholes in the area and according to interviews with some borehole owners, the depts are not more than 50 metres. Lake Victoria is a permanent surface water body in the area.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
The area has high agrobiodiversity as most farms are under crops and trees.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Semi-nómada
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
- ancianos
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
The farmer uses the land together with his other family members.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
Comentarios:
Farmers with more than 2 ha in the area are considered to have large pieces of land since there is high level of land fragmentation in the area.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
No
Especifique:
Each landowner has full control of the way he/ she wants to use his/ her land.
Comentarios:
The farmer has a title for his piece of land.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Comentarios:
The above rating varies from one village to the other.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
2
Cantidad luego de MST:
4
Comentarios/ especifique:
Quantity refers to the number of 90 Kg bags of maize produced per acre. Based on estimation by the farmer.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Not easy to quantify but according to the farmer, the crops are doing better compared to how they were before the retention ditches were dug.
producción de forraje
Cantidad antes de MST:
1
Cantidad luego de MST:
3
Comentarios/ especifique:
Quantity refers to harvesting cycles for nappier grass from the same farm. Based on estimation by the farmer.
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Not easy to quantify but according to the farmer, fodder is doing better compared to how it was before the retention ditches were dug.
producción animal
Cantidad antes de MST:
1
Cantidad luego de MST:
3
Comentarios/ especifique:
Quantity refers to the amount of milk in litres from one cow. Milk production is often at the peak during early lactation months. Based on estimation by the farmer.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
80
Cantidad luego de MST:
40
Comentarios/ especifique:
Quantity refers to the percentage probability of the crop failing to do well. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Ingreso y costos
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Refers to the number of hours that the farmer can be free in any working day. During the rainy season, the farmer spends some time desilting the ditches. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Cantidad antes de MST:
5
Cantidad luego de MST:
2
Comentarios/ especifique:
Quantity refers to the number of months in a year when there is total lack of food in the house, and the farmer has to buy all the food required in the house. Based on estimation by the farmer.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Cantidad antes de MST:
10%
Cantidad luego de MST:
80%
Comentarios/ especifique:
Quantity refers to the estimated percentage of knowledge in SLM/ land management. This is a farmer's estimate.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cosecha/ recolección de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Not easy to quantify. Based on estimation by the farmer.
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Refers to the amount of water that flows through the farm. Not easy to quantify. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Suelo
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Not easy to quantify.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Refers to the farmer's estimated percentage vegetation cover at the farm. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
No recorded data is available for reference. All are estimates based on the farmer's explanation or as given by her.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Not easy to quantify. Retention ditches have reduced the amount of water that flows to the farms in the lower areas. This has reduced soil erosion in these farms.
colmatación río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Not easy to quantify. All silt is deposited in the retention ditches and scooped by the farmer for replenishing parts of the farm with low soil levels.
daño a campos de vecinos
Comentarios/ especifique:
Not easy to quantify. Retention ditches have reduced the amount of water that flows to the farms in the lower areas. This has reduced soil erosion in these farms.
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
It was not possible for the farmer to quantify the above.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien | |
| temperatura estacional | estación seca | incrementó | moderadamente |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
The retention ditches have generally improved crop production.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 11-50%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 11-50%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Controls soil erosion. Silt collected in the ditches is used to replenish other sections of the farm with poor soils. |
| Improved crop yields. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Controls road damage due to runoff as most of the water is collected by the ditches before it destroys the road. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Establishment investment is capital and labour intensive. | The farmer has to be committed. |
| Maintenance is labour intensive. | The farmer has to be committed. Proper planning of farm work. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| If not managed properly by regular removal of silt, the ditch can easily fill up. | The farmer must be committed to remove silt regularly. |
| May overflow and collapse during high rainfall leading to high levels of soil erosion. | Proper designing in consideration of runoff volumes and slope angle. Regular maintenance. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
One visit at one farm
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
One farmer interviewed at his farm. Follow-up questions on phone.
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
ProSoil team and project implementers from Welthungerhilfe consulted.
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
Siaya County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022 and online sources reviewed.
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
27/01/2023
Comentarios:
One field visit and several follow-up consultations.
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Climate Smart Extension Manual by KCEP - CRAL, 2021
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Download free at https://www.kalro.org/files/kcep/CSA-extension-manual-18-06-21.pdf
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Siaya County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022
URL:
https://repository.kippra.or.ke/bitstream/handle/123456789/1218/2018-2022%20%20Siaya%20County%20CIDP.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
7.4 Comentarios generales
1. Provide a function to be able to link the documented SLM to similar work that has been documented in other databases e.g., LandPortal, UNCCD, etc.
2. Some of the impacts (section 6) cannot be quantified.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Community Resource Persons (CRP) in agricultural extension [Kenia]
Community Resource Persons (CRP) form a farmer-to-farmer learning approach that bridges the gap in agricultural extension, increases farmers' access to agricultural information (SLM knowledge), and increases the adoption of SLM practices.
- Compilador: William Akwanyi
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos