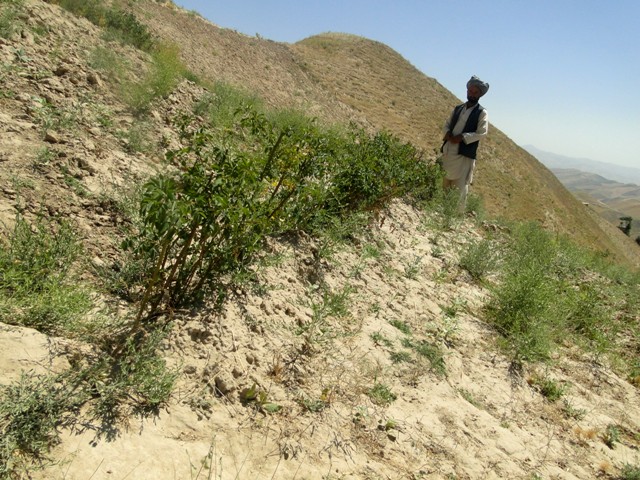
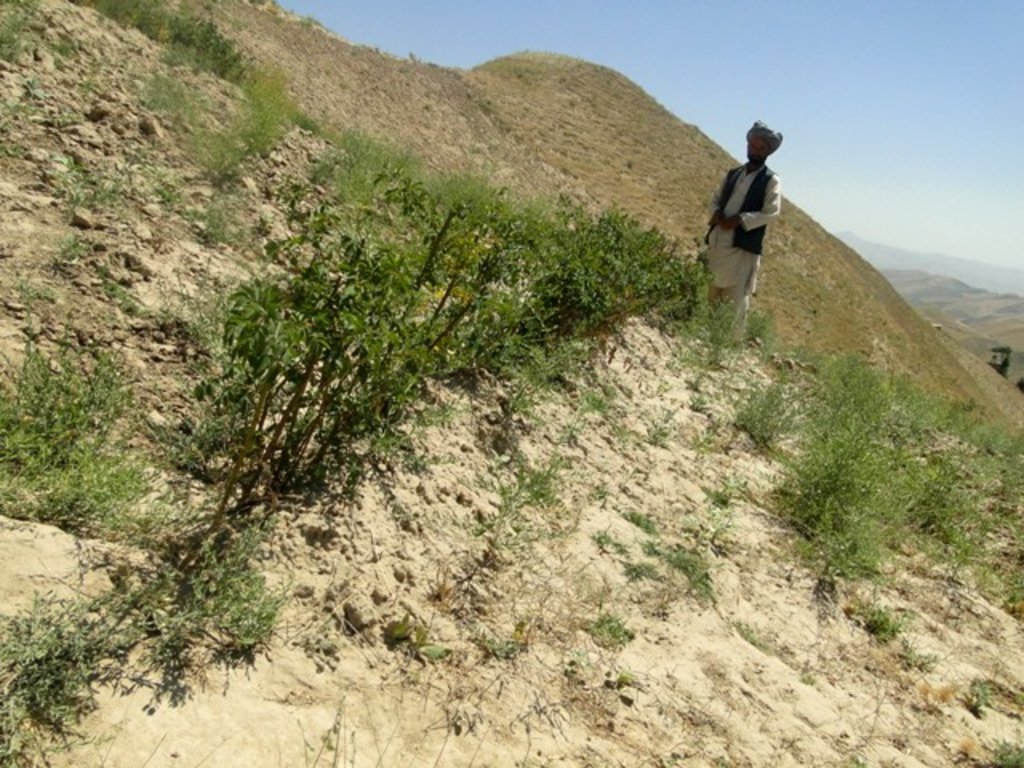
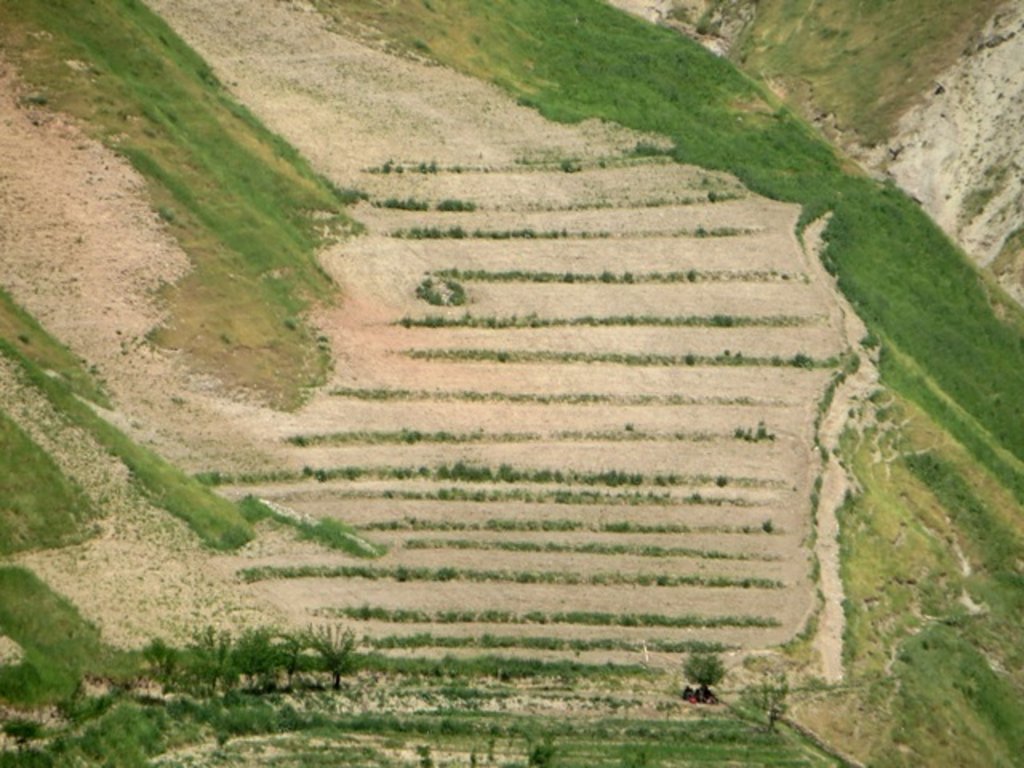
Contour hedgerows of alfalfa in annual cropland [Afganistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Bettina Wolfgramm
- Editores: Roziya Kirgizbekova, Aslam Qadamov, Aqila Haidery
- Revisor: William Critchley
Khati sabz, Qamarbandi sabz
technologies_670 - Afganistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
Mohammad Azim Habibullah
Natural Resources Management Comittee (NRMC)
Sari Joy Village, Rustaq District, Takhor Province
Afganistán
Especialista MST:
Maroofi Mia Jan
+93 700 019 054
mia.maroofi@gmail.com
Livelihood Improvement Program Takhor Afghanistan
Tdh Office Behind Jamai Masjed, Rustaq Town, Takhor Province
Afganistán
Especialista MST:
Researcher:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Bern University of Applied Sciences, School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences (HAFL) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
27/10/2016
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
SLM practices documented in the frame of the Rustaq NRM study were established only recently (1-3 years ago). It is too early for a final judgment on the sustainability of these technologies within the human and natural environment of Chokar watershed.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Hedgerows are vegetative strips of perennial grasses, shrubs or legumes - such as alfalfa - located along contours across a slope. These vegetative strips form a barrier to halt soil erosion and improve soil fertility. Hedgerows of alfalfa also provide quality animal fodder for a period of 5-10 years.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Project supported implementation of hedgerows has taken place in the villages of Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana, located in Chokar watershed of Rustaq District in Northern Afghanistan. The Chokar watershed is a mountainous area situated between 600 m and 2,500 m above sea level. The climate is semi-arid with harsh and cold weather in winter and hot and dry summers. The annual precipitation in average years is 580mm. Land degradation affects all forms of land use and includes sparse vegetation cover, severe top soil erosion through rainfall runoff, and poor soil fertility. Unsustainable agricultural practices, and over-exploitation of the natural resources are adversely impacting the socio-economic well-being of local communities, as well as contributing to the risk of being adversely affected by drought, landslides and flash foods triggered by heavy rainfall. The data used for the documentation of the technology are based on field research conducted in Chokar watershed, namely in the villages of Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana. These villages represent the upper and the middle zone of Chokar watershed, respectively. They differ considerably in access to services and infrastructure, but in general are poorly served. The communities depend on land resources for sustaining their livelihoods. In a good year with high yields, wheat self-sufficiency lasts about 5 months. The three villages are home to ethnic Qarluq communities. Since 2012 the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland has initiated a range of NRM interventions.
Hedgerows are vegetative strips, planted as contour barriers. In this case they are composed of the perennial legume alfalfa (sometime called lucerne: Medicago sativa), Using an A-frame, contours are defined and demarcated horizontally across the hillside. The distance between the contours depends on the slope gradient. For moderate slopes above 6%, and hilly slopes below 30%, the distance between the contours is 4-5 meters. Using such contouring measurements, a plot area of 0.2 ha is divided into 8 hedgerows along the slope. Once all the contours are established, the topsoil is levelled using a shovel. On each marked contour a soil ridge is created, some 10-20 cm high. On these ridges alfalfa seeds are sown to form the vegetative hedgerow. This stops soil wash, and prevents most of the rainfall runoff. The area between the grass strips is cropped with wheat. The hedgerows are protected for one year, to allow the alfalfa to become established.
Hedgerows were introduced in the local villages to promote low-cost land management practices, which are sustainable and well adapted to the local environmental conditions. Apart from reducing soil erosion, this new practice takes into account the needs of local people to improve soil fertility and increase agricultural yields. Local land users were trained to establish hedgerows on their own land using low amount of inputs. They were given the technical knowledge required. Over the past four years of implementation the land users report noticeable improvements on their plots. The soil is protected from erosion, and the households harvest wheat for the family and alfalfa for their livestock.
One of the key benefits of the technology is that it does not require many or costly inputs and it is relatively easy to establish without technical support. Improved production and availability of alfalfa is a primary benefit from the land users' point of view. They can harvest fodder from the plot for up to 10 years without reseeding.
Hedgerows are among the least labour-intensive SLM practices and thereby do not have a significant influence on the daily household workload of local women. This feature of the technology is perceived as its strength by many female family members.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Afganistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
Especifique más el lugar :
Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana Villages
Comentarios:
This documentation is based on the experiences of SLM implementers from Sari Joy (3 plots) and Jawaz Khana, (3 plots) as compiled during FGDs. Additionally insights were gained through interviews in the villages on farmers experiences and observations of hedgerow plots, with both SLM implementers (5) and observers (7).
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des Hommes (Tdh) Switzerland, supported by Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC) from 2012-17
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Agroforestería
Principales productos/ servicios:
Alfalfa, wheat (ferula in later years)
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
- medida de pendiente transversal
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 0.1-1 km2
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas estructurales

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
Comentarios:
After establishment activities the area is put on quarantine for one year.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Autor:
Aslam Qadamov; Roziya Kirgizbekova
Fecha:
15/02/2017
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Hedgerows are vegetative strips, planted as contour barriers. In this case they are composed of the perennial legume alfalfa (sometime called lucerne: Medicago sativa), Using an A-frame, contours are defined and demarcated horizontally across the hillside. The distance between the contours depends on the slope gradient. For moderate slopes above 6%, and hilly slopes below 30%, the distance between the contours is 4-5 meters. Using such contouring measurements, a plot area of 0.2 ha is divided into 8 hedgerows along the slope. Once all the contours are established, the topsoil is levelled using a shovel. On each marked contour a soil ridge is created, some 10-20 cm high. On these ridges alfalfa seeds are sown to form the vegetative hedgerow. This stops soil wash, and prevents most of the rainfall runoff. The area between the grass strips is cropped with wheat. The hedgerows are protected for one year, to allow the alfalfa to become established.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
1 ha
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
67,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
5.2-5.3 USD per day
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of the area for establishing a hedgerow | Manejo | End of autumn |
| 2. | Design of the hedgerows using an A-frame | Estructurales | End of autumn |
| 3. | Leveling of the land | Agronómicas | End of autumn |
| 4. | Alfalfa seed sowing | Vegetativas | End of winter (February) |
| 5. | Area under protection | Manejo | For one year |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Designing of the hedgerow using A-frame | person-day | 5,0 | 9,0 | 45,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Leveling the land | person-day | 25,0 | 5,3 | 132,5 | |
| Mano de obra | Ploughing the land with animal traction | person-day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | |
| Mano de obra | Wheat and Alfalfa seed sowing | person-day | 10,0 | 5,3 | 53,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Rake | piece | 1,0 | 5,3 | 5,3 | |
| Equipo | Shovel | piece | 1,0 | 3,8 | 3,8 | |
| Equipo | Twine | meter | 50,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 | |
| Equipo | A-frame | piece | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Alfalfa seed | Kg | 17,5 | 0,42 | 7,35 | |
| Material para plantas | Wheat seed | Kg | 140,0 | 0,42 | 58,8 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | DAP | Kg | 250,0 | 0,9 | 225,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Urea | Kg | 250,0 | 0,45 | 112,5 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Herbicide | Liter | 50,0 | 0,25 | 12,5 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 788,25 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Livelihood Improvement Program in Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh)
Comentarios:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.2-0.4 ha or 1-2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing the land with animal traction (Men) | Agronómicas | |
| 2. | Wheat sowing | Agronómicas | |
| 3. | Weeding | Agronómicas | |
| 4. | Fertilizer application | Agronómicas | |
| 5. | Repair the damaged section of the hedgerow by adding soil | Estructurales | End of winter (February/March) |
| 6. | Reseeding alfalfa in the repaired section | Vegetativas | End of winter (February/March) |
| 7. | Wheat and alfalfa harvesting and delivering | Agronómicas |
Comentarios:
Sowing of alfalfa is done once in 5-10 years. The maintenance activities do not require reseeding of alfalfa every year (only where damaged). Mostly damage to hedgerows occur as a result of heavy rainfall and require maintenance work in early spring.
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Ploughing the land with animal traction | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Sowing of wheat | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Weeding and Fertilizer application | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Harvesting and delivering wheat and alfalfa | person day | 35,0 | 3,0 | 105,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Sickle | Pcs | 1,0 | 2,25 | 2,25 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Pitchfork | Pcs | 1,0 | 5,3 | 5,3 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Alfalfa seed | kg | 1,0 | 0,42 | 0,42 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Wheat seed | kg | 140,0 | 0,42 | 58,8 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | DAP | Kg | 250,0 | 0,9 | 225,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Urea | Kg | 250,0 | 0,45 | 112,5 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 588,77 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Livelihood Improvement Program in Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh)
Comentarios:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.2-0.4 ha or 1-2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the Technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as plant material, fertilizers and agricultural tools are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
564,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Average annual precipitation for the area was calculated with 564 mm, with minimum in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximum in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolute maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the period from 1979 to 2014.
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR), http://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Derived from the publicly available dataset on length of growing period (LGP) (Fischer 2009 / IIASA-FAO). Internet link: http://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P8Cok4qAP1sTVE59/arcgis/rest/services/Length_of_growing_period/MapServer
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
-SLM implementers information provided in the Land User Protocol (LUP) during an FGD
-Elevation and slope statistics derived for terraced plots from ASTGTM. ASTGTM is the ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model V002 with a 30 m spatial resolution. More information on ASTGTM is available here: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/node/1079. The data can be downloaded here: https://gdex.cr.usgs.gov/gdex/
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Hedgerows are implemented on light soil - a locally defined category for soil types. Light soil corresponds to moderately deep soil; medium topsoil texture; medium below surface texture and low topsoil organic matter.
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water differs for the two study villages Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana. Sari Joy has relatively good surface water availability, also for drinking. Jawaz Khana has poor water both in quality and availability. Water has to be fetched from a lower lying stream.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- rico
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- niños
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
The land users in the area where the Technology is applied belong to the Uzbek ethnic minority group Qarluq. Although the men are generally the main land users, however, women and children also take active part in the related work. The functions of men and women are clearly distinguished within the Afghan society. At the same time within the family this division of work and functions also results in men and women working hand-in-hand. An improvement of the family’s livelihood situation is expected to positively affect all family members. While, it is recognized that the involvement of women is key in order to secure basic human rights for everyone, to achieve good governance, sustainable development, and to efficiently contribute to poverty reduction (SDC 2004), it is also clear that a context sensitive approach is of great importance.
Women in rural Afghanistan are involved in many production and income generating activities that contribute to the overall household income, however, very few women own resources such as land and livestock, and their income generating options are fewer in comparison to that of men.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Comentarios:
Those who own a land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for water. The payment is made either in kind or in cash to Mirob - the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Wheat grows well on the plot where the contour strips support moisture retention, as well as prevent the seeds and fertilizers to be washed off.
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Alfalfa is produced on the hedgerows to ensure stable supply of livestock fodder.
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
The livestock of the household benefit from the improved production of alfalfa as a fodder crop.
producción de madera
producción de productos forestales no madereros
diversidad de producto
área de producción
Impactos socioculturales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Land users learned how to implement SLM practices.
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
Female headed households are not included. Technology is implemented on private land, therefore people without land are excluded. However, they have the opportunity to earn income as a hired worker for the SLM implementers.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Suelo
pérdida de suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
colmatación río abajo
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios acerca de la evaluación del impacto:
Based on the Land User Protocols: SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits from hedgerows individually. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in product diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all hedgerow implementers are reflected here.
Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of the Technology on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by all implementers are reflected here.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | muy bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Comentarios:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: SLM implementers were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly, well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrixes compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
SLM implementers from three villages were asked to jointly discuss and rate the SLM technologies short term (1-3 years) and long-term (10 years) return. As most of the technologies have only been implemented 1-2 years ago, it is too early to compare benefits to maintenance costs. Farmers have little experience so far on the actual benefits of the SLM technologies. The ratings are mostly based on expected benefits and not on actual benefits.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
16.4 ha
Comentarios:
Based on the Land User Protocol: Individual SLM implementers were asked whether they received support for implementing the Technology. Each indicated the type of support he received from the proposed options: "Full Support 100%, Some Support, No Support 0%".
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The contour alfalfa strips preserve moisture and makes the land less vulnerable to dry spells. Longer moisture retention also helps the crop to grow better. |
| Production of livestock fodder such as alfalfa has been improved as observed by the land users. The hedgerow protects the soil from heavy rainfall, which would wash off the topsoil otherwise. |
| The establishment and maintenance activities are well compatible with the daily work of the land user compared to other more demanding field work. |
| Alfalfa can be grown without reseeding for up to 5 years and there is no need to buy alfalfa seeds every year. |
| Hedgerows are considered as the least labour-intensive technology for women and does not impact their daily household activities. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| The establishment of hedgerows is not very technically demanding and does not require great technical knowledge |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The costs of establishment are high for the land user, including the labour and material inputs | |
| The alfalfa strips need to be reseeded in 5-10 years and the land user may not have the seeds and has to buy them himself |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Hedgerows are among least popular practices among the land users and the adoption rates have been very low. The reasons behind might be the high establishments costs. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
No field work was conducted.
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Focus group discussions (FGD) were organized by the CDE team to collect information from SLM implementers. Total of 6 land users who have implemented hedgerows participated in the FGDs held in the villages of Sari Joy and Jawaz Khana.
Interviews were conducted by the HAFL team to collect information from persons representing all the three study villages. Very detailed interviews were conducted with 12 persons interested in hedgerows implementation, of which 5 persons are from households that already have implemented hedgerows.
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Close collaboration took place during the compilation of this material with the technical staff of the LIPT project in Rustaq.
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
Information provided in the reports of the LIPT project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Guidelines for Focus Groups Discussions
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Methods section of the Rustaq NRM study
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos