Learning Site to promote Sustainable Land and Forest Management Practices in Khost [Afganistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Mohammad Arif
- Editores: Megha bajaj, Mohammad Aslam Hasand, Afghanistan Safi
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi
په خوست ولایت کی د ځنګل او ځمکی بنسټیزه مدیریت عملی کارونو د پاره دزده کړی ساحی رامینځ ته کول
technologies_7460 - Afganistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
usuario de la tierra:
Akbar Muhajir
Sparkai Forest and Rangeland Management Association
Afganistán
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Combating land degradation and biodiversity loss by promoting sustainable rangeland management and biodiversity conservation in AfghanistanNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - Afganistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Stakeholder collaboration for building Learning Site for landscape … [Afganistán]
To raise awareness and ensure clear role delineation, a series of consultations were held with the local community, the Forest Management/Rangeland Management (FM/RM) association, and other key stakeholders. Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) that formally outlined the roles and responsibilities of each party was signed. Additionally, the FM/RM association issued a …
- Compilador: Mohammad Arif
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
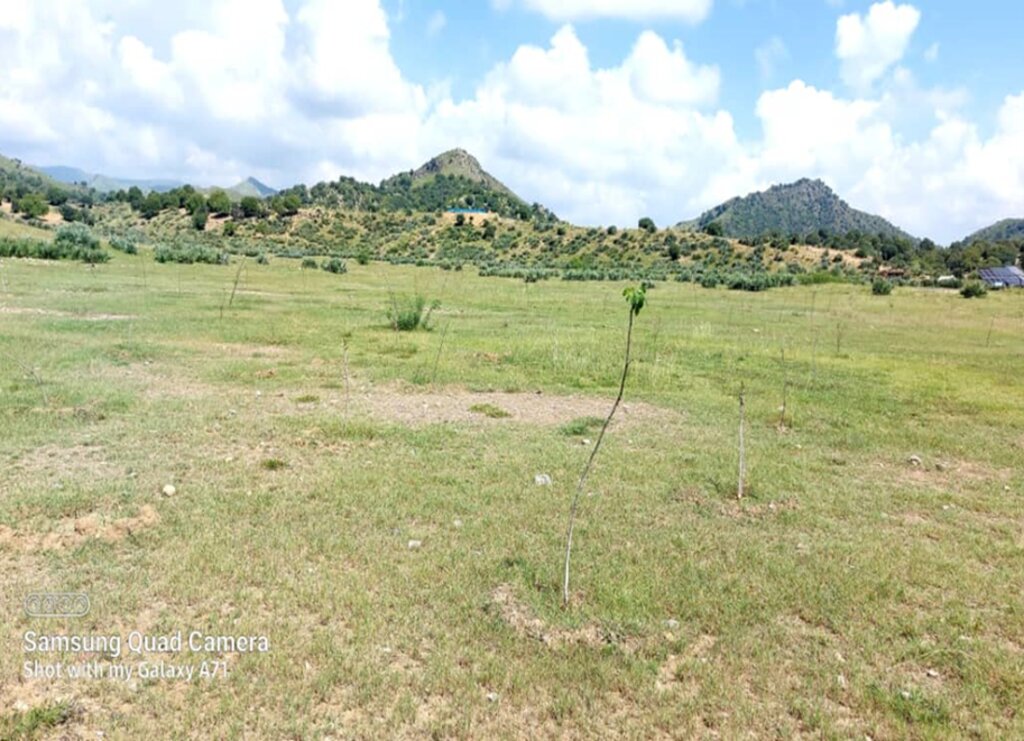
The learning site incorporates several key elements of the technology including a solar-powered water lifting system, three reservoirs and an adopted irrigation system. It features demonstration plots for various initiatives, such as tree planting (walnut, almond, pomegranate and mulberry, the cultivation of fodder (alfalfal Mazari palm) and and medicinal plants (e,g, cumin), and a nursery (walnut) established through the community’s own contributions.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
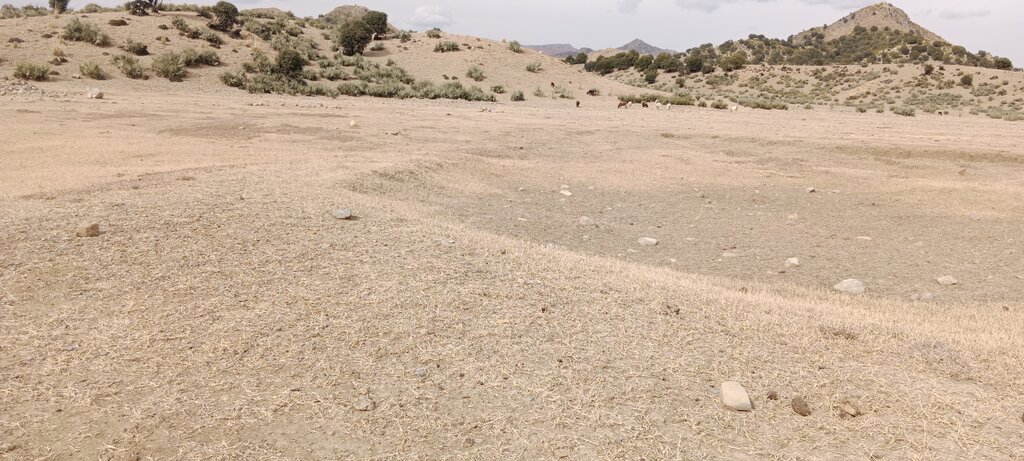
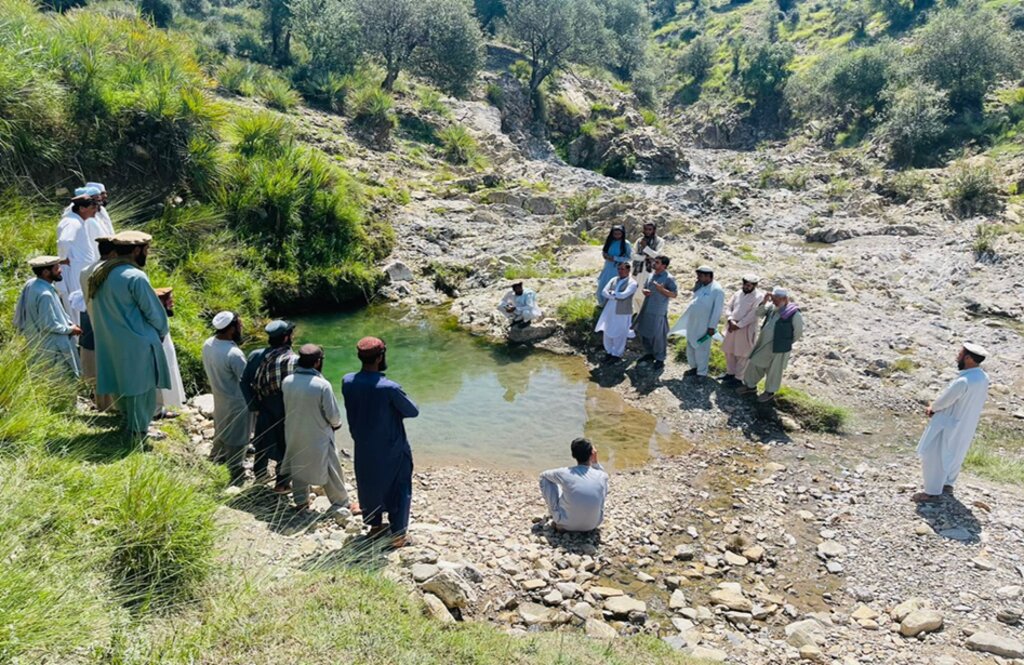
The site was rich in flora and fauna, but human and animal interference has led to significant degradation. Many indigenous plants have been uprooted, and wildlife has migrated due to the loss of habitat. In response, the community has begun to manage and restore the land through practices like rotational grazing and quarantine measures to combat illegal logging. The degradation of natural resources, particularly forests and rangelands, has significantly impacted local communities in Khost. Many residents rely on these resources for fuel, heating, and grazing livestock. However, challenges such as overgrazing, the uprooting of bushes and shrubs, and deforestation for fuel have led to considerable environmental degradation. The lack of proper management of these natural resources has resulted in consistent flooding, which erodes and pollutes agricultural lands. Additionally, local communities often do not recognize the value of these resources, leading to unsustainable land-use practices. Poverty, ongoing conflicts, political instability, and unemployment have driven residents to cut down trees for sale in local markets to support their livelihoods.
To address these challenges, we conducted a participatory assessment involving local communities and stakeholders, aiming to establish a learning site for sustainable land and forest management practices. Our assessment revealed that many local residents were unaware of sustainable practices or the ecological significance of these resources, contributing to ongoing environmental degradation.
After assessing the natural resources and community needs, we established a learning site for sustainable forest and rangeland management. Feasibility studies helped us identify available water sources, assess community interest, and select suitable land next to forests and rangelands. The site selected is easily accessible, located about 10 kilometers from the main road.
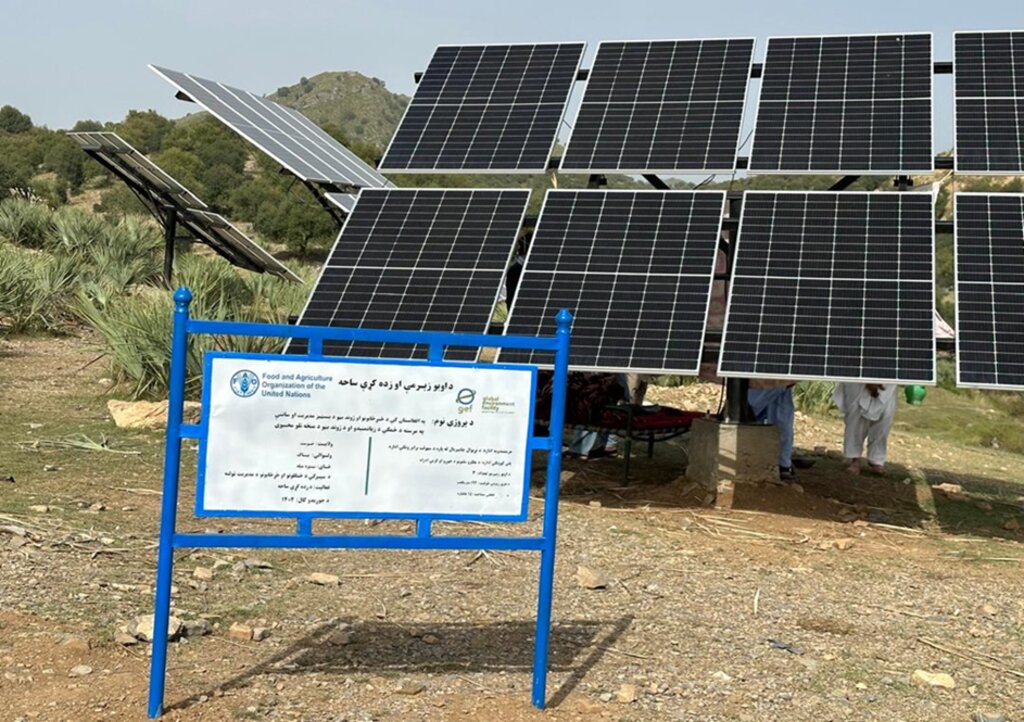
In the initial phase, we installed 26 solar panels on three metal stands, each with a capacity of 400 watts, positioned 200 meters from the water source. At the water source, we installed a 2-inch submersible pump to lift water to the learning site, which encompasses approximately 20 hectares of land across three small hills, each situated 300 meters apart.
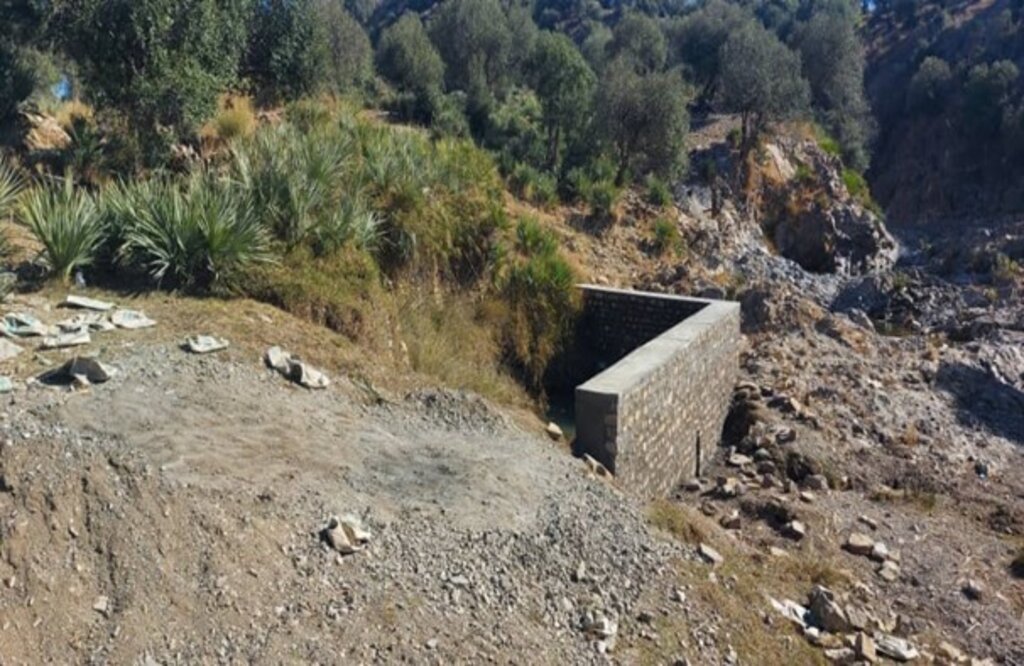
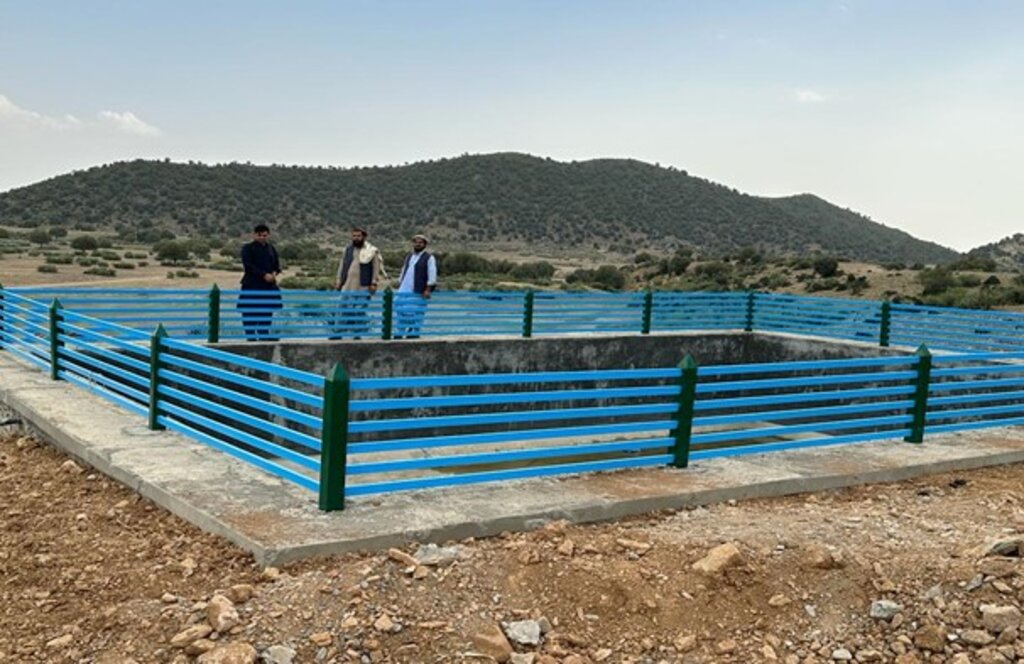
We constructed three reservoirs, each with a capacity of 192 cubic meters. The first reservoir is located 300 meters from the water source and is fed by the solar system. A pipe network system utilizing 2-inch pipes connects the water source to the first reservoir and the other two reservoirs. This system allows the reservoirs to supply water to lower fields or demonstration plots via gravity.
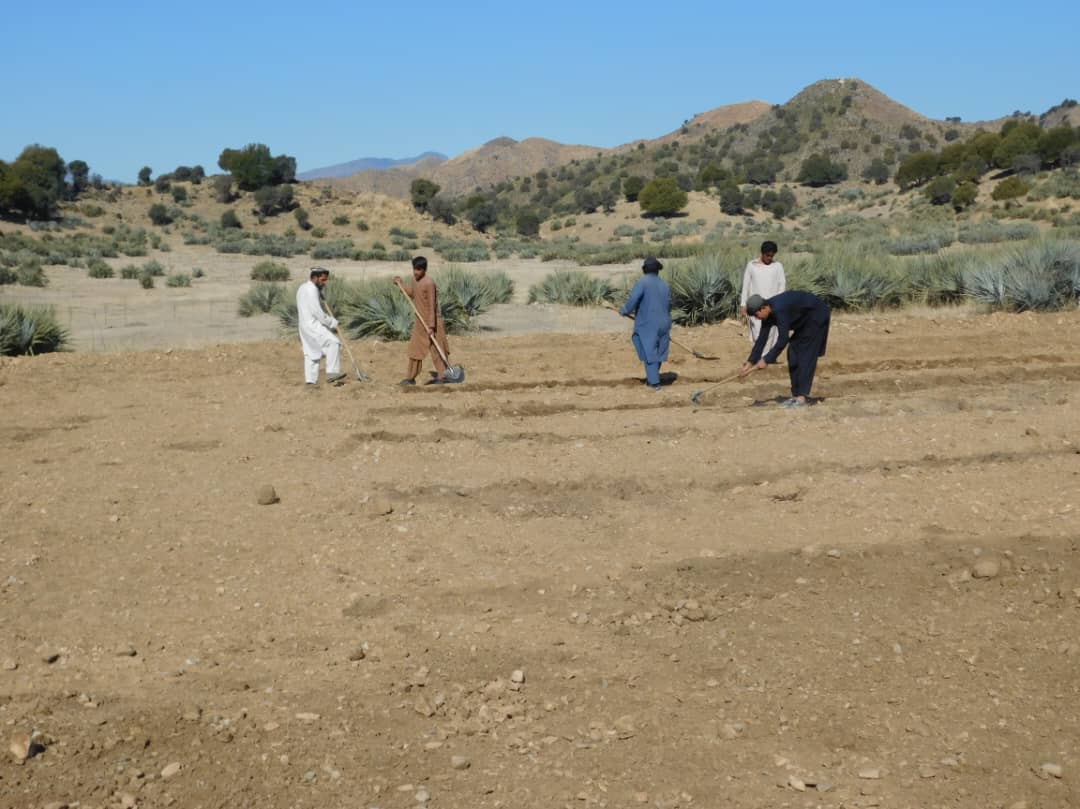
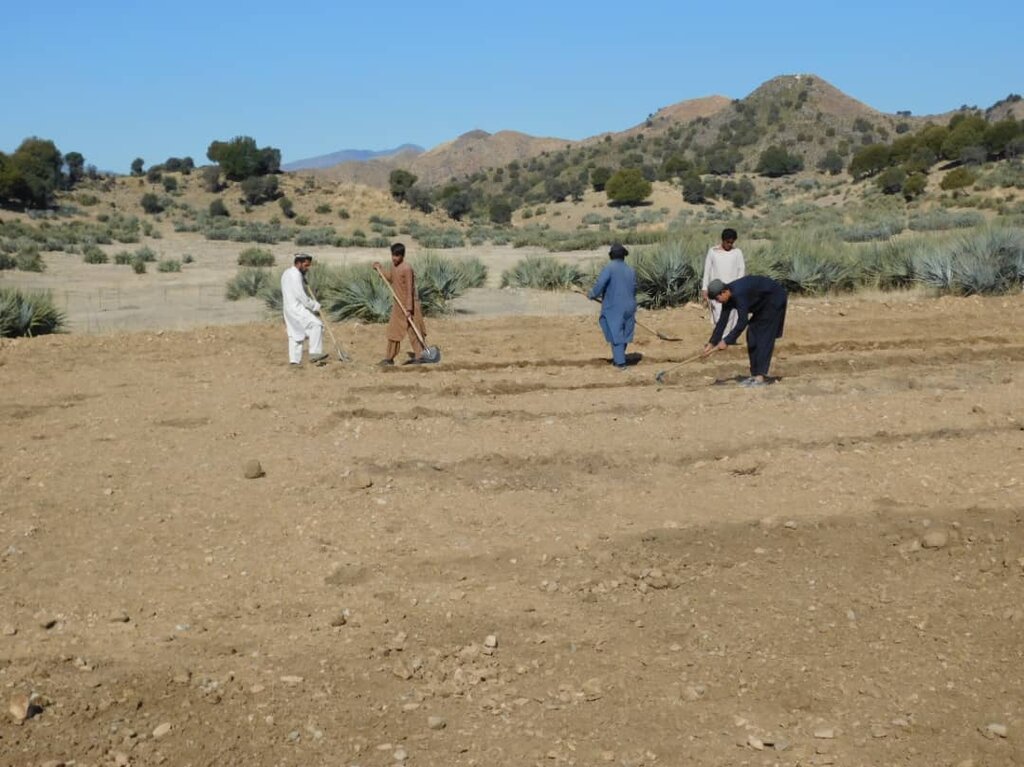
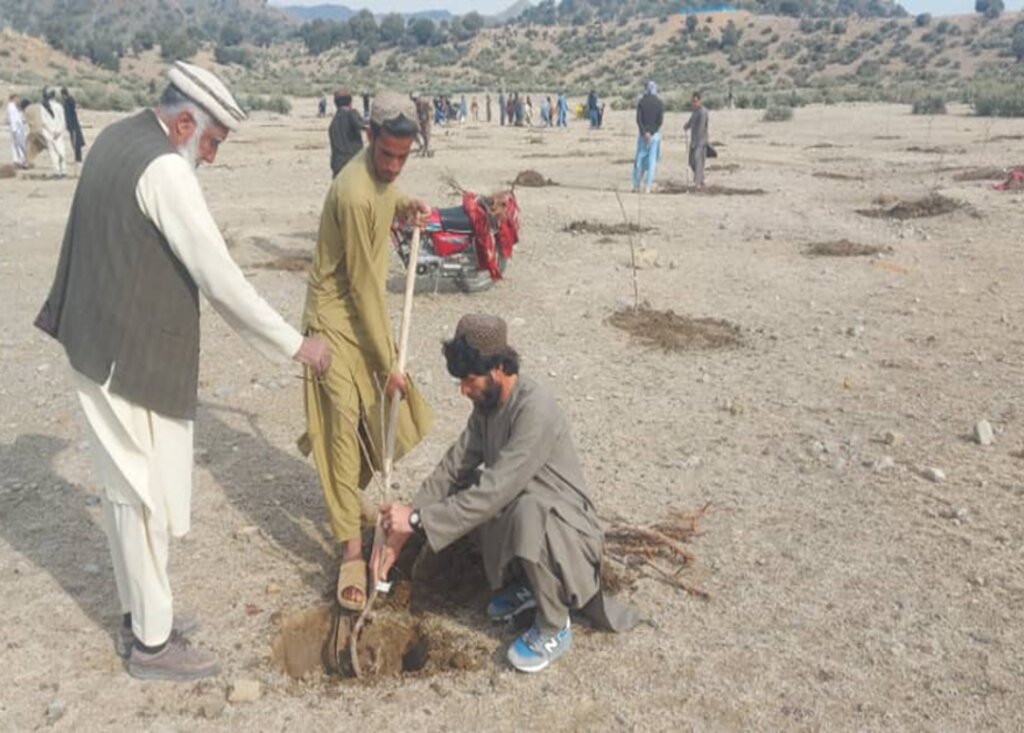
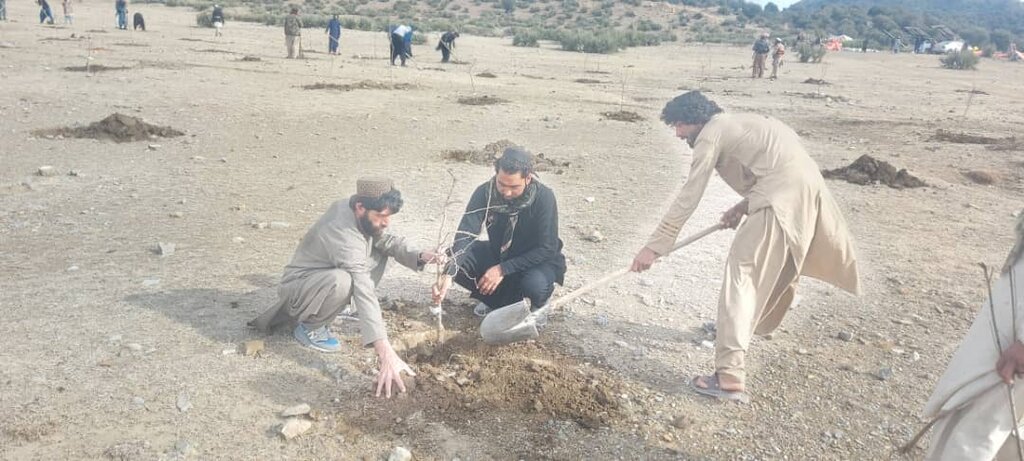
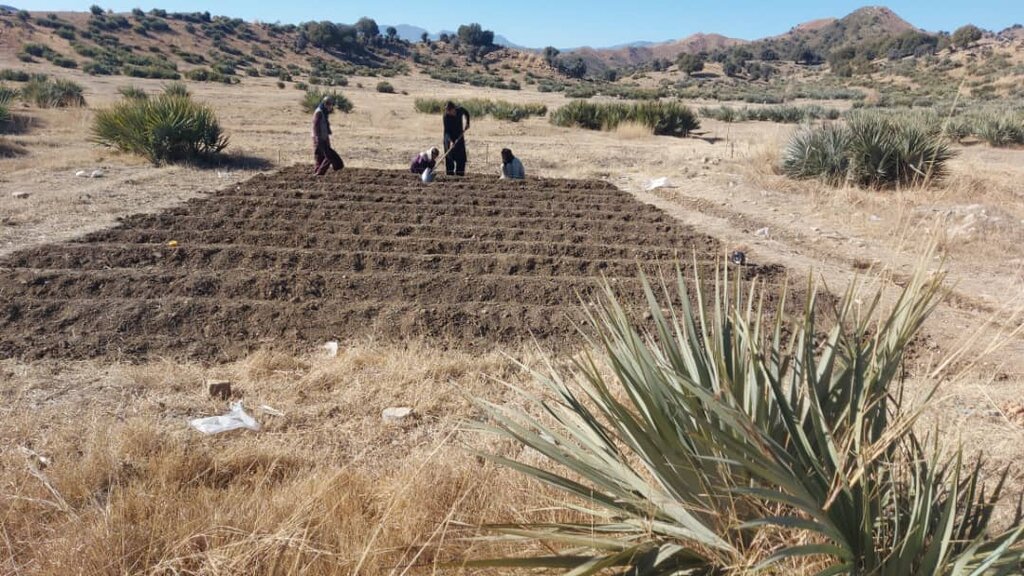
In the demonstration plots, a network of pipes was installed every 50 meters, with taps placed accordingly. We established a 20-hectare learning site focused on sustainable forest and rangeland management practices, featuring demonstration plots for reforestation, fodder and medicinal plant production, reseeding, and a forest nursery. The dimensions of these plots include 10 hectares for reforestation, 2 hectares for fodder production, 0.5 hectares for medicinal plants, and 0.1 hectares for the walnut nursery. A total of 3,000 forest species were planted in the reforestation plot, along with alfalfa and Mazari palm in the fodder plots, and black cumin in the medicinal plot.
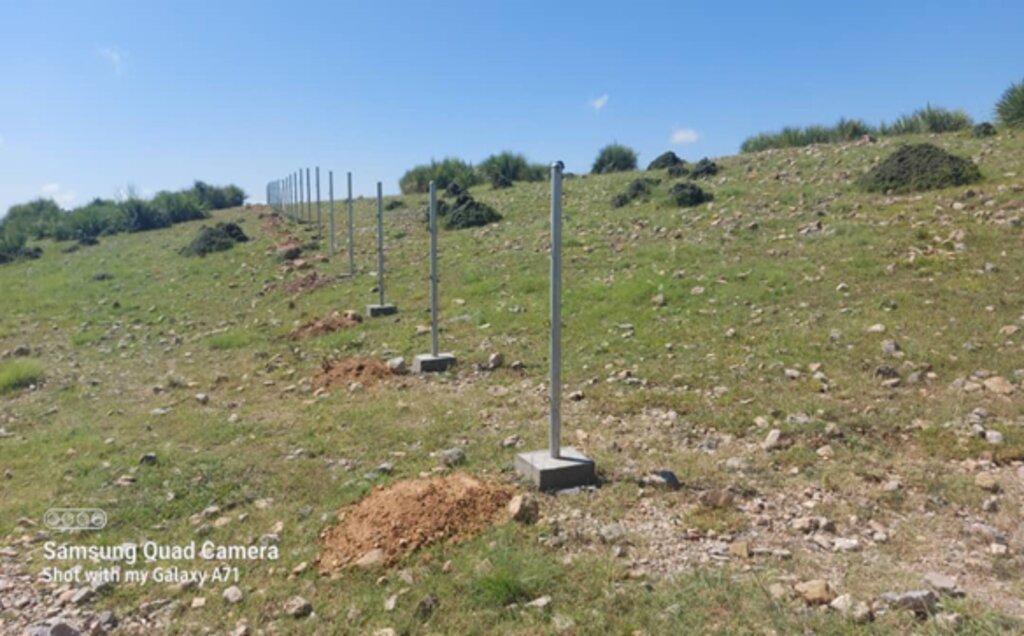
These plots are irrigated using flexible 1-inch pipes connected to the taps installed every 50 meters. Given Khost Province's favorable weather conditions, the plants require irrigation primarily from April to August; outside of this interval, the irrigation system provides sufficient water to sustain the site. The site were fenced with barbed wire for protection.
The technology is applied to communal land adjacent to forests and rangelands. It serves as an educational center for the local community, focusing on sustainable landscape restoration and management. A savings box was created, and a Forest and Rangeland Management Association was established. Social funds were set up, along with fencing and hiring guards for the maintenance of the technology.
Key infrastructure was established, including a solar-powered lifting system, constructed reservoirs, and a piping network for irrigation. Various forest species were planted in reforestation plots, while local seeds were planted in fodder and medicinal plots. Additionally, walnut seeds were sown in a nursery for diverse restoration practices. These efforts have revitalized the land. Barbed wire fencing was installed for protection, and the site is now fully operational as a learning site.
The introduction of this technology led to positive changes in the local community. They have successfully quarantined forest and rangeland, implemented rotational grazing, and collected local seeds and cuttings to plant on degraded lands and riverbanks. Community-based nurseries were also established to transplant seedlings into degraded forest areas, helping to revitalize natural resources.
The local community is optimistic about the technology, particularly the reservoir construction and solar-powered lifting systems that ensure water availability, as well as the restoration techniques employed. However, they expressed concerns about interference from neighbors, livestock grazing, floods that can clog pumps, and damage from hail and windstorms to solar panels.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
The photo was taken with a low-quality smartphone.
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Comentarios, descripción breve:
N/A
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Afganistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Khost
Especifique más el lugar :
Stara Mila, Sparkai village of Baak district
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
The site is situated near a forest and rangeland, approximately 20 km from the Baak main road, extending towards the Zazi Maidan district. It is classified as communal land
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2023
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
FAO- GEF-07 Combating land degradation and biodiversity loss by promoting sustainable rangeland management and biodiversity conservation in Afghanistan (GEF7)
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- conservar el ecosistema
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- serves as educational centre for the local community on sustainable landscape restoration and management
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Silvo-pastoralismo

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- frutas, otros
- frutos secos (castañas, pistachos, nuez, almendras, etc.)
- walnut, almond, pomegranate, mulberry
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
No
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
No

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo extenso:
- Nomadismo
- Pastoralismo semi-nómada
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Cortar y llevar/ cero pastoreo
- Pastoreo mejorado
Tipo de animal:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- cabras
- ovejas
¿Se practica el manejo integrado de cultivos - ganado?
No
Productos y servicios:
- carne
- leche
Especies:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Conteo:
510

Bosques
- Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi) naturales
Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi-) naturales: Especifique tipo de manejo:
- Eliminación de madera muerta/ de poda
- Uso de productos forestales no madereros
Tipo de bosque (semi)natural:
- vegetación natural de sistemas de montañas subtropicales
- wild olive, black thorn, hop bush, Mazari palm, cumin
¿Los árboles especificados son deciduos o imperecederos?
- mixto deciduo/ imperecedero
Productos y servicios:
- Madera
- Otros productos forestales
- Recreación/ turismo
- Protección contra desastres naturales
Comentarios:
Due to poor management, the land has been overgrazed. To address this, we established a learning site focused on restoration through various interventions: reforestation, fodder and medicinal plant demonstration plots, and a 50-square-meter nursery for sapling production. The site is protected by fencing to prevent herders from grazing, allowing them to collect fodder instead. Some fodder is left in the field to produce seeds for natural regeneration.
Forest and Rangeland Management Association focuses on:
Local seed collection: Gathering native seeds to enhance biodiversity and ensure ecosystem resilience.
Ecotourism development: Encouraging visitors to explore the sites, fostering appreciation for local flora and fauna while supporting conservation efforts.
Regeneration of native species: Implementing strategies to restore and regenerate various native plant species, which play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance.
Fodder production for silage: Cultivating high-quality fodder crops that contribute to livestock nutrition and support sustainable agriculture.
Sapling production through nurseries: Establishing nurseries dedicated to growing saplings of native forest species as well as fruit and nut trees, which can be used for reforestation, habitat restoration efforts and generating income.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agropastoralismo (incluyendo cultivo-ganado integrados)

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo extenso:
- Nomadismo
- Pastoralismo semi-nómada
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Cortar y llevar/ cero pastoreo
- Pastoreo mejorado
Tipo de animal:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- cabras
- ovejas
¿Se practica el manejo integrado de cultivos - ganado?
No
Productos y servicios:
- carne
- leche
Especies:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Conteo:
510

Bosques
- Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi) naturales
Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi-) naturales: Especifique tipo de manejo:
- Eliminación de madera muerta/ de poda
Tipo de bosque (semi)natural:
- vegetación natural de sistemas de montañas subtropicales
- wild olive, Mazari palm, hop bush, black thorn and grasses
¿Los árboles especificados son deciduos o imperecederos?
- mixto deciduo/ imperecedero
Productos y servicios:
- Madera
- Leña
- Recreación/ turismo
- Protección contra desastres naturales
Comentarios:
The area is a dry mountainous terrain with natural vegetation including wild olive, mazari palm, hopbush, and grasses. It supports nomadic and semi-nomadic pastoralism, primarily grazing goats, sheep, and cows.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Comentarios:
Near the learning site, a gully and springs provide a year-round water source. We have installed a solar-powered lifting system and constructed three reservoirs to distribute water across 20 hectares, including the planted areas and demonstration plots. A network of pipes and taps with flexible hoses ensures efficient water distribution. This water source is exclusively for this site and does not affect neighboring villages or farmers.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo de plantación forestal
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas estructurales
- S6: Muros, barreras, vallas, cercas
- S7: Equipo para cosechar agua / provisión de agua/ irrigación
- S10: Medidas de ahorro de energía

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
- M3: disposición de acuerdo al entorno natural y humano
Comentarios:
The whole area 20 hectares have been fenced with barbed wire, under the structure measures, reservoirs have been constructed and dug pits for plants.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bh: pérdida de hábitats
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hg: cambio en nivel de aguas subterráneas/ nivel de acuífero
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de subterráneas
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de aguas subterráneas
Comentarios:
The local community relies on natural resources for their livelihoods, leading to deforestation, overgrazing, and the uprooting of shrubs and bushes for fuel. Severe runoff, droughts, and climate change have further contributed to environmental degradation.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
- adaptarse a la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
An educational center (learning site) has been established on degraded land to enhance the capacity of the local community and other stakeholders about best practices for landscape restoration.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
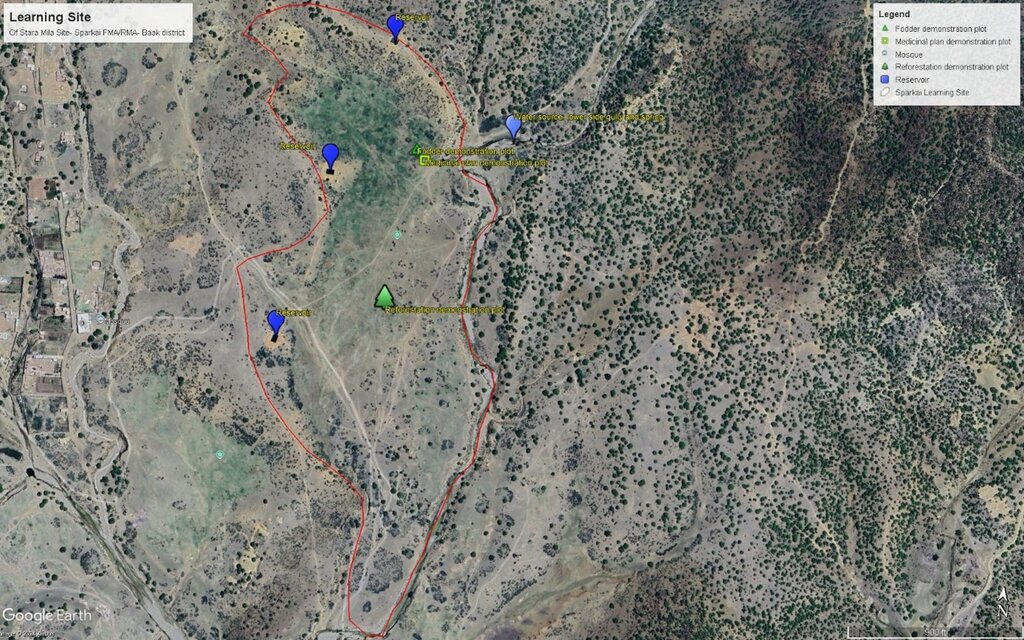
This GIS map highlights learning site elements. The blue pins indicate water source and reservoirs, while the green rectangular pins represent fodder demonstration plot. Yellow squire pin mark area dedicated to medicinal plants, and green tree-shaped pin indicate reforestation plot. Finally, the red track pin indicates location of barbed wire fencing. The site map has been prepared after the completion of intervention.
Autor:
Mohammad Omar Dost
Fecha:
17/09/2024
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
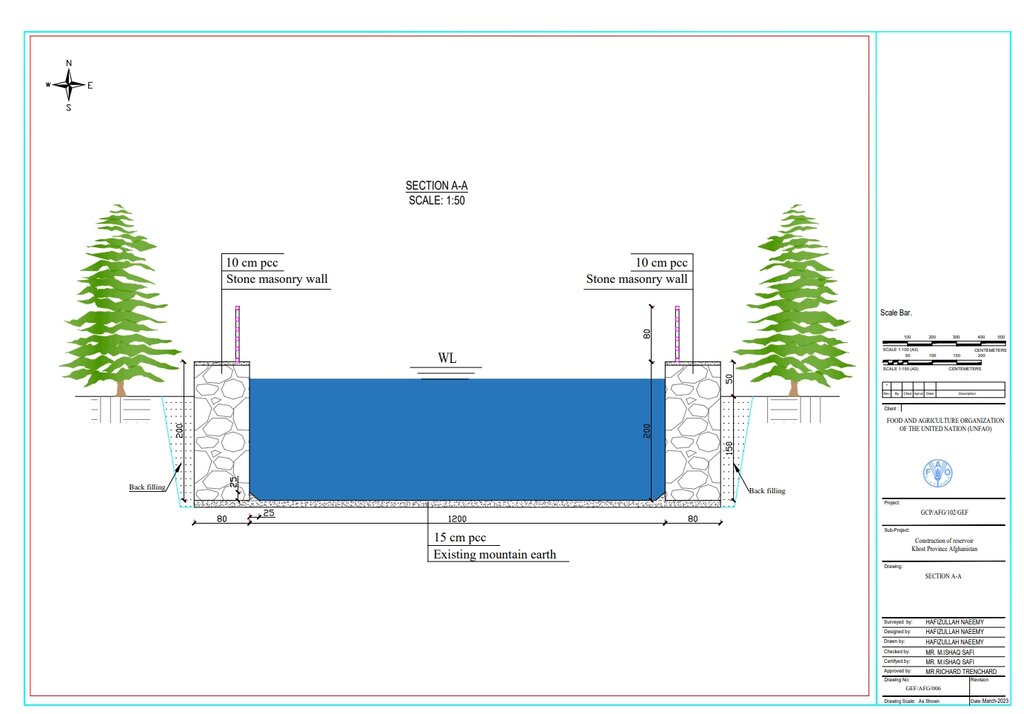
Each of the three reservoirs measures 2m x 8m x 12m with a water depth of 2m, holding a total capacity of 192 cubic meters.
Autor:
Hafizullah Naeemy
Fecha:
18/01/2023
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
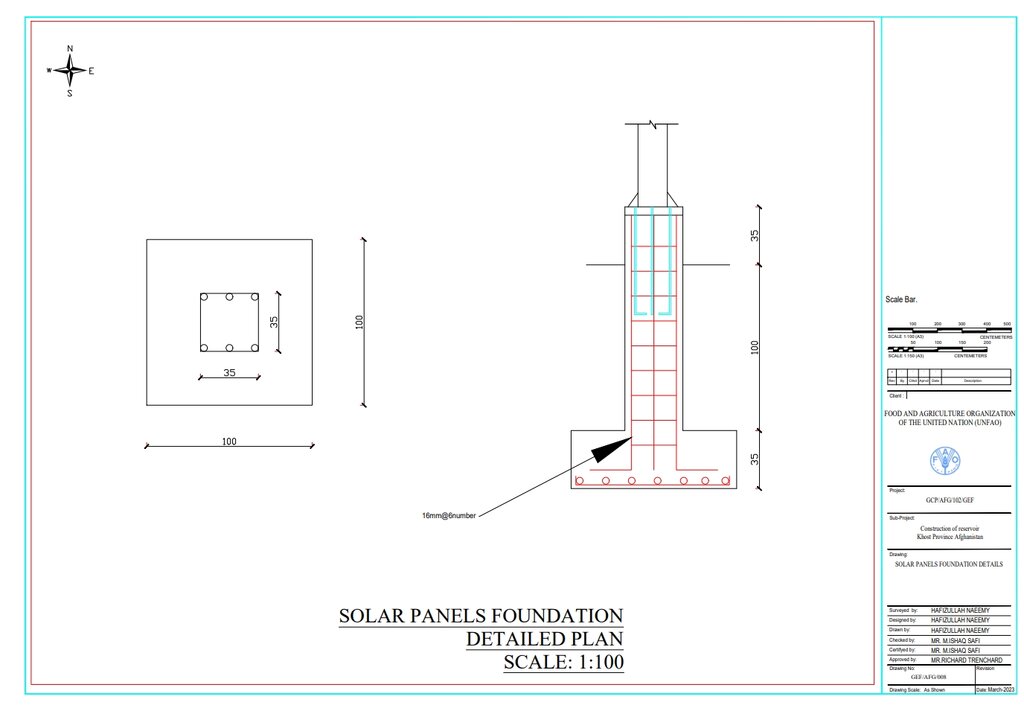
The solar panel stands, including their foundations, are 2 meters in height, with each panel measuring 1.2 meters high and 0.6 meters wide. The panels are installed at a 45° slope angle.
Autor:
Hafizullah Naeemy
Fecha:
22/01/2023
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
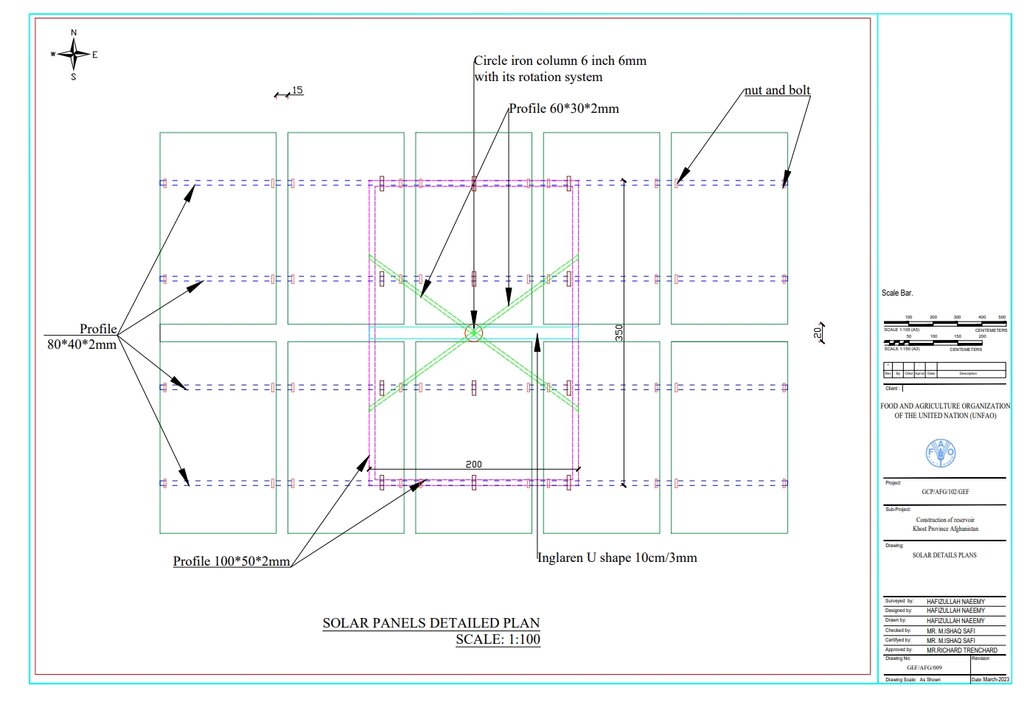
Detailed plan for solar panel installation: Three metal stands designed to support and rotate 26 solar panels, optimizing sunlight exposure throughout the day.
Autor:
Hafizullah Naeemy
Fecha:
23/01/2023
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
20 Hectares
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
5 USD
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Conduction of survey, feasibility study, and site selection | 1st month |
| 2. | Finding of water source | 2nd month |
| 3. | Installation of solar power lifting system | 4rd month |
| 4. | Construction of reservoirs | 5th month |
| 5. | Installation of irrigation piping system | 12th-1st month of the year |
| 6. | Saplings delivered by supplier to the site from contracted nurseries | 1st-2th month |
| 7. | Planting of saplings | 2-3rdmonth |
| 8. | Preparation of two demonstration plots for fodder and medicinal plants | 3rd month |
| 9. | Planting of seeds for fodder and medicinal plants | 3rd month |
| 10. | Installation of barbed wire fencing for 20 hectares | 7-9th month |
| 11. | Ensurance of operation and maintenance of all systems | 24th month |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Installation of solar system and pipe installation | Person/day | 100,0 | 6,0 | 600,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Digging pits, plantation and irrigation of Plants | Person/day | 453,0 | 6,0 | 2718,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Excavation of foundation | Person/day | 80,0 | 5,0 | 400,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Preparing demonstration plots for fodder and medicinal plants | Square meter | 25000,0 | 0,13 | 3250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Stone Masonry | Person/day | 136,0 | 6,0 | 816,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Plastering | Person/day | 72,0 | 5,0 | 360,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Plain cement concrete | Person/day | 57,0 | 5,0 | 285,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Plain cement concrete PCC M20 | Person/day | 390,0 | 5,0 | 1950,0 | |
| Equipo | Entrance Gate | Number | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| Equipo | Solar panel 400W | Sheet | 26,0 | 140,0 | 3640,0 | |
| Equipo | Rotating PV panel mount | Number | 3,0 | 350,0 | 1050,0 | |
| Equipo | Submersible pump 2 inch (10PH-7500W) | Number | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Equipo | DC-AC current inverter 7.5-11kw | Number | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| Equipo | Distribution board | Number | 1,0 | 75,0 | 75,0 | |
| Equipo | Sign board | Number | 3,0 | 3,0 | 9,0 | |
| Equipo | Sign board | Number | 1,0 | 150,0 | 150,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Walnut | Sapling | 2000,0 | 0,56 | 1120,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Almond | Sapling | 500,0 | 0,67 | 335,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Mulberry | Sapling | 100,0 | 0,44 | 44,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Pomegranate | Sapling | 500,0 | 0,51 | 255,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Alfalfa seed | Kg | 50,0 | 2,72 | 136,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Black Cumin seed | Kg | 15,0 | 6,72 | 100,8 | |
| Material de construcción | Tap | Number | 30,0 | 3,0 | 90,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Flexon 1 inch rubberized pipes | Meter | 1250,0 | 2,0 | 2500,0 | |
| Material de construcción | DC current wire | Meter | 100,0 | 2,0 | 200,0 | |
| Material de construcción | AC current wire | Meter | 150,0 | 2,0 | 300,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Polyethylene pipe 1.5 inch | Meter | 2000,0 | 2,0 | 4000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Polyethylene pipe 2 inch | Meter | 780,0 | 3,0 | 2340,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Polyethylene pipe 3 inch | Meter | 300,0 | 5,0 | 1500,0 | |
| Otros | Delivery to the site | Lump sum | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Otros | Galvanized iron pipe 2 inch for pillar | Meter | 125,0 | 5,0 | 625,0 | |
| Otros | Galvanized iron pipe 1.5 inch for bracing | Number | 470,0 | 10,5 | 4935,0 | |
| Otros | Fence | Meter | 15,0 | 25,0 | 375,0 | |
| Otros | Double strand galvanized barbed wire for fencing | Meter | 4200,0 | 0,25 | 1050,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 36208,8 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 36208,8 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
FAO under GEF-7 project
Comentarios:
The land users contributed primarily by digging pits for planting, preparing demonstration plots, and maintaining the system. Additionally, they hired guards to protect the area from disturbances. All other costs associated with the project were covered by the FAO GEF-7.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removal of sediment from reservoirs | Spring/annually |
| 2. | Safeguarding the site such as solar system, and on-site interventions | All seasons/regular |
| 3. | Repairing solar system & water pump and pipes | Regularly |
| 4. | Demonstration plots maintenance (pest-diseases control, mulching, weeding and Irrigation | Spring & Automn/annually |
| 5. | Replacing dead and dried plants | Feb/two times (1st & 2nd year) |
| 6. | Repairing fencing | Year around |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour for cleaning the reservoir from sediment annually | Person/day | 15,0 | 5,0 | 75,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Hiring guards for safeguarding the site | Person/day | 12,0 | 100,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Fixing pump when needed | Lump sum | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Repairing pipes | Lump Sum | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Repairing solar panel when required | Lump sum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Weed control | Person/day | 10,0 | 5,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Integrated Pest Management | Lump sum | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Irrigation | Person/day | 8,0 | 50,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Saplings | Number | 1500,0 | 0,56 | 840,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Local Seed | Kg | 15,0 | 26,0 | 390,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Barbed wire | meter | 3000,0 | 0,14 | 420,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Replacing dead and dried plants | Lump sum | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 4830,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 4830,0 | |||||
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Construction materials cost
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones convexas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
The site is situated near a forest and rangeland, with a gentle slope of approximately 45 degrees and an elevation of 1,279.49 meters above sea level. Surrounding mountains are covered with wild olive forests.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea y superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
Sí
Frecuencia:
frecuentemente
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
The water quality meets site requirements; however, seasonal fluctuations occur due to droughts. Floods in the lower gully, carry debris and sediments that can impact the source.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
The site was rich in flora and fauna, but human and animal interference has led to significant degradation. Many indigenous plants have been uprooted, and wildlife has migrated due to the loss of habitat. In response, the community has begun to manage and restore the land through practices like rotational grazing and quarantine measures to combat illegal logging.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- personas de mediana edad
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
The land in question is communal and remains undivided, with no plans for future distribution. Most users have limited agricultural land downstream, typically no more than 0.5 hectares per household for crop cultivation. The learning site has been dedicated by the local community for future generations and educational purposes. Previously, this land was unused and primarily designated for grazing.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
Land use rights in traditional legal systems are generally straightforward, with each family in a village having equal access to natural resources.
Comentarios:
Overall, this traditional approach emphasizes community and family roles in resource management, balancing individual rights with communal responsibilities
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Comentarios:
Due to three to four decades of political conflict, people lack access to essential services and infrastructure. This situation has been largely overlooked, with insufficient attention given to providing these services. Additionally, there has been a lack of budget allocation and support from the government and NGOs. As a result, communities continue to suffer from inadequate resources and infrastructure development.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
The local community is adopting rotational grazing and quarantine measures on rangeland, while also exploring silage-making and hay production techniques. Additionally, they are identifying alternative winter feed options for their animals.
calidad de bosques
Comentarios/ especifique:
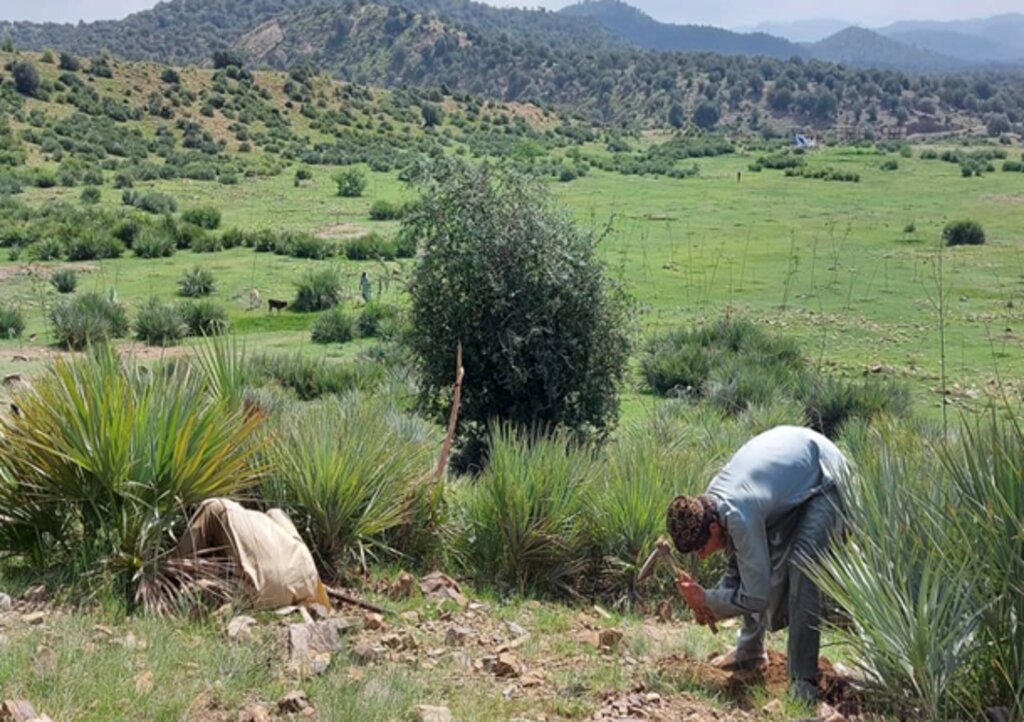
The local community has successfully quarantined all forest areas, effectively controlling illegal logging and managing grazing. As a result, the forest has been revitalized and is undergoing natural regeneration
producción de productos forestales no madereros
Comentarios/ especifique:
The local community is utilizing Mazari palm for handcrafted products while also focusing on agroforestry. They have established fruit orchards and are collecting blackthorn, which they sell in the bazaar to support their livelihoods.
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Previously, the community overgrazed the land and cut down trees for their livelihoods. However, after implementing quarantine measures and rotational grazing practices, the area is now showing signs of regeneration and has the potential to become a productive landscape in the future.
manejo de tierras
Comentarios/ especifique:
Following these practices, the local community has effectively managed more land under proper stewardship, including forest and rangeland quarantine and controlled grazing. They are now applying these methods in their vicinity, leading to the successful management of additional areas.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
Through revegetation and improved land cover, water seeps into the ground, recharging the water table and increasing availability for irrigation.
Ingreso y costos
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Impactos socioculturales
oportunidades recreativas
Comentarios/ especifique:
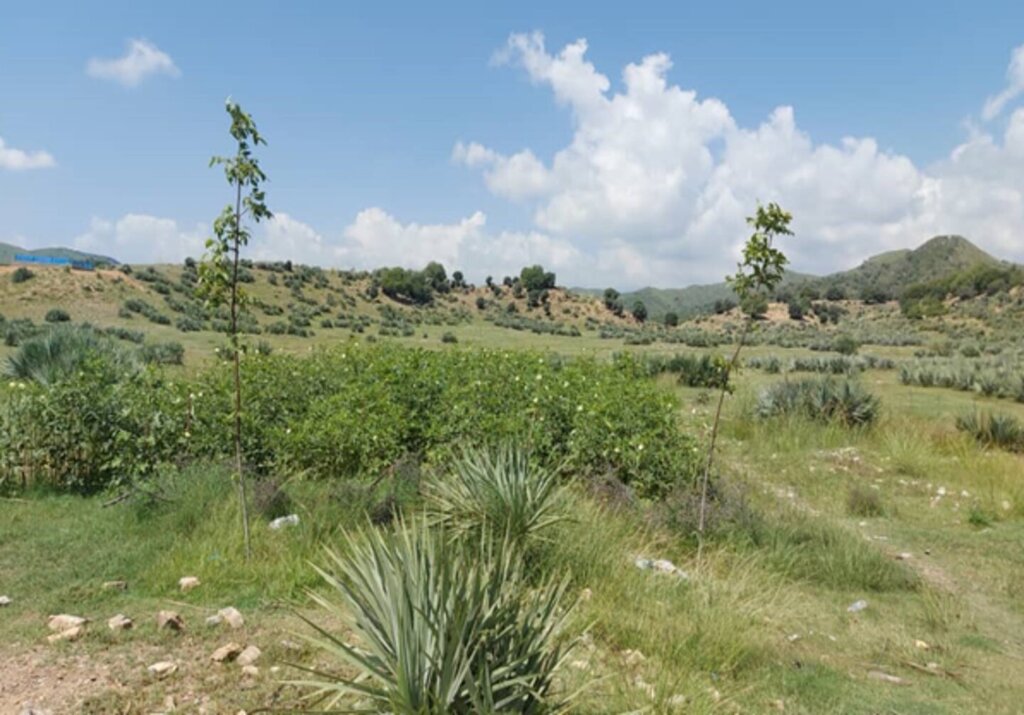
FAO and Forest and Rangeland Management Association have successfully revitalized this area, transforming it into a lush and green landscape. Many of the previously destroyed species regenerated, creating a thriving ecosystem. This site is now a focal point, surrounded by majestic mountains and rich forests, with water flowing from the upper watershed. It has become a popular destination for picnics and visits, where people can enjoy the soothing sounds of birds and the vibrant greenery of the surroundings.
instituciones comunitarias
instituciones nacionales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
mitigación de conflicto
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Through applying quarantine, rotational grazing, control grazing the vegetation covered increased.
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Biomass above the ground is increased
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
most of the seed regenerating and all the cut trees and bushes revegetated.
diversidad animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Various migratory animals and birds have returned to the area due to the protection measures in place and the prohibition of human activities.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
Comentarios/ especifique:
Most of the riverbanks have been successfully revegetated through effective control measures, including water filtration during rain and floods. Local communities have also learned to plant cuttings along the riverbanks and shorelines, contributing to the restoration of these vital ecosystems.
impactos de sequías
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Healthy ecosystems like forests and wetlands act as carbon sinks, absorbing more CO2 through photosynthesis. Improved soil health and vegetation cover also enhance carbon storage, while restoring habitats promotes biodiversity, creating a more resilient ecosystem that sequesters carbon effectively.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Through revegetation and improved land cover, water seeps into the ground, recharging the water table.
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
sedimentos transportados por el viento
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
impacto de gases de invernadero
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | disminuyó | nada bien | |
| lluvia anual | incrementó | nada bien | |
| lluvia estacional | verano | incrementó | nada bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de nieve local | nada bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| ola de calor | nada bien |
| sequía | nada bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación repentina | nada bien |
Comentarios:
Before the implementation of the project land users faced severe challenges, including drought, high temperatures, water scarcity for irrigation, reduced yields, and a lack of winter feed alternatives for livestock.
Following the introduction of sustainable rangeland management and biodiversity conservation, local communities adopted rotational grazing practices and protected forests from cutting, which had previously been their main source of income. As a result, vegetation cover improved, carbon stocks increased, and rainwater began to seep into the ground, recharging the water table, springs, canals, and Karezes. These efforts reulted in a more resilient and productive environment.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
The adoption of the technology in the specified area has primarily been spontaneous, significantly influenced by the support provided by the project. While a small percentage of land users may have received material incentives, the majority embraced the technology due to its demonstrated benefits and the project's educational efforts. This support helped to build trust and confidence among the land users, enabling them to implement the technology effectively in their practices. Overall, this highlights the importance of community engagement and capacity building in fostering sustainable land management practices.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| It is crucial for local communities to learn sustainable land and forest restoration techniques. These methods are not only accessible but also involve minimal operational costs. By empowering land users with this knowledge. |
| We can adopt sustainable land and forest management practices to revitalize our degraded land. This learning process is straightforward and easily applicable. |
| We have great opportunities and abundant resources to utilize. This area serves as a hub for scaling sustainable practices, allowing us to learn, observe, and implement solutions that will benefit future generations. |
| We can efficiently use surface water for irrigation instead of groundwater, helping to restore degraded land through these initiatives. |
| Reduce greenhouse gas emissions through effective carbon sequestration. |
| Learn regeneration techniques, rainwater harvesting, and grazing management methods like rotational grazing. Focus on producing fodder and medicinal plants, while understanding indigenous plants and shrubs for the future. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| This site is highly accessible, surrounded by dense forests and extensive rangelands that can be utilized sustainably. |
| Local community members, university students, and stakeholders can easily visit this site. |
| This site is an excellent destination for tourists to visit, enjoy, and learn about the importance of natural resources and their management techniques. |
| The local community can easily adopt these simple techniques to learn sustainable land and forest restoration practices. |
| The local community has hired guards to maintain the site effectively. They are gaining knowledge and enhancing their capacity for future interventions, contributing positively to development initiatives. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Insufficient maintenance and repair services for the technology. | Establishing strong linkages with service providers and maintenance support. This also facilitates nationwide technology transfer, enabling broader adoption and implementation of sustainable practices. |
| There is a lack of qualified professionals on-site to teach visitors the technical aspects of the technology. This gap hinders effective learning and limits the ability of visitors to fully understand and engage with the technology. | Hire on-farm officers to oversee and manage the learning site and provide information to visitors. |
| A check dam is required in the gully to store water for sustainability, especially during drought seasons when water availability decreases. | Construct a check dam in the lower section of the gully to store water for sustainability, allowing visitors to learn about water harvesting techniques. |
| There are currently no available resources for replacing the dead plants. | Establish nurseries for forest species to produce saplings that can replace dead and dried plants in the future. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| There are concerns about windstorms and hail potentially damaging the solar panels. | The local community should establish a social fund to cover repairs for any damage to solar panels caused by windstorms or hail, as well as to fund the installation of fencing around the solar panel stands. |
| Concerns have arisen regarding land disputes as the local community acts on land distribution amidst a growing population. | All villagers should receive a formal guaranteed letter, signed by the district governor, ensuring that no future actions will be taken to redistribute this site among the villagers. |
| There is a lack of essential water structures, such as percolation tanks and detention ponds, for effective rainwater harvesting. | Construct percolation tanks and detention ponds to harvest rainwater, which can be used to water livestock. Additionally, this initiative will provide an opportunity to learn and implement dryland farming techniques. |
| Too much water is wasted through flexible pipe basin irrigation methods. Additionally, required live hedges for fencing and windbreaks. | Install a drip irrigation system with an efficient piping layout and plant pine, poplar, and other trees alongside barbed wire to create a windbreak and a natural barrier for site protection. This will also provide an opportunity to learn various agricultural techniques. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
20
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
11
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
5
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
3
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
10/10/2024
Comentarios:
The project was actively involved in all phases, from selection to implementation. Data was collected from local community volunteers, as well as SLM specialists and engineers.
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
N/A
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
N/A
7.4 Comentarios generales
The questionnaire is well-structured, but some sections, particularly 6.2 and 6.3, need simplification. Additionally, the database should provide outputs during data processing, highlighting both best practices and common mistakes related to the technology. This will help us generate a comprehensive report that showcases effective practices and identifies areas for improvement.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Stakeholder collaboration for building Learning Site for landscape … [Afganistán]
To raise awareness and ensure clear role delineation, a series of consultations were held with the local community, the Forest Management/Rangeland Management (FM/RM) association, and other key stakeholders. Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) that formally outlined the roles and responsibilities of each party was signed. Additionally, the FM/RM association issued a …
- Compilador: Mohammad Arif
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos