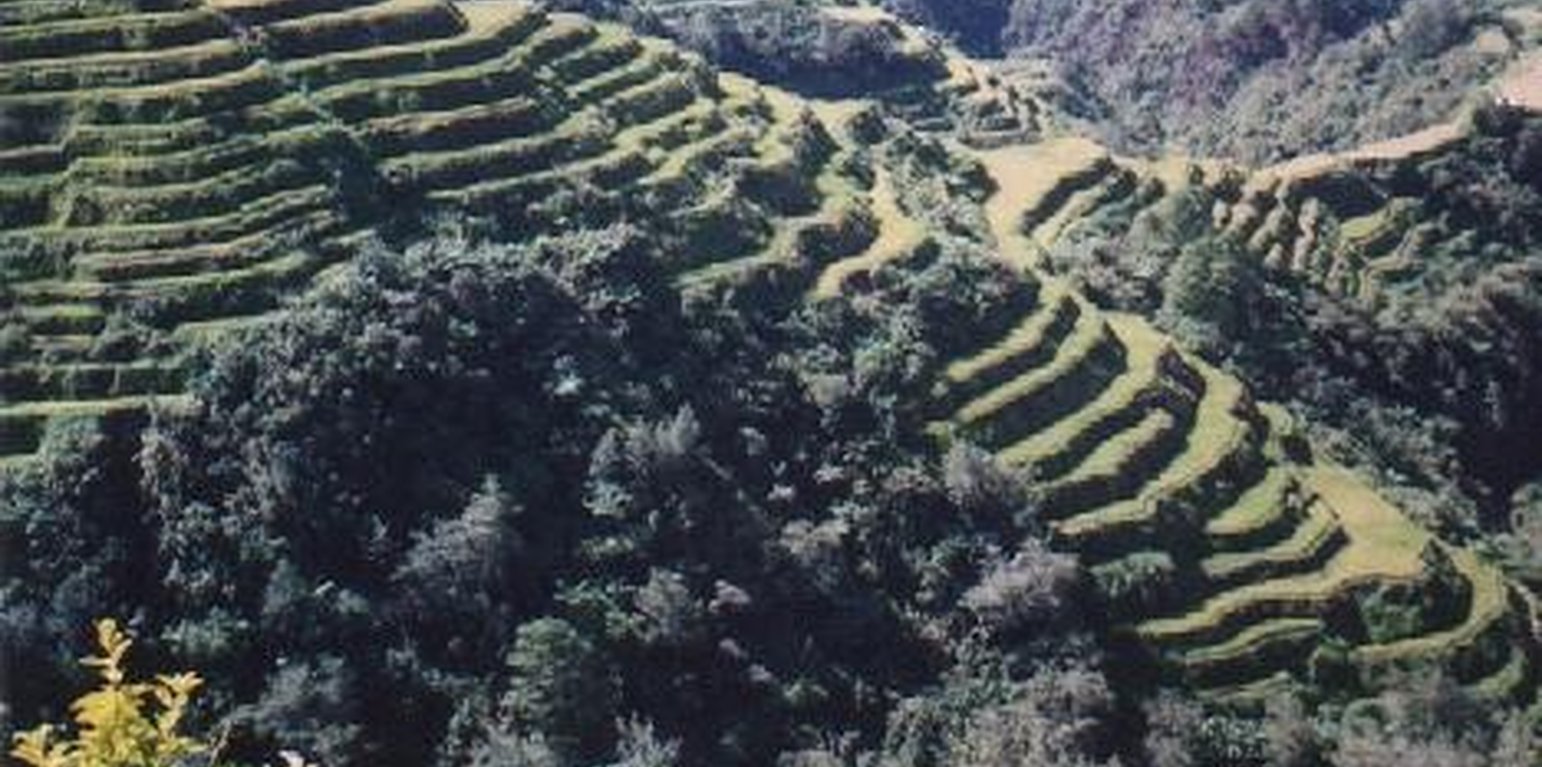
Woodlot
(Philippines)
Muyong
Description
Woodlot is a forest management approach which aims the to provide food, wood for fule, construction and material for woodcarving and to provide a steady source of water for the lower-hilly riceland area.
Woodlot or 'muyong' as it is called in the local language is basically a timber management system. The harvesting of non-timber products like fruits and other benefits like the maintenance of a stable water supply are secondary objectives. Fuelwood and construction timber are the major products of woodlot. The usual size of woodlot is not more than one hectare and is individually owned. The approach is believed to have started at least a century ago. It began when it became apparent that sources of fuelwood near homes were becoming difficult to find. The approach also came about when people realized the need for accountability in the use and management of natural resources. The ancestors of the present-day owner of the woodlots were influenced by the relationship of a reliable and steady water supply and the existence of forest. Woodlots normally evolved from swidden fields. The owners encouraged the growth of prefered species either by direct seeding or by transplanting seedlings uprooted fron nearby forest.
Present practices involve the growing of introduced-fast growing species such as mahogany (Switeria macrophylla) and gmelina (Gmelina arborea). Rattan a valuable material for the furniture industry is also raised in the woodlot. Medicinal herbs are also gathered. Mushrooms and nuts are also grown. Woodlot is an approach unique to the indigenous tribes of the Cordillera. Boundaries, tenures and disputes are settled based on local traditions and beliefs. Common disputes arise from illegal gathering of fruit products. Transfer of ownership is upon the discretion of parents and only to married children. Inheritance of a woodlot denotes the handling down of authority and responsibility over the family. Woodlot or 'muyong'has been hailed as one of the nine successful 'Traditional Forest Related Knowledge' (TFRK). In terms of sophistication and social organization, woodlot is no equal among the approaches being practiced by the different ethnic groups in the country.
Lieu
Lieu: Mountain Province and Ifugao, Philippines
Géo-référence des sites sélectionnés
Date de démarrage: sans objet
Année de fin de l'Approche: sans objet
Type d'Approche
-
traditionnel/ autochtone
-
initiative/ innovation récente locale
-
fondé sur un projet/ programme
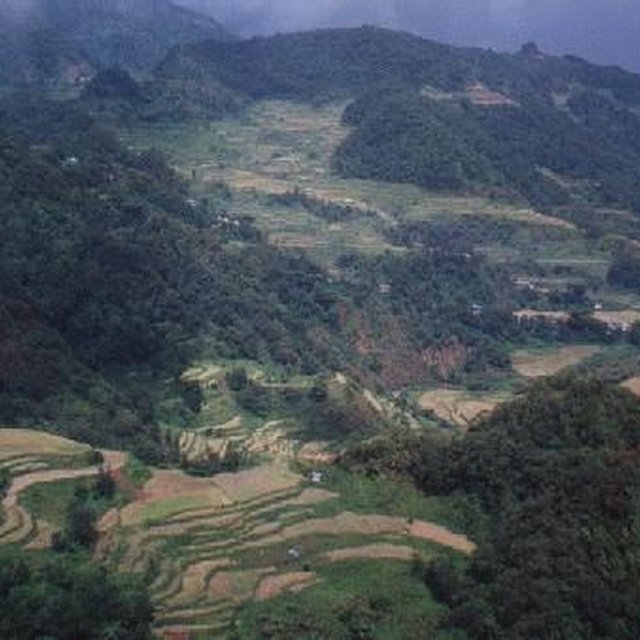

Agriculture and forest in harmony with nature in the Cordillera.
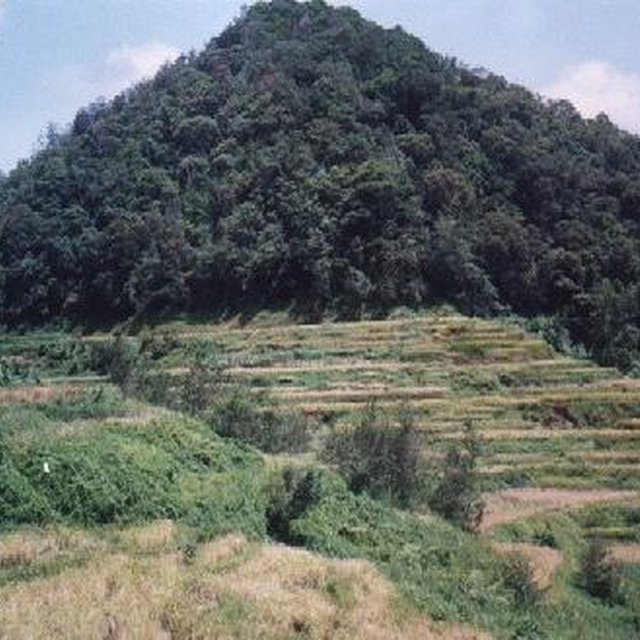

A well-maintained woodlot above the terraces.
Objectifs de l'approche et environnement favorable
Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
Sustainable use of forest resources by employing traditional beliefs, customs and traditions. Promote ecological balance.
Conditions favorisant la mise en oeuvre de la/(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
-
Cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau): Regalian doctrine which says that all public lands are owned by the state. -> Regular maintenance of a portion of the forest by weeding, removing of vines and undesirable species.
-
Connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques: Lack of knowledge on the proper care and maintenance of forest resources. -> Provisions of traditional skills, customs and beliefs in the care and maintenance.
Conditions entravant la mise en oeuvre de la/(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
| Quels acteurs/ organismes d'exécution ont été impliqués dans l'Approche? |
Spécifiez les parties prenantes |
Décrivez le rôle des parties prenantes |
| exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales |
Specific ethnic groups: The indigenous tribes in the Cordillera and Caraballo mountain ranges in Northern Luzon. |
|
Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
aucun
passive
soutien extérieur
interactive
auto-mobilisation
Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie de GDT
Les décisions ont été prises par
-
les exploitants des terres seuls (auto-initiative)
-
principalement les exploitants des terres soutenus par des spécialistes de la GDT
-
tous les acteurs concernés dans le cadre d'une approche participative
-
principalement les spécialistes de la GDT, après consultation des exploitants des terres
-
les spécialistes de la GDT seuls
-
les responsables politiques/ dirigeants
Les décisions ont été prises sur la base de
-
l'évaluation de connaissances bien documentées en matière de GDT (prises de décision fondées sur des preuves tangibles)?
-
les résultats de recherches?
-
expériences et opinions personnelles (non documentées)
Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
Les activités ou services suivants ont fait partie de l'approche
-
Renforcement des capacités/ formation
-
Service de conseils
-
Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
-
Suivi et évaluation
-
Recherche
Renforcement des capacités/ formation
La formation a été dispensée aux parties prenantes suivantes
-
exploitants des terres
-
personnels/ conseillers de terrain
Formats de la formation
-
sur le tas
-
entre agriculteurs (d'exploitants à exploitants)
-
zones de démonstration
-
réunions publiques
-
cours
Sujets abordés
Informal training among family members on the management of forest for sustainable use.
Service de conseils
Le service de conseils était fourni
-
dans les champs des exploitants?
-
dans des centres permanents
Environmental protection particularly watershed management is a top priority of the government and NGO's. The 'woodlot' approach of watershed protection is regarded as a perfect example of forest management being employed by indigenous people.
Renforcement des institutions
Institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place
-
non
-
oui, un peu
-
oui, modérément
-
oui, beaucoup
Décrivez l'institution, ses rôles et responsabilités, ses membres, etc.
by promoting aesthetics
Type de soutien
-
financier
-
renforcement des capacités/ formation
-
équipement
Plus de détails
Suivi et évaluation
Recherche
La recherche a traité les sujets suivants
-
sociologie
-
économie/ marketing
-
écologie
-
technologie
Researches on traditional forest knowledge of different ethnic groups.
Financement et soutien matériel externe
Budget annuel en dollars US de la composante GDT
-
< 2 000
-
2 000-10 000
-
10 000-100 000
-
100 000-1 000 000
-
> 1 000 000
Precise annual budget: sans objet
land users 100%
Les services ou mesures incitatives suivantes ont été fournis aux exploitants des terres
-
Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
-
Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques
-
Crédits
-
Autres incitations ou instruments
Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
La main d'oeuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était
-
volontaire
-
vivres-contre-travail
-
payée en espèces
-
récompensée avec un autre soutien matériel
Analyses d'impact et conclusions
Impacts de l'Approche
Non
Oui, un peu
Oui, modérément
Oui, beaucoup
Est-ce que l'Approche a mobilisé/ amélioré l'accès aux ressources financières pour la mise en œuvre de la GDT?
The approach contributed to effective water conservation to sustain the rice terraces
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les questions foncières et des droits d'utilisation qui entravent la mise en œuvre des Technologies?
The land use right (no land titles) is being respected and honored and the approach fits well in the over-all scheme. The land use right is well respected in the communities. Conflicts are peacefully resolve through compromises and agreements.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
The concept is being adopted in other areas with different degrees of success. It is being talked about as a classic example of resource management.
Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en oeuvre la GDT
Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en oeuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur) ?
Conclusions et enseignements tirés
Points forts: point de vue de l'exploitant des terres
-
Strong respect for customs/traditions in the management of resources.
-
Strong backing from local government units (LGU's)
Points forts: point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne-ressource clé
-
Respect for land users rights even though there is no legal documents to hold on for the land
-
Continous replanting
-
Strong resolve of the land users on the need for sustainability.
Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques: point de vue de l'exploitant des terrescomment surmonter
-
Woodlot can be a sanctuary for pests for the nearby rice fields.
Maintenance and cleanliness.
Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques: point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne-ressource clécomment surmonter
-
Not all members of the community is involved/benefited.
Wider involvement using other areas within the vicinity of the community.
-
Tendency for the woodlot to be commercialized and over-exploited.
Carrying capacity of the woodlot should be determined.
Références
Date de mise en oeuvre: 14 mars 2017
Dernière mise à jour: 14 mars 2017
Description complète dans la base de données WOCAT
Données de GDT correspondantes
La documentation a été facilitée par
Institution
Projet
- Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)
Références clés
-
Report on the Study of Traditional Forest Related Knowledge of the Ifugao and Bontoc Ethnic Groups in the Cordillera Region of the Philippines: Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Quezon City
-
Environmental and Socio-Economic Impact, Analysis of an Indigenous and Introduced Agroforestry Systems in Luzon.: University of the Philippines Los Banos Library, Los Banos, Laguna






