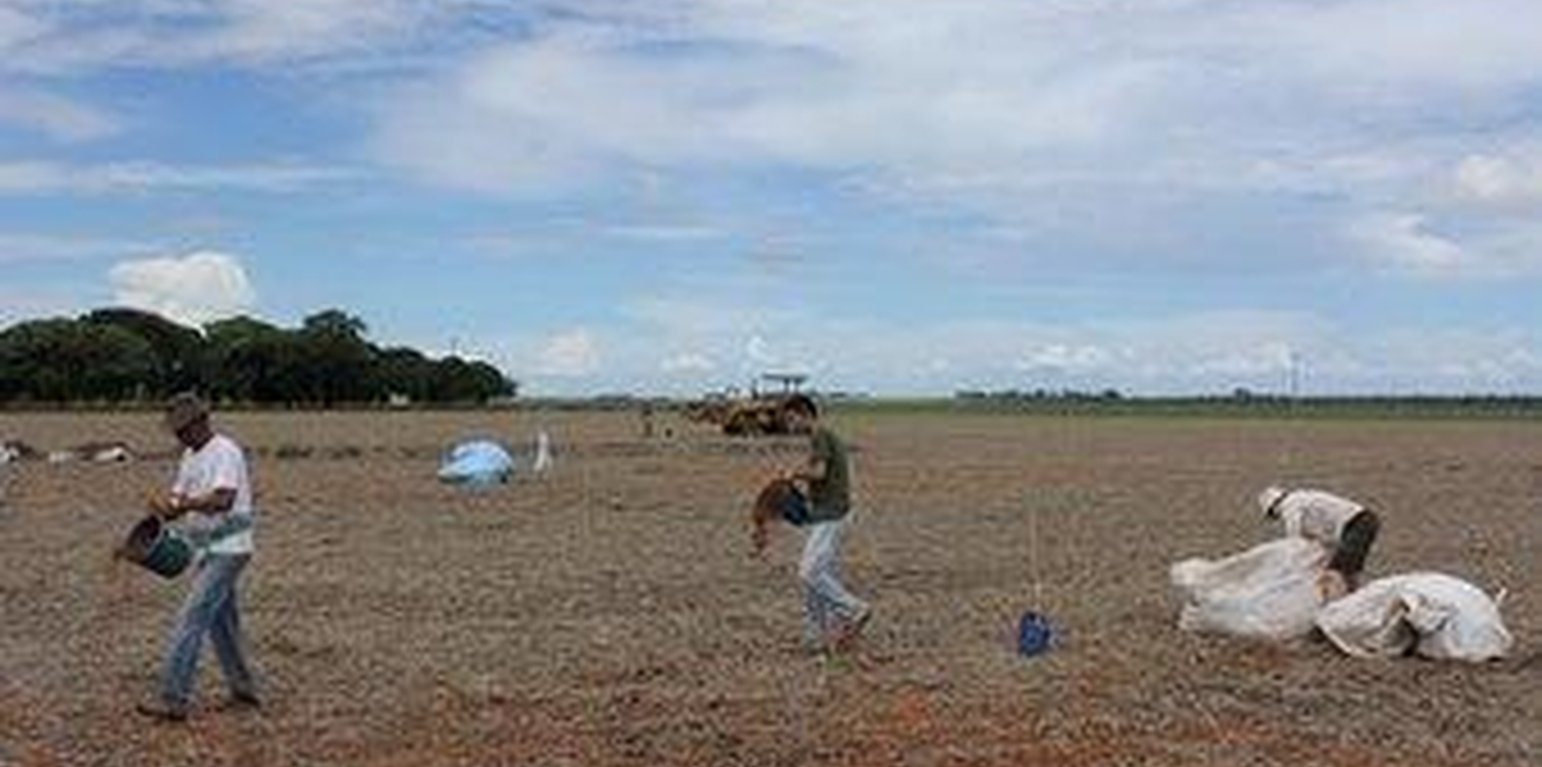




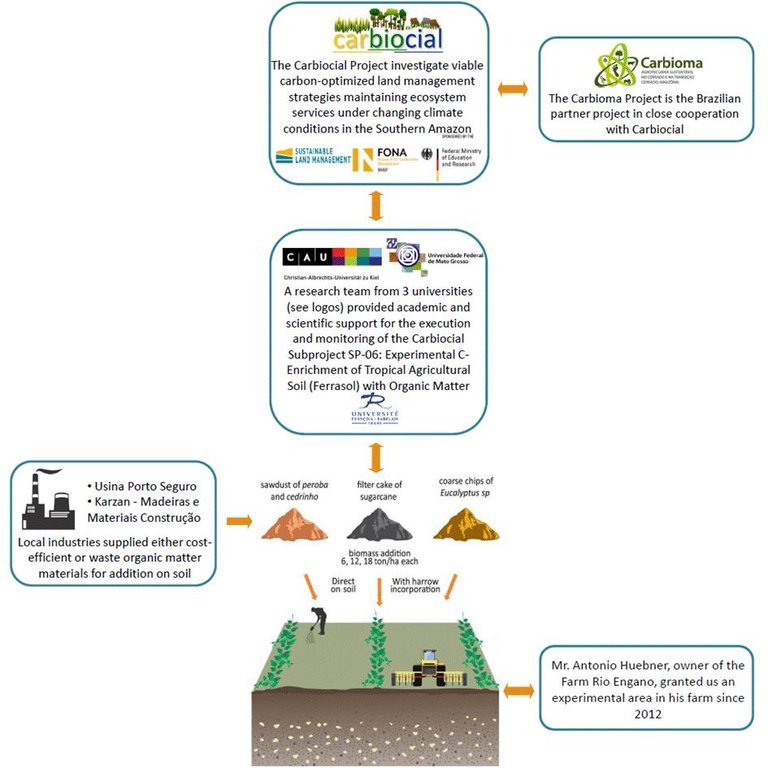
Aims / objectives: Use local available organic matter (OM) to enrich Tropical agricultural soil (Ferrasol) as a strategy for sustainanle land use to improve efficiently soil fertility and/or crop production in the Brazilian Cerrado agroscape. The applied OMs are either cost-efficient or waste materials from nearby industrial suppliers.
Methods: We applied three different types of OM amendments. They include (a) Filter cake of sugarcane residues (Saccharum officinarum from alcohol/sugar-production, (b) sawdust of Peroba and Cedrinho (Peroba jaune and Erisma uncinatum, respectively) and (c) coarse chips of Eucalyptus sp.
We added 0 (control), 6, 12 and 18 tons of each amendment per hectare; using two disposition methods: direct on the soil and with harrow incorporation. Each treatment was done in triplicate. Subsequent to the first amendment application; there have not been further experimental OM additions. The experimental site was not fenced to allow the land user to continue with their arable field routines on all treatment plots.
By sampling soil and biomass, we have assessed the effect of OM addition on soil organic carbon, nutrients, water holding capacity and crop (soy and corn biomass and grain) production, after one, two and three years of a single application.
Stages of implementation: The experiment was set up in February 2012. The last soil and biomass sampling was carried out in February-March 2015.
Role of stakeholders: Mr. Antonio Huebner, owner of the Farm Rio Engano, provided us an experimetal area in his farm.
The local industies supplied the applied OM amendments.
Professors and researchers from the Christian-Albrechts University of Kiel (CAU Kiel), Federal University of Mato Grosso (UFMT) and François Rabelais University have given academic and scientifical support to the approach.
Other important information: From our outcomes, we intend to provide information for the development of soil C-enrichment schemes and carbon-friendly landscape management programs for land users, applying local resources in the Brazilian Cerrado.
Lieu: Campo Verde, Mato Grosso, Brésil
Date de démarrage: 2011
Année de fin de l'Approche: 2016
Type d'Approche
| Quels acteurs/ organismes d'exécution ont été impliqués dans l'Approche? | Spécifiez les parties prenantes | Décrivez le rôle des parties prenantes |
| exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales | The farm owner where the soil C-Enrichment was done | |
| Spécialistes de la GDT/ conseillers agricoles | SLM specialists from the CAU University of Kiel, Federal University of Mato Grosso and François Rabelais University | |
| gouvernement national (planificateurs, décideurs) | ||
| organisation internationale | Carbiocial Project |
Organisation/flow chart of the experimental C-Enrichment of Tropical agricultural soil with organic matter amendments and monitoring (2012-2015) at the Farm Rio Engano, Brazilian Cerrado.
Les décisions ont été prises par
Les décisions ont été prises sur la base de
A detailed study on the enrichment effects of different organic matter types on soil carbon enrichment was undertaken (laboratory analysis of field samples). Further topics covered include sustainable land management and crop production.
By research staff from the Department of Applied Ecology, Institute for Ecosystem Research, CAU university of Kiel,
Germany; the Soil and Rural Eng. Department, Faculty of Agronomy, Veterinary Medicine, and Zootechnology (FAMEVZ),
Federal University of Mato Grosso, Cuiabá, Brazil and the Interdisciplinary Research Center for Cities, Territories,
Environment and Society (CITERES-CNRS UMR 7324), François Rabelais University, Tours, France.
Research was carried out on-farm
With this approach was demonstrated that soil organic carbon in tropical agricultural soil (Ferrasol) can be enhanced by applying local available organic matter, starting from only 6 ton/ha. Even when the studied soil has been under conservational farming practices, i.e. no-tillage, for more than 20 years.
• OM addition to tropical agricultural soil (Ferrasol) can increase significantly soil organic carbon and water retention, even in small amounts such as 6 ton/ha • Biomass reapplication should be done in 2 years intervals • The biomass type and disposition method did not have a significant effect on increasing soil organic carbon