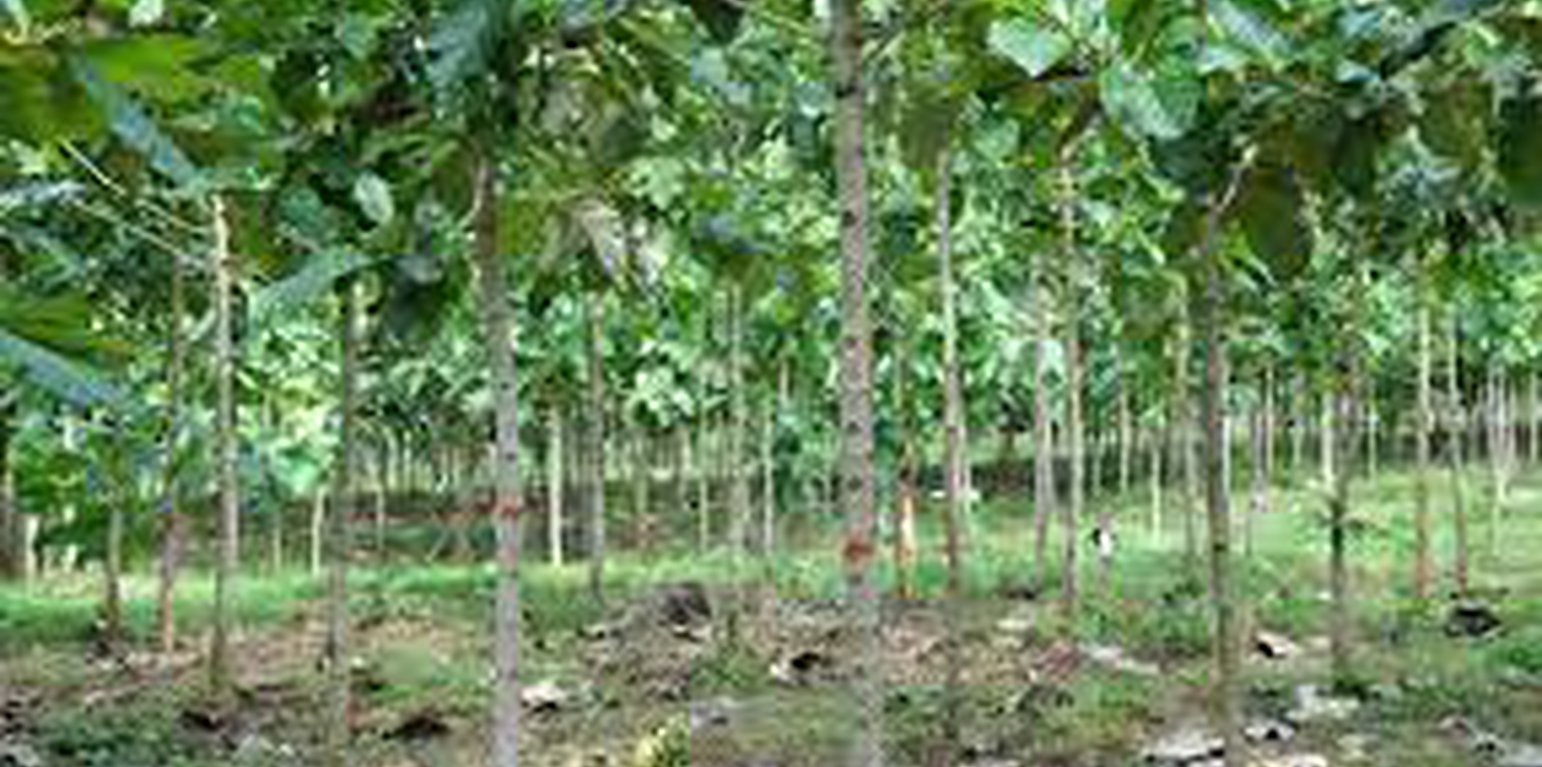




To establish this practice, the land-user puts into consideration the following: pitting at a depth of 3.5 inch, trees to be planted and spaced at 3 metres x 3 meters using the following inputs: tree seedlings, wheelbarrow, hoes, pangas and labour.
During the process, the tree stems are cut at 30cm length and planted. The stem is placed upright and later covered with soil. If there is adequate rain then some tip of the stem is left exposed but if rainfall is inadequate then the stem tip is covered in order for the plant to have enough moisture for its growth. It takes two weeks for the tip to get exposed on the surface when fully covered. The plant automatically appears with two leave lets.
The leaves when exposed to excessive sunlight can dry up and this retards its growth. This may require watering by the land user. At the early stage, the teak plantation can be inter cropped with beans and other crops such as sesame since the teak plantation has not yet formed a big canopy. This can be done for two years and later only slashing within the plantation needs to be done to maintain the plantation. The dry fallen leaves also kill weeds hence easing maintenance work. The trees are to be protected from fire outbreaks during dry season. In the month of November, fire lines are to be created and the dry leaves collected to mulch the plantation.
The cost of establishing a Teak plantations is high in the first 2-3 years but reduces significantly after first thinning. The cost of weeding can be reduced by spot-weeding of seedlings up to age 3 years, after which slashing or spraying with herbicides, usually Round-up is used for weed control. Wood from thinning is also sold as firewood or construction poles to recover some the establishment costs.
Shedding of teak leaves is heavy during the dry season and this causes a risk of fire. It’s advisable at this stage that the land user puts in place fire lines, an open space of 6 meters to separate the plantation into compartments in order to restrict fire from spreading from one part to another part.
Teak plantations are good at responding to dry conditions and can provide high-quality timber which in turn provides income. Teak trees provide hardwood timber, poles and modify the micro-climate through evapotranspiration. Fencing is done using bulb wires to avoid damage by wild animals and encroachments. The teak trees occupy land for a long period of time that can be used for other purposes like planting food crops. The piled dry teak leaves may harbour dangerous animals like snakes. Community members also complain about too much rainfall brought about by the plantation.
Lieu: Northern Uganda, Ouganda
Nbr de sites de la Technologie analysés: site unique
Diffusion de la Technologie: répartie uniformément sur une zone (approx. < 0,1 km2 (10 ha))
Date de mise en oeuvre: 2009
Type d'introduction






Spécifications techniques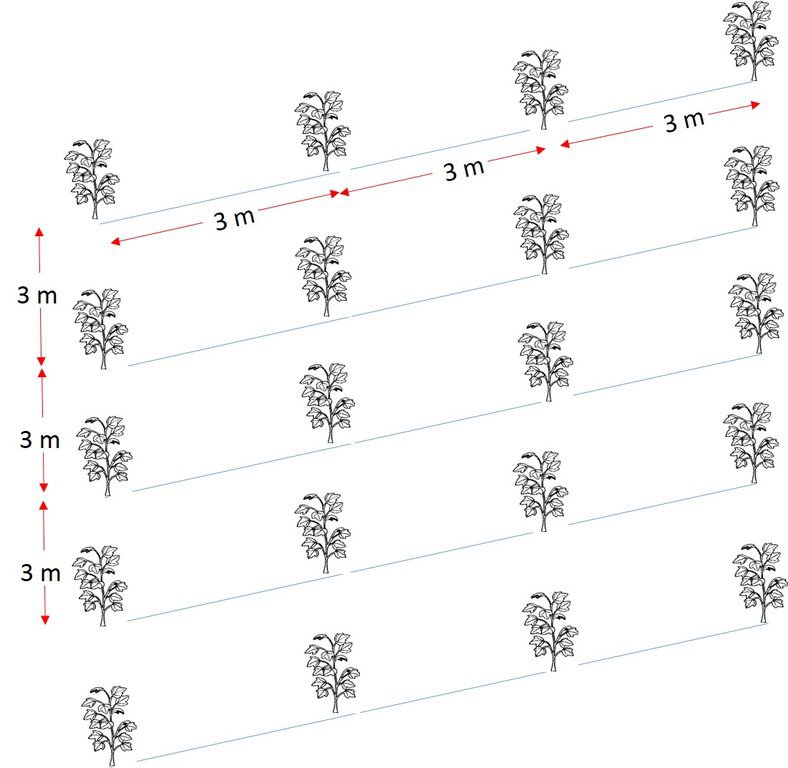
Auteur : Betty Adoch
Teak is planted on a gently sloping natural environment with pitting done at a depth of 3.5 inch Trees are spaced at 3 metres x 3 meters using the following in puts: tree seedlings, wheel barrow hoe, pangas and labour.
|
|||||||||||
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (UGX) | Coût total par intrant (UGX) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Hired labours | Manday | 30,0 | 3000,0 | 90000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | |||||
| Ox-plough | pieces | 1,0 | 280000,0 | 280000,0 | 100,0 |
| Pangas | pieces | 15,0 | 10000,0 | 150000,0 | 100,0 |
| Axes | pieces | 7,0 | 15000,0 | 105000,0 | 100,0 |
| String for lining | bundle | 2,0 | 10000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | |||||
| Teak-seedlings | Stem | 6000,0 | 1000,0 | 6000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 6'645'000.0 | ||||
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (UGX) | Coût total par intrant (UGX) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Plantation watchman | acres | 2,0 | 150000,0 | 300000,0 | 100,0 |
| Labour for fenching | acres | 8,0 | 100000,0 | 800000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | |||||
| Poles for fenching | acres | 790,0 | 2000,0 | 1580000,0 | 100,0 |
| Bulb wires | bundle | 4,0 | 150000,0 | 600000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fellkin (for termites) | bottles | 5,0 | 7000,0 | 35000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 3'315'000.0 | ||||
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Fuel wood obtained from teak pruned branches
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Shrub vegetation maintained with no cultivation taking place at the technology site
Quantité avant la GDT: Low
Quantité après la GDT: High
Hard wood timber provided for construction purposes
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Woodfuel provided from the pruned branches
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
From the sale of branches, poles and timbers sold to generate income
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Income from poles and timber production other than only crop
Quantité avant la GDT: high
Quantité après la GDT: low
Teak forests are easy to maintain since the dense canopy kills weed underneath
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
High water retention in the soil
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Quantité avant la GDT: High
Quantité après la GDT: low
Forest cover reduces the loss by binding the soil partials together
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Dense vegetation cover
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Teak plantation acts as carbon sink
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Different plant species like grass, shrubs exist inside the forest
Quantité avant la GDT: Low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Snakes, rabbits and other creators survive within the plantation
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Improved trees variety fast maturing and drought resistant
Quantité avant la GDT: high
Quantité après la GDT: low
Forest act as carbon sink
Quantité avant la GDT: high
Quantité après la GDT: low
Trees acts as wind breaks
Quantité avant la GDT: low
Quantité après la GDT: high
Forest modify the micro climate through evapotranspiration