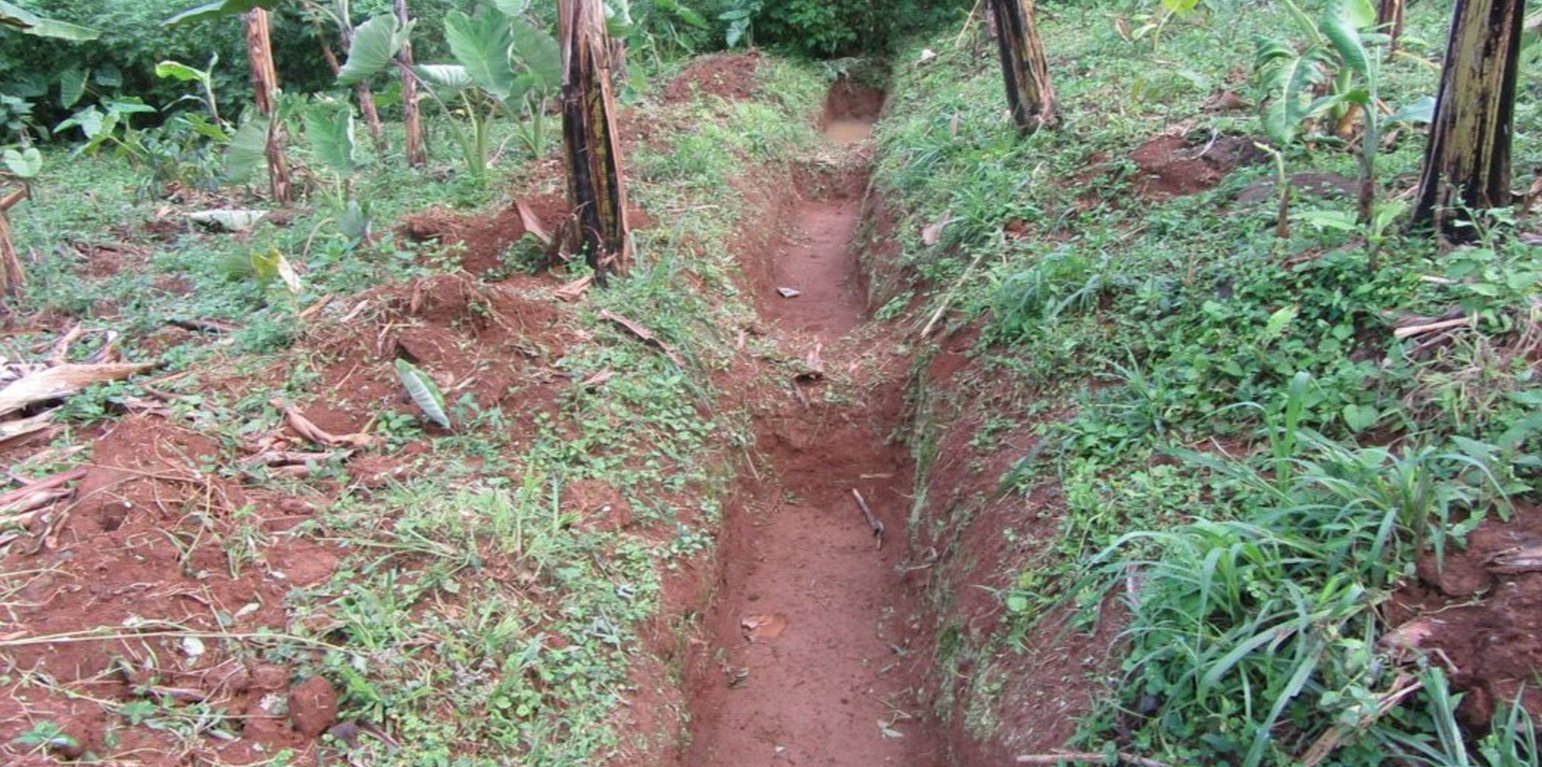




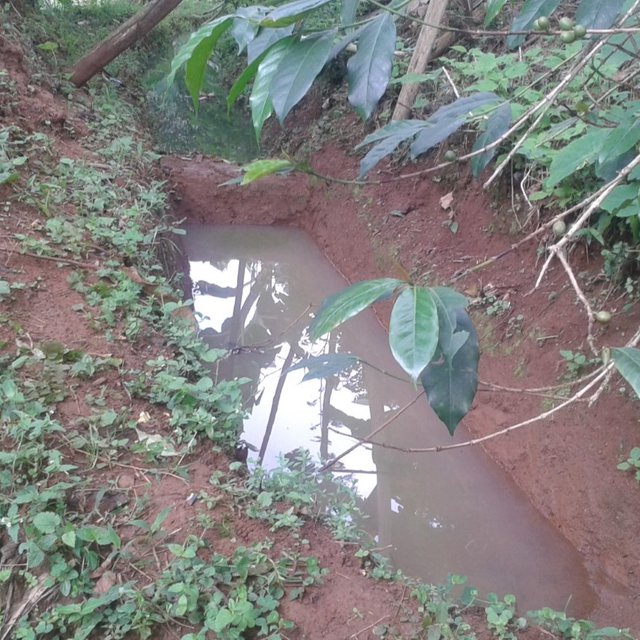
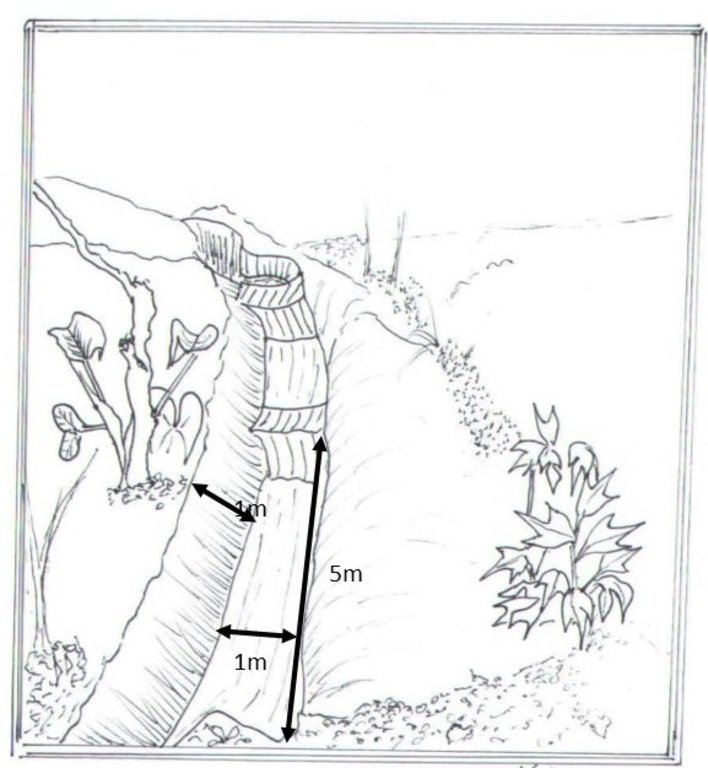
Water harvesting is the deliberate collection and storage of water that runs off on natural or manmade catchment areas. Catchment includes rooftops, compounds, rocky surface or hill slopes or artificially prepared impervious/ semi-pervious land surface. The amount of water harvested depends on the frequency and intensity of rainfall, catchment characteristics, water demands and how much runoff occurs. Contour trenches and pits are one of the oldest and most commonly used water management systems in the hilly areas of Mbale district. Contour trenches and pits are ditches dug along a hillside and run perpendicular to the flow of water. Their main objective is to slow down and attract runoff water which infiltrates into the soil which is used as soil moisture for crop cultivated after a rainfall event.These trenches and pits are constructed and maintained during the dry season. The size of the trenches is based on the slope and soil type. Bulabuli subcounty in Mbale district being a hilly area has trenches which are 5 metres long and 1 metre in width and depth. The materials needed in the construction of the trenches and pits are a hoe and spade. For maintenance they should be checked for build up soil, leaves and branches before the rainy season.The major advantages of rainwater harvesting are that it is simple, cheap, replicable, efficient, sustainable and adaptable and can be applied on any soil type and terrain. It can be implemented in small-scale, easily maintained and requires low investements which suites the rural community in Mbale district. Rainwater harvesting also has been shown an advantage as it reduces soil erosion, improves soil fertility and increases agricultural productivity as it reduces damage on the crops hence increases income and improves livelihood.
Lieu: Wahura village, Bunazoma Parish, Wanale subcounty, Eastern Uganda, Ouganda
Nbr de sites de la Technologie analysés: 100-1000 sites
Diffusion de la Technologie: répartie uniformément sur une zone (approx. 100-1 000 km2)
Date de mise en oeuvre: 1989; il y a entre 10-50 ans
Type d'introduction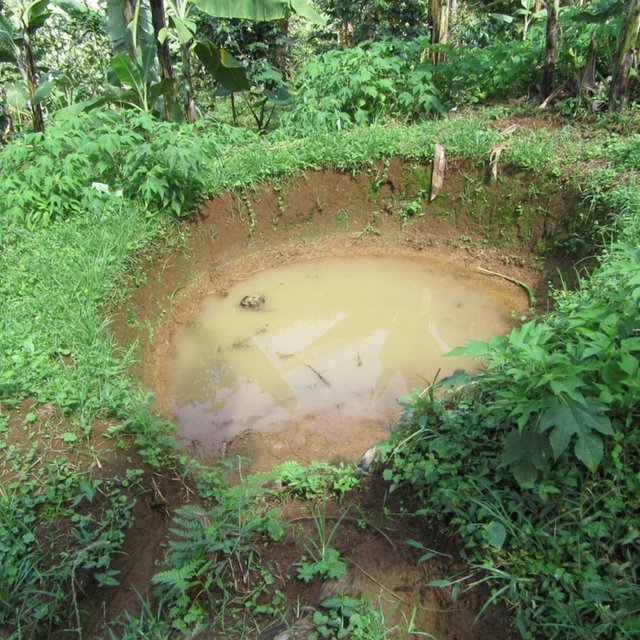







| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (Ugandan Shilling) | Coût total par intrant (Ugandan Shilling) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Man Power | Trenches | 58,0 | 4000,0 | 232000,0 | |
| Equipements | |||||
| Handhoe | piece | 3,0 | 10000,0 | 30000,0 | |
| Spade | piece | 3,0 | 15000,0 | 45000,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 307'000.0 | ||||
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (Ugandan Shilling) | Coût total par intrant (Ugandan Shilling) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Labour | Trenches | 58,0 | 1500,0 | 87000,0 | |
| Equipements | |||||
| Handhoe | pieces | 2,0 | 10000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| Spade | Pieces | 2,0 | 15000,0 | 30000,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 137'000.0 | ||||
Reduced crop failure due to soil and water conservation
The soil is kept moist and it is a source of water for the crops after rains.
Promotes soil and water conservation and salinity of low ground water bodies through control of soil erosion.
Through increased crop production hence increased sales
Source of on farm income to those who provide labour in the digging of the trenches and pits
Increased productivity due to reduced crop failure
Through knowledge sharing in their farmer groups
Reduced soil erosion hence reduced land slides
Reduced sheet erosion as a result of trenches trapping runoff water
Water is trapped in the trenches which infiltrates into the soil and also used for irrigation
Soil is trapped in the trenches and also reduced soil erosion through reduced water runoff
Soil trapped in the trenches is removed and put into the field
Reduces salinity of water bodies due to reduced soil erosion
Soil cover or mulch and top soil are conserved
Ground cover is conserved since sheet erosion is controlled
Controls flooding to low lands since some water is diverted into the trenches and pits
Reduced land slides since water is trapped in the trenches and also the water speed is reduced
Water trapped in the trenches and pits is used for crop irrigation
Water trapped in the trenches and pits can be used for spraying and making organic manure mixture from animals
Water is trapped in the trenches hence reduced runoff and water logging in low areas
Soil is trapped in the trenches
Soil erosion is controlled hence controlled salinity of water souces
Run off water is trapped hence reduced erosion and flooding in low land areas
Controlled soil erosion reduces land slides which would have blocked the roads affecting the transport system and maintenance costs