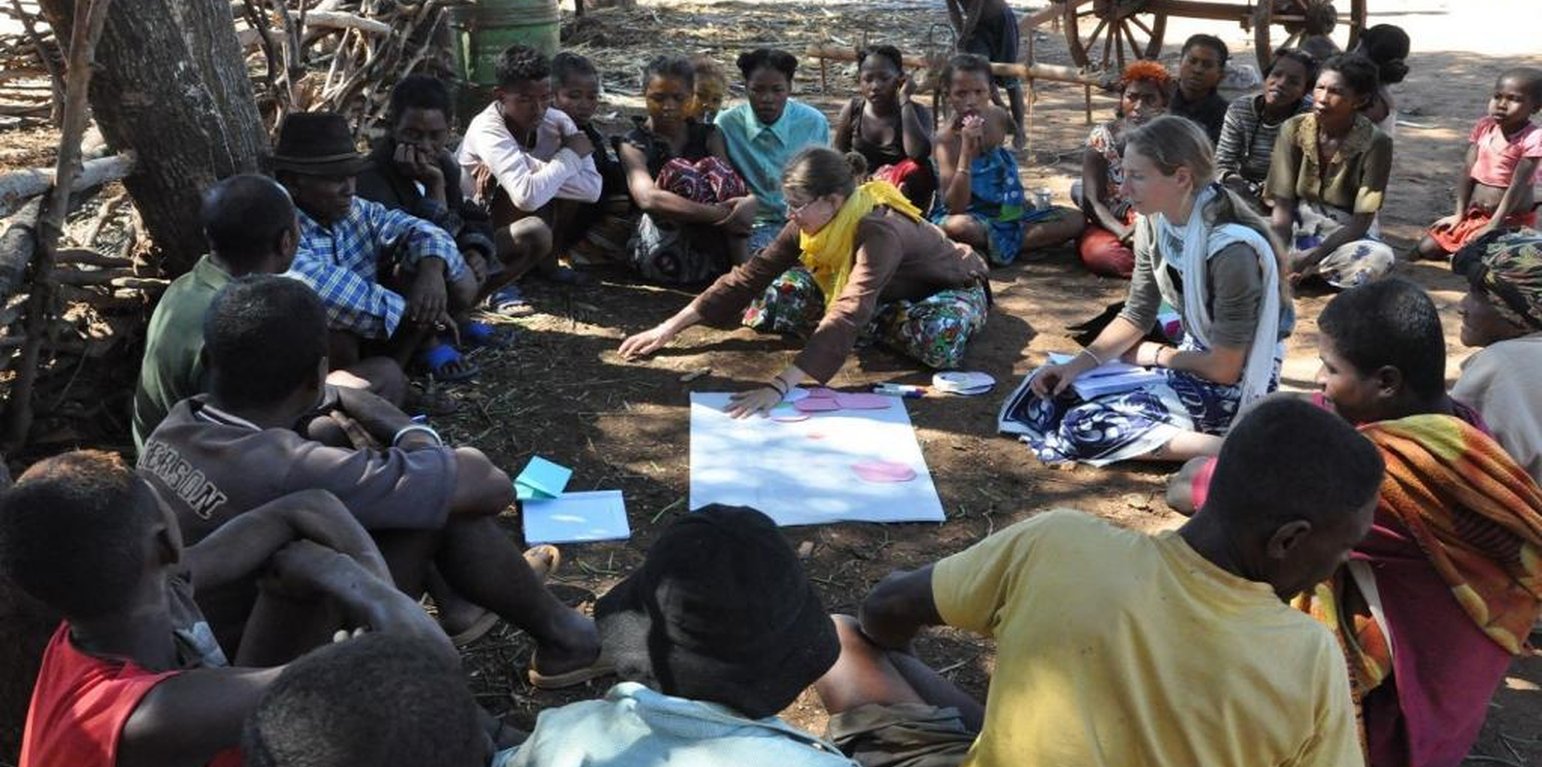




Aims / objectives: ‘MARP’ is a methodology for assessing local situations that is both participatory and rapid. It was used during the initial stage of a six-year research project (2011-2016) on sustainable land management (SLM) in Madagascar conducted by a consortium of German and Malagasy universities in collaboration with a NGO. The aim of the MARP study was to facilitate the local population to express their perspectives on local livelihoods and natural resource use. The approach sought to integrate local voices into project planning. Specific objectives were (a) to build a link between German and Malagasy researchers from different disciplines, (b) to train them in the MARP methodology, (c) to understand the broad outlines of subsistence strategies, and (d) to explore the diversity of social and environmental situations in the Mahafa-ly Plateau region.
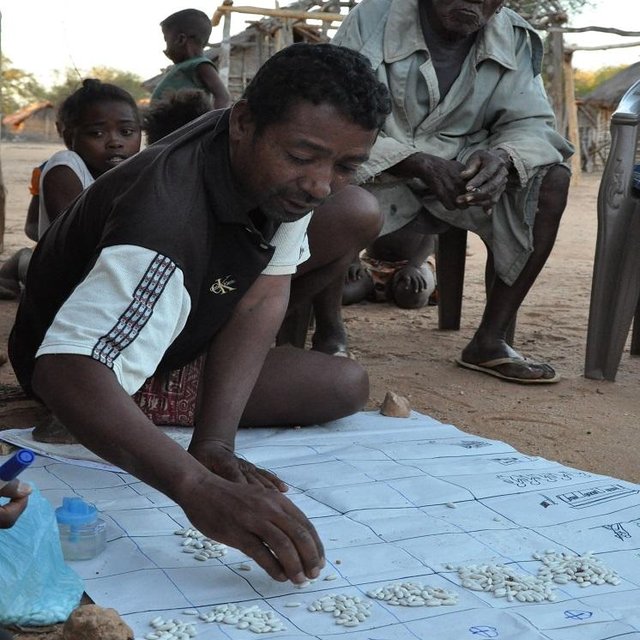
Methods: The MARP methodology facilitated an exchange between the local population (in-cluding land users and village representatives) and researchers about selected themes. Participants were invited to express themselves about their lives, social and ecological conditions and their use of natural resources. Four villages were chosen for the study, two at the coast and two on the plateau. The researchers were divided into two groups. Each group was accompanied by a facilitator and translators and each collected data in one village at the coast and one village on the plateau. Differ-ent techniques were applied to gather the information including semi-structured interviews, social maps, calendars (demonstrating cropping systems and historic developments etc), venn diagrams, and transect walks. In group discussions among researchers, information was triangulated and validated. After assessing a village, researchers called its villagers for feedback and discussion about the collected data. In this meeting the researchers presented a summary of results on local livelihoods, cropping systems and socio-cultural events, to discuss how accurate they were.
Stages of implementation: The MARP study was developed and carried out by researchers from various disci-plines including agriculture, livestock farming, silviculture, economics and human geography. It was divided into four phases, (1) an introductory workshop and tech-nical training, (2) data collection, (3) data analysis, and (4) a final workshop. In phase (1) two external experts in the MARP techniques introduced these to the par-ticipating Malagasy and German researchers in a four-day workshop. Phase (2) and (3) were implemented in the study region over a four-week period. In phase (4) the MARP study closed with a final workshop in the regional capital Tuléar, where re-sults were discussed with regional stakeholders.
Role of stakeholders: The local population played a particularly important role in the MARP study through providing key information about livelihoods and natural resource use etc. People from different clans and lineages, social status and both men and women were stra-tegically included. The MARP study group comprised 27 people who participated in the assessment: they included researchers, facilitators, socio-organizers, and trans-lators. Researchers had to develop contact with the local population, to learn from their insights, to collect and analyse data and to discuss the results with them. The facilitators’ role was to give directions to the teams during the study process. Social organizers dealt with equipment and accommodation, and translators accompanied non-native researchers during the information-gathering process.
Lieu: Beheloke-Atsimo, Mahafaly Plateau, south-western Madagascar, Madagascar
Date de démarrage: 2011
Année de fin de l'Approche: 2016
Type d'Approche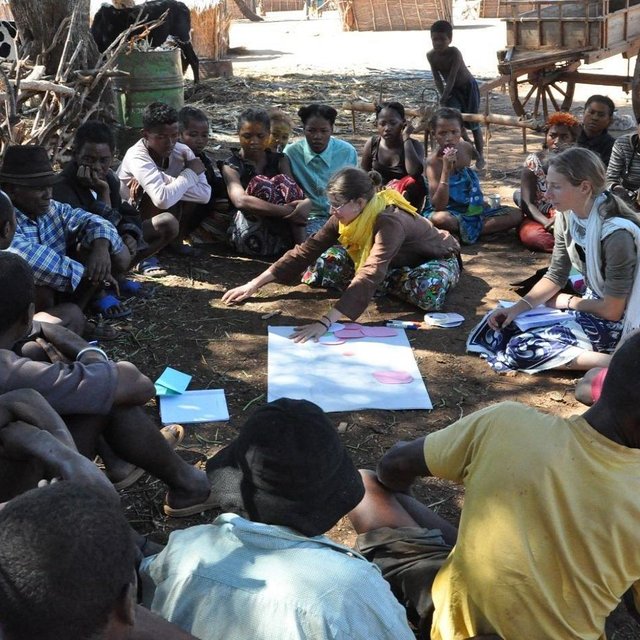

| Quels acteurs/ organismes d'exécution ont été impliqués dans l'Approche? | Spécifiez les parties prenantes | Décrivez le rôle des parties prenantes |
| exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales | More men participated in group meetings, according to local customs men dominate village meetings, women do not have the right to speak, however, it was sought to also involve women in the study through approaching groups of women in the villages. People from different lineages, status and age were deliberately involved | |
| ONG | WWF, Madagascar National Parks | |
| gouvernement local | village representatives | |
| gouvernement national (planificateurs, décideurs) | ||
| organisation internationale | international research consortium |
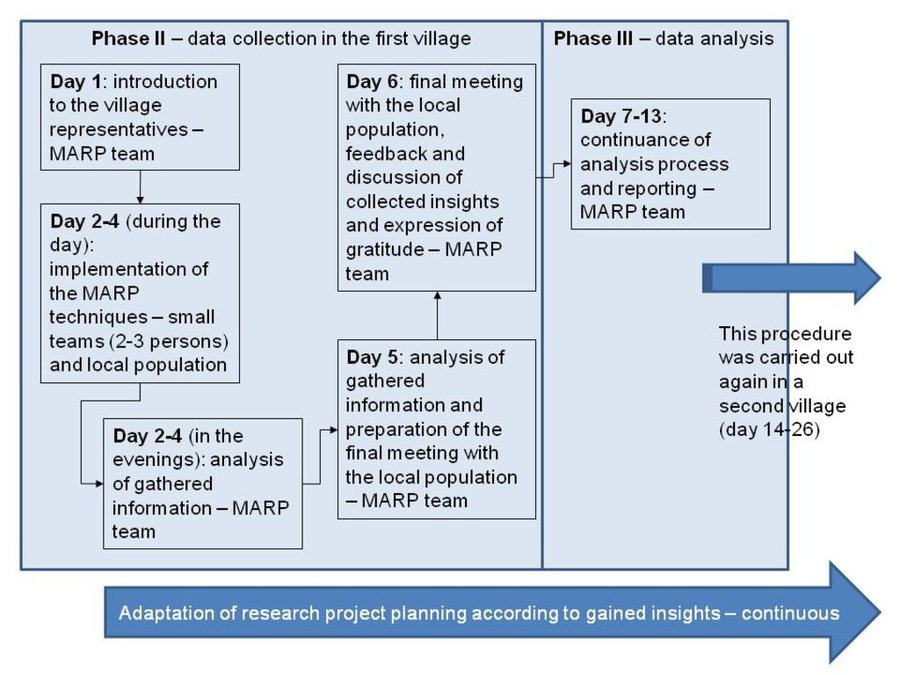
Flow chart shows the MARP study procedure exemplified by the first village.
Right after the introductory workshop and technical training the MARP team went off into the field. It spent six days in the first village starting with an introduction followed by a structured guidance through the MARP exercis-es and reflection on gathered information. The MARP study process in the first village closed with a final meeting of villagers and the MARP team in order to discuss the outcome. Subse-quently the MARP team moved to another place for data analysis and reporting before prepar-ing the stay in the second village.
Les décisions ont été prises par
Les décisions ont été prises sur la base de
Rapid and Participatory Rural Appraisal Methodology in the field of local livelihoods and natural resource use for researchers; local population was provided with awareness raising about the research project and the way how to participate in the research process
The aim was to gain a collective picture about local livelihoods, subsistence economy, and natural resources use.
Research was carried out on-farm
La main d'oeuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était
the focus of the MARP study was to gain insights into local people's perceptions regarding livelihoods and natural resource use rather than helping local land users to improve sustainable land management – though improved SLM was the aim of the overall research project to which the study contributed.
socially and economically disadvantaged people participated in the MARP study and explained their situation.