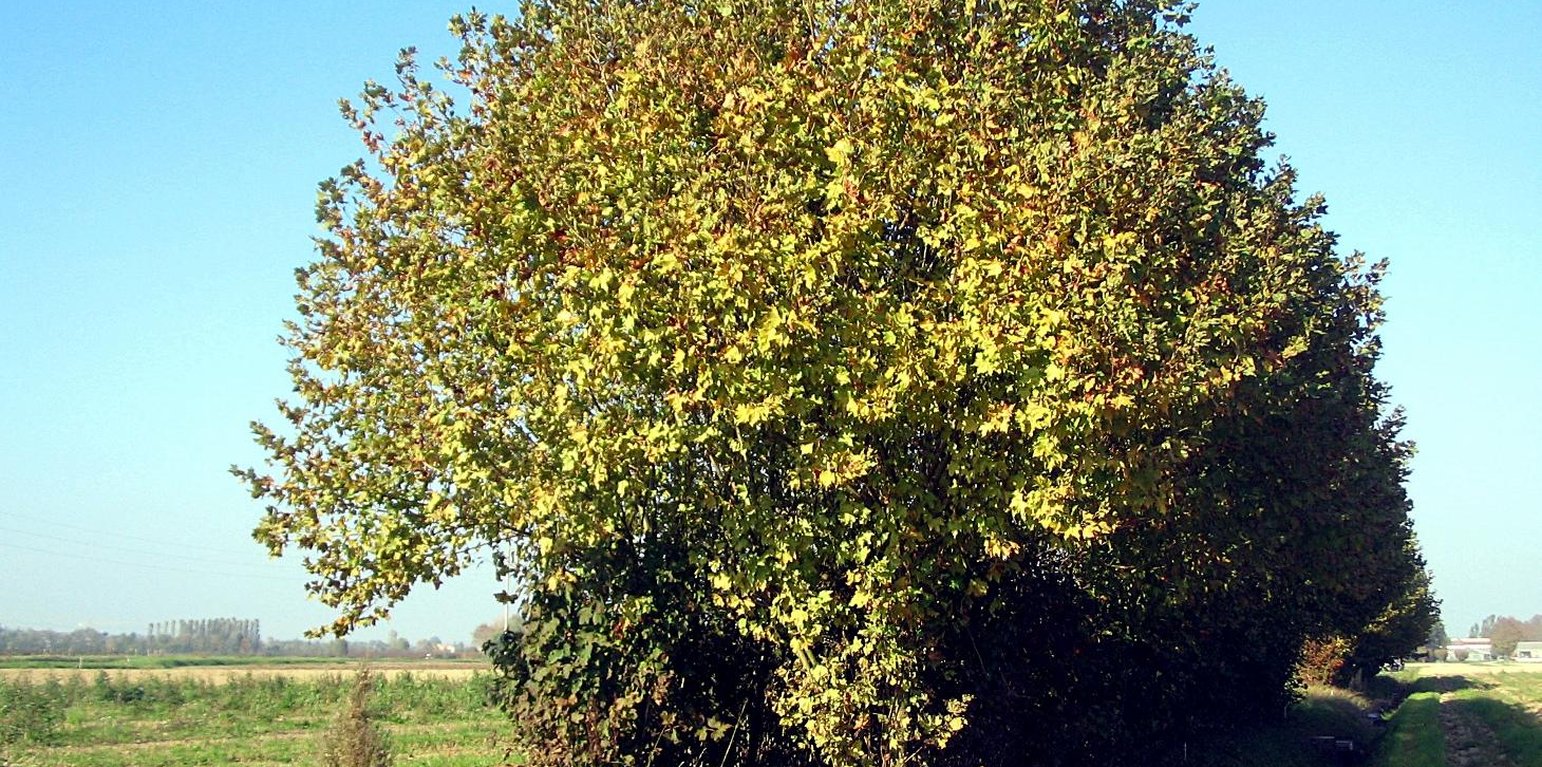




Vegetated buffer strips are agricultural areas with permanent vegetation designed to prevent surface water pollution and minimize soil erosion. In the Veneto region they are generally used along streams, canals and roads and can be composed of grass, hedges, trees or their combination. Buffer strips were a major component of agricultural landscape that has been replaced by intensive monoculture practices by increasing tillable areas. In recent years, the re-introduction of buffer zones in the Venetian plain (and generally in the whole territory of the region) has been supported as an agri-environmental measure for a sustainable land management.
Purpose of the Technology: Vegetated buffer strips, recently promoted by the regional government, are an efficient and economical way to improve surface water quality by agricultural nonpoint source pollution. Farmers take advantage of using buffer strips to help control soil erosion and sediment loss, stabilize riverbanks and reduce flood damage to crops. The continuous soil cover and diversification of habitats improve agroecosystem biodiversity and diversification of farmers income.
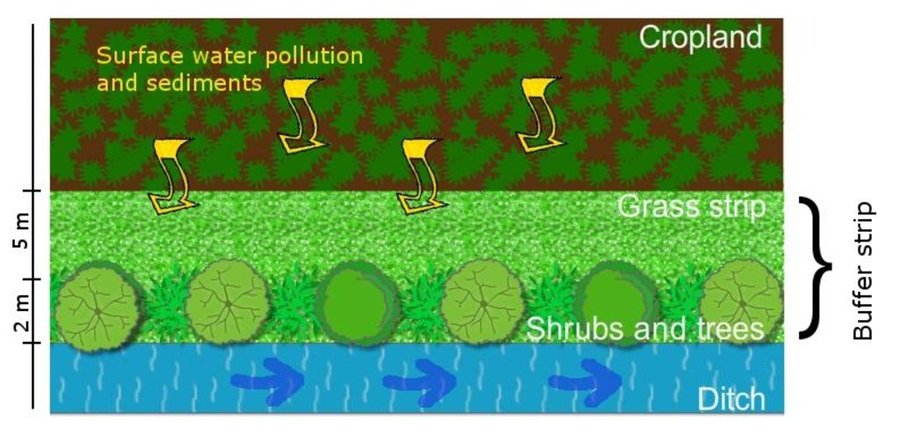
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Vegetated buffer strips are generally composed of a shrub or tree belt of 1 m combined with an herbaceous band of 5 m, usually placed on the sides of cultivated fields in order to maximise their depuration efficacy as well as ensure crop production. Their function to reduce water pollution is optimal if arranged along a water course in order to intercept suspended solids and sediment-bound nutrients.
Natural / human environment: Adopting vegetated buffer strips achieves several environmental benefits with a low initial economic investment. The agroecosystem biodiversity is improved by the creation of continuous buffers that provide food, nesting cover, shaded environment and connecting corridors from one habitat to another to wildlife species, while the continuous soil cover with herbaceous and woody plants enhances soil protection and below-ground biodiversity. Water resources benefit from reduced nutrient supply and sediments that cause excessive growth of algae and diminish oxygen level of the water. Vegetated buffer strips, thanks to the maintenance and differentiation of species in the territory, enhance the quality of life through the improvement of agricultural landscape.
Lieu: Veneto region, Italy, Italie
Nbr de sites de la Technologie analysés:
Diffusion de la Technologie: répartie uniformément sur une zone (approx. 100-1 000 km2)
Dans des zones protégées en permanence ?:
Date de mise en oeuvre: il y a entre 10-50 ans
Type d'introduction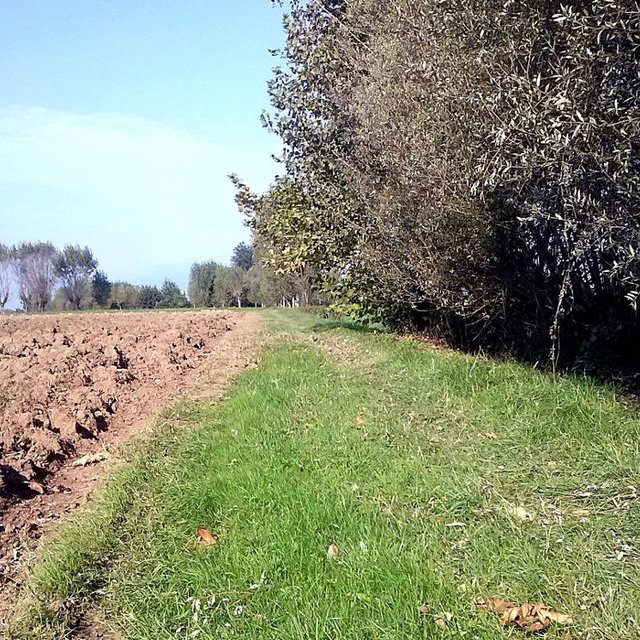





| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (Euro €) | Coût total par intrant (Euro €) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Planning, mulching, soli preparation, fertilisation | ha | 1,0 | 306,0 | 306,0 | |
| Planting | ha | 1,0 | 2,5 | 2,5 | |
| Grass strip establishment | ha | 1,0 | 152,0 | 152,0 | |
| Equipements | |||||
| Machinery for mowing, pruning | ha | 1,0 | 4000,0 | 4000,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | |||||
| Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 119,0 | 119,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | |||||
| Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 14,0 | 14,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 4'593.5 | ||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 5'741.88 | ||||
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (Euro €) | Coût total par intrant (Euro €) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Pruning, replanting, additional irrigation | ha | 1,0 | 127,0 | 127,0 | |
| Grass strip maintenance | ha | 1,0 | 127,0 | 127,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 254.0 | ||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 317.5 | ||||
Quantité avant la GDT: 0 t/100 linear metres
Quantité après la GDT: 1-1.5/100 linear metres