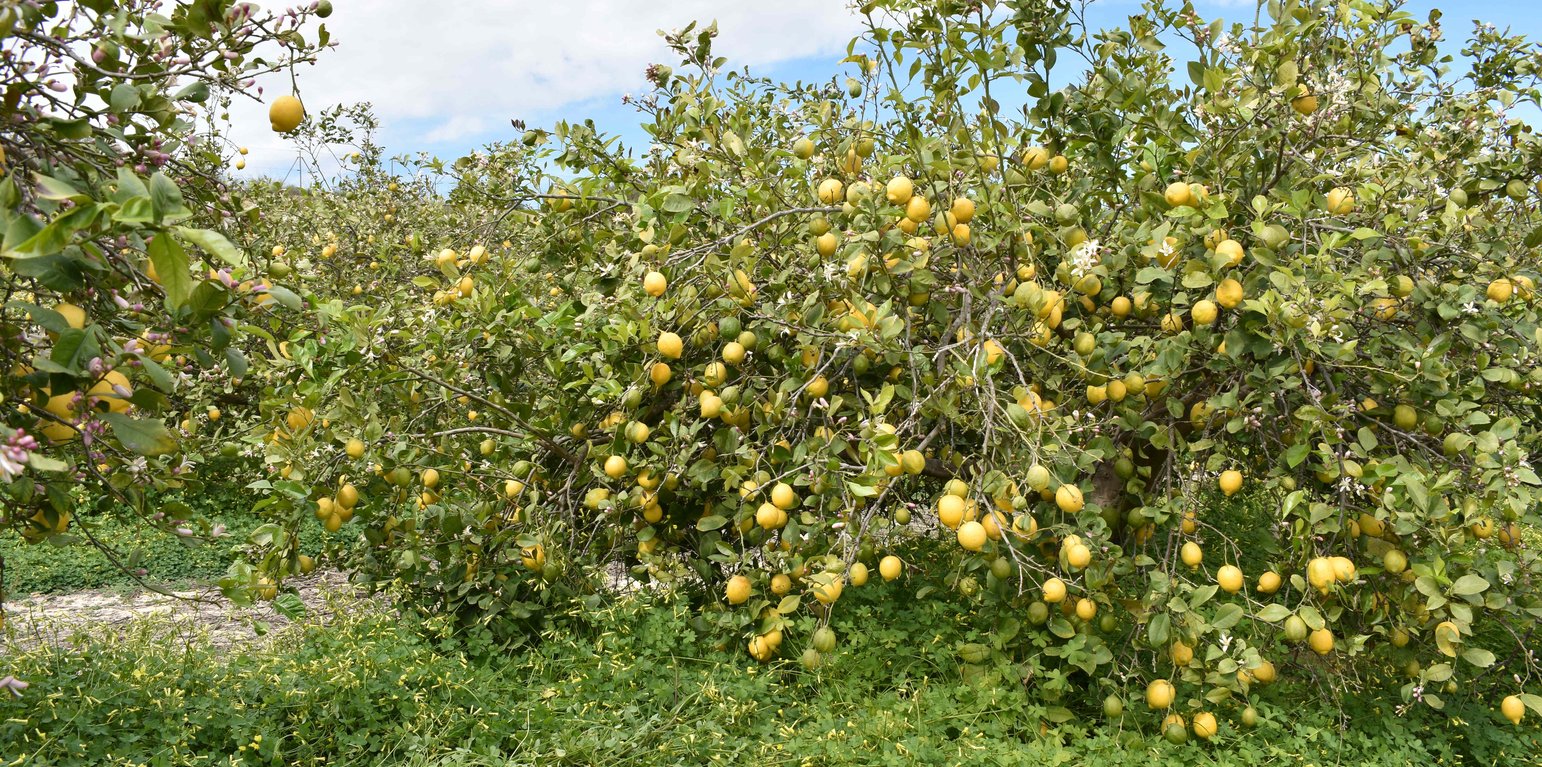




Natural / human environment: This SLM technology was established in land under sustainable agricultural in the region of the Vega Baja del Segura (Spain). The region under study is the most southerly county within the Valencian Community (Comunidad Valenciana). Our study site focuses on the province of Alicante. The county is Vega Baja del Segura, which has a total area of 957.73 km2. The county of Vega Baja de Segura covers the region from Orihuela to the mouth of the Segura, where it meets the Mediterranean Sea in Guardamar del Segura (Alicante). Agricultural production in this county is of a very high quality and is intensely competitive. Despite this, the region’s traditional agriculture industry is nonetheless being overtaken by other sectors, with the scarcity of water emerging as a key factor in this shift. Currently, 67% of the arable area relies on irrigation systems. In this area, small holdings yield the majority of the agricultural production: 76% of agricultural estates cover less than five hectares. The main cultivation, in terms of area, is in trees (22,900 ha). Citrus trees (lemon, orange, and mandarin) are the main trees grown in the area (INE, 2009).
Purpose of the Technology: Initially, the main objective of the land user applying the technology was to improve the soils and crop production in his fields by promoting sustainable agricultural management in the Vega Baja region. The previous use of land was conventional with inorganic fertilization and intensive ploughing. The land user had to convert the conventional lemon tree orchard to organic farming with more sustainable practices. The initial investment was very high and he needed nearly 7 years to get certified in Eco-certification and labelling by the Comité de Agricultura Ecológica de la Comunidad Valenciana.
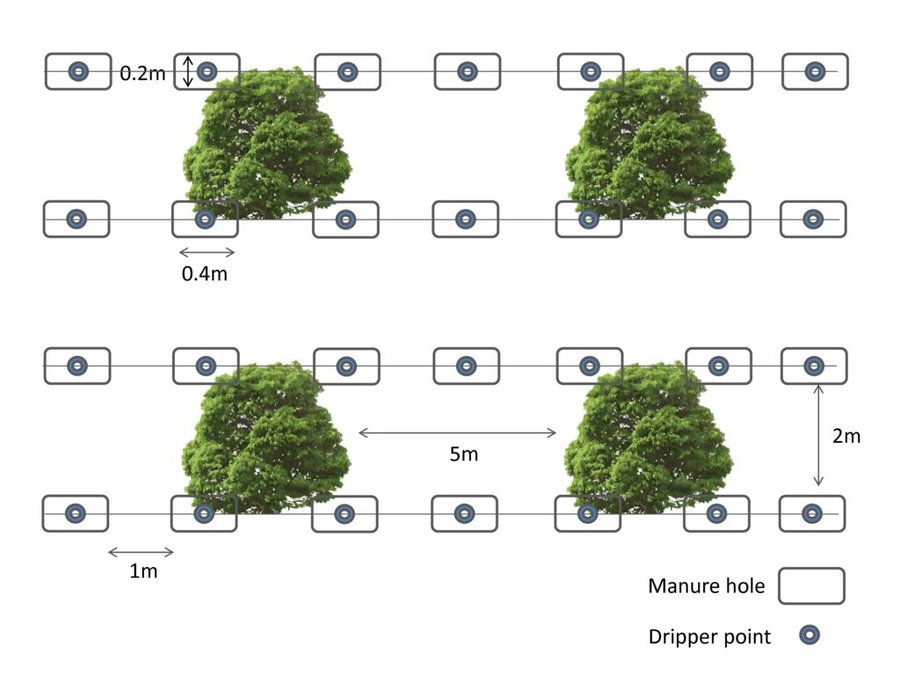
The land user makes all kind of innovative practices to improve soil fertility and crop production; the most pioneering initiative was to apply organic amendment located in dripper points. Organic certified sheep manure is applied every year in September in holes under the foot of every lemon tree. The following year, the position of the hole is moved around the tree. The holes are dug with a shovel; each hole is 0.4 m wide and 0.2 m deep. The eco-certificate sheep manure is bought from sheep holders. The sheep manure is composed of NPK (2.9; 1.8; 2.4%) with a C/N ratio of 8.8. The organic matter content is 44.5% and the moisture value is 53.8%. The irrigation is by drippers and it includes fertilizers in it. The land user is controlling the fertirrigation dose, changing the amount depending on the nutritional state of the orchard and climatological conditions. As part of the organic agriculture, the weed is not removed anymore. Pest control is done by biological methods: fly adhesive traps, pheromones moths traps, Bacillus thuringiensis solution sprayed, paraffin oil and copper sulphate applied by drip irrigation. The pruning remains are kept on the soil surface as a mulching.
The major benefit is an enhancement of the soil organic content in the long term. There is also an improvement of the orchard productivity. The lemon trees become less prone to diseases and pests. The major disadvantage is the high costs at the beginning to change from conventional to organic and to get the Eco-certificate.
Lieu: Orihuela, Vega Baja/Alicante, Espagne
Nbr de sites de la Technologie analysés: site unique
Diffusion de la Technologie: appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Dans des zones protégées en permanence ?:
Date de mise en oeuvre: 2014
Type d'introduction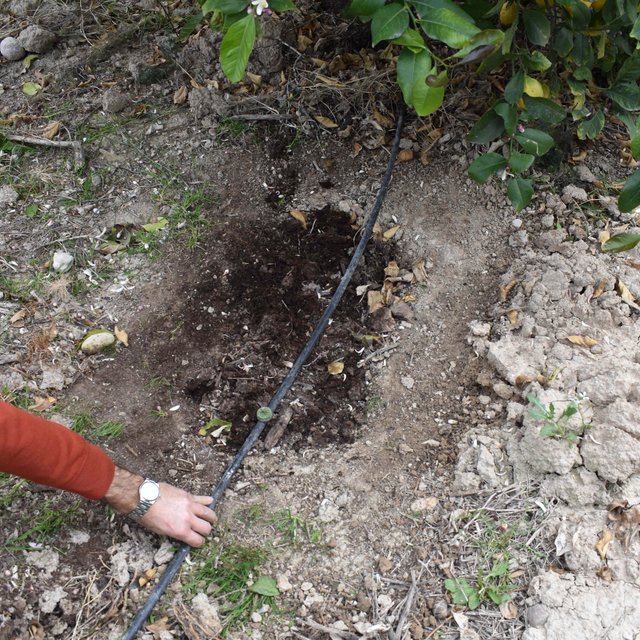





| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (Euro) | Coût total par intrant (Euro) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Equipements | |||||
| Engrais et biocides | |||||
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (Euro) | Coût total par intrant (Euro) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Organic amendment | person/hour | 5,0 | 6,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Pruning | person/hour | 100,0 | 6,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertirrigation | person/hour | 100,0 | 6,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Biological control | person/hour | 30,0 | 10,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | |||||
| Tractor with trailer (hire per day) | piece | 2,0 | 30,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | |||||
| Organic amendment | kg | 1200,0 | 30,0 | 36000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertirrigation | Litres | 1400,0 | 8,0 | 11200,0 | 100,0 |
| Bacillus thuringiensis | Kg | 60,0 | 20,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| Copper sulphate solution | Kg | 5,0 | 30,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| Paraffin oil | Litres | 10,0 | 30,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Adhesive trap | piece | 100,0 | 10,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Pheromone trap | piece | 10,0 | 40,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 51'840.0 | ||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 54'885.72 | ||||
The land user observe that the crop production increased two times with the organic agriculture management.
The lemon fruit with the organic farming management is bigger than before with conventional management.
Changing the irrigation to drip irrigation the land user can save water.
Less use of fertilizer, less tillage, no herbicides/pesticides.
The price of eco-certified lemon in the market is 3 times higher than conventional and the expenses on agricultural inputs are lower.
Only work for digging the hole, maintaining fertirrigation, harvesting and pruning, but no work for applying pesticides, tillage and weeding.
Improved health due to non-application of herbicides/pesticides.
The farmer can buy more land due to this income.
Due to this eco-management, the farmer became well-known and recognized in the region. He appears in television and teaches other farmers and became the president of the regional farmer association.
The farmer learned a lot about the soil and enhanced his continued education.
Less water is used through drip irrigation.
Better infiltration due to better soil structure due to the manure application, thus less runoff.
Less soil compaction due to better soil structure due to the manure application.
Adding sheep manure increases nutrients.
Adding sheep manure increases organic matter.
The organic farming enforces the lemon trees against pests and diseases.
The organic farming enforces the lemon trees against pests and diseases.
Flood impacts is less due to better soil structure.
Land movements decrease due to better soil structure.
Drought impacts decrease due to more soil moisture.
Increase the carbon in the soil due to organic farming and the manure application.
No pollution by herbicides/pesticides.
Increase the carbon in the soil due to organic farming and the manure application.