



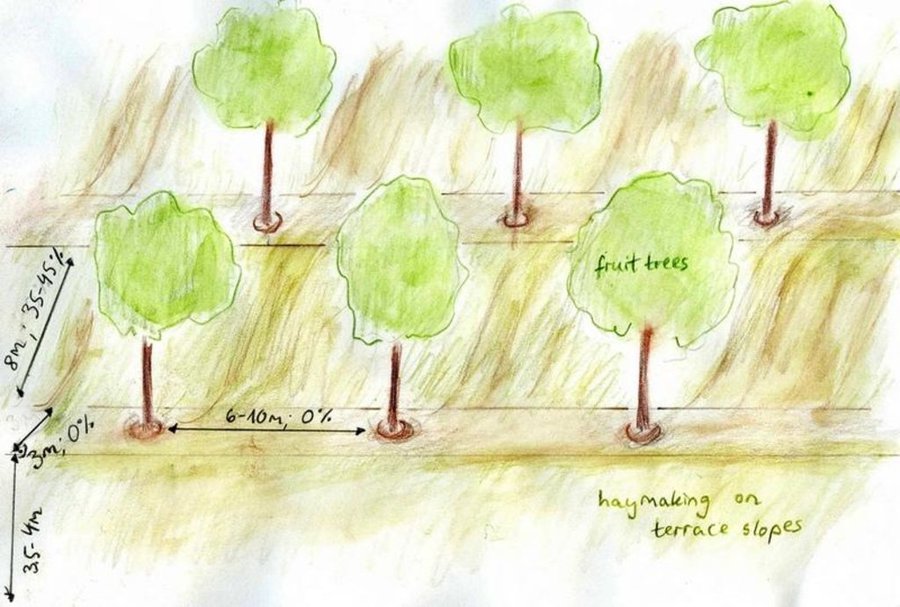
Fruit- and nut-trees give the production system the characteristics of an orchard, whereas sour cherry trees rather provide for a jungle atmosphere. They spread very quickly once they are planted. Hayproduction substitutes other uses of the lowest vegetation layer, since grazing is forbidden. The whole territory is concipied as a research station.
Purpose of the Technology: In general trees act against erosion: By their stabilising function they prevent soil from being washed out. Especially nut-trees with their 20 to 25 m long roots preserve soil moisture and by that consolidate soil structure. Terraces contribute to this moisture-preserving and production-enhancing function. They are very important in order to make rather steep land exploitable by reducing slope. Haymaking does not damage soils, but is only allowed after the end of June so that grasses can reproduce before.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Both the establishment of terraces and the planting of trees on such a big surface are costly in terms of labour and money. Maintenance means taking care of trees, taking measures against diseases and conserving soil fertility. Fertilisers are very costly and therefore dung has been substituting them in the last years.
Natural / human environment: From the two research stations of the orchard institute - one in the upper hill-zone and one close to the village Karsang - only the second one is assessed. This area is surrounded by two rivers in the West and in the East, with its main exposition to the South. It is in direct competition for irrigation water, especially needed for the trees, with the village. The orchard is situated on a ridge that is in the haymaking area, but is accessible for animals from the village.
Lieu: Faizabad, Region of Republican Subordination, Tadjikistan
Nbr de sites de la Technologie analysés:
Diffusion de la Technologie: répartie uniformément sur une zone (approx. 0,1-1 km2)
Dans des zones protégées en permanence ?:
Date de mise en oeuvre: il y a entre 10-50 ans
Type d'introduction










| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (dollars américains) | Coût total par intrant (dollars américains) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Tree planting | ha | 1,0 | 714,0 | 714,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | |||||
| seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | |
| Autre | |||||
| Terrace establishment | ha | 1,0 | 614,0 | 614,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1'428.0 | ||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1'428.0 | ||||
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (dollars américains) | Coût total par intrant (dollars américains) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Maintenance | ha | 1,0 | 93,0 | 93,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | |||||
| Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 28,0 | 28,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 121.0 | ||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 121.0 | ||||
The reason is the decision not to plant wheat anymore, partly because of droughts and partly because of the trees having reached a critical height (shadow).
Animals eating this fodder give more milk.
On the neighbour-ridge no irrigation water.
Trees require more water than simple pastures, especially in the establishment period.
Especially fruit production is important, to make jams, dried fruits etc. for winter.
The milk is of better quality and leads to less sicknesses
The institue is in conflict with the village for irrigation water.
No strong effect, because it is a research territory.
Is especially a function of cover and infiltration capacity
Plants are greener and less dusty thanks to moisture
Plants are taller, wider and denser.
Thanks to strongly reduced erosion, organic matter is conserved
Less crusting than without technology, but more than without droughts.
Due to lacking drainage system
More nutrients given, for example by the trees' leaves.
More than 50 pasture species
Forest administration considers the proportion of trees to be one of the decisive factors of fire-risk.
High proportion of trees leads to longer snow cover and thus soil protection in spring