



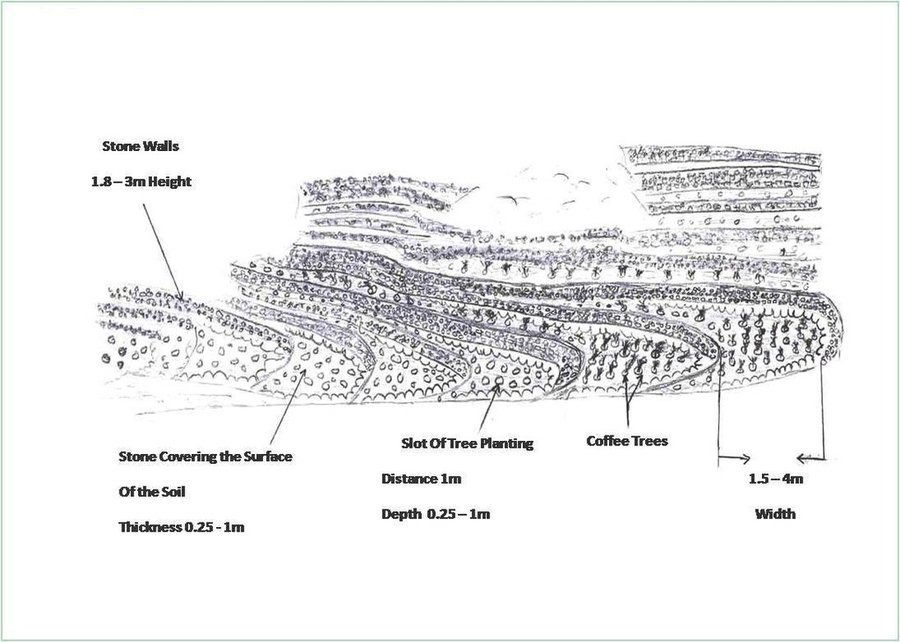
Cutting and collecting stones for the construction of terraces on steep slopes of the mountains, structural measure to reduce the length and angle of the slope and the speed of runoff. This makes it easier to harvest water and reserving deposits. A wall terraces is built of stones where the height of a wall should be increased height of 1.8 - 3 m, a width of 1.5 - 4.3 m and the length from 8 - 14 m to keep the accumulated deposits. The cutting stones are brought from distant places for the purpose of building the walls. These terraces are similar to mountain terraces but the top soil surface can be covered with stones to protect it from heavy rain storms and prevent sheet erosion that results from raindrops hitting the bare top soil surface. The stone layer, also prevents evaporation and maintains soil moisture. The stones are arranged in a layer of about 0.25 – 0.7 m thickness over the entire surface of the soil except where to put the coffee trees with an average diameter of 1 m. It is difficult to use equipment in the process of building the terraces due to severe slopes. Therefore it is a labor intensive process of manually building terraces. Due to the slow process of construction it requires a lot of time. However, building terraces on steep slopes can lead to increased erosion in the absence of well maintaining outlets that allow draining the excess water from one terrace to another, avoiding breaking of terraces' walls. In any case, terraces need regular maintenance to ensure the sustainability of this technology. The landscape of the region is mountainous, bench terraces which are used for crop production exist in slopes exceeding 60%. The texture of the soil is silty loam and the depth of the terraces is moderate to deep. Due to small holdings and steepness of the terraces, the local implements are used for land preparation. The climate in the region is arid to semi-arid and annual precipitation ranges between 200 and 450 mm. The major crop in this area is coffee, which is cultivated because of its high economic value on the market.

Lieu: Bani Ismail- Manakha District, Sanaa governorate, Yémen
Nbr de sites de la Technologie analysés:
Diffusion de la Technologie: répartie uniformément sur une zone (approx. 0,1-1 km2)
Dans des zones protégées en permanence ?:
Date de mise en oeuvre: il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
Type d'introduction






| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (dollars américains) | Coût total par intrant (dollars américains) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Building terraces | ha | 1,0 | 42430,0 | 42430,0 | 11,0 |
| Equipements | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 42'530.0 | ||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 42'530.0 | ||||
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (dollars américains) | Coût total par intrant (dollars américains) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Main d'œuvre | |||||
| Repair walls that were destroyed | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Inverse the soil covered with stones | ha | 1,0 | 186,0 | 186,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 236.0 | ||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 236.0 | ||||
Due to coverage of the top surface of soil with stones
As a result of not repair the damage occurring in some of the terraces and that lead to the damage of other terraces.