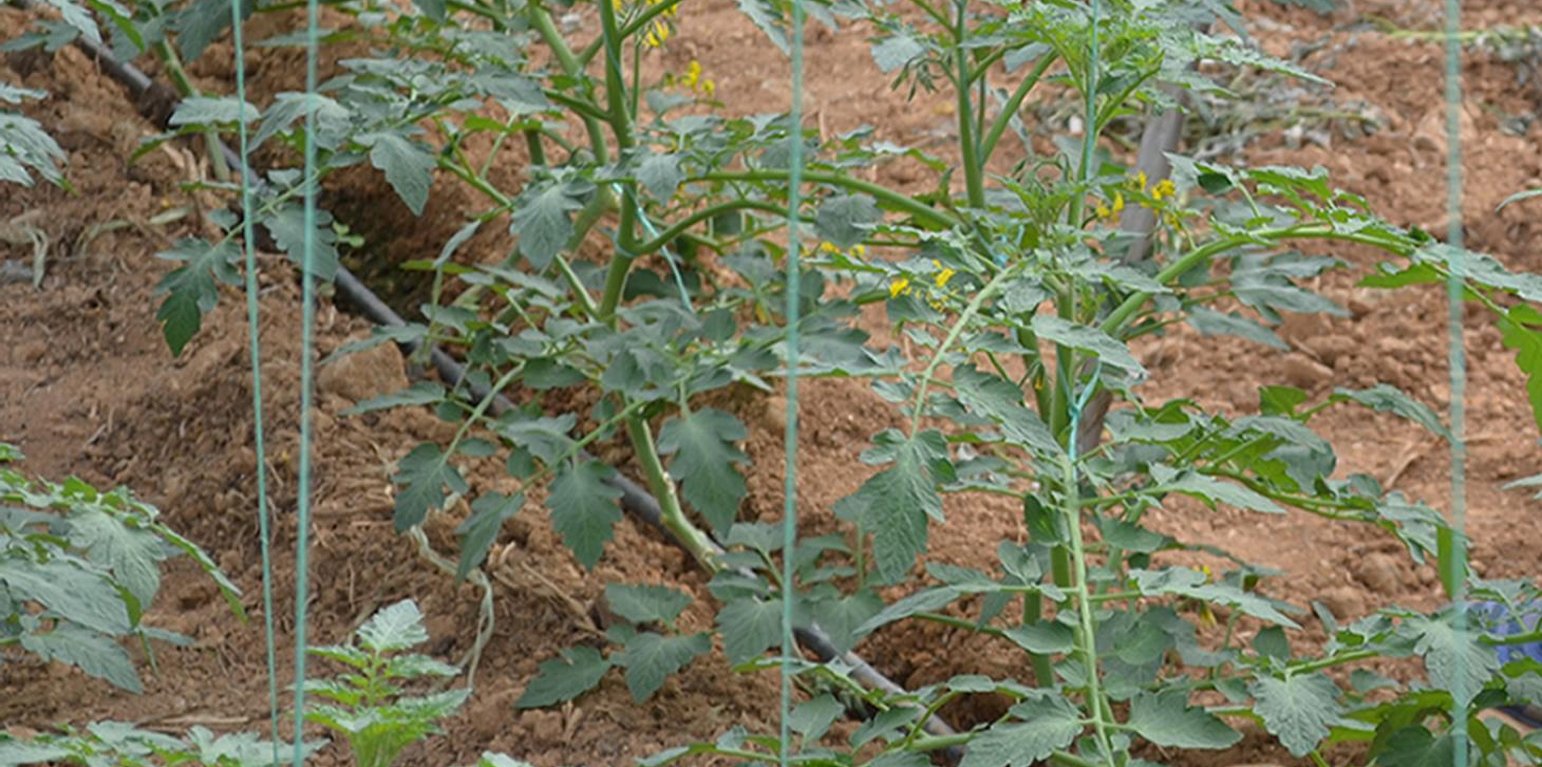




The Trichoderma harzianum fungus and different various types of symbiotic associations of mycorrhizae are used in greenhouse cultivations in coastal Timpaki, Crete, Greece, in order to mitigate the impacts of salinity on crops and to improve the existing soil properties. These biological agents are supplied commercially as soil amendments, and specific treatments vary according to cultivation type.
Purpose of the Technology: The technology is applied as an effective agronomic measure for the increase of plants salt tolerance, the reduction of soil borne diseases that affect plant roots and increase of water and nutrients absorption. This technology prevents or mitigates soil degradation by improving the subsoil structure by causing plant root system expansion and increasing the ability of the plant to absorb nutrients and water. This effect can potentially decrease agricultural inputs (water and fertilizers) up to 40%. An additional benefit is the maintenance and increase of subsoil faunal diversity and the subsequent biodegradation. The improved soil structure leads to higher infiltration rates, mitigates salt accumulation in the root zone and combats soil salinity, one of the main soil degradation problems in the coastal zone. Finally, the application of the biological agent helps to keep the plants healthy thus leading to increased crop yield, and reduced production risk.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The implementation of such agents usually takes place once per plant as the microorganisms coexist with the plant (symbiotic association) and can be performed in different stages of the crop cultivation depending on the commercial product, e.g. as solution in the irrigation water, as solid soil amendment in the early growing stages, or optimally, to be applied in the plant nursery (seed bio-priming), or during planting (plant inoculation). Biological agents require increased organic matter in the soil, absence of toxic substances (e.g. copper, fungicides, and pesticides), and, depending on agent type, suitable soil moisture and temperature. Here we instigate the effects of biological agents in tomato plantations, which are implemented in the early growing stages through irrigation.
Natural / human environment: The average annual precipitation in the area is 500 mm and the climate ranges between sub-humid Mediterranean and semi-arid. Average annual temperature is 18.5 °C with 6 months below 18 °C but above 5 °C, thus classifying the area as subtropical. In the location where the technology is applied, land is mostly privately owned and water rights can be public, cooperative or private. The financial means of the land user applying this technology are more or less on par with those of the rest of the community, although he has wider empirical and theoretical education and higher impact acquired though his involvement in the local agricultural association as agronomist.
This Technology was documented within the scope of FP7 RECARE Project, grant agreement no 603498.
Lieu: Timpaki, Heraklion, Grèce
Nbr de sites de la Technologie analysés: site unique
Diffusion de la Technologie: appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Dans des zones protégées en permanence ?: Non
Date de mise en oeuvre: il y a entre 10-50 ans
Type d'introduction





| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité (Euro) | Coût total par intrant (Euro) | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres |
| Engrais et biocides | |||||
| Biological agents (powder) | ha | 1,0 | 3232,0 | 3232,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 3'232.0 | ||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 3'551.65 | ||||