Entertainment-education for ecological engineering [Viêt-Nam]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Monina Escalada
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
Cong Nghe Xanh (Vietnamese)
approaches_2613 - Viêt-Nam
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Spécialiste GDT:
Heong Kong Luen
+60 11-3604 7833
kl.heong@gmail.com
Centre for Agricultural BioSciences International (CABI) South East Asia Regional Centre
PO Box 210, 43400 UPM Serdang
Malaisie
Spécialiste GDT:
Settele Josef
+49(0)345 558 5320
Josef.Settele@ufz.de
Helmholtz-Zentrum für Umweltforschung GmbH - UFZ
Theodor-Lieser-Straße 4 Halle 06120
Allemagne
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Visayas State University (VSU) - PhilippinesNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) - AllemagneNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Centre for Agricultural BioSciences International (CABI) - Royaume-Uni1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
Entertainment-education for ecological engineering involves a series of TV pro-grammes that educate rice farmers about ecosystem services, as well as ecologi-cal engineering techniques to conserve biodiversity in rice landscapes.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
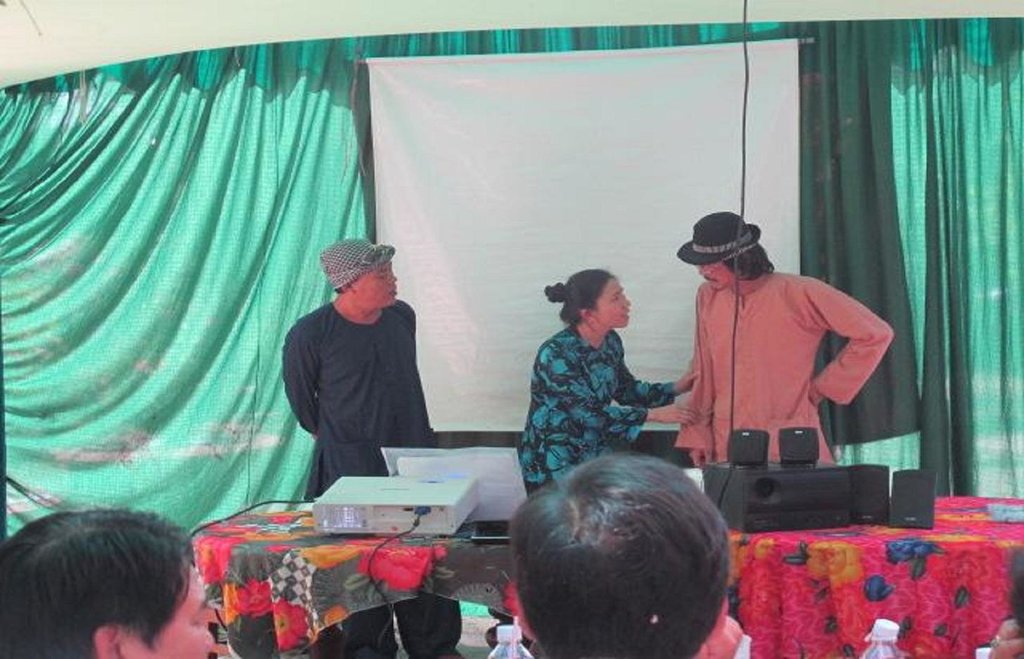
Aims / objectives: A multi-stakeholder participatory process was adopted in formative research, then designing and developing a soap-opera series, launching the programme, followed by implementing on-the-ground support, and monitoring of progress. The stakeholders involved were from research, extension, a video production company and local government. To make sure the educational content was accurately and seamlessly woven into drama, the collaborating team was composed of technical experts and scriptwriters, nicknamed the ‘‘turtles and peacocks’’. Each 15-minute episode is composed of 3 parts: a short drama by comedians, an explanation by experts, and then a summary of the lesson portrayed in that particular episode.
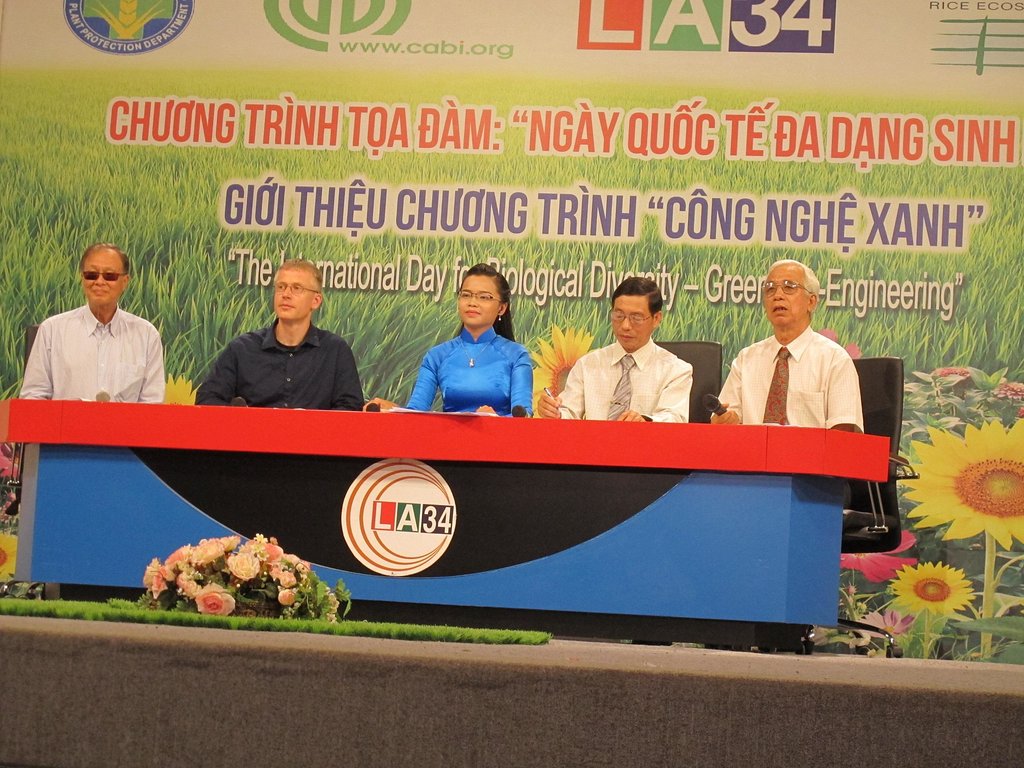
Methods: The LEGATO TV series was produced by Viet Idea, a video company based in Ho Chi Minh City, and was broadcast on Long An TV (LA34) weekly for 20 weeks. The 18 episodes were based on the values grid that LEGATO scientists had developed. They covered a range of topics including organic matter decomposition, organisms and microorganisms, straw burning, rural habitats, the food chain, the architecture of traditional houses, the role of silicon in rice production, honey bees, plant health, eco-tourism and eco-engineering.
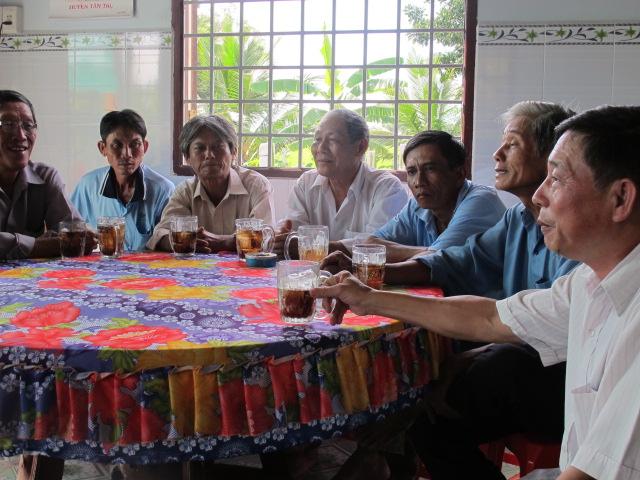
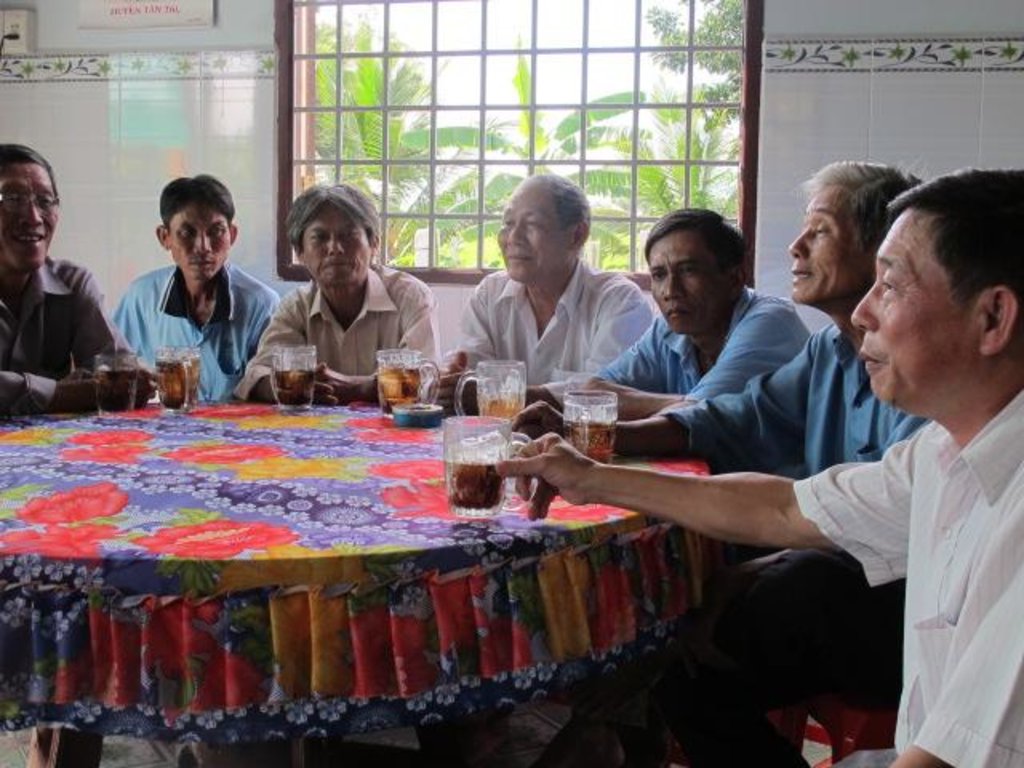
Stages of implementation: To popularize and enhance the viewership of the LEGATO Ecological Engineering TV series, a “Meet the Actors Day” was organized in Khanh Hau village, Tan An Town, Long An Province. The organisers comprised “Cong Nghe Xanh”, Long An TV (LA34), Y Tuong Viet (Idea Vietnam), and the Southern Regional Plant Protection Centre. The event was attended by the village People’s Committee Chair, farmers, Long An TV staff and plant protection officers. The “Meet the Actors” day is one of the elements in the entertainment-education approach. To track viewership and audience reactions to the TV series, four focus group discussions (FGDs) were conducted with 41 rice farmers in four villages in Long An province. A post-broadcast survey was carried out in January 2015 among 396 randomly selected rice farmers in Long An and Tien Giang Provinces.
Role of stakeholders: The role of the different stakeholders in the approach was as follows: 1) Farmers provided feedback on the relevance and usefulness of the TV episodes and sug-gested other topics; 2) Plant protection officers worked with TV episode scriptwriters and served as subject matter specialists to simplify the educational content of each episode; 3) Local plant protection experts provided the scientific explanation behind the topics tackled in the episodes; 4) Local government was represented by Dr Nguyen Van Khang, former Director of Agriculture in Tien Giang province who agreed to allocate a portion of the provincial pesticide budget into ecological engineering demonstrations as he required data to be generated locally. Since then, from 2010 to 2014, more demonstration fields were set up.
Other important information: Preliminary analyses showed no significant differences in farmers’ insecticide use, but significant differences were found in beliefs and positions about growing flowers, biocontrol, and silicon use. A follow-up farmer survey was conducted to further eval-uate the effects of the TV series on rice farmers in Tien Giang and Long An Provinces.
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Viêt-Nam
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Long An and Tien Giang
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Tan An town, Tan Tru, Thu Thua, Ben Luc, Chau Thanh,Tan Phuoc, Cai Lay
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
2014
Date (année) de fin de l'Approche (si l'Approche n'est plus appliquée):
2016
2.7 Type d'Approche
- initiative/ innovation récente locale
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The Approach focused on SLM only (reducing insecticide use, restoring biodiversity in rice landscapes )
Improve farmers’ pest management, reduce their insecticide use and improve their land use to include conservation of biodiversity.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Lack of funds to support SLM; Unregulated pesticide marketing continues to negate the gains obtained by SLM.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- entrave
Educate farmers to appreciate parasitoids that are too tiny to be seen by the naked eye.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: As the parasitoids and bees belong to the same insect group, hymenoptera, we associated parasitoids with bees that farmers are familiar with.
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- entrave
Funds to support education system.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Encourage local governments to provide support.
cadre institutionnel
- entrave
Lack of direct linkage between agricultural and TV broadcast stations.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Use stakeholder meetings and field activities to establish these new links.
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- favorise
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- entrave
Technical information.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Explore research findings for information.
charge de travail, disponibilité de la main-d'œuvre
- entrave
Lack of work force dedicated to this entertainment-education process.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Encourage provincial government to allocate more staff who can simplify and disseminate scientific information.
autre
- entrave
Unregulated pesticide sales continue to erode gains from education.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Encourage government to review and reform current pesticide sales regulations.
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
Communication specialist (female), regional director of plant protection (male), ecologist (male)
Farmers, male and female, Vietnamese
- Spécialistes de la GDT/ conseillers agricoles
Ecologist (male), plant protection director (male)
- chercheurs
Visayas State University, Leyte, Philippines
- gouvernement local
Local government of Long An province
People's Committee chair (provincial)
- gouvernement national (planificateurs, décideurs)
- organisation internationale
Center for Agricultural BioSciences International (CABI), Malaysia
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | passive | SLM promoters |
| planification | interactive | All stakeholders |
| mise en œuvre | auto-mobilisation | All stakeholders |
| suivi/ évaluation | auto-mobilisation | SLM promoters and local implementers |
| Research | interactive | SLM promoters |
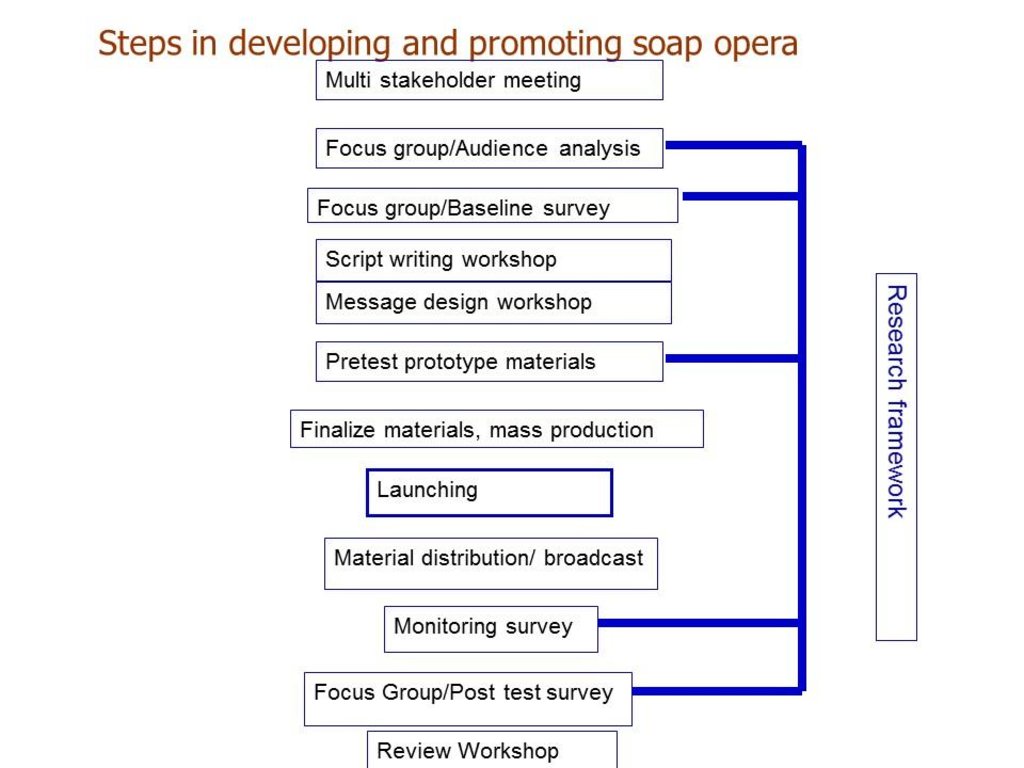
3.3 Diagramme/ organigramme (si disponible)
Description:
Steps in developing and promoting a soap opera
Auteur:
Kong Luen Heong, Monina Escalada (CABI, Kuala Lumpur; Visayas State University)
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- principalement les spécialistes de la GDT, après consultation des exploitants des terres
Expliquez:
A stakeholder consultation workshop was organized at the initial stage.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. Through stakeholder consultation and focus group discussions
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- exploitants des terres
- personnels/ conseillers de terrain
Formats de la formation:
- sur le tas
- entre agriculteurs (d'exploitants à exploitants)
- zones de démonstration
- réunions publiques
Formats de la formation:
- Communication campaign
Thèmes abordés:
Principles of ecological engineering and pest management
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
- Consultation
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- non
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by land users through measurements
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Oui
Spécifiez les thèmes:
- écologie
Donnez plus de détails et indiquez qui a mené ces recherches:
Research was carried out on-farm
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- 10 000-100 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (German Ministry of Education and Research, BMBF (70,000 USD)): 70.0%; government (30,000 USD): 30.0%
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Oui
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- intrants agricoles
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| Flower seedlings | en partie financé | |
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- volontaire
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Reduction in fertilizer and pesticide use
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les groupes socialement et économiquement défavorisés?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les questions foncières et des droits d'utilisation qui entravent la mise en œuvre des Technologies?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- augmenter la production
- augmenter la rentabilité/ bénéfice, rapport coûts-bénéfices
- conscience environnementale
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- incertain
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Our research partners find the use of Entertainment-Education an easy approach to implement as there is often a warm response from the audience - farmers, women's groups and local government officials. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
The use of entertainment-education approach has been found to be highly successful in Vietnam. An evaluation survey of a radio drama program we launched in 2004, after completion of the program, showed that farmers who had listened to at least two episodes of the program reduced their insecticide sprays by 60%, their fertilizer and seed rates by 9% and 33% respectively (Heong et al., 2008). (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: It can be sustained if there is funding to support the activities.) |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The land users would rely on funding to be able to implement this approach as there is a cost in producing the TV series. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| An important challenge is the longer-term sustainability of the TV series. The challenge is to mainstream such programs into the TV station’s regular programming. To maintain a long TV series will require funding. A further threat to sustain the gains made by the TV series is “advertising piracy” where the TV series is being used to advertise new pesticides. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Westpal, Catrin, Vidal, Stefan, Horgan, Finbarr G., Gurr, Geoff M., Escalada, Monina, Chien, Ho Van, Tscharntke, Teja, Heong, Kong Luen & Settele, Josef. (2015). Promoting multiple ecosystem services with flower strips and participatory approaches in rice production landscapes. Basic and Applied EcologyHeong, K.L., Escalada, M.M., Chien, H.V. and Cuong, L,Q. 2014. Restoration of rice landscape biodiversity by farmers in Vietnam through education and motivation using media. In G. Mainguy (ed) Special issue on large scale restoration of ecosystems. S.A.P.I.E.N.S (online) Vol 7 No. 2. http://sapiens.revues.org/1578. Electronic ISSN 1993-3819Heong, K.L., Escalada, M.M., Huan, N.H., Ky Ba, V.H., Quynh, P.V., Thiet, L.V. and Chien, H.V. 2008. Entertainment-Education and rice pest management: A radio soap opera in Vietnam. Crop Protection, 27: 1392-1397.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Basic and Applied EcologyG. Mainguy (ed) Special issue on large scale restoration of ecosystems. S.A.P.I.E.N.S (online) Vol 7 No. 2. http://sapiens.revues.org/1578. Electronic ISSN 1993-3819 Crop Protection, 27: 1392-1397.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Heong, K.L., Escalada, M.M., Chien, H.V. and Cuong, L,Q. 2014. Restoration of rice landscape biodiversity by farmers in Vietnam through education and motivation using media. In G. Mainguy (ed) Special issue on large scale restoration of ecosystems. S.A.P.I.E.N.S (online) Vol 7 No. 2. http://sapiens.revues.org/1578. Electronic ISSN 1993-3819
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
G. Mainguy (ed) Special issue on large scale restoration of ecosystems. S.A.P.I.E.N.S (online) Vol 7 No. 2. http://sapiens.revues.org/1578. Electronic ISSN 1993-3819
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Heong, K.L., Escalada, M.M., Huan, N.H., Ky Ba, V.H., Quynh, P.V., Thiet, L.V. and Chien, H.V. 2008. Entertainment-Education and rice pest management: A radio soap opera in Vietnam. Crop Protection, 27: 1392-1397.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Crop Protection, 27: 1392-1397.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé