Subsidies for conservation agriculture [Suisse]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Umstellungsverträge
approaches_2632 - Suisse
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Personne(s) ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Wyler Roman
Suisse
Spécialiste GDT:
Hofer Peter
+41 (0)31 970 53 37
Peter.hofer@vol.be.ch
Amt für Landwirtschaft und Natur des Kantons Bern LANAT
Rütti, 3052 Zollikofen
Suisse
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Amt für Landwirtschaft und Natur des Kantons Bern (LANAT) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT

Direct seeding [Suisse]
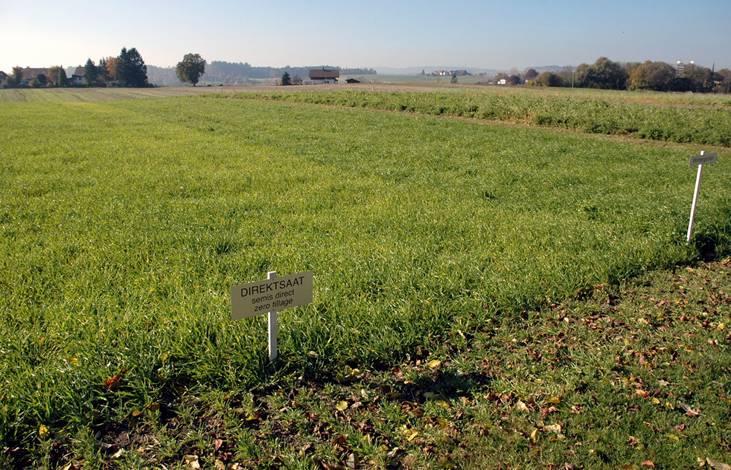
A cropping system which allows to plant the seeds directly into the soil without ploughing. The soil is covered with plant remainders.
- Compilateur : Unknown User
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
Land users commit to apply conservation agriculture on parts of their land for a period of 5 years. In return they get subsidies during this period.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
Aims / objectives: The Swiss environment protection law defines that soil fertility must be conserved on a long term basis. The cantons have to execute this national law. The way this is done differs from canton to canton. In this study the strategy of the canton of Berne is documented. It has three major goals: The prevention of soil erosion, the reduction of nitrate wash out and the prevention of soil compaction.
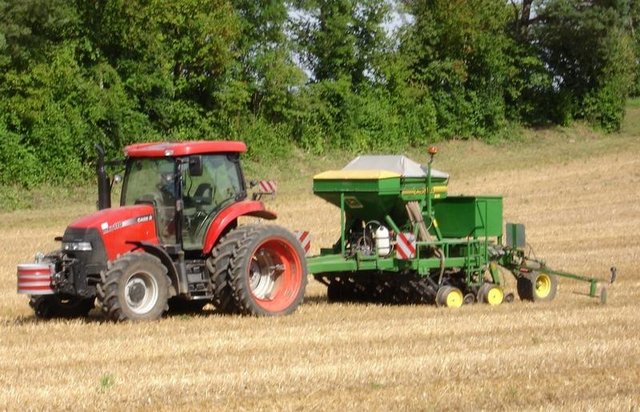
Methods: To reach these goals, farmers who accept to use conservation technologies can get additional subsidies for a period of 5 years. Furthermore they are supported by advisors. In this way land users are encouraged to change to soil conservation technologies, financial risk during the establishment phase is reduced due to the subsidies. The approach consist basically of a contract between land users and the office for soil conservation, in which land users commit to apply only soil conservation technologies on parts or on all their land during a period of 5 years. During that time direct seeding must be applied at least 2 times for main crops and for half of the catch crops. For the remaining crops ploughing is not allowed either. Technologies which reduce the reworking of the soil such as maize strip tillage ('Streifenfrässaat') or mulching need to be applied. In return land users get subsidies (during 5 years) which depend on the crop and the technology used. The highest subsidies are granted if direct seeding is used. The office for soil conservation is running a demonstration study comparing direct seeding to conventional agriculture. This helps land users to estimate the effects the new technology would have when applied in practice. If a specific farm receives the subsidies depends on whether in the running year there is still financial resources for the program. Resources have been limited by the government. Additionally it depends on where the farm is located. Farms that located in regions of major nitrate contamination, enhanced risk of eronsion or soil compaction or in regions with drinking water sources or polluted surface water are incorporated first. Land users can have their whole farm or single fields under contract. However a specific field can not be under contract for more than one period (5 years). As soon as a farmer gets a contract, details about which crop to plant where and when, with which technology are discussed by the farmer and an advisor.
Other important information: The goal is to find the best solution for every land user. Meetings of that kind take place on a regular basis. Besides supporting the farmer, advisors also check if conservation agriculture technologies are really being applied. After the 5 years under contract, it is the land users choice whether they want to continue using conservation technologies or not. Monitoring of the office for soil conservation shows that 85% keep on using conservation technologies. Its seems that the approach has a long term influence and subsidies are needed in the beginning only.
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Suisse
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Canton of Berne
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
1996
Commentaires:
It is possible to get subsidies in the whole canton of Berne. Cropland area in the canton is 539 km2, 2517 ha were under contract in the year 2006.
2.7 Type d'Approche
- fondé sur un projet/ programme
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The Approach focused on SLM only
Spreading of conservation agriculture in areas with an enhanced risk for soil erosion and or washing out of nutritients. Good quality support so that farmers will not have lower crop yield due to the technology and therefore continue using conservation agriculture after 5 years without external support.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Water erosion under intense rainfall. Washing out of Nitrate to the ground water. Soil compaction.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- entrave
Ploughing is an important part of the tradition of agriculture. People are very critical towards no-tillage technologies, since they don't fit the common understanding of agriculture.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The people working in the project are farmers themselves. They can give on their practical experience. Furthermore a demonstration study can be visited
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- entrave
Most farmers have achinery for conventional agriculture. To change to conservation agriculture major investments need to be done or contractors need to be tasked. Furthermore crop yield can be lowered in the beginning.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: When changing to conservation agriculture farmers are supported financially for a period of 5 years.With this money the risk in case of crop failure ond the costs for a contractor are lowered.farmers can test a new techniquewithout major expenses or risks
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- entrave
If the owner of the farm changes, the new owner often returns to conventional agriculture.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: No solution inside the project
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation In Switzerland the number of farms is decreasing. New owners of land sometimes change back to conventional agriculture. It is possible however, that the new owner introduces conservation technologies.
autre
- entrave
In Switzerland there are subsidies to support farmers in hilly terrain. This encourages farmers plant crops on steeper slopes and therefore enhances the risk of erosion. This is not a constraint for the technology however.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Conservation agriculture helps to reduce erosion. However the project cannot change the fact, that these subsidies enhance the risk of erosion.
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
Contracts are signed by the office for soil conservation and the head of the farm, who in general is male. The decision about which technology is applied is usually taken at the household level including both women and men.
- Spécialistes de la GDT/ conseillers agricoles
- gouvernement national (planificateurs, décideurs)
The national government tasked the cantons with soil conservation. Therefore approaches differ from canton to canton.
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | aucun | The project was introduced through the office for soil conservation |
| planification | interactive | Landusers who wish to get subsidies have contact the office for soil conservation. It is the land users decision on which of their fields they want apply the technology. |
| mise en œuvre | soutien extérieur | Land user get subsidies for a period of 5 years, during which they have to apply soil conservation technologies. To actually use the technology they task a contractor or do the work on their own. |
| suivi/ évaluation | interactive | As there are discussions with the advisor on a regular basis, the implementation of the technology is monitored both by the farmer and the advisor. |
| Research | aucun | There is a demonstration study where direct seeding and conventional agriculture is compared. |
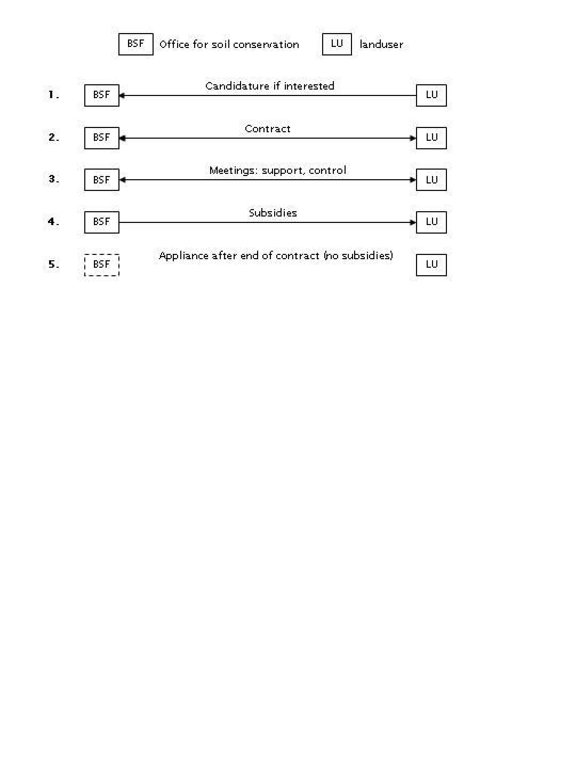
3.3 Diagramme/ organigramme (si disponible)
Description:
Interactions between the office for soil conservation and land users during the progression of the project.
Auteur:
Roman Wyler
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- principalement les spécialistes de la GDT, après consultation des exploitants des terres
Expliquez:
The decisions were taken by the office for soil conservation. Since these people are working as farmers, too, land users perspective could be included.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. To get the subsidies criteria from the contract need to be accepted. Besides this, land users can decide on their own how land is cultivated.
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Non
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
Spécifiez si le service de conseils est fourni:
- dans les champs des exploitants?
Décrivez/ commentez:
nnual meetings between land user and advisor; Key elements: Technical support, Planning of crop rotation and technologies applied, Monitoring
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Following a study of the office for soil conservation most land users continue to use conservation technologies after the end of the contract.
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, un peu
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
Donnez plus de détails:
The office for soil conservation was involved in Swiss no-till, which is a platform to exchange knowledge.
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: advisory meetings
technical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: advisory meetings
economic / production aspects were None monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: farmer himself
area treated aspects were None monitored by government through measurements; indicators: only the area under contract is known
no. of land users involved aspects were None monitored by 0 through None; indicators: only the number of land users under contract is known
survey aspects were None monitored by land users through None; indicators: afther the first two years there was an evalution of the project. Farmers were asked for their opini
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Oui
Spécifiez les thèmes:
- technologie
Donnez plus de détails et indiquez qui a mené ces recherches:
Research is not part of the actual project. However the advisors are involved in research projects through other activities. Therefore new knowledge is usually incorporated in the advisory meetings.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- 100 000-1 000 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (Kanton Bern): 100.0%
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Oui
Si oui, spécifiez le(s) type(s) de soutien, les conditions et les fournisseurs:
Canton of Berne
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- intrants agricoles
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| semences | en partie financé | |
| fertilisants | en partie financé | |
Commentaires:
There are subsidies per field under contract for a period of 5 years. During that time direct seeding must be applied at least 2 times for main crops and for half of the catch crops. For the remaining crops ploughing is not allowed either.
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
the advisory meetings help land users to better understand soil processes.
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les groupes socialement et économiquement défavorisés?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Other cantons in Switzerland have started to subsidise conservation agriculture too.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
income is slightly enhanced in most cases.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- augmenter la rentabilité/ bénéfice, rapport coûts-bénéfices
- paiements/ subventions
- conscience environnementale
prevention of erosion
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
on a long term perspective conservation agriculture is rather cheaper. Only in the beginning it costs more.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Not land user, but advisor of the project! |
| The structure of the project enables individual solutions. Still there are incentives for conservation agriculture. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Working together with the land users, searching for the best individual solution.) |
| After the end of the contract, there are no costs anymore. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: armers should be supported as good as possible, so that they are familiar with the technology and continue to apply it after the end of the contract.) |
| Advisors involved in the project all have an agricultural background, they are therefore familiar with the problems of farmers. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Working together with the farmers and trying adjust the program to their needs.) |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Compared to the total number of farms the number of participants is rather small. | conditions for participation could be reduced in order to reach more people. This would however increase the costs. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Subsidies are expensive for the state. Since resources are limited there is already a waiting list for the farmers. | soil consvervation should get a higher importance in politics. This is not the case because most people don't even know that soil degradation is a problem. |
| f there is no possibility to rent the machines in the region, costs are very high, even if there are subsidies. | here it could be a possiblity to support contractors to buy the machines needed, so that land users could apply the technology at lower costs. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Amt für Landwirtschaft und Natur des Kantons Bern LANAT, Rütti, 3052 Zollikofen. Kanton Bern fördert Ressourcen schonenden Ackerbau.AGRARForschung 14 (3): 128-133, 2007.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
http://www.vol.be.ch/site/lanat-3155-mbressourcen.pdf
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Direct seeding [Suisse]
A cropping system which allows to plant the seeds directly into the soil without ploughing. The soil is covered with plant remainders.
- Compilateur : Unknown User
Modules
Aucun module trouvé