Irrigation of orchards by using low cost drip irrigation technique [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Aslam Qadamov
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Обёрикунии богхо бо истифода аз технологияи обзахиракунии камнарх
technologies_1452 - Tadjikistan
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Irrigation of orchards by using low cost drip irrigation technique: 14 mars 2017 (inactive)
- Irrigation of orchards by using low cost drip irrigation technique: 19 juillet 2017 (inactive)
- Irrigation of orchards by using low cost drip irrigation technique: 20 août 2019 (inactive)
- Irrigation of orchards by using low cost drip irrigation technique: 2 novembre 2021 (public)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Abdulkodirov Adab
MSDSP Aga Khan Foundation
Tadjikistan
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Pamir Biological Institute (Pamir Biological Institute) - TadjikistanNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Kyrgyzstan Mountain Societies Development Support Programme, Aga Khan Development Network (MSDSP KG) - Kirghizistan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
11/04/2011
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
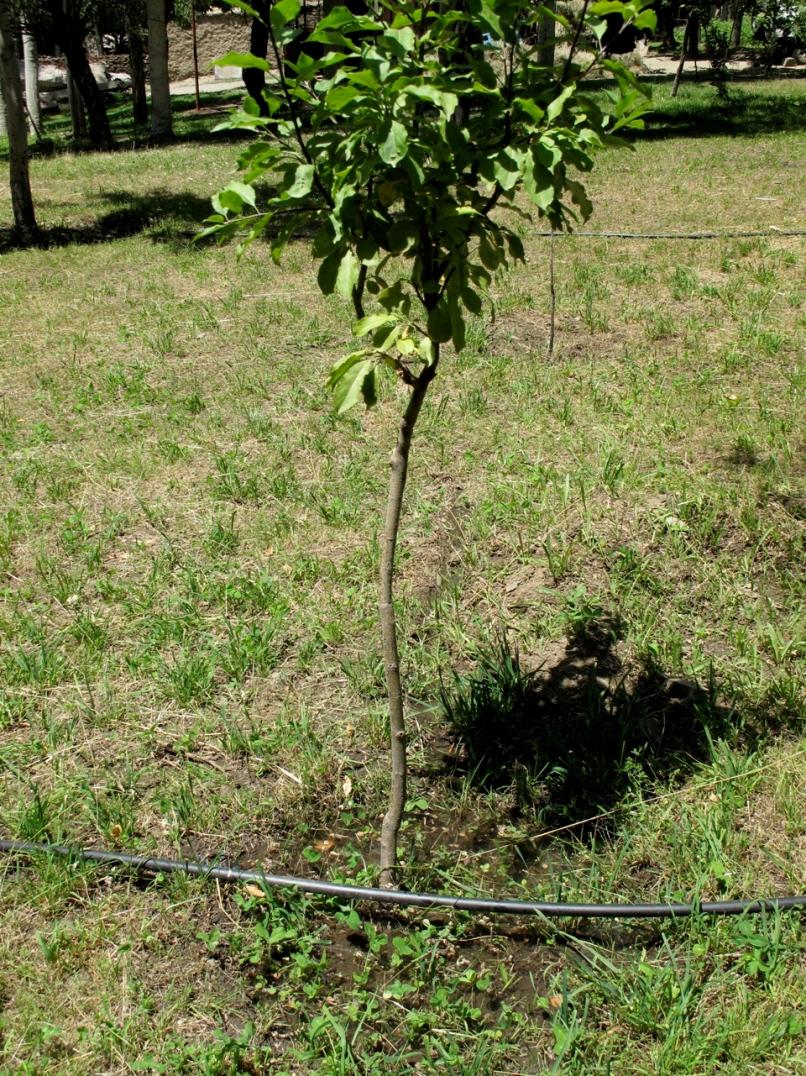
Irrigation of a young orchard using locally available and low-cost materials for a drip irrigation system in the Pamir’s arid zone
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
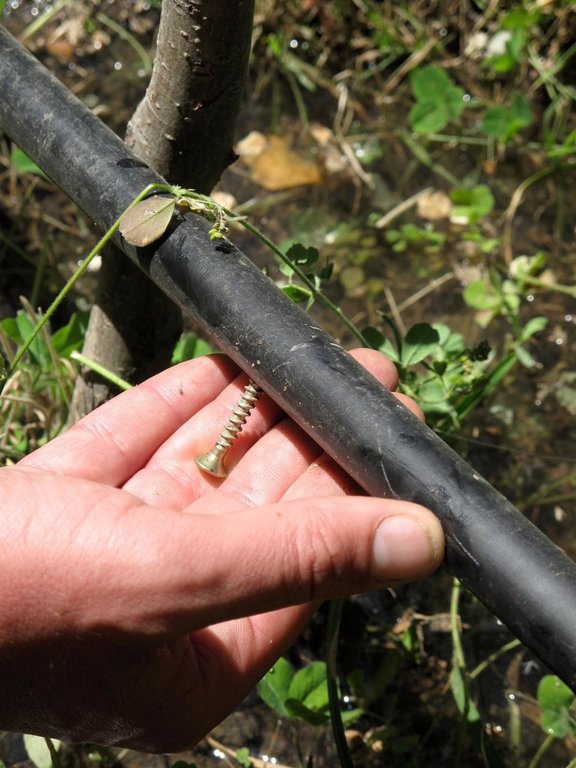
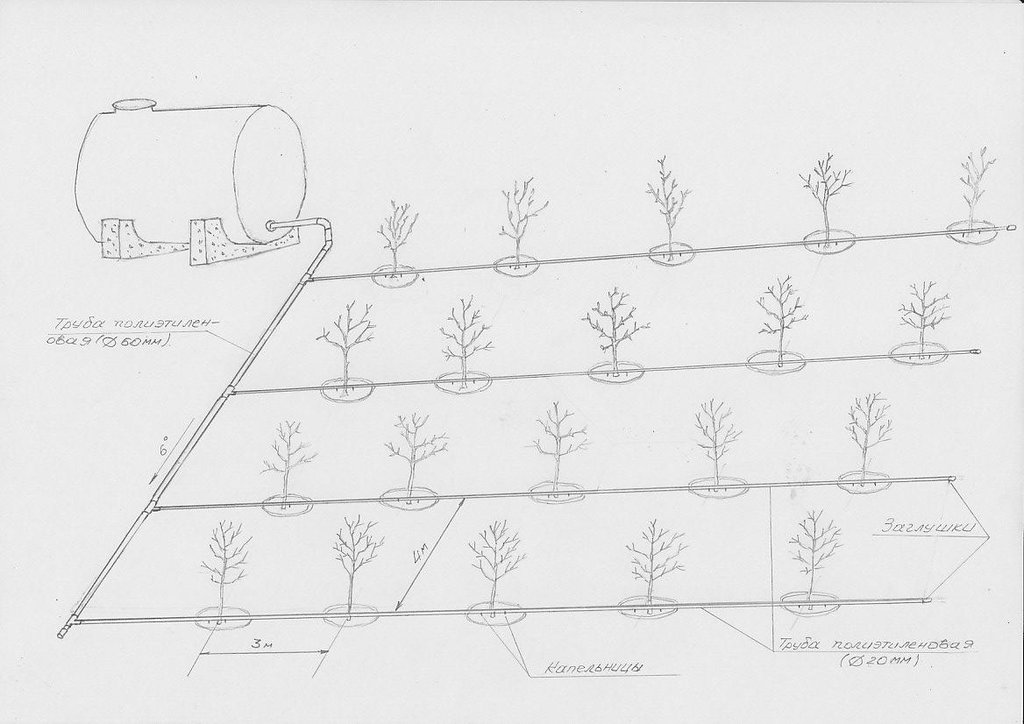
The system consists of a reservoir and polyethylene irrigation tubes and emitters installed along the rows of trees. Water accumulates in the reservoir during spring and early summer when there is no deficit in irrigation water. During the dry summer months water is then used for drip irrigation. Located in the upper part of the system, the reservoir ensures water pressure in the system. Due to the complex local topography, this irrigation method can be used without water pumps since natural water pressure ensures normal functioning of the system. Even though this water saving technology is quite effective, drip irrigation is rarely used since both the construction and maintenance of the system are quite expensive. With the introduction of this technology into the poor mountain communities of GBAO, the overall objective was to make drip irrigation technology cheaper and more easily available to farmers. The objective was achieved by the use of simple polyethylene irrigation tubes, simple screws instead of expensive emitters, and natural water pressure excluding the construction of a water pump station. Water is dripped directly to the roots of the trees, thus excluding loss of water and soil erosion. Fertilisers can be added directly to the water reservoir. This technology allows increased water savings of 50%, and 90% of fertilisers. During the growing period trees are watered once every 6 days.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology is to improve the water supply for fruit orchards during the growing period in the arid conditions of the Pamirs where available water is very limited.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Steps to implement the technology include the following: dig holes for trees, plant trees, establish water reservoir, lay polyethylene tubes, install emitters and regularly clean irrigation system.
Natural / human environment: The plot is located in an arid zone at the height of 2000m above sea level. It is a high mountain area with typical brown soils and slopes up to 60 degrees steepness. Annual precipitation is quite low and mainly occurs in the autumn and winter period. Summers are extremely dry. The main occupations of the local population include agriculture and cattle breeding.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
GBAO
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Shugnan
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
the project was implemented in 2006
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- adapt to enviroment
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
major food crop: apple, apricot, walnut
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): lack of water, soil erosion, reduction of yield, reduction of soil fertility
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): lack of irrigation water, reduction of yield
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pleine irrigation
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 190Longest growing period from month to month: from April to October
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
0.01 ha
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

modes de gestion
- M4: Changement majeur dans le calendrier des activités
Commentaires:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), change in temperature, change of seasonal rainfall
Secondary causes of degradation: over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), droughts, population pressure, poverty / wealth
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
The system consists of a reservoir and polyethylene irrigation tubes and emitters installed along the rows of trees.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Fruit trees / shrubs species: apricot, peach, european walnut, apple
Perennial crops species: alfalfa
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8.00%
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Tajik Somony
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
4,45
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
3.00
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | tree planting | Végétale | first year |
| 2. | mounting of drip irrigation system | Végétale | before planting |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Tree planting | Persons/day | 2,0 | 11,0 | 22,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Mounting of drip irrigation system | Persons/day | 5,0 | 25,2 | 126,0 | |
| Equipements | Tools | pieces | 5,0 | 1,2 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Other Tools | pieces | 5,0 | 2,2 | 11,0 | |
| Equipements | Polyethylene tube | meters | 2200,0 | 0,445454545 | 980,0 | |
| Equipements | Watertank | pieces | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Tree seedlings | pieces | 360,0 | 0,675 | 243,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | kg | 10,0 | 1,7 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 2005,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | sanitary cutting of trees | Végétale | every 3-5 years |
| 2. | hay harvest | Végétale | three time per year |
| 3. | unclogging the irrigation tubes | Végétale | every year |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Sanitary cutting of trees | Persons/day | 0,6 | 16,66667 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Hay harvest | Persons/day | 1,0 | 9,0 | 9,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Unclogging the irrigation tubes | Persons/day | 1,0 | 11,0 | 11,0 | |
| Equipements | Tools (Scissors) | pieces | 2,0 | 2,5 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tool for harvesting | pieces | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools for unclogging tubes | pieces | 2,0 | 2,25 | 4,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Polyethylene tube | meters | 56,0 | 0,445454545 | 24,95 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Water tank | repair | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings tree replacement | pieces | 15,0 | 0,675 | 10,13 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | kg | 10,0 | 1,7 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 103,58 | |||||
Commentaires:
For creation of drip irrigation system on a plot of 1 ha (May 2011)
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
equipment for irrigation system (polyethylene tubes)
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
260mm per year, winter summer rains. Length of dry period is about 120 days.
Zone agro-climatique
- aride
Thermal climate class: temperate. 2 mounth below 5°C and 6 mounth above 10°C
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone is 2100m above sea level
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil texture is about 40% silt
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
< 5 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 70% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In dry season the harvest is about 20 - 30% higher as compared with the farmers which did not use the technology
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
45kg per ha
Quantité après la GDT:
80kg per ha
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
water availability increase production of fruits
production fourragère
Quantité avant la GDT:
5 centner/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
20 centner/ha
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
grass between rows used for fodder
qualité des fourrages
Quantité avant la GDT:
bad
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
before natural grass - after alfa alfa
production animale
Quantité avant la GDT:
2- 5per hose
Quantité après la GDT:
6-15 per hose
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increase of fodder production stimulate livestock development
production de bois
Quantité avant la GDT:
0.5 m3/hose
Quantité après la GDT:
1-5m3/hose
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
sanitary cutting of tress
risque d'échec de la production
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased water availability
surface de production
Quantité avant la GDT:
10%
Quantité après la GDT:
70%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
technology helps to use steep slopes
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
50%
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
10%
Quantité après la GDT:
80%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased harvest
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
apaisement des conflits
Quantité avant la GDT:
50%
Quantité après la GDT:
0%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreased conflict related to irrigation water use
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
50%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased incomes of poor farmers
Livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
After the implementation of the technology the households were protected from negative influence of dry season.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
10%
Quantité après la GDT:
60%
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
100%
Quantité après la GDT:
0%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
all the water can be absorbed by soil
évaporation
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
transpiration of trees and grass
Sols
humidité du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
80%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
during the dry season
couverture du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
20%
perte en sol
encroûtement/ battance du sol
compaction du sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
diversité des habitats
Autres impacts écologiques
Hazards towards adverse events
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
reduced dry season effect
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
50%
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
Increase of irrigation water availability will improve agricultural production and cover all the expenses that were needed for the establishment of the irrigation system
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- plus de 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
18 households (area is 10 ha)
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 10-50%
Commentaires:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
15 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
3 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: some land users have already adopted the system
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Increase water resources for irrigation of orchards |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Increases water saving up to 50% |
| Opportunity to irrigate orchards during droughts and dry spells (when there is no irrigation water available) |
| Opportunity to apply this technology on steep slopes |
|
Reservoir can be filled with rainwater How can they be sustained / enhanced? through installation of rainwater harvesting system |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The system has to be regularly cleaned from sediments | use filters to clean water from sediments |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé