Composting using Indigenous Microorganism (IMO) [Philippines]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1317 - Philippines
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Penaranda Melijoy
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Bernardino Renel
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Magno Beatriz
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
exploitant des terres:
Ambrocio Acosta
Master's Garden
Philippines
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - PhilippinesNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
The Master's Garden - Philippines1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Composting is the natural process of decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms under controlled conditions.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
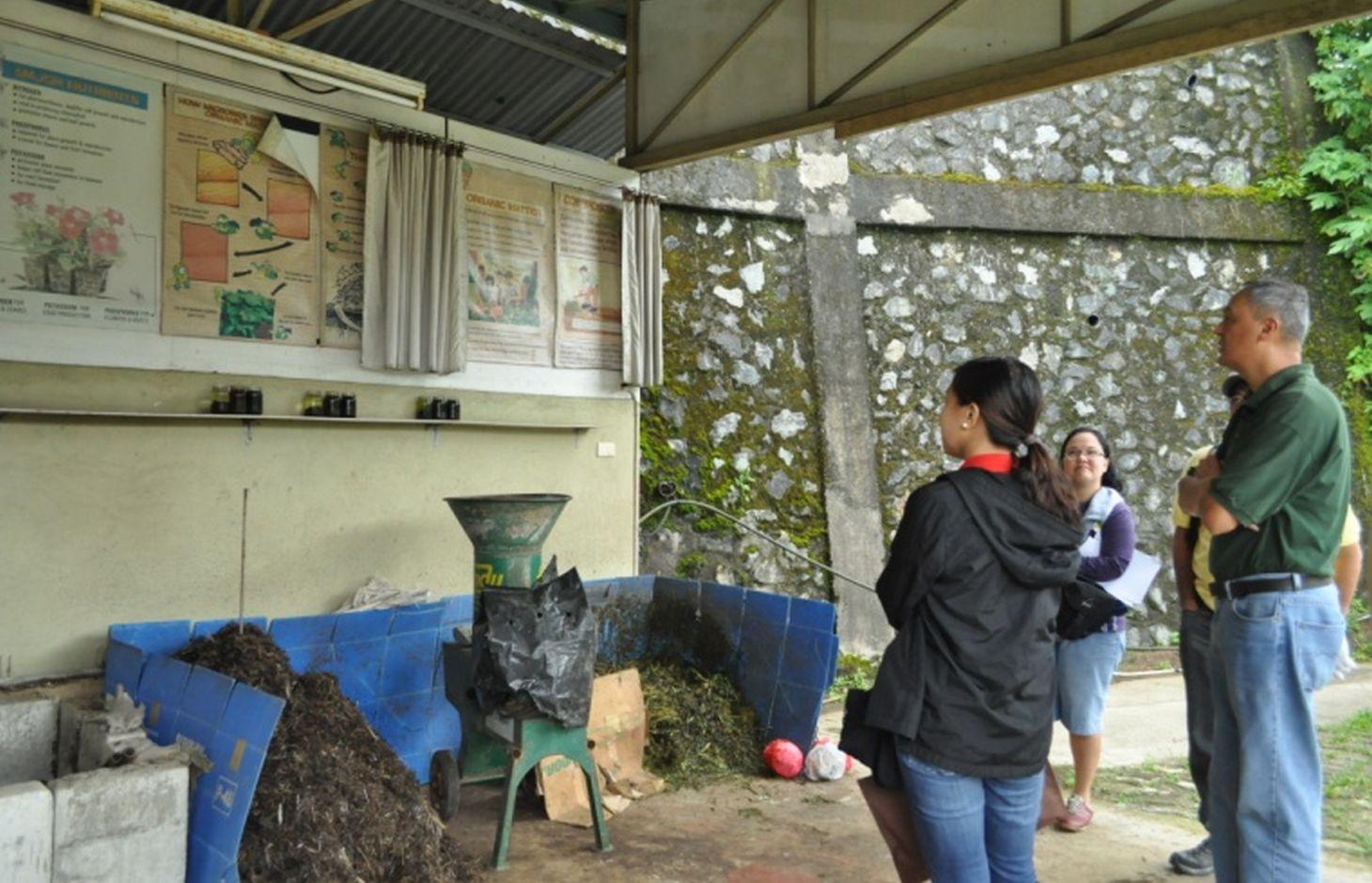
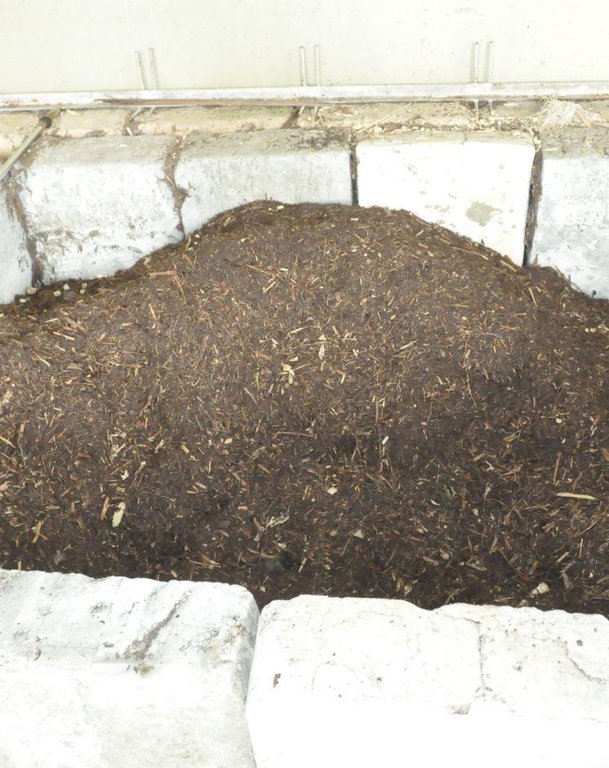
Composting is the decomposition of grass and weeds as fertilizer with the aid of indigenous microorganisms (IMO). This technology is practiced to produce compost used in the farm. Compost is a rich source of organic matter which improves soil tilth. Its decomposition slowly release available nutrients for plant uptake.Material used in the production are weeds and bio waste available in the farm which include Agetarum houstonianum, Dentella repens, Setaria palmifolia, Ipomea aquatica, Echinochloa crusgali, Helianthus annuus and Digitaria ciliaris. The compost is applied in the organic vegetable production of the farm. Vegetables planted include lettuce, herbs, kale and others that are used for garden salads.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of composting is to produce compost that is utilized as fertilizer for the soil. It is done to reduce the input cost of using chemical fertilizer and to avoid lasting harms to the soils and the environment (e.g. formation of impermeable layer "hardpan", affection of micro-organisms, and upsetting of pH).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The initial step in making compost is gathering of raw materials such as weeds and grasses available in the farm. Then, these are shredded and sprayed with IMO to hasten the decomposition. IMO is produced by mixing one tablespoon of forest soil and one tablespoon of sugar/molasses in one liter of water. A portion of the mixture (250ml) is extracted and diluted in a 16 liter knapsack sprayer. The diluted mixture is sprayed to the shredded grasses/weeds and left to decompose for 14 days. For a 1 ton of shredded grass and weeds, 16L of diluted mixture is needed.
Natural / human environment: Master’s Garden of Mr. Ambrocio Acosta is located at Barangay Puguis, La Trinidad, Benguet. The province is under Type I climate by the Coronas system of classification with distinct wet and dry seasons with an average annual rainfall of 3,879 mm. The dry season is from November to April while the wet season is from May to October. The farm has an elevation of 1,342 meters above sea level with less than 40% slope. The farm was manually terraced and arranged into beds with UV treated plastic shed. The production system is managed and cultivated by Mr. Acosta and his two farm laborers.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
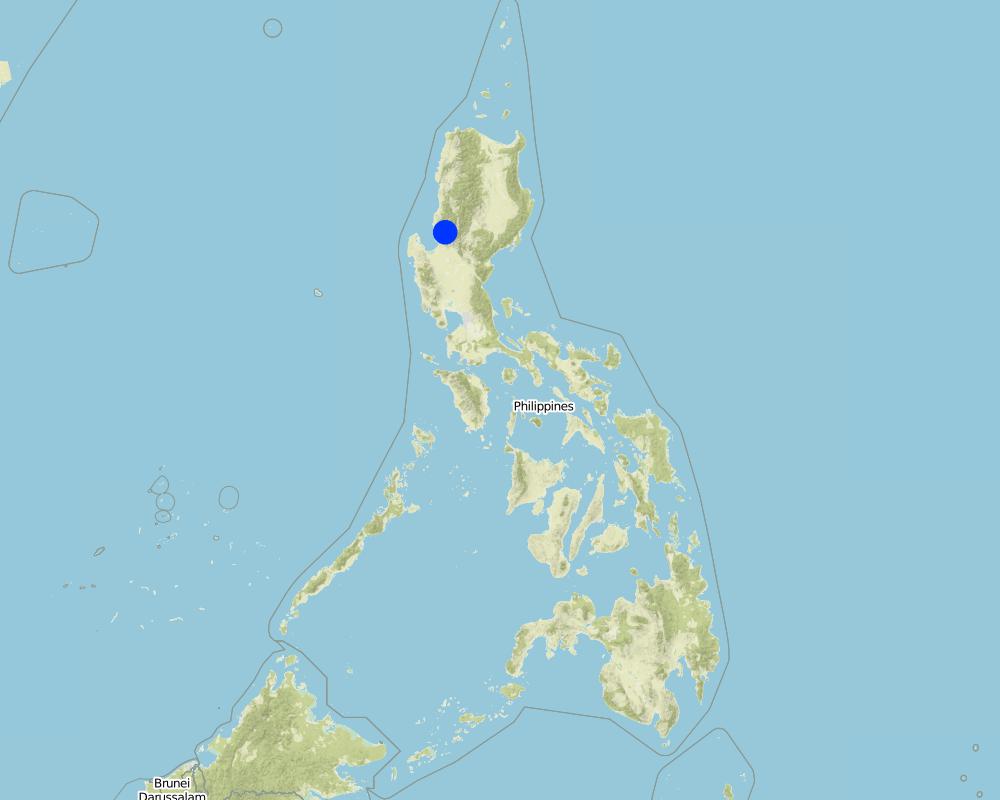
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Philippines
Région/ Etat/ Province:
La Trinidad, Benguet
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Composting was practice since they started developed the farm on year 2000.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- plantes et herbes médicinales/ aromatiques/ pesticides
- plantes à racines et à tubercules - betterave à sucre
- légumes - légumes à feuilles (laitues, choux, épinards, autres)
- tomatoes, cucumbers
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- plantes et herbes médicinales/ aromatiques/ pesticides - pérennes
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Commentaires:
Major cash crop annual cropping: lettuce, tomatoes, cucumber, sugar beets, salad pe
Major cash crop perennial (non woody) cropping: Thyme, mint, tarragon and chives
Major food crop annual cropping: lettuce and tomato
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Since the farm has steep slope, soil erosion was prevalent resulting to low fertility of the soil
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion caused by rainfall leaving them nothing but an exposed subsoil layer.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)

Pâturages
- Extensive grazing
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pleine irrigation
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
Commentaires:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Average annual rainfall is 3,879 mm), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (extreme topography(steep slope >40%)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
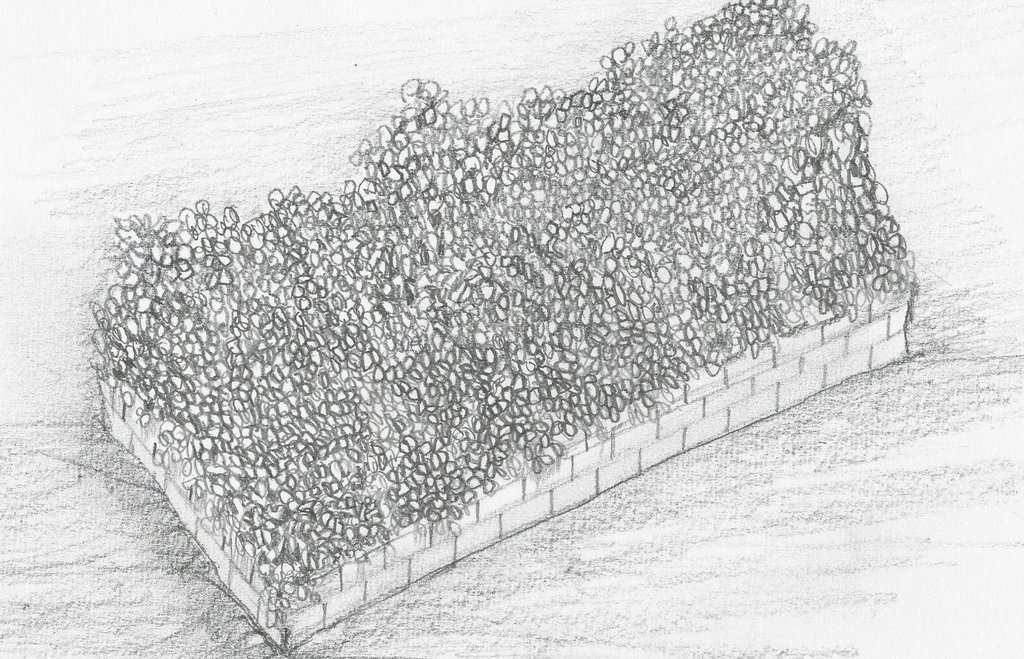
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Compost piled in a cemented box.
Location: Brgy. Puguis. La Trinidad, Benguet
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of infiltration
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Grass and weeds available in the farm( Ageratum houstonianum, Dentella repens, Setaria palmifolia,
Quantity/ density: 500kg
Remarks: the pile to be converted into compost should be under a shed protected from rain to prevent the avai
Agronomic measure: Indigenous microorganism (IMO) solution
Material/ species: forest soil, sugar/molasses, water
Auteur:
Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water Management
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
pesos
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
45,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
5.56
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Procurement of sprayer, shredder, seedling pots and trays | |
| 2. | Establishment of composite chamber (shed) |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipements | Sprayer | ha | 1,0 | 22,22 | 22,22 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Shredder | ha | 1,0 | 2222,22 | 2222,22 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Compost chamber | ha | 1,0 | 155,56 | 155,56 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Seedling trays | ha | 1,0 | 55,56 | 55,56 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Seedling pots | ha | 1,0 | 2,22 | 2,22 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 2457,78 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 54,62 | |||||
Commentaires:
Life span of sprayer and shredders more than 20 years
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hauling of grass and weeds available in the farm | Once a month |
| 2. | Shredding of grass and weeds | Once a month |
| 3. | Spraying the shredded grass and weeds with indigenous microorganisms (IMO) | |
| 4. | Leave for 14 days to decompose | |
| 5. | Application of Compost |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 55,57 | 55,57 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 55,57 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1,23 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: shredder
The calculation is based on the initial establishment cost (e.g. machine and tools) spend by Mr. Acosta on 2003.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The determinate factor affecting the cost is the cost of mechanical shredder. This machine is considered as important investment to those who is serious in engaging and practicing organic farming in a sizable farm like Mr. Ambrocio Acosta.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 1001-1500 m a.s.l. (1,342 meters above sea level)
Landfroms: Mountain slopes (the technology was applied at the farm with > 25 ° or >40 % slope and in concave situation)
Slopes on average: steep (31-60%) (the mean slope is 40%)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage is low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Level of mechanization: manual labour (Vegetables and herbs were planted at beds which were cultivated manually)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence and commercial) ( Harvested vegetables and herbs were for the subsistence of his family and were sold commercially at leading groceries and supermarket through a private marketing corporation known as KIAS Organic Gree)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase in yield was observed as response to compost especially as a source of N and P on the soil
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Grass and weeds are free and readily available in the environment thus reducing the expenses.
revenus agricoles
Impacts socioculturels
situation sanitaire
opportunités culturelles
possibilités de loisirs
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Composting is the decomposition of organic matter into compost which is the alternate for chemical/inorganic fertilizer as source of nutrients for crops. The use of compost prevents the farmers from exposure to harmful effects of chemical fertilizer and protects the consumer on the adverse effects of chemicals on the farm produce. Increased awareness and market demands including premium price for organic crops makes the Organic Farming an impressive source of livelihood and business.
Impacts écologiques
Sols
compaction du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Soil aggregation was enhanced because of the added organic matter from compost
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
Commentaires:
The pile of shredded grass and weeds that will be decomposed into compost were housed under a shed protected from rain and exposure from heat of the sun.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Voluntary adoption of the technology was observed since the land owner, Mr. Ambrosio Acosta , was a member and a previous officer of a small group of organic farmers, the La Trinidad Organic Producers (LATOP) and was also an accredited resource speaker/ trainer for Organic Agriculture-related events/forum.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: It was observed that there is an increased awareness on the harmful effects of chemical inputs on the soil and its negative impact on human health. There is also an increase in demand for organically grown vegetables in the local market.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Compost increases the organic matter of the soil thus improving soil tilth. Also, it contributes to prevent incidence of plant pathogens,and insect diseases, infestation. |
| Compost as fertilizer provides nutrients to the crops |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Application of compost increases soil organic matter that promotes soil aggregation and improves soil condition. |
| Decomposition of the compost slowy releases nutrients like N, P and K that were readily available to plants. |
| It reduces farm production cost. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High initial investment cost in the purchase of equipment, tools and other supplies to start the technology. | Equipment and materials purchased are used for long term. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé