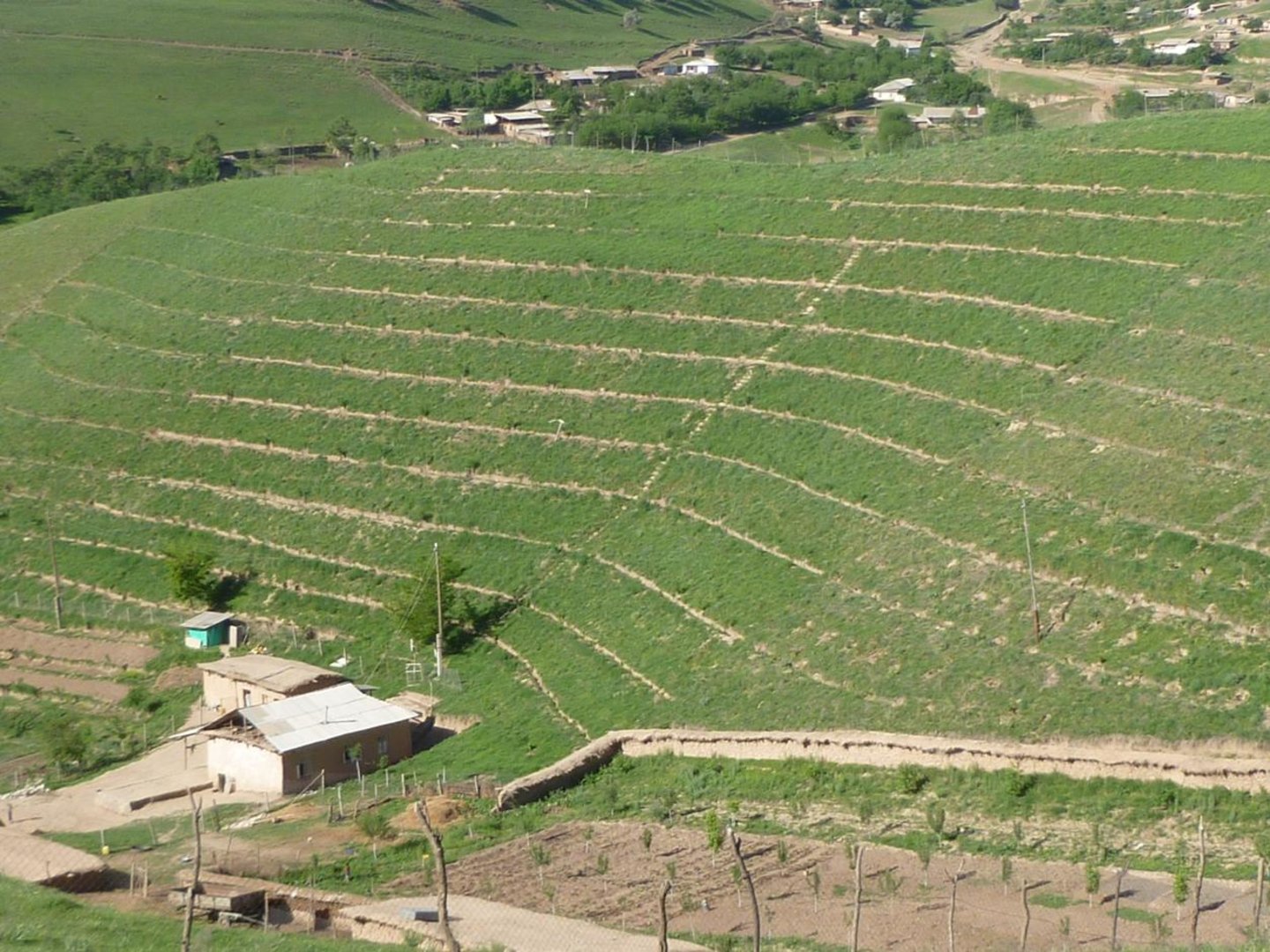
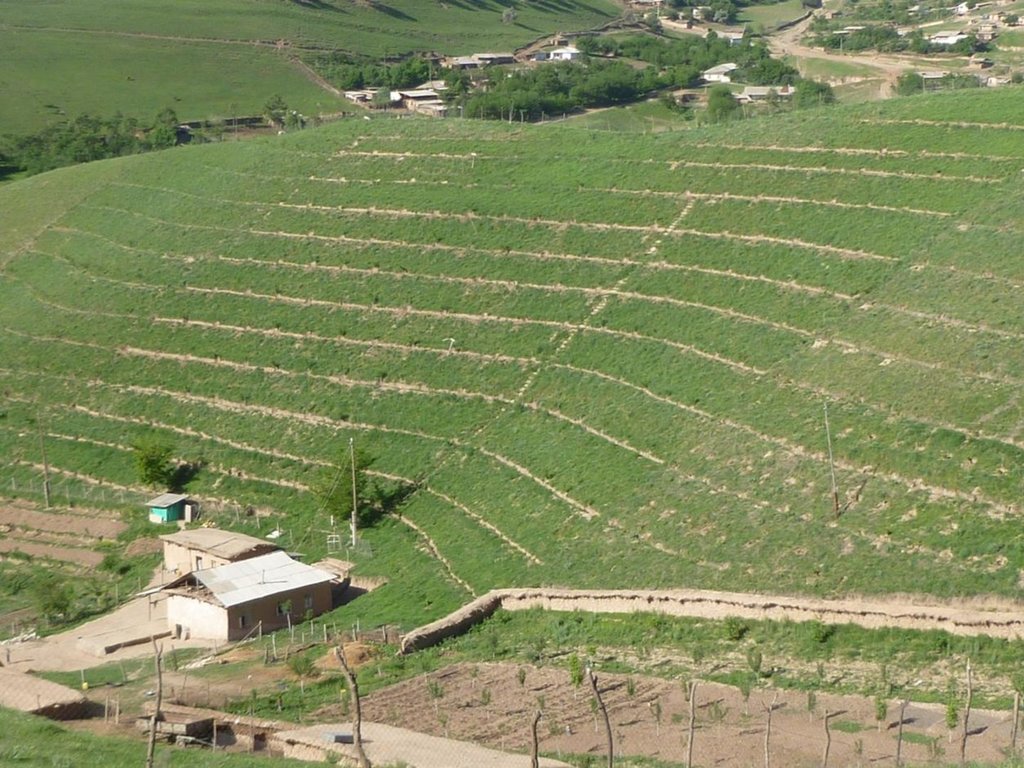
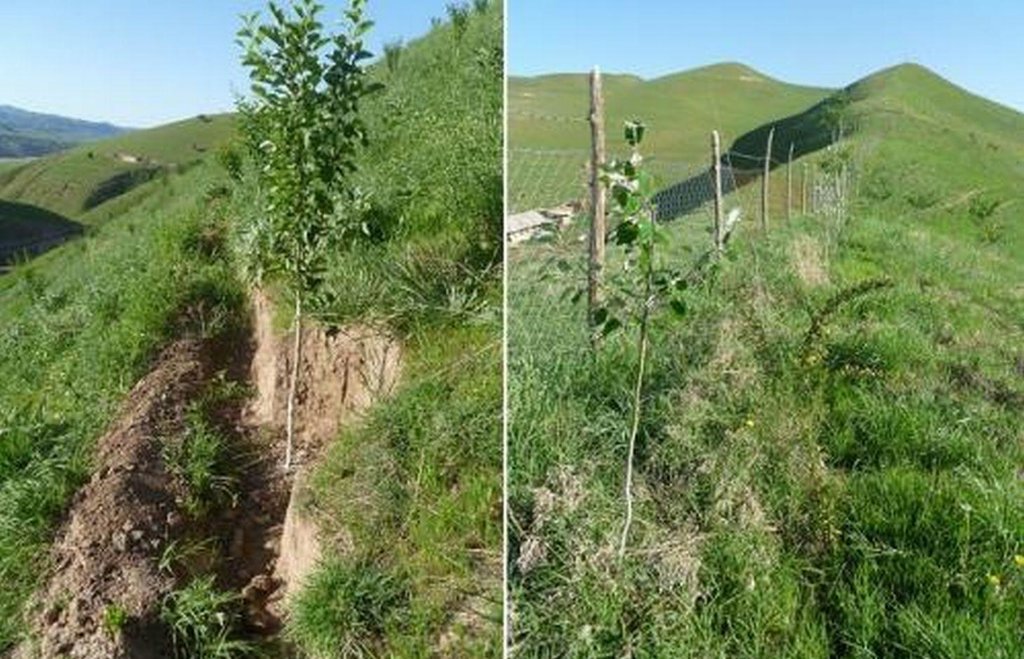
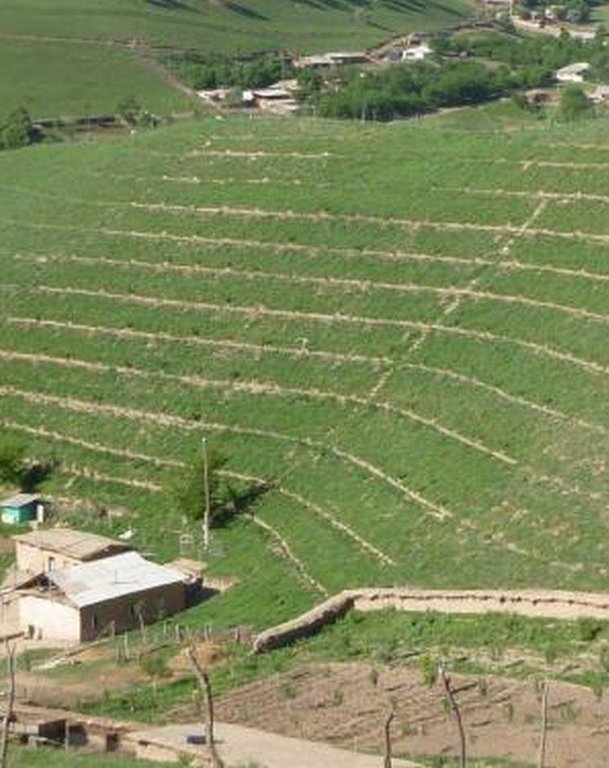
Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Laura Ebneter, Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger, Joana Eichenberger
Ташакули тадричии терассахо тавассути чуйборхои контури
technologies_1043 - Tadjikistan
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: 20 août 2019 (inactive)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: 2 novembre 2021 (public)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: 22 juillet 2017 (inactive)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: 2 juin 2017 (inactive)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: 31 mai 2017 (inactive)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: 27 décembre 2016 (inactive)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
hafizova tahmina
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe, Tajikistan
Tadjikistan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Welthungerhilfe (Welthungerhilfe) - Tadjikistan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)
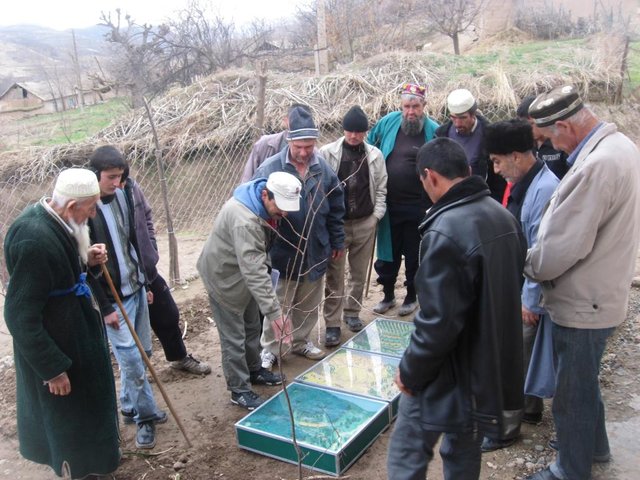

Facilitation of micro-watershed management for farmers [Tadjikistan]
Relying on integrated watershed management principles, farmers were assisted by the project to implement soil and water conservation measures in a microwatershed.
- Compilateur : Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Use of the SLM technology facilitates the development of bench terraces from contour channels by gradually removing soil material up the slope for an estimated 5 years until the terraces on the slope reach a desired width of 1.2 m.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The SLM technology is thought to stop water run-off resulting in the prevention of damage to the top soil on steep slopes. This enables better distribution and infiltration of water into the soil. A complementing live fence, along with a metal net along the perimeter aim to stop livestock grazing. Contour ditches are planted in intervals with fruit trees, and the live fence is made of a combination of fire wood, trees and bushes. This combination makes possible the establishment of an agro forestry system on a slope in an area with limited irrigation using making use of the natural rainfall.
Details: 1. Ditches are dug out along the contour lines drawn by an "A" frame on the slope. 2. Seedlings are planted in 5 metre intervals, positioned right in the middle of the ditch. 3. The back wall behind each tree (upslope) has a half moon cutting to enable an even water/moisture supply. 4. The ditches are barriered with "septas" between two trees to trap water in the individual sections. 5. Horizontally across the ditches, the tree species vary, but vertically are homogeneous. 6. The strips between ditches are left free to enable natural grass to grow. 7. The residual soil material is mounted in front of the ditches in piles the width of a shovel. 8. The complementing perimeter live fence and metal net (1.5m height) is supported by wooden poles made of Acacia trees. (Assumed life span of poles is 25 years). 9. Improvised drip irrigation with 5 litre plastic bottles is used together with mulch coverage beneath the trees. 10. Species composition: apple, cherry, apricot, grape, walnut, pomegranate. In the garden; species of Acacia, Ailantus, dogroses and willow act as a live fence.
Purpose of the Technology: The aim of this system is to significantly reduce the water run-off that removes the top soil, and to subsequently prevent water erosion, and the formation/development of gullies. This can be achieved through the following methods; conserving the available resources and using them more efficiently, prevention overgrazing and improving the natural soil cover, as well as changing the type of land management towards a more sustainable and profitable one.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The plot was established on one side of a micro watershed. In mid February the contour lines were identified using an “A” frame. Digging of contour ditches then took until late February. The material was accumulated down the slope in deposits the width of a shovel to build a riser. At the beginning of March all the fruit tree seedlings were planted in the middle of the ditches. Perimeter fencing was constructed and live fence plants were planted up until late March. In May, the grass around the trees was cut and used for mulching beneath the trees. During June and July in the first year the plants needed watering 3 times a week which was done using a drip irrigation system with 5 litre plastic bottles. To help prevent the water heating and evaporating, the bottles were left under the mulch cover. Mulching and irrigation are repeated every dry and hot season. Every spring, the soil material is removed alongside the inner wall of the ditch just taking an amount that equals the width of a shovel, and accumulated down the slope to extend the riser. Materials required include: (1) Ditches: hand tools, stakes, rope, “A” frame, (2) Live fence: seedlings of Acacia, Ailantus, willow and dog rose, (3) Fencing: metal net, wooden poles, metal wire, (4) Cow dung, lime suspension, straw, mulch, plastic bottles.
Natural / human environment: The watershed can be characterised as follows: Hydrology - surface water is available only at times of rain and snow melt, this can be used for irrigation only. No sources of potable water exist. Soils are of loess type, as generally characteristic to the whole area. Flora - natural grasses prevail in the micro watershed, 9 species could be identified. Natural bushes and trees were completely removed due to high demand for fuelwood. Cultivation of rare tree varieties and household gardening was practiced in advance of the project. Fauna - Wild animals are often still seen such as turtles, lizards and snakes. Farm animals - mixed breeds of cattle, sheep and goats are very important. The households in this micro watershed area own almost 350 animals. The majority of these are kept for the summer season in adjacent pastures. The micro watershed was first inhabited in early 2000. Five households were established with a total of around 40 inhabitants. Family heads tend to be in their early 40s. Families have 7 to 9 members, including 5 to 7 children. All are of Tajik ethnicity, and Muslim, open to secular values. Of these 5 households, only 4 households have adopted the SLM technology. The fifth household only decided to join the project after witnessing their neighbour’s positive experiences. Both spouses tended to be involved in the activities. Both men and women took part in the training sessions and orientation meeting. However, it is likely that most decisions were made by the men, after the women had shared their ideas. Work load: providing the external inputs, construction and the heavy manual labour were done by the men. Maintenance work: watering, mulching and grass cutting was shared between men and women. Digging and fencing were performed in "hashars" - community labour groups. As women spend more time at home working within their households, they tend to perform more maintenance work on the plot compared to men. Other activities away from the farms are important to the family budget providing a means of extra income. This often includes men’s long term migration to Russia to find work.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tajikistan, Khatlon
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Baljuvon, Khirob
Commentaires:
Boundary points of the Technology area: North - 38.284233°N 69.639420°E
South - 38.278485°N 69.639555°E
East - 38.281854°N 69.641276°E
South - 38.281250°N 69.638009°E
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.112 km2.
The application of the SLM technology is planned for the whole micro watershed which has a total area of 0.112 km2. Currently it has been impemented in 0.07km2 of this watershed.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- cultures fourragères - luzerne
- espercet
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- petits fruits
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- raisins
- fruits à noyaux (pêche, abricot, cerise, prune)
- fruits à coque (noix du Brésil, pistaches, noyers de bancoule, amandes)
- fruits à pépins (pommes, poires, coings, etc.)
- Ailantus, Acacia, dog rose, willow, poplar
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: March - August
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
tomatoes, paprica

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Nomadisme
- Pastoralisme de type semi-nomade
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
- Livestock density (if relevant): 50-100 LU /km2

Forêts/ bois
- Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ bois
Produits et services:
- Bois d'œuvre (de construction)
- Bois de chauffage
- Fruits et noix
- Autres produits forestiers
- Pâturage/ broutage
- Conservation/ protection de la nature
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Implementation of land tenure rights at a local level was also a major barrier.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is a soil and water conservation project in place to manage water runoff, soil erosion and gully formation. Low land productivity only allows for wheat production with long fallow periods. Improper pasture management has led to overall overgrazing.
Nomadism: animals taken to summer pastures
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: animal graze around villages
Ranching: no practice
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: almost extinct
Improved pasture: no practice at all
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: No selection in times of electricity cuts in winter season.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): no irrigation network, heavy transports costs
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Pâturages

Implantations, infrastructures
- Trafic: routes, réseaux ferroviaires
- Energie: pipelines, lignes haute tension
Commentaires:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Commentaires:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated, rainfed
Water supply: post-flooding
post-flooding
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol
A3: Différenciez les systèmes de travail du sol:
A 3.1: Systèmes de culture sans travail du sol

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S1: Terrasses

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, contour planting / strip cropping, mulching, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, zero tillage / no-till, pits
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>, aligned: -along boundary
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Tillage on steep slope >35%.), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Natural tree and shrubs removed completely.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (Stocking rates do exceed the standards in multiple times), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Run-off is induced by maximum removal of vegetation cover.), land tenure (Unclear land right situation induces irresponsible attitudes.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Very limited infrastructure development, vital infrastructure points are a long distance away.)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Induces gully formation and mass movement.), droughts (If vegetation is dry then less soil cover is provided.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (The gradient is over 30%.), population pressure (Large family sizes, and high growth rates causes increased need for food and living space in the area.), poverty / wealth (Very limited financial power to develop the land.), labour availability (Though cheap labour is available, it takes much effort to organise communities to work together for SLM activities.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Basic schooling of children, no state provided extension or training after school age.), war and conflicts (The after-effects of recent civil war still have some influence.), governance / institutional (Communist attitudes still persist, very slow institutional development.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
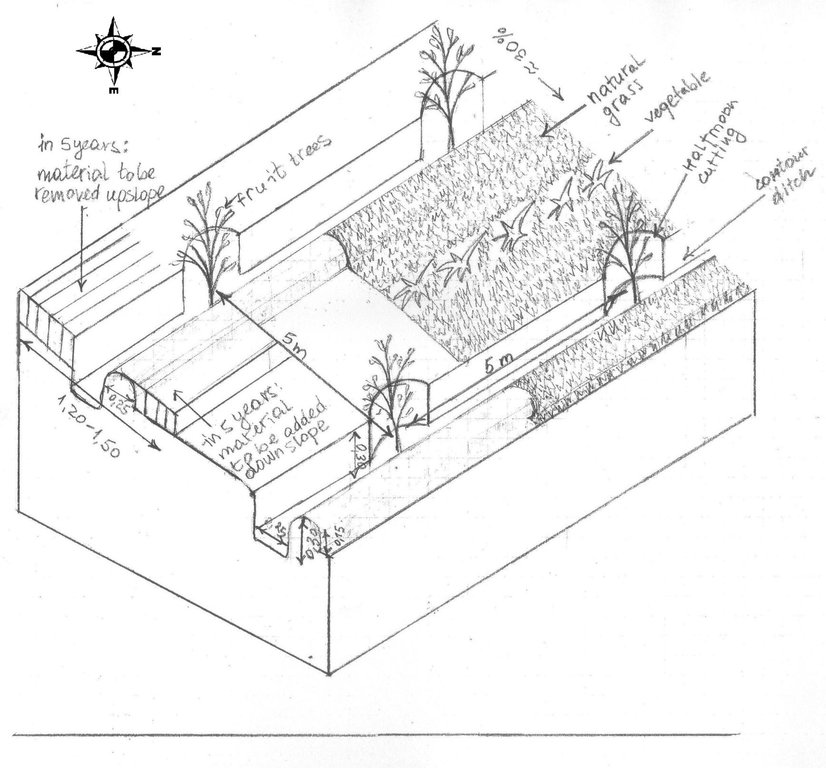
The drawing shows the contour ditches on a slope with a 25 - 30 % steepness. The gradient is 3-5%.
Vertically, the contour ditches are spaced at 5 m intervals. The upper left part of the drawing shows how the material on the slope will be removed in portions during the five years to create a levelled terrace. The ditches are planted with fruit trees, and strips of natural grass cover the space between the ditches. In the middle line of the strips in the bottom part of the plot the farmer has grown vegetables.
Location: Khirob village. Baljuvon/ Khatlon/ Tajikistan
Date: 06.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Specific knowledge needed in the issues of integrated watershed management and technology.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Training needed in terms of technology, planning and implementation of activities.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Growing a few tomatoes and paprica on the bottom strips.
Quantity/ density: 4plants m2
Remarks: Down slope alongside the ditches.
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Wild vegetation is left to grow.
Quantity/ density: very dense
Remarks: Over 9 species counted on the plot all palatable, cut for hay and mulch.
Mulching
Material/ species: Mulching from natural grass, over 9 species.
Remarks: Ditches and trees covered beneath.
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 2 raisers.
Remarks: As a test to cover raiser surface.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Cattle dung suspended in water.
Quantity/ density: Once.
Remarks: Applied while planting the trees.
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: No tillage for intercropping completed.
Pits
Material/ species: Pits were dug to plant seedlings.
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): na
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Trees/ shrubs species: Ailantus, Acacia, dog rose, willow, poplar
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Apple, grape, pear, apricot, cherry, pomegranate, mulberry, walnut
Perennial crops species: little alfalfa and espercet
Grass species: 9 naturally growing species
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 25.00%
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 5
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.25
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.15
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.25
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3.50-3.80
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.25
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.20-1.50
Construction material (earth): the earth is removed upslope and added downslope to the front bank (raiser)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25-30%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 3-5%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Communal pasture land was turned into an agroforestry system
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Self subsistance, market orientated agroforestry system
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Along the contour lines of the slope
Major change in timing of activities: Major seasonal activities in three seasons: spring agronomic and vegetative measures, summer and autumn yield harvesting, clearing the branches
Auteur:
Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov, 16, Firdavsi street, 734003 Dushanbe
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Somoni
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
4,5
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
5.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting seedlings in contour ditches | February-March |
| 2. | Planting seedlings and bushes along the perimeter | March |
| 3. | Cost of seedlings: frutiouse and firewood trees | February -March |
| 4. | Gradual terracing by Broadening the ditch onslope and extending the raiser downslope | every spring during 5 years |
| 5. | Membership fees | |
| 6. | Attending the training | |
| 7. | Management of staff | |
| 8. | Taxes | |
| 9. | Membership fees | |
| 10. | None |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | 1,0 | 355,0 | 355,0 | 100,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Mulching | 1,0 | 4,5 | 4,5 | 100,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting seedlings in contour ditches | person days | 20,0 | 4,4 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting seedlings and bushes along the perimeter | person days | 10,0 | 4,4 | 44,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Set of shovels, hoes, picks | Set | 1,0 | 66,0 | 66,0 | 50,0 |
| Matériel végétal | mulching | 1,0 | 4,5 | 4,5 | 100,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | seedlings | 1,0 | 333,0 | 333,0 | 50,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings: frutiouse and firewood trees | ha | 500,0 | 0,666 | 333,0 | 50,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Wood frame | Piece | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Labour: Gradual terracing by Broadening the ditch onslope and extending the raiser downslope | person days | 150,0 | 0,68 | 102,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1333,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 296,22 | |||||
Commentaires:
Number of parties sharing for Mulching, tools, labour and a wood frame: 5
Lifespan for tools and wood frame: 5 years
Life span of mulching: 3 years
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Drip irrigation with plastic bottles | first 3 years |
| 2. | Mulching | once a year |
| 3. | Shaping the trees, cutting branches | Autumn |
| 4. | Shaping the trees, cutting branches | Autumn |
| 5. | Grafting | March |
| 6. | Manuring | March |
| 7. | None | None |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Drip irrigation with plastic bottles | person days | 15,0 | 4,44 | 66,6 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Mulching | person days | 5,0 | 4,44 | 22,2 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Shaping the trees, cutting branches | person days | 5,0 | 4,44 | 22,2 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Grafting | person days | 5,0 | 4,44 | 22,2 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | mulching | 1,0 | 22,0 | 22,0 | 100,0 | |
| Autre | Labour: Manuring | person days | 3,0 | 4,4 | 13,2 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 168,4 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 37,42 | |||||
Commentaires:
Labour costs apply to the cultivation of the whole 7ha plot.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The most affecting factors were the high cost inputs for construction material which usually has to be imported into the area: Fuel, metal nets for fencing, cement, etc.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Summer, >120 dry days
250-500 mm
Late summer, late autumn, rain prevails until the late autumn
500-750 mm
Late autumn mid spring, rain, snow.
750-1000 mm
avarage annual, usually up to 800mm
1000-1500 mm
not often, 1000mm heppen in single years
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate. winters with possible extreme cold, warm summers, with hot spells in July August
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
hilly area, located on the foot of Vakhsh mountain range; micro watersheds feeding the bigger watershed of the Kyzylsu river
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- très pauvre
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Very few women are trusted to run a farm or make decisions about land use. Usually women have taken leading roles only if the men leave the family for long term migration, or have died. Only 8 women in the whole district are farm owners out of the total of 350 existing farms.
Women's involvement and level of freedom given to them are influenced by existing patriarchal values, and in many areas women often remain unaware of their rights.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
3% of the land users are very rich and own 20% of the land.
5% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
22% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Complemented by salary from state job, NGO activity, transport service and construction work in capital town and other regions, labour migration to Russia.
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), mixed (subsistence/ commercial, mixed (subsistence/ commercial, commercial/ market
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha, 2-5 ha, 5-15 ha, 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production fourragère
Quantité avant la GDT:
very little fodder could be collected
Quantité après la GDT:
cut and carry fodder production
qualité des fourrages
production animale
production de bois
Quantité avant la GDT:
not possible
Quantité après la GDT:
may cover 40 -50 percent of HH need only in 5 year
risque d'échec de la production
Quantité avant la GDT:
no
Quantité après la GDT:
yes
diversité des produits
Quantité après la GDT:
yes
surface de production
Quantité avant la GDT:
no
Quantité après la GDT:
yes
gestion des terres
Quantité après la GDT:
yes
production d'énergie
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
no
Quantité après la GDT:
yes
diversité des sources de revenus
Quantité avant la GDT:
no
Quantité après la GDT:
yes
charge de travail
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
possibilités de loisirs
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
compaction du sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
risques d'incendies
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
capacité tampon/de filtration
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
dommages sur les champs voisins
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
4 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Project subsidised only 50% of material inputs.
Comments on adoption trend: Metal for the net was costly- farmers had to convince the project to subsidise prior to adoption, otherwise would reject adopting (area has high risk of crop damage- high livestock density, grazing not controlled).
Year following implementation: 3 farmers in neighbourhood have adopted on own funds; much more are willing to adopt, but need external support
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| It helped to acquire more land user rights. |
| Land users feel they have an increased status in local society. |
|
It has good potential for replication in other areas. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It would be better if the more expensive parts of the input were subsidised. |
| Good long term perspectives for improvement of livelihoods. |
| It allows a positive long term change in household provision regarding food, employment and energy sources, allowing more spare time for cultural events and education. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| It made possible the change to more sustainable land management techniques. |
| The technology is well suited to the sloping landscape and is easy to adopt. |
| The technology allows the use of locally available materials, and has low maintenance costs. |
|
It fits well to the local needs for land reclamation and conservation, and sits within the legislative frameworks. How can they be sustained / enhanced? There has been a recent state decree to encourage promotion of orchard development. |
|
It has a positive effect on the areas downstream. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Prior to implementation of the technology, areas downstream were often were damaged by floods. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| It needed some immediate on-site adjustments when structuring the half moon cuttings in the contour ditches. | The farmer's opinion should be considered during the adoption of the technology, and to assist with any changes made. |
| It caused some disagreements between the farmers and the consultant over what part of the material input should be subsidised. | The consultant should try to ensure they understand the social and economic factors affecting the locals. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Needs more until the final structure is finished | This depends on the length and intensity of any precipitation/drought/dry spells etc. |
| It is a new technology in this area so will need some time to be proven effective. | |
| External knowledge is needed for the establishment and maintainance of the technology. | |
| Extra workers are needed for the complementary drip irrigation - child labour is often used for this. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Scetch map of Khirob Microwatershed
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
DWHH Baljuvon Office
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Interim Narrative Report 01.05.2009-30.04.2010 Project TAJ 1068
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
DWHH Baljuvon Office
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Grant Application Form to EU Commision: "Individual incomes & Improving Living Standards in Khatlon and Sughd Regions", Tajikistan
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
DWHH Regional Office, Dushanbe mail to:
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Facilitation of micro-watershed management for farmers [Tadjikistan]
Relying on integrated watershed management principles, farmers were assisted by the project to implement soil and water conservation measures in a microwatershed.
- Compilateur : Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov
Modules
Aucun module trouvé