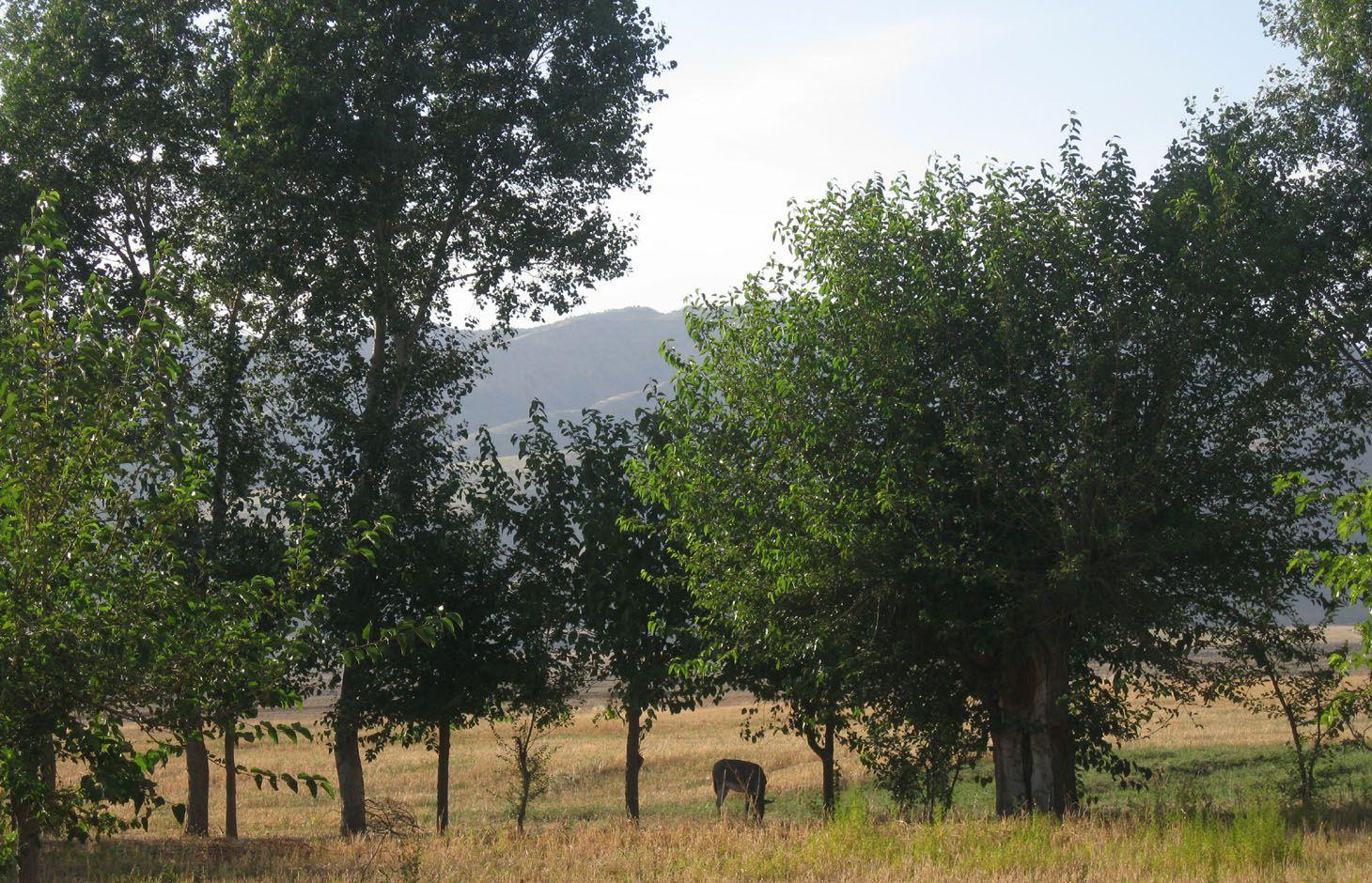
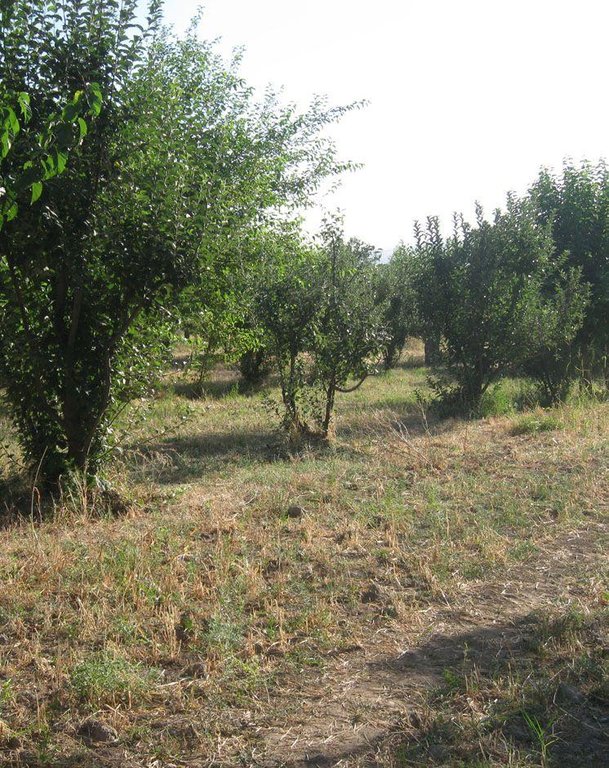
Current agroforestry: orchard with wheat intercropping [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Malgorzata Conder
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1134 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Current agroforestry of a degraded mulberry and apple orchard with wheat intercropping
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Since 1992 an area of around one ha has been owned by the farmer. He planted mulberry trees the same year. At that time, orchards were established in the whole surrounding area because the government decreed that a territory should have plenty of mulberry trees. Despite the government plan, all the land users of that area began to switch their orchards into wheat crops. Five years later the farmer planted apple trees within the mulberry orchard. The orchard had 200 mulberry and 100 apple trees. The motivation was to feed the working farmers of the fields around. Five years later the apple trees gave fruits. But only the first two years gave a good yield and income from selling them. Later on the fruits were just eaten by the farmer’s family. After another seven or eight years the farmer grew a wheat crop in between the tree lines. Nowadays it's the only remaining orchard in that area. Due to the lack of proper maintenance and water availability the orchard is degraded and the output is very low.
Purpose of the Technology: The government established a large territory of mulberry orchards, for three reasons: First to reduce the impact of natural hazards, second to increase silk production and last to improve fire wood availability. The planting of apple trees should be beneficial for farmers working in the surrounding crops and well as for the family, who sell the fruits and the mulberry leaves. As the yield started to decrease the wheat crop was established to have a bigger output for that crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Due to the government’s order to establish orchards, the local authorities provided the mulberry trees. Hence, it was in the responsibility of the farmer to plant the trees and to look after them by soil loosening and pruning. The latter activity must be done once in the first five years after planting. The farmer bought the apple trees himself as they were cheap at that time. To establish the wheat crop, ploughing, seeding, fertilizing and finally harvesting must be done. One person is supposed to guard the orchard and wheat crop every day. Yearly maintenance consists of soil loosening around the fruit trees and the above mentioned task for cropping. The maintenance of the orchard seems to be abandoned more and more, probably because the output decreases year by year.
Natural / human environment: The orchard is situated below Momandion village, on the very last foot slope before the valley plain begins and, hence, it has a slight slope,. In the past, orchards were numerous, but nowadays wheat crops have mostly replaced the orchard. As there is no fence and no one to control it regularly, livestock invades the property. During its first two years there was a water source, which had dried up by the time. The orchard is a relic being the only and last one in that area. Broken branches, unpruned trees and a trampled crop, show signs of insufficient control and maintenance and therefore of a gradual abandonment of the orchard.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Muminabad
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
According to farmer it's 1 ha, according to GoogleEarth around 1.6 ha
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
- government
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Since 1992 it's property of the farmer
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - blé de printemps
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- petits fruits
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- fruits, autres
- fruits à pépins (pommes, poires, coings, etc.)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept/Oct
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
wheat crop

Pâturages

Forêts/ bois
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Trampled and degraded soil as a consequence of no fences or control. Soil crusting and compaction because of lack in organic matter resulting in a low infiltration rate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): water scarcity and low soil moisture, small yield of the fruit trees
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: In the past the wheat and apple yield was much higher thereby they were cash crops. As the yield decreased by then and he gets low yield the use them as food crops.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
- système de rotation (rotation des cultures, jachères, agriculture itinérante)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
Commentaires:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction
- Pk: scellage et encroûtement

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (monocropping, lack of maintenance)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Because if no fence), education, access to knowledge and support services (More agronomic/ technical advice needed)
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Location: Muminobod, South of Momandion, Obishur Watershed. Khatlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (How to regenerate the poor soil and water conditions, which species are useful to plant etc)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: wheat intercropping within orchard
Agronomic measure: vertical plowing
Aligned: -linear
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mulberry, apple
Change of land use type: Mulberry and apple orchard combined additionally with wheat crop
Change of land use practices / intensity level: More pressure on natural resources because of additional wheat crop in the orchard
Auteur:
Malgorzata Conder
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Somoni
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
4,83
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
12.40
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying, transport and planting of mulberry trees, 10 days (7 hours/day), 3 people | once, 1992 |
| 2. | Buying, transport and planting of apple trees, 5 days (7 hours/day), 3 people | once, 1997 |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 497,4 | 497,4 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 311,0 | 311,0 | 33,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 808,4 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 167,37 | |||||
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plowing vertically, 4 hours of labour, tractor and petrol | every year, spring (since 2007) |
| 2. | Buying (200 kg) and sowing wheat, 2 hours, 3 persons | every year, spring (since 2007) |
| 3. | Applying fertilizer, 2 hours, 1 person, 2 bucks à 50 kg | once a year, september |
| 4. | Cutting wheat, 4-5 days (6 hours/ day), 4 people | September, once a year |
| 5. | Guardening | every day |
| 6. | loosening around trees (ca. on 1/3 of the trees), 4-5 trees a day | every year, spring |
| 7. | pruning (ca. 1/2 of mulberry trees), 7-8 days (2-3 hours/ day), 3 persons | every year, autumn |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 572,2 | 572,2 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 24,8 | 24,8 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Petrol | l | 25,0 | 28,5 | 712,5 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 82,8 | 82,8 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 76,6 | 76,6 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 1468,9 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 304,12 | |||||
Commentaires:
The cost were calculated for 1 ha, but one have to consider that an orchard and wheat crop is on the same plot. This means that there's not fully a wheat crop of 1 ha.
Mulberry seedling were paid by the government, apple trees by the farmer.
Machine use and petrol, are all included in the labour input in the establishment phase, as it was not separately mentioned by the farmer.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Labour is the most important input, but as it is done mostly by the farmer or the family itself it's mainly agricultural material as seedlings, seeds and fertilizer. Latter particularly as recurrent costs.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: temperate, LPG from end of March until September
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked1, mostly) and rolling (ranked 2)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (ranked 1, no rainfall from July to August) and medium (ranked 2, winter and spring season with frequent rainfalls (700mm))
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- employé (entreprise, gouvernement)
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Level of mechanization: Manual work (ranked 1) and mechanised (ranked 2, only for plowing)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1, mainly subsistent, depending on yield more or less commercial) and mixed (ranked 2)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Commentaires:
Based on land user's Certificates
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
less apple and wheat production
risque d'échec de la production
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More fertilizer and pesticides needed than in the past
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced crop production and fruit yield
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
less maintenance work
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mulberries were shared with other people working next to the field (no fence)
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
negligible thanks to a little slope
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
encroûtement/ battance du sol
compaction du sol
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
capacité tampon/de filtration
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas connu |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas bien |
Commentaires:
Higher vegetation cover, which would make the land use more resistant to drought, more stable in case of floods and heavy rainfalls.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| The orchard gave by-product as leaves for silk production and branches. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
It is the only orchard in the neighbourhood, which is why it would be worthy to maintain it. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Put more effort and labour into the orchard, currently only the wheat crops seems to be of interest for the farmer. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Currently the orchard is too old to get a good yield and maintenance activities are comparatively high. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Lack of maintenance and guarding or fencing. | More focus on the orchard as it has also ecological benefits. Enhance the farmer to put more labour into the orchard. |
| Show good examples of orchards and their resulting benefits. Round tables by and for farmers to share experiences. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé