Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Julie Zähringer
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_1453 - Tadjikistan
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: 21 mars 2017 (inactive)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: 23 juillet 2017 (inactive)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: 14 août 2019 (inactive)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: 2 novembre 2021 (public)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Kyrgyzstan Mountain Societies Development Support Programme, Aga Khan Development Network (MSDSP KG) - KirghizistanNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
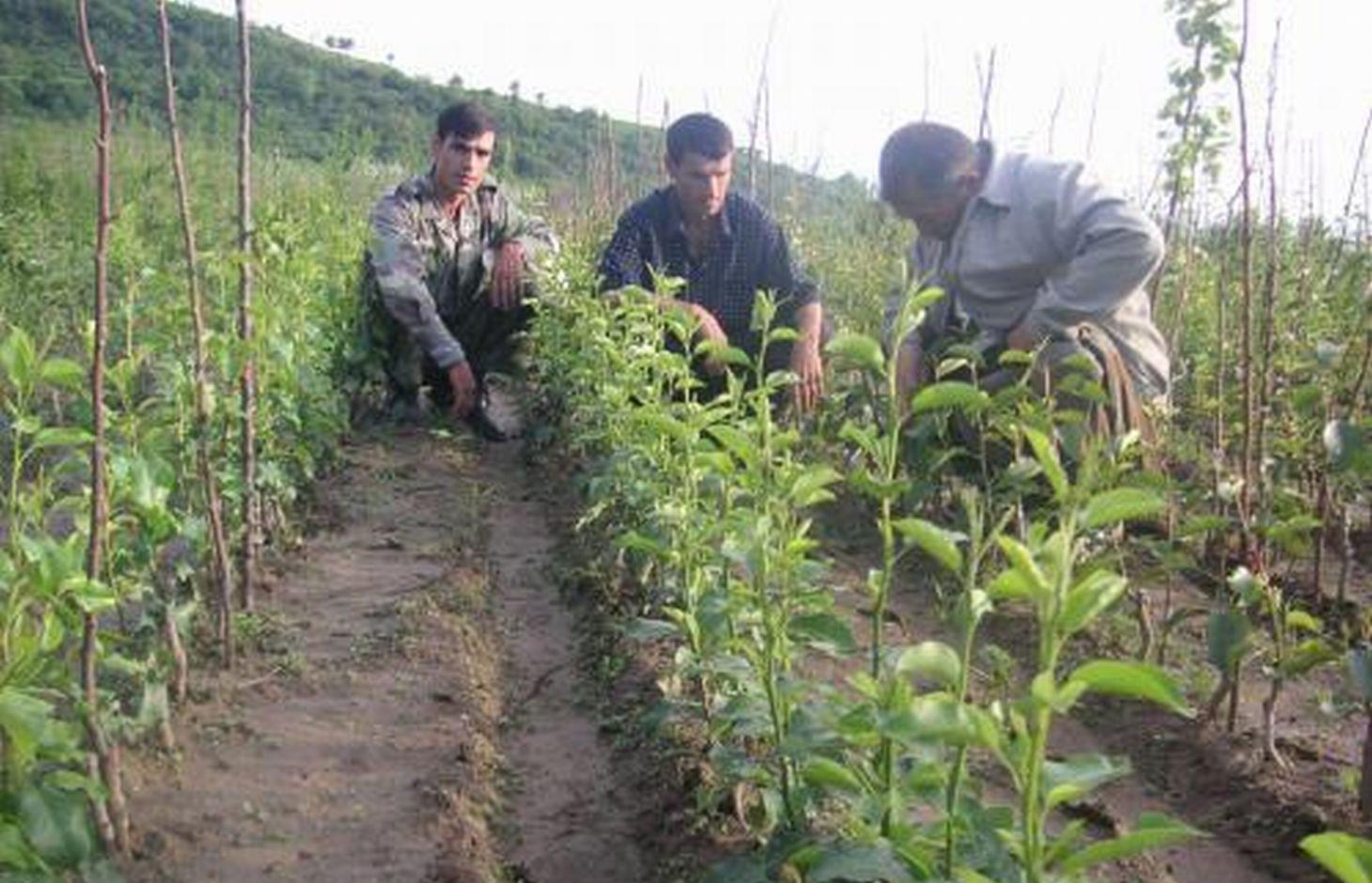
Tree nurseries are established to test and identify varieties of tree species that are tolerant to climate change in the region.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
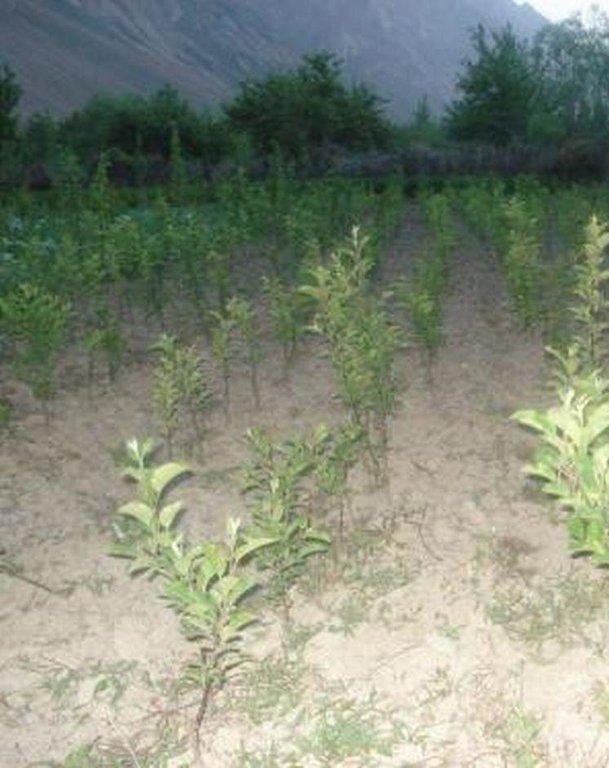
In 1995-96 the first tree nursery was established in the Vanj valley with support from the Mountain Societies Development Support Programme (MSDSP) of the Aga Khan Foundation. During Soviet times there were no tree nurseries in this region and seedlings had to be brought in from outside. Only the Pamir Biological Institute (PBI) was able to obtain seedlings for research purposes. A nursery of about 0.1 ha was established by one farmer on his own land. Tree species grown in the nursery include apple, peach, apricot, walnut, cherry and pear.
Purpose of the Technology: The main goal of the project was to make varieties of tree species adapted to different climatic conditions in GBAO locally available. The seedlings are used for other MSDSP projects, such as orchards for soil stabilisation, and are also purchased by private land users for their own land. In addition, the land user was taught how to establish a business by selling seedlings to other land users. There is a strong need for quality tree seedlings in the whole region and even people from as far away as Ishkhashim (7 hour journey by car) travel to Vanj valley to purchase seedlings from this nursery. The economic benefit for the land user is very high as during one year he can make more than 18,000 TJS (4000 USD) of profit from selling seedlings while the investments in fertilisers are comparably small.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The steps necessary for the establishment of a tree nursery are the following: (1) a suitable plot of flat land is chosen by the farmer, (2) the plot is fenced with dead branches to protect it from roaming animals, (3) in March, the farmer prepares several wooden boxes filled with humid soil in which he distributes 10 kg of seeds of different tree species and varieties. Those boxes have to be irrigated for a month while the seeds are germinating, (4) in April, the nursery plot is ploughed along the contour using animal traction and 1 ton of organic manure, 20 kg of phosphor and 2.5 kg of nitrogen is mixed with the soil, (5) seedlings are planted linearly along the contour with small irrigation ditches running parallel to the planting lines. These ditches were automatically established through the ploughing process, (6) two more times during the first season another 3 kg of nitrogen are applied. In the second year the grafting process is started and in the third year the farmer starts selling the seedlings. The farmer therefore splits up the nursery plot in three parts so that he can always have newly planted seedlings at the same time with second-year seedlings for grafting and third-year seedlings for selling
Natural / human environment: The technology was adopted by two other farmers from the village who had successfully applied to MSDSP for financial support for seeds and fertilisers. Many other farmers from neighbouring villages are interested. The bridge that is currently being built to allow for more trade between Afghanistan and Tajikistan might open further market opportunities for the land user. Furthermore this type of experience is being widely replicated in other districts and supported by MSDSP.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tajikistan
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Vanj
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
1995, through MSDP project
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- fruits à noyaux (pêche, abricot, cerise, prune)
- fruits à coque (noix du Brésil, pistaches, noyers de bancoule, amandes)
- fruits à pépins (pommes, poires, coings, etc.)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 90Longest growing period from month to month: March-May
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): reduction of vegetation cover, erosion of slope areas, decline of soil fertility,
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?

Terres cultivées
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pleine irrigation
Commentaires:
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- amélioration des variétés végétales, des races animales
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bh: perte d’habitats
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats
Main causes of degradation: soil management, deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature, change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (avalanches, mud flows), population pressure, poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 3000 / 0.1 ha
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Trees/ shrubs species: apple, peach, apricot, walnut, cherries, pear
Change of land use practices / intensity level: from cropland to tree nursery
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Somoni
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
4,5
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
4.50
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a place with enough water and good soil fertility on flat land for establishment of nursery | |
| 2. | Fencing with dead branches | |
| 3. | Ploughing and distribution of fertilisers | March-April |
| 4. | Plant seeds in box with humid soil and irrigate | March |
| 5. | After one month transfer seedlings to planting lines | March-April |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Fencing with dead branches | Persons/day | 80,0 | 20,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Ploughing and distribution of fertilisers | Persons/day | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Plant seeds in box with humid soil and irrigate | Persons/day | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Transfer seedlings to planting lines | Persons/day | 28,0 | 20,0 | 560,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | kg | 10,0 | 5,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | kg | 30,0 | 3,0 | 90,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 2370,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 526,67 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | during first year |
| 2. | Apply nitrogen fertiliser twice more during the growing season | during the growing season |
| 3. | Grafting | second year |
| 4. | None | None |
| 5. | None |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Apply nitrogen fertiliser | Persons/day | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Weeding | Persons/day | 28,0 | 20,0 | 560,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Grafting | Persons/day | 28,0 | 20,0 | 560,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | kg | 6,0 | 3,0 | 18,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 1158,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 257,33 | |||||
Commentaires:
The costs were calculated for a nursery of 0.1 ha.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The most determinate factors affecting the costs are for labour, although in the documented example, labour was provided voluntarily by the family of the land user. Costs for labour are estimates for a situation in which labour had to be paid in Tajikistan.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
500,00
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 1800 m a.s.l.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Off-farm income specification: teacher
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
The land belongs to the state but the land user has a certificate.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Nursery established on cropland
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The economic benefit for the land user is very high as during one year he can make more than 18,000 TJS (4000 USD) of profit from selling seedlings while the investments in fertilisers are comparably small.
diversité des sources de revenus
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Availability of fruits
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More fruits provide a more balanced diet with more vitamins
possibilités de loisirs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Aesthetic value of trees
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Higher income from selling the tree seedlings, about 3,000 USD per year, allowing people to provide better education for their children and better access to healthcare
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
qualité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
diversité végétale
diversité des habitats
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Autres impacts écologiques
Hazard towards adverse events
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Increased income and benefit start after three years when seedlings can be sold.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
3 households
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: people from other villages in the valley contacted MSDSP because they would like to adopt the technology (however, they would need financial or material support).
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
The technology is very important to the whole of the GBAO region as nurseries were not available during Soviet times and all tree seedlings were brought from outside How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improved access for farmers of interesting tree varieties that they can reproduce in their nurseries |
|
Creation of business opportunities. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Experience sharing between farmers from outside GBAO |
|
Through the spreading of this technology there will be more seedlings available to all interested households How can they be sustained / enhanced? Establishment of farmer field schools to disseminate the positive experiences of this technology and to increase the number of nurseries |
|
Varieties of trees that are adapted to local climate can be more easily obtained How can they be sustained / enhanced? Access to other new varieties should be improved |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| It is quite a complicated process that requires some expertise; the farmer needs to know about planting technologies, grafting and market opportunities etc. | Farmer to farmer dissemination of knowledge could be facilitated through the establishment of farmer field schools. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé