Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China [Chine]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Christian Rumbaur
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
罗布红麻 and 罗布百麻 (Chinese)
technologies_1721 - Chine
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China: 9 mars 2017 (inactive)
- Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China: 4 avril 2018 (inactive)
- Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China: 19 mars 2019 (public)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Rouzi Ahmatjan
Catholic University Ingolstadt-Eichstaett
Allemagne
Spécialiste GDT:
Thevs Niels
World Agroforestry Center, University of Central Asia
Kirghizistan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Sustainable Management of River Oases along the Tarim River, China (SuMaRiO / GLUES)Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Catholic University Ingolstadt-Eichstaett (KU) - AllemagneNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - Kenya1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
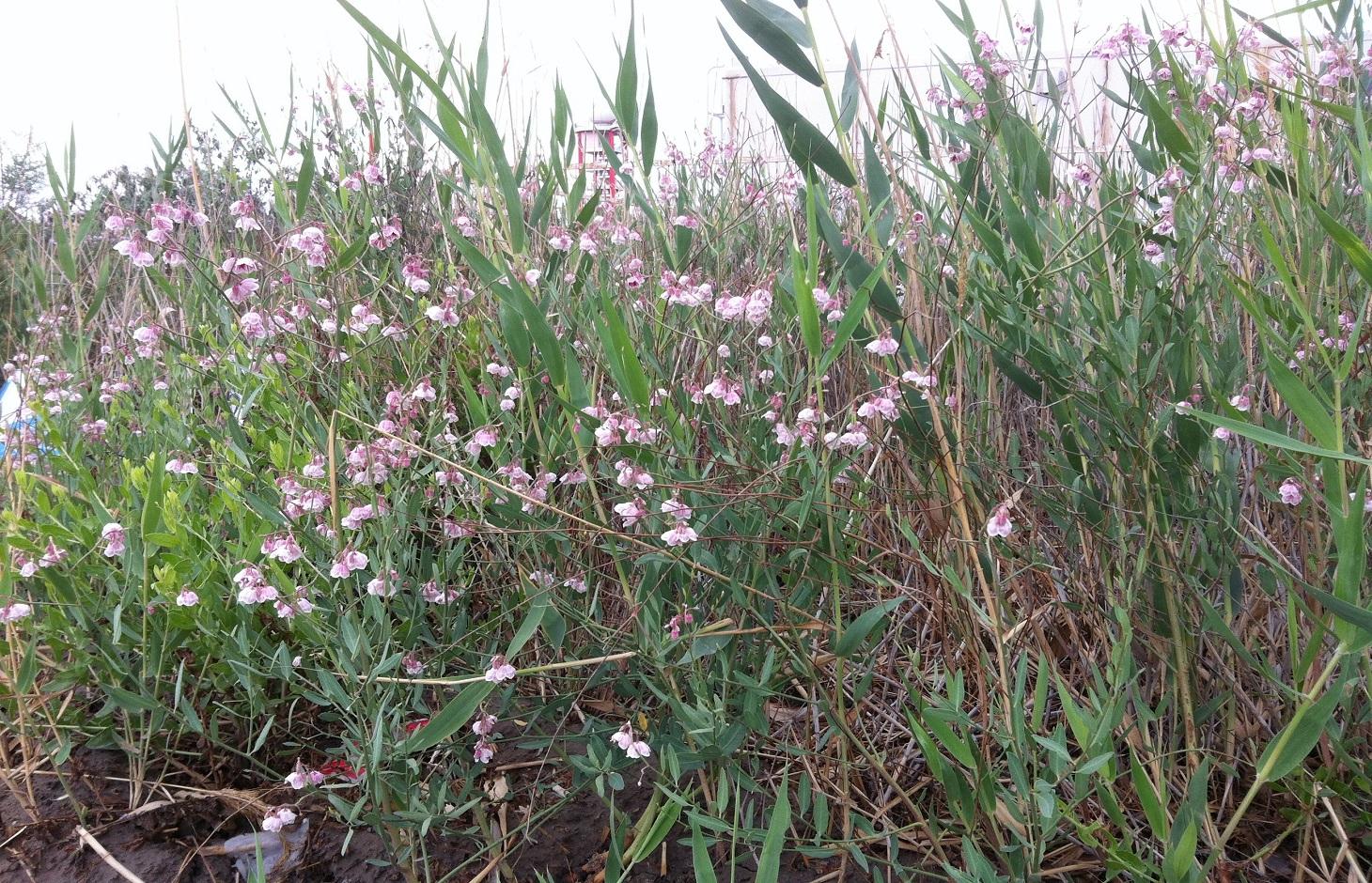
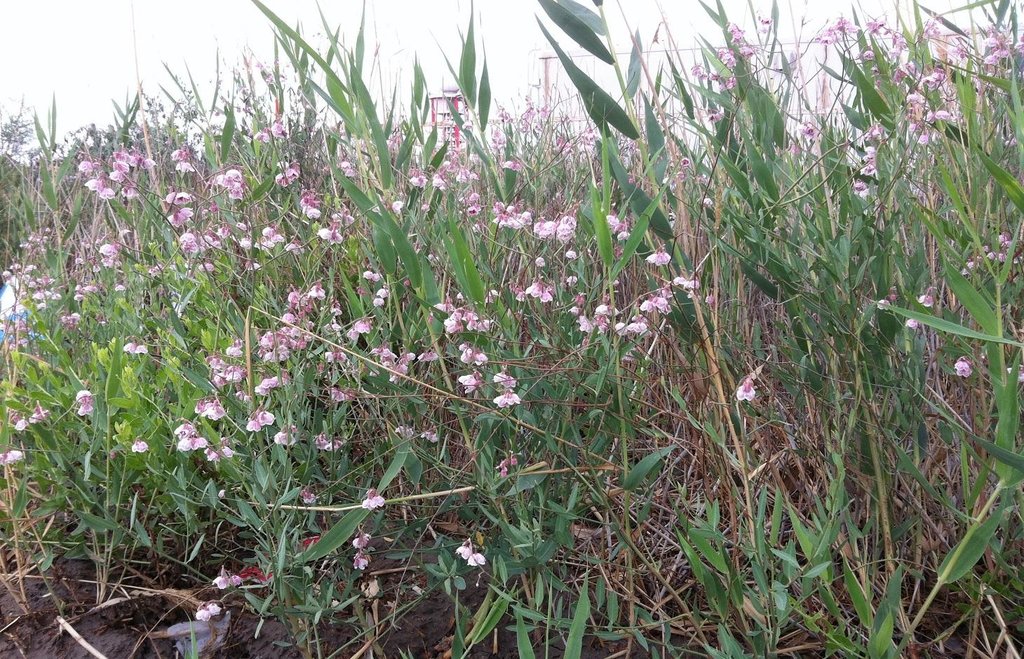
Plantation of Apocynum pictum and Apocynum venetum as protective and profitable indigenous plants - on soils made saline through irrigation of cotton without adequate drainage.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
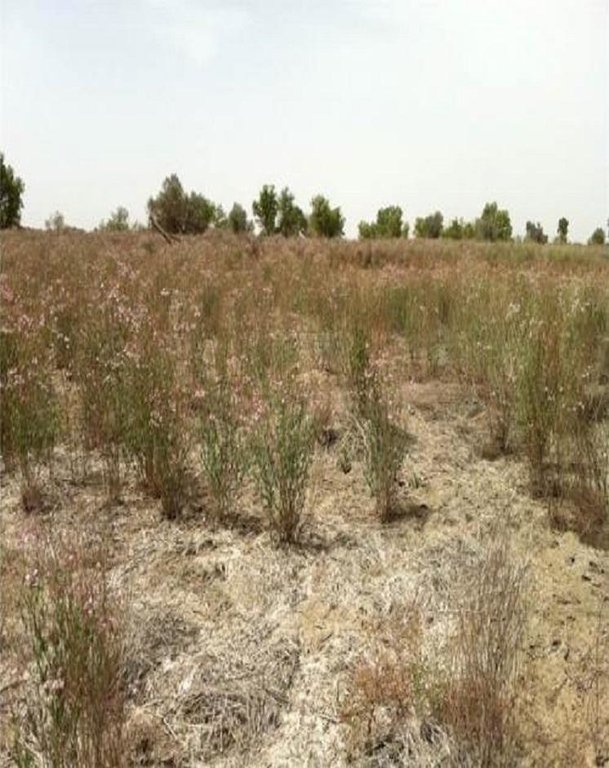
The natural ecosystems in north-west China, especially in Xinjiang Province, are dominated by steppes, semi-deserts and desert. Riparian forests along the Tarim River Basin have been reduced and degraded by the expansion of irrigated agriculture since the 1950s. The main crop planted is cotton. In the arid temperate cold desert climate, precipitation is very low and evaporation high. The only water source for the region is the Tarim River. Xinjiang is being promoted to become the main cotton production area of China, especially in the upper reaches of the Tarim River, and reservoirs with a large irrigation infrastructure have been established. Farmers water their fields with flood and drip irrigation. But most of the fields have no drainage system. With the high evaporation and the capillary rise of the shallow groundwater, salts dissolved in the water accumulate on the soil surface and in the soil. This salinization makes the fields unusable for cotton production and are abandoned as farmers move on. These barren saline soils are prone to wind erosion, as almost no plants can grow on them. Large-scale desertification is the result.
Purpose of the Technology: To halt desertification the barren saline soils need to be protected by vegetation to avoid soil loss by wind. But if this can be done through vegetation that yields an income then the advantage is double: a win-win situation. Apocynum venetum and Apocynum pictum are indigenous and both are drought and salt tolerant. They are phreatophytes: deep-rooted plants that tap groundwater or the soil layer just above the water table. A.venetum and A. pictum are rhizomatous perennials – and importantly they are cash crops too. Fibre from the stems are used to produce textiles, though the extraction process is time and labor consuming. The advantage of apocynum yarn is that it has antibacterial properties. The leaves and flowers are also sold and used to produce tea which is a Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that reduces blood pressure. On a per hectare basis, the stem generates a potential income of US$ 3,650, the leaves US$ 1,995, and the flowers US$ 1,815: nevertheless the market for apocynum products is small. In Xinjiang most of the apocynum plantations are under commercial large-scale farmers. They have the capital to deal with the costly establishment of apocynum.
Natural / human environment: Fields on which apocynum is sown should have a groundwater level not deeper than 2m. Nevertheless the soil should be well-drained: best is a sandy loam. Waterlogged, calcareous, clayey soils are not suitable. Apocynum can withstand periods of water inundation; however, prolonged submergence or waterlogging inhibits its growth. The topsoil under apocynum is often saline, reaching salt contents of up to 20%. Apocynum can grow on sites with a pronounced surface salinization, as long as the subsoil and the groundwater are not strongly salinized. There are two methods of planting apocynum: by seed or by vegetative means. While irrigation helps establishment and good yields, this is at a much lower level than for cotton. In conclusion, A.venetum and A. pictum provide profitable options on saline soils, grow with minimal irrigation, and protect the land against wind erosion.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Chine
Région/ Etat/ Province:
China / Xinjiang Province
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Tarim River Basin
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
6000,0
Commentaires:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Location in China between 37°~46°N and 76°~104°E. Location in Tarim River Basin: 41°12'34.94"N and 84°19'28.19"E
In China the area of Apocynum vegetation, natural or artificial, amounts to 1,330,000 ha. One third to half of this area is located in Xinjiang, ie approximately 600,000 ha
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
- naturally
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- cultures de plantes à fibres - coton
- wheat
- Apocynum
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March to October with irrigation
Commentaires:
Apocynum venetum and Apocynum pictum
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Salinization, desertification, mismanagement of cotton monoculture, inadequate drainage under irrigation, abandonment of degraded land.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water scarcity, salinization, land use rights.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: salt crust on the top soil layer and high salt content in the soil
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles

Terres improductives
Précisez:
Desertification: Wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- brise-vent/ plantations abris
- amélioration des variétés végétales, des races animales
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cs: salinisation/ alcalinisation

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bh: perte d’habitats
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Most fields have no drainage -> Increase of groundwater -> salinisation of soils), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Cotton monocultures), wind storms / dust storms (Duststorms, blow ou tof topsoil), droughts (It is an arid climate), population pressure (doubling the population during the last thirty years), land tenure (land belongs to the state), education, access to knowledge and support services (poorer farmers have less access to extension services)
Secondary causes of degradation: discharges (point contamination of water) (Non-point source pollution and drainage water discharge from the fields), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Most fields have no drainage -> Increase of groundwater -> salinisation of soils), floods (Floods are necessary for the region (riparian forests)), poverty / wealth (family farmers are poorer than city dwellers)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Apocynum planted in a levelled field with strips of 8 to 18 cm height and 30 to 40 cm width with 40 cm space between each strip
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (for regeneration and multiplication)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 20,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3 to 0.4
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 60,000 to 70,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
-0,42
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Manuring (3700 to 5000 kg/ha) and ploughing | Before sowing |
| 2. | Site establishment/ preparation | |
| 3. | Planting of seedlings/ root cuttings/ transplants | most suitable seeding time is mid April to May or transplantation |
| 4. | Irrigation at establishment (10000-12000 m3/ha) | After sowing |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Site establishment/ preparation | ha | 2,0 | 18,7 | 37,4 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 100,0 | 2,5 | 250,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 100,0 | 6,18 | 618,0 | |
| Autre | Manure | ha | 171,1 | 18,7 | 3199,57 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Waterfee | - | 1,0 | 460,0 | 460,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 4564,97 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | -10868,98 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 15 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | irrigation and weeding labor | 6 times |
| 2. | Fertilizer | |
| 3. | Harvest labor | at harvest |
| 4. | Transport | after harvest |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | irrigation and weeding labor | ha | 10,0 | 114,0 | 1140,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Harvest labor | ha | 1,0 | 359,0 | 359,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Transport | ton | 1,0 | 11,0 | 11,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer (Phosporus) | kg | 150,0 | 4,12 | 618,0 | |
| Autre | Waterfee | 1,0 | 2280,0 | 2280,0 | ||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 4408,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | -10495,24 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, shovel, tractor and plough
Costs were calculated for 2015, per hectare. Labour has become more expensive over the last few years. In the beginning (first two years) cultivation of apocynum is very labour and input intensive. After 1.5 to 2 years the plants can be harvested for the first time. The price for the products of apocynum (leafs and stems) are very high. Direct seeding as compared to vegetative propagation is the most labour-saving method to cultivate apocynum.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Per year: 90 mm; Jan, Feb, Apr, May: 3 mm; Mar, Sept: 5mm; Jun: 33 mm; Jul: 18 mm; Oct: 0 mm; Dec: 8 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- aride
Thermal climate class: temperate. cold desert climate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: Altitude between 800 and 1300 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: medium - high
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table also < 5 m: Apocynum is a phreatophyte. The most productive sites of Apocynum venetum are found on a groundwater not deeper than 3 m with salt contets between 1g/l and 10g/l.
Ground water table 5-50 m: Apocynum pictum is mainly found on groundwater levels of 4-6m below surface with a maximum groundwater depth of 8 m. Apocynum is restricted to groundwater levels not deeper than 4 m below surface.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
- très riche
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Man are doing the hard work in the fields, women do more the harvesting
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 7%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The plantation of Apocynum brings a high income to the farmers.
Level of mechanization manual labour: harvesting
Market orientation of production system commercial/ market: Apocynum is planted for fibre, tea and medicinal products
Level of mechanization mechanized/motorized: field preparation
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
< 0.5 ha: family farms
5-15 ha: state farms
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- loué
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
- loué
Commentaires:
All the land belongs to the state. Farmers have the right to use the land for 70 years.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
production de bois
risque d'échec de la production
diversité des produits
surface de production
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
revenus agricoles
diversité des sources de revenus
charge de travail
Autres impacts socio-économiques
market for apocynum fibre
market for TCM
Impacts socioculturels
opportunités culturelles
possibilités de loisirs
apaisement des conflits
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
qualité de l'eau
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
encroûtement/ battance du sol
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
diversité des habitats
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas connu |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
In the beginning (first two years) the plantation of Apocynum is very labour and input intensive. After 1.5 to 2 yearsthe plants can be harvested for the first time. The price for the producst of Apocynum (leafs and stems) are very high.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
No number on households
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Most of the plantations are planted by large investing farmers. The farmers sell the products of Apocynum to the pharmaceutical companies for Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Both species yield fibres and leaves for fiber production and the leaves for medicinal products or tea on considerable areas under the arid climate of Xinjiang Province, China, without intensive irrigation, because they use the groundwater as for example cotton. Furthermore, both species can withstand higher soil salinization levels than cotton. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The plantations can be enhanced by analyzing the water consumption and the water use efficiency to apply only as much water to the plants as they need Not decreasing the yields. |
|
Both species can provide an income to local people - fibre and leaves for medicinal products or tea - under conditions which are unfavorable to grow crops under irrigation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote apocynum on saline wastelands and subsidize the establishment of the plantations. Explore further markets and promote the products. |
|
Through apocynum plantations wastelands are reclaimed. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Highlight the potential to reduce wind erosion and ‘dust bowls’. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Difficult process to extract fibre from the stems. | New technology needs to be developed. |
| Small market. | New uses need to be explored to expand the market. |
| High investment in the beginning of the plantation. | Planting of apocynum should be subsidized. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
N Thevs et al. (2012) Apocynum venetum L. and Apocynum pictum Schrenk (Apocynaceae) as multi-functional and multi-service plant species in Central Asia: a review on biology, ecology, and utilization.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Journal of Applied Botany and Food Quality 85, 159-167.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé