Marab - Water Harvesting Based Floodplain Agriculture [Jordanie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Joren Verbist
- Rédacteurs : Mira Haddad, Enrico Bonaiuti
- Examinateur : Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Marab in Arabic “المرب”
technologies_5770 - Jordanie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Strohmeier Stefan
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Jordanie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Natural Resources Economist Social, Economy & Policy Research:
Dhehibi Boubaker
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Jordanie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management InitiativeNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - Liban1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
This technology conserves soil and water; it reduces surface water and sediment losses from dryland watersheds. The technology is located in downstream/lowland floodplains, and ideally, it is implemented in an integrated watershed approach. In the present case study, the ‘Marab’ is linked with two main upstream measures: Upland micro-water harvesting (Vallerani system) and gully/channel measures (gully plugs)
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
The Marab is a local downstream water harvesting measure in an integrated watershed context, where up/midstream users and applied land management practices affect the Marab.
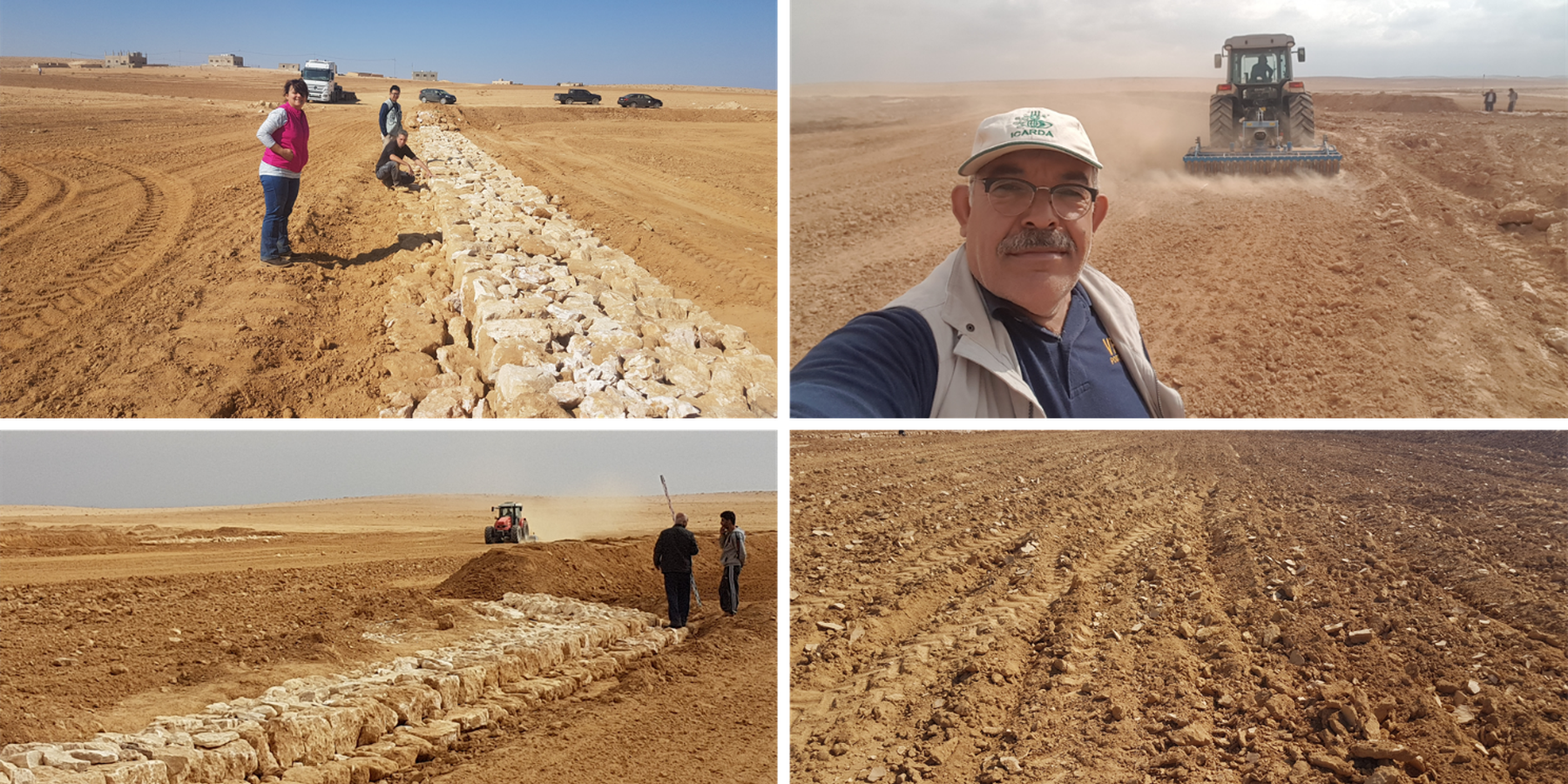
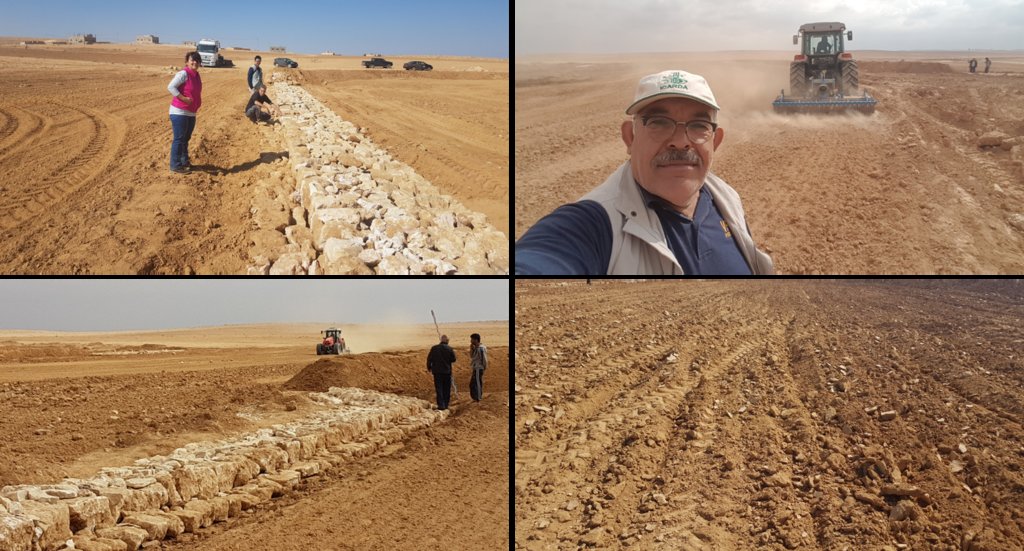
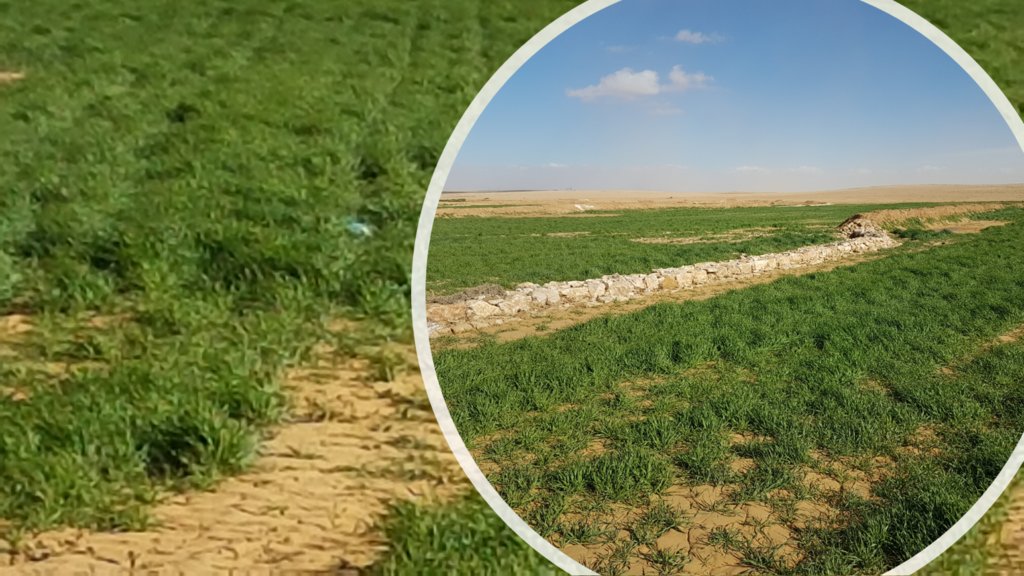
The technology diverts and spreads excess runoff over deep-soil flood plains. The technology comprises local gully-filling, grading/leveling of seed bed, and construction of a bund-and-spillway system creating several compartments for flood-irrigated agriculture.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Arid drylands of Jordan receive less than 200mm average annual rainfall. The specific site is located close by Al Majeddyeh village, around 30km south-east of Amman. The average annual rainfall at the site is around 130mm. The average temperature is above 18 degrees Celsius. The human environment is characterized by agro-pastoralists. These are farmers that live in permanent houses but transport their livestock to graze. As consequence of the natural environment and mis-management (e.g. overgrazing) desertification has been an increasingly problem, not only from an environmental perspective (e.g. carbon stocking; lack of water), but also from an socio-economic perspective, because desertification leads to reduced productive lands, consequently resulting in less income for the rural population.
Therefore, the aim of the technology is to achieve high-yield agriculture through flood/macro-catchment water harvesting in arid environments commonly unsuitable for field crop agriculture, creating beneficial impact for local land users. The high yield barley is fed to the livestock (goats and sheeps) of the local agro-pastoralists. Applied in an integrated watershed approach, it meets agricultural demands and motivates sustainable dryland ecosystem management in the uplands. The Marab-technology has a buffering effect on extreme runoff through water retention, for further use in downstream areas, including the trapping of relative fertile sediments from upstream. As the Marab increases yields, it also improves the livelihood of the local population.
The Marab-technology is a macro-catchment water harvesting technology. The Marab is located in the natural depression of the watershed (10 square kilometres), therefore most of the water from the watershed is captured here, instead of being spilled away. Combining this natural depression with the construction of bunds and specific soil leveling, leads to decreased run-off, thus highly increased water infiltration and soil moisture. Thereby, the biomass-production increased as well.
The watershed is characterized by degraded lands upstream (720 ha), where low yield and subsidized barley cultivation is practiced, and by gullies. In a limited part (12 ha) of the upstream area, Vallerani micro-catchments are implemented as a pilot-plot. This might seem contradicting since upstream micro-catchment water harvesting decreases the water in the Marab downstream. However, the Vallerani micro-catchments also have beneficial impacts on the watershed and the Marab, such as flattening peak water flows, reducing erosion and providing fodder. The reduction in water run-off for the Marab as consequence of the Vallerani structures is not significant, due to the small size of the pilot area. But the relations between upstream and downstream should be taken into account.
Upstream watershed measures to buffer and/or avoid extreme runoff events (extreme downstream flooding) in the Marab such as micro-catchment water harvesting structures (Vallerani tractor plow system) and the out-planting of native shrub seedlings, as well as the stabilization of erosive gully systems through gully plugging and revegetation of side banks are advised to be taken before implementing the Marab technology downstream, as they safeguard and protect the Marab. But they are not further into account in this documentation.
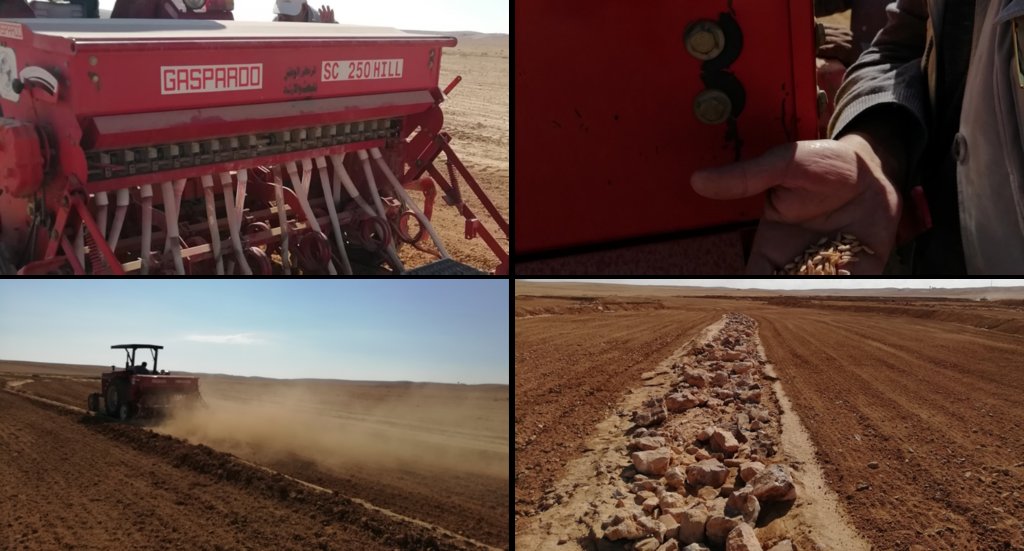
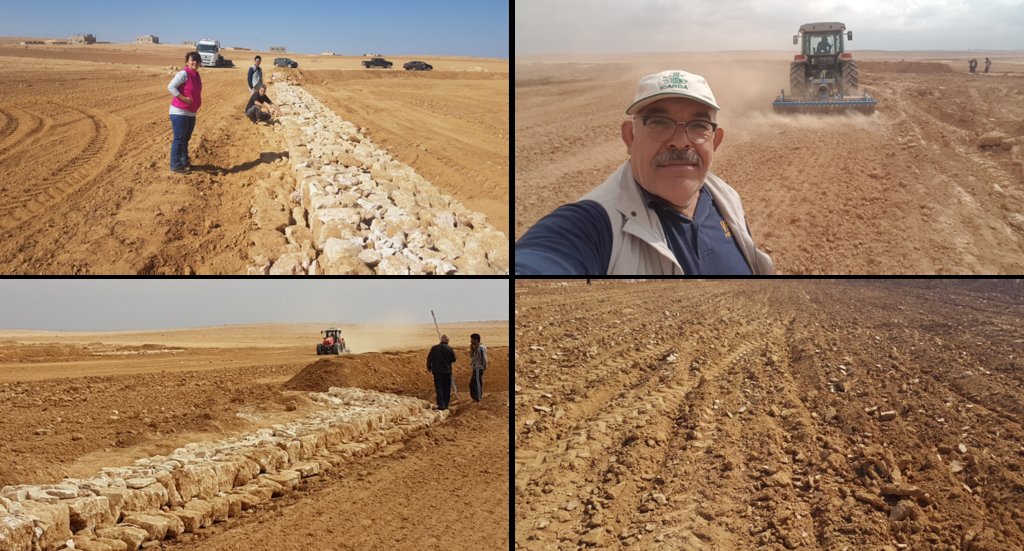
Establishment of the downstream Marab system includes:
•Local filling of downstream gull(system) with deep soil
•Leveling/grading of flood plains
•Construction of earth bunds
•Construction of the spillways (stone made)
• Seedbed preparation for planting annual crop such as barley
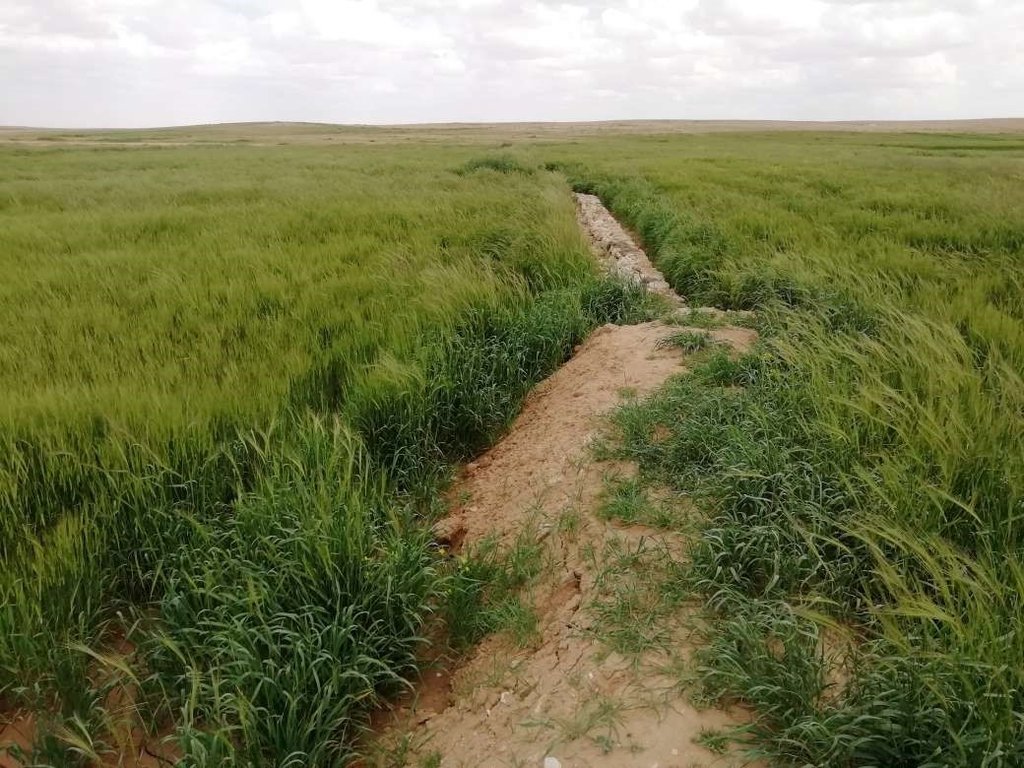
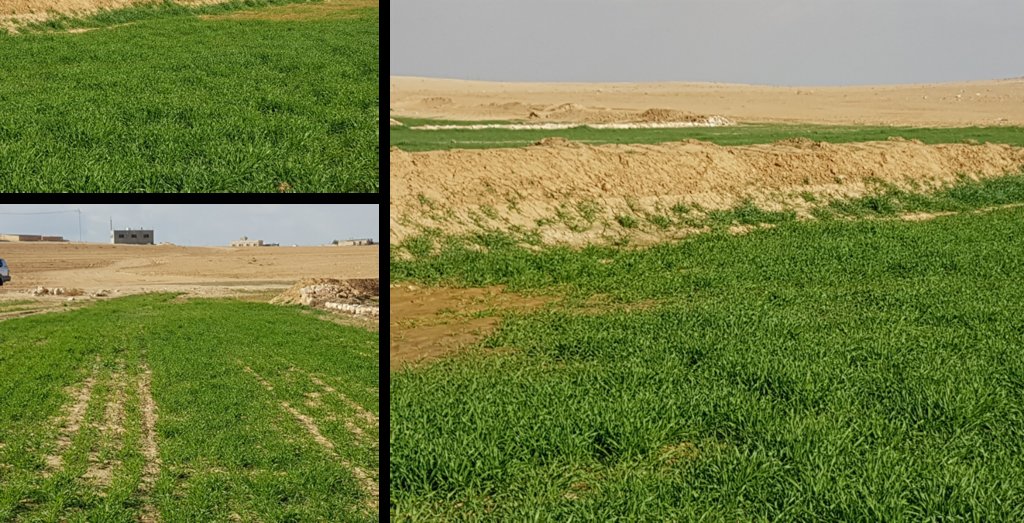
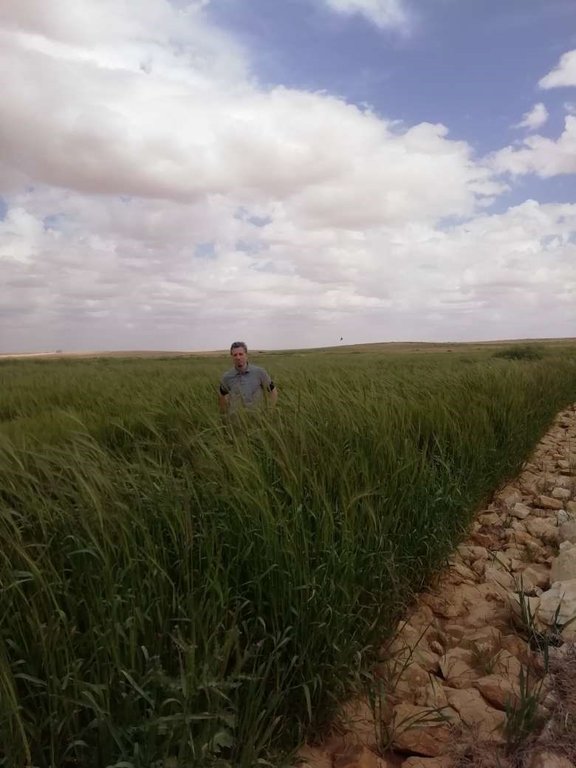
Marab agricultural production is high and stable. It can reach around 5-6 t ha-1 of barley, compared with the low and strongly varying yields of around 0.05-0.30 t ha-1 in traditionally, without macro water harvesting, cultivated barley. Marab barley produces grains (for fodder and reseeding purposes) and requires local inputs, such as fertilizer. The Marab mitigates downstream flooding and loss of sediments from the watershed. Local farmers applying the Marab technology are very satisfied, because of the extremely increased yield as consequence of the technology. However, as water is captured in the watershed, tensions may arise between the downstream (Marab) users and the upstream users.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Jordanie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Al Jiza District
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Al Majeddyeh Village
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2017
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agropastoralisme (y compris les systèmes culture-élevage intégrés)

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - orge
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Non
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Non

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Pastoralisme de type semi-nomade
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
Type d'animal:
- caprine
- ovins
Est-ce que la gestion intégrée cultures-élevage est pratiquée?
Non
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Non (Passez à la question 3.4)
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
The Marab facilitates uniform distribution of excess rainwater obtained from the upland (partly Vallerani micro-catchments) and the water is conveyed through rehabilitated gullies to the Marab. (Some) Micro catchments and rehabilitated gullies are essential to avoid damaging water peaks, harming the Marab-structures. The Marab is rainfed and naturally flood irrigated.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol
- A4: Traitement de la couche profonde du sol

structures physiques
- S2: Diguettes, digues
- S3: Fossés étagés, canaux, voies d'eau
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation

dégradation physique des sols
- Pk: scellage et encroûtement

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Retaining surface runoff and locally infiltrating water through bunds increase soil moisture hence agricultural yield increases (e.g. biomass, vegetation cover) , soil crusting decreases (in some selected ponding areas it might increase) - and because of trapping top-soil sediments and residues from the uplands, soil fertility increases likewise.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
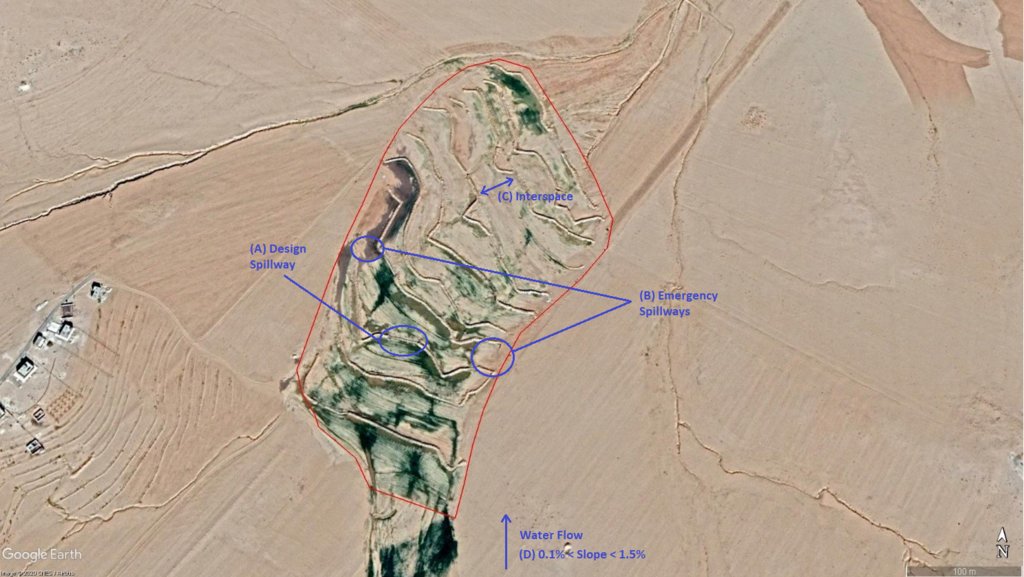
The overall Marab (reshaped flood plain) area is 10 hectares. The natural flood plain was leveled up to the sides; the natural slope in flow direction ranges between 0.1 and 1.5% (D). The later stone bund construction (soil relocation) and siltation/erosion processes over time develop a slight step-terraced bund compartment system, with the single compartments having much smaller slope than the overall Marab. At the sides, the levelled area slightly increases towards the natural terrain (natural terrain at the sides is around 0.1 to 0.3m higher compared with the leveled Marab). This avoids side outflow of water during design storms (*). Bund structures, along the contour, are built with a loader up to around 0.7 to 1.0m height and around 2.0 – 3.0m bottom width. The bunds are built with compaction through the loader. Interspace between the bunds is between 10-50 meters (C), depending on the local slope in the flow direction, having around 0.1 to 0.3m soil surface elevation difference between the bunds. Stone made design-spillways (A) are being constructed around the middle of each bund, with certain position change between the bund in downstream direction. Thus, spillways do not perfectly align with respect to the bund, but create a meandering flow around the center. The stone-protected design-spillways are designed to safely route at least the expected 2-5 year return period flood event. The Marab plain is not perfectly even, especially at the sides, to avoid water flowing around the bunds during design storms. However, the Marab-technology is also designed to cope with more extreme events, a storm of 5-10 return period, without significant damages. Therefore, there are emergency-spillways (**) implemented at the sides of each bund (B). These emergency-spillways allow excess water to flow out sideways rather than flow over the bund which would damage the structures. Note:
Based on above considerations and calculations bund spillway lengths reach 50-60m in the specific watershed.
* A design storm is a rainfall event that results in a flood event as water accumulates throughout the watershed. The Marab is designed to harvest the water optimally by (design) spill ways that keep the water in the Marab. A design storm relates to a certain return period. In general a longer return period (i.e. less frequent) accounts for a more intense event hence a more severe flooding event.
** An emergency spill way is a structure that is designed to discharge excess water coming from storms more extreme than the design storm (i.e. with less frequent storms). In practice this means that the Marab is protected from excess water.
Auteur:
Joren Verbist (Extracted from Google Earth Pro on Jan 7th 2019)
Date:
19/12/2020
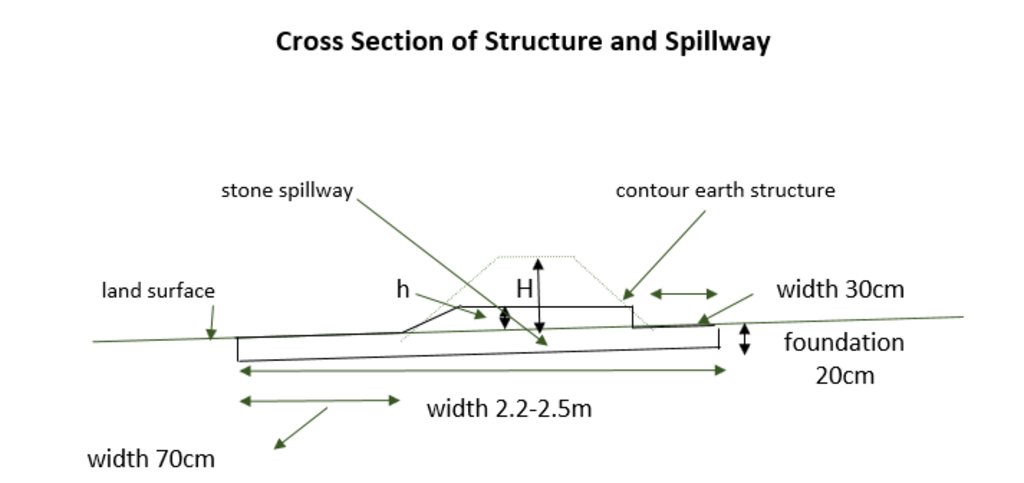
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
The cross-section shows the dimensions. Downstream of a bund the width is 70 centimeter. The foundation is 20 centimeter high. The upstream width is 30 centimeter. The total width of the bund varies between 2.2 meter and 2.5 meter.
Auteur:
Stefan Strohmeier
Date:
01/07/2020
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
10 ha
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
35
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Implement upstream watershed rehabilitation measure (e.g. Upstream Vallerani micro water harvesting) | Prior of Marab-Technology construction |
| 2. | Implement gully rehabilitation measure (e.g. Midstream gully rehabilitation) | Prior of Marab-Technology construction |
| 3. | Marab site selection (flood plain): topographic assessment (slope, soil depth, etc.) and consideration of watershed hydrology (e.g. for bund and spillway design) | Before the rainy season |
| 4. | Grading/levelling of natural flood plain incl. gully fill (with soil material) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 5. | Implement bund structures (based on step 4) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 6. | Construct stone made design and emergence spillways (based on step 5) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 7. | Preparation of compartmentalized agricultural fields (bund interspaces) for field crop agriculture | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
Commentaires:
The upstream measures as the Vallerani System and gully rehabilitation are strongly recommended but are not taken into account as costs in this documentation. Because this documentation focuses specifically on the Marab-technology.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Local Workers | person-days | 50,0 | 35,0 | 1750,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Land Survey | person-days | 6,0 | 35,0 | 210,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Engineer (+assistance) | person-days | 15,0 | 50,0 | 750,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Drivers of heavy machinery | person-days | 12,0 | 35,0 | 420,0 | |
| Equipements | Grader | machine-days | 3,0 | 250,0 | 750,0 | |
| Equipements | Loader | machine-days | 10,0 | 250,0 | 2500,0 | |
| Equipements | Deep Plow | machine-days | 3,0 | 200,0 | 600,0 | |
| Equipements | Tractor (to pull the shallow and deep plow) | machine-days | 5,0 | 200,0 | 1000,0 | |
| Equipements | Shallow Plow | machine-days | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | |
| Equipements | Water Tank Truck | Tank | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | |
| Equipements | Small Equipment (Shovel, pickaxe, buckets) | Equipment | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stones | Kubic Metre | 200,0 | 10,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Autre | Transportation of heavy machinery | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | ||
| Autre | Security | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | ||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 12930,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 12930,0 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
ICARDA and National Agricultural Research Centre (NARC)
Commentaires:
These costs are for establishment (so one-time) and are for the total Marab-technology i.e. 10 ha.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintaining the structures based on observations and possible damages after the rainy season, so no clear maintenance plans | Before the rainy season (Oct. – Nov.)/upon observation |
Commentaires:
Excludes annual farming costs (e.g. seedbed preparation)
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Engineer | person days per year | 2,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Worker | person days per year | 6,0 | 35,0 | 210,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Loader | machine days per year | 1,0 | 250,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Stones | Kubic Metre | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 660,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 660,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
The costs of practicing agriculture (e.g. cost of seeds and fertilizer) are not taken into account, since these costs were also made before the implementation of this technology.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The special and heavy machinery affect the cost significantly, since these were not available in the area. The implementation of the technology is labour intensive, therefore labour costs are significant as well. However, these costs are initially, so these specific costs are almost zero after establishment. In addition, all the maintenance is payed for by the land users. So, only the establishment was payed for by external parties.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
130,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
In the specific site/dry areas of Jordan rainy season usually ranges from November until April
Queen Alia International Airport long-time avergae annual rainfall is around 150 mm (around 10km west of the site)
At the site a rainfall tipping bucket has been installed in 2016.
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Queen Alia International Airport
Zone agro-climatique
- aride
The maximum temperature usually occurres in August.
The average daily maximum temperature is 25.01 °C.
The average daily minimum temperature is 8.5 °C
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations convexes
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
The Marab itself is rather concave (depression shape) / natural depression. However, the bund structures are convex, spreading water over the field.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau inutilisable
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
fréquemment
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Semi-nomade
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- jeunes
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
The actual land users are often poor Jordanians or Syrian refugees. However, the owners of the livestock are relatively rich. The landowners are responsible for the maintenance of the intervention.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
10ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
- NA
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The crops produced are used as fodder
production fourragère
Quantité avant la GDT:
0.05ton/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
5ton/ha
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The production of the fodder is increased as the barley yield is mostly used to feed animals and also the stubble is grazed.
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The barley is fed to the livestock
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to the bunds (but very limited and inevitable)
gestion des terres
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Expenses are slightly increased due to possible maintenance of the Marab. However, the increased yield justifies this.
revenus agricoles
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to possible maintenance
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
During the construction, local community were hired as workers, this has significantly boosted their knowlegde about SLM.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
drainage de l'excès d'eau
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
accumulation de sol
encroûtement/ battance du sol
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
impacts de la sécheresse
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced downstream flooding is desired
envasement en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced downstream siltation is desired
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| précipitations annuelles | décroît | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | très bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| crue éclair | très bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The initial investment is quite large. Therefore, the short term returns is classified as slightly negative. After some seasons with good (stable) crop yield the return of investment is positive. Long term benefits are classified positively.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 1-10%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
These are some farmers that live near the Marab. They try to copy the Marab in their fields.
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
The local farmers like the technology and acknowledge its positive impacts. They would like to have a Marab themselves (even if their locally owned lands are not suitable in many cases). Local agro-pastoralists copy and apply parts of the technology (especially the bund
system). However, it strongly recommended that implementing a Marab-technology is done as a community-based project/intervention; the Marab technology should be part of an integrated watershed management plan, located at the most suitable location for the entire community.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- changements/ extrêmes climatiques
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
The spillway design can be adapted to variable surface runoff occurrence (affected by climate change).
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| The farmers highly appreciate the improved economic situation as consequence of the increased yield. |
| A strength of the Marab technology is that water is harvested and minimally spilled away, preventing top-soil erosion and accumulating soil organic matter consequently preserving soil fertility. |
| The crop produces grains: can be (partially) used for re-seeding in the coming seasons; economic gain + increase resilience. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Economic improvement through targeted agricultural interventions in the most suitable location(s) of a watershed. This aims at decreasing the pressure on the fragile dry land ecosystem. The locally increased yield raises awareness on non-sufficient field crop agriculture in uplands (commonly achieved) and might increase the willingness for more nature-based sustainable land management measures in the less fertile and runoff generating (more vulnerable uplands) parts of the watershed. Therefore, the Marab technology could be a starting point for a watershed rehabilitation initiative. |
| The Marab technology creates an opportunity for multiple crop introduction (due to natural flood irrigation) – aside from barley monoculture (agro-diversity). |
| Increased water infiltration conserves water and might lead to deep percolation (groundwater recharge). |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The Marab depends on upstream water users; can lead to increased tensions | Agreement among the community - conducting contacts/contracts among upstream and downstream farmers. Joint watershed management and benefit share could be mediate these tension. And might even lead to watershed rehabilitation. |
| High initial investment and partially high maintenance costs (including machinery) | Once the implementation is linked with larger environmental benefits – communities might receive funds from the government or international donors. |
| Loss of cultivation area where the bunds are placed | Unavoidable. However, the gain of interspaces exceeds these losses several times. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Tensions among multiple actors in the watershed (selection of Marab area) | Develop institutions that could avoid these tensions by establishing agreements, contracts, rules, or regulations. |
| Heavy machinery in a vulnerable ecosystems – can induce other requests/use by locals (improper use) | Targeted policies in place & enforcements |
| Increasing wealth inequality between farmers and/or communities. | Creation of institutions, which assure fair distribution. This would benefit the whole watershed. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
15/04/2020
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Strohmeier, S. (2017). Dimensioning of Marab in Majidyya.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Strohmeier, S. (2017). Watershed Restoration in Baia Areas of Jordan Technology Packages for Controlling and Monitoring Gully Erosion.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://mel.cgiar.org/projects/jordan-watershed-restoration-project
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Mira Haddad, Stefan Strohmeier. (12/12/2017). Treated upland areas map. Jordan: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9108
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Stefan Strohmeier, Mira Haddad, Ismail Shukri. (8/11/2018). Marab - water harvesting based agriculture.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9069
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mira Haddad, Stefan Strohmeier, Masnat El-Hiary. (24/7/2020). Enhancing a Traditional Water Harvesting Technique in Jordan’s Agro-pastoral Farming System. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/11506
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
WATER HARVESTING FOR RESTORING RANGELANDS IN JORDAN
URL:
https://www.icarda.org/media/drywire/water-harvesting-restoring-rangelands-jordan
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé