Establishment of improved orchards and vineyards [Afghanistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm
- Rédacteur : Roziya Kirgizbekova
- Examinateur : Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Bunyodi boghi va boghi anguri behbudyofta
technologies_669 - Afghanistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Mirza Bay Gholam Sakhi
Natural Resources Management Comittee (NRMC)
Afghanistan
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Researcher:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Bern University of Applied Sciences, School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences (HAFL) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
SLM practices documented in the frame of the Rustaq NRM study were established only recently (1-3 years ago). It is too early for a final judgment on the sustainability of these technologies within the human and natural environment of Chokar watershed.
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Local and new varieties of fruits are planted on degraded land in accordance with improved management practices. The established orchards and vineyards serve double purpose of soil protection and income generation for the rural households. The alfalfa under the trees supports tree growth and is used for livestock fodder.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
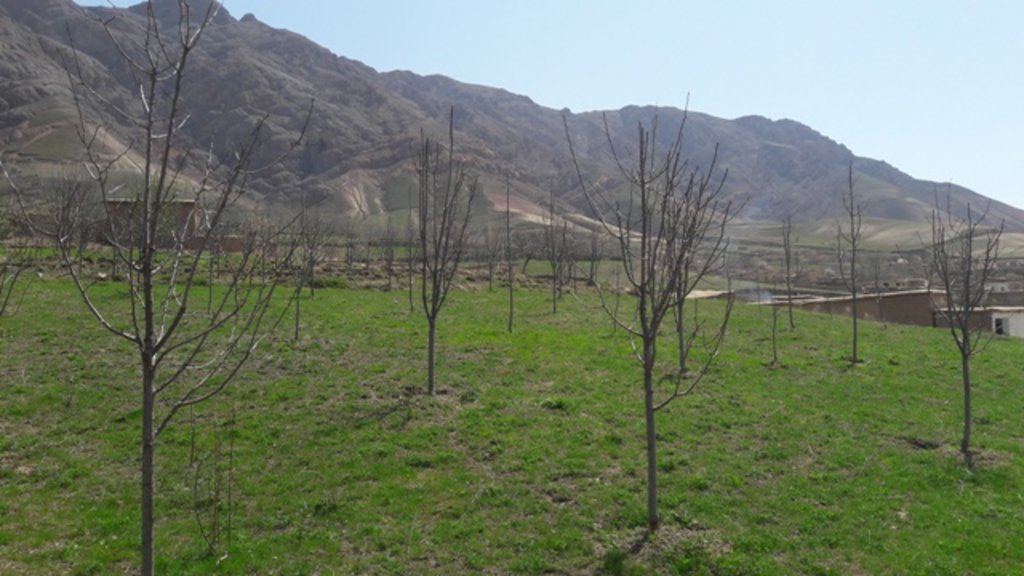
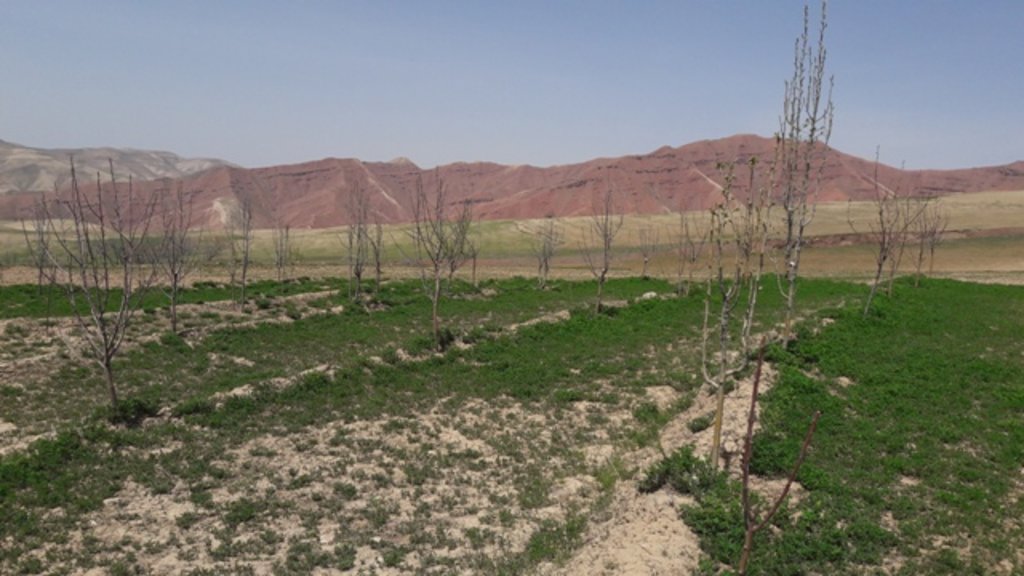
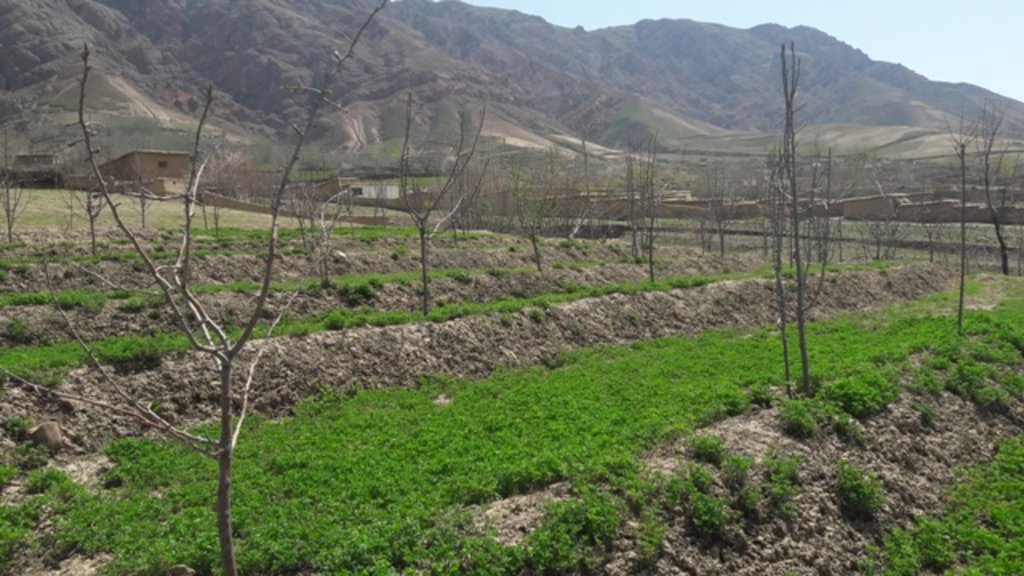
Project supported implementation of improved orchards and vineyards has taken place in the villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai, located in Chokar watershed of Rustaq District in Northern Afghanistan. The Chokar watershed is a mountainous area situated between 600 - 2,500 m above sea level. The climate is semi-arid with harsh and cold weather in winter and hot and dry summers. The annual precipitation in average years is 580mm. Land degradation affects all forms of land use and includes low vegetation cover, heavy top soil erosion from water, and poor soil fertility. Unsustainable agricultural practices, over-exploitation and high pressure on the natural resources are adversely impacting on the socio-economic well-being of local communities as well as contributing to the risk for being adversely affected by drought as well as landslides and flash foods triggered by heavy rainfall. The data used for the documentation of the technology is based on field research conducted in Chokar watershed, namely in the villages: Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai. These villages represent the upper, the middle and the lower zone of Chokar watershed, respectively. They differ considerably in access to services and infrastructure, but in general are poorly served. The communities depend on land resources for sustaining their livelihoods. In a good year with high yields, wheat-self-sufficiency lasts about 5 months. The three villages are home to ethnic Qarluq communities. Since 2012 the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland has initiated a range of NRM interventions.
The rural population in Rustaq district of Afghanistan traditionally grows local varieties of apples, pears and grapes. Mostly it is subsistence farming with a small-scale local marketing. Shortage of irrigation water and lack of specific knowledge about horticultural and viticulture practices, negatively affects fruit yields. Apart of providing diverse fruits for consumption, orchards are also important for providing fodder for the livestock, retaining soil moisture and protecting the soil from erosion.
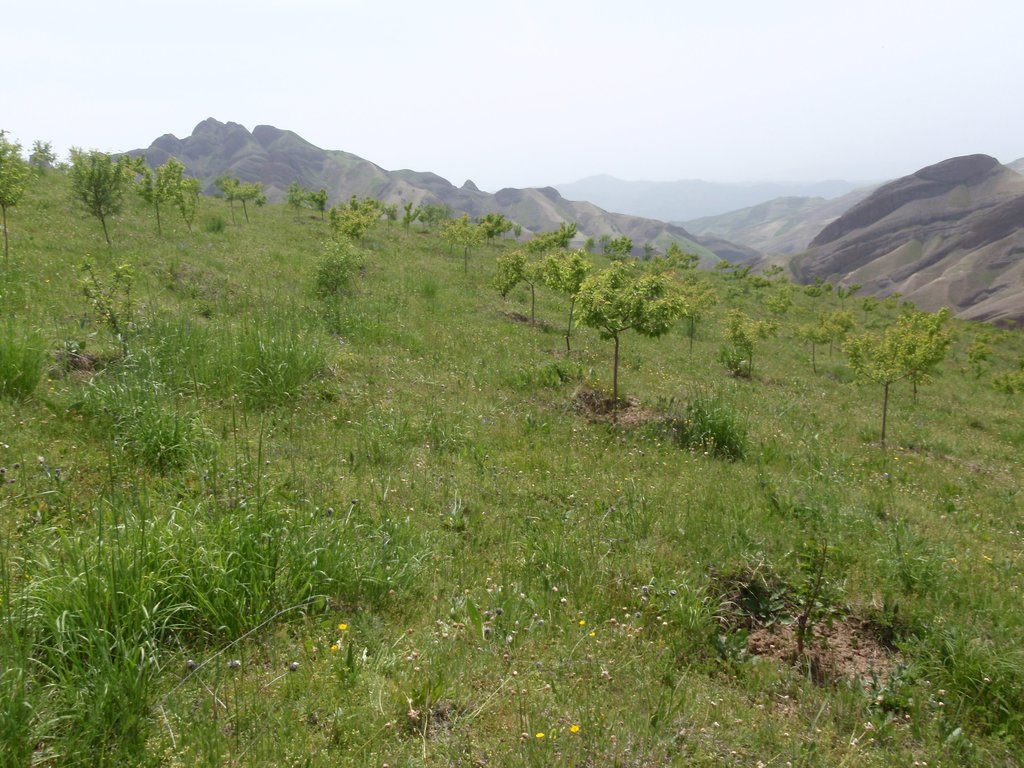
The local land users interested in the establishment of improved orchards and vineyards were mobilized through the Natural Resources Management Committees (NRMC) in Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai villages. In addition to the local varieties of pears, apples and grapes, new improved varieties were used for orchards and vineyards on 6.5 ha of degraded land. Such orchards were established inside or close to the villages on mountain slopes with gentle (3-5%) and moderate (6 -15%) steepness. Fruit trees are planted on locally identified dark and light soils, which correspond to moderately deep and loamy soil of medium soil fertility. Considering the medium quality of the soil, the first step of tree plantation is application of organic fertilizer. Afterwards, the plot is designed according to 4m x 4 m spacing between the trees. Under such parameters, on 1 jirib (0.2 ha) of land 125 fruit tree (apple or pear) seedlings are planted. The depth of the planting pits is 60 x 50 cm. The planted tree is watered and the lower trunk is covered with lime and water solution. Alfalfa is sown under the trees to serve as a fodder for the livestock. The orchards are irrigated mostly during summer once a week. In areas where there is shortage of irrigation water the trees are rainfed. Other maintenance activities include pest and disease control provided by a trained local specialist.
The new orchards only recently started giving fruits. The actual fruit yields are expected in 2017-2018. Expected higher yields of improved verities of pears, apples and grapes serves as a strong incentive for the local land users and their families to establish and maintain the orchards. Orchards are very demanding, but their reward is very promising in terms of improved harvest and more opportunities to sell the produce. Some land users have successful experience on their plots and already have fruits in their gardens and plan to enlarge their garden and plant more varieties of fruit trees, such as persimmons. Alfalfa which grows under the trees has important production value, particularly during the early years after the establishment phase, when the trees are too young to give fruits.
Female members of the households, which implemented orchards are also involved in establishing and maintaining orchards and vineyards. They take part in planting trees, watering, hay making and protecting the trees from livestock and people. Their contribution, plays an important part for the successful implementation of improved orchards and vineyards in Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Afghanistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, Dashti Mirzai
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
This documentation is based on the experiences of SLM implementers from Sari Joy (8 plots), Jawaz Khana, (6 plots), and Dashti Mirzai (3 plots). Additionally insights were gained through interviews with both SLM implementers and observers from all three villages.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) supported by Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC) from 2012-17
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agro-sylvo-pastoralisme

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- cultures fourragères - luzerne
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- arbres fourragers (Barbe jolote, Faux mimosa, Prosopis, etc.)
- raisins
- fruits à pépins (pommes, poires, coings, etc.)
- fruits à coque (noix du Brésil, pistaches, noyers de bancoule, amandes)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1

Pâturages

Forêts/ bois
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)

Terres cultivées
Commentaires:
About half of orchard plots are established on cropland.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
Often the trees are watered with supplementary irrigation, from irrigation channels, or fetching the water in buckets.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Many land users establish a fence around their orchards to protect the trees from animal and the fruits from theft.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
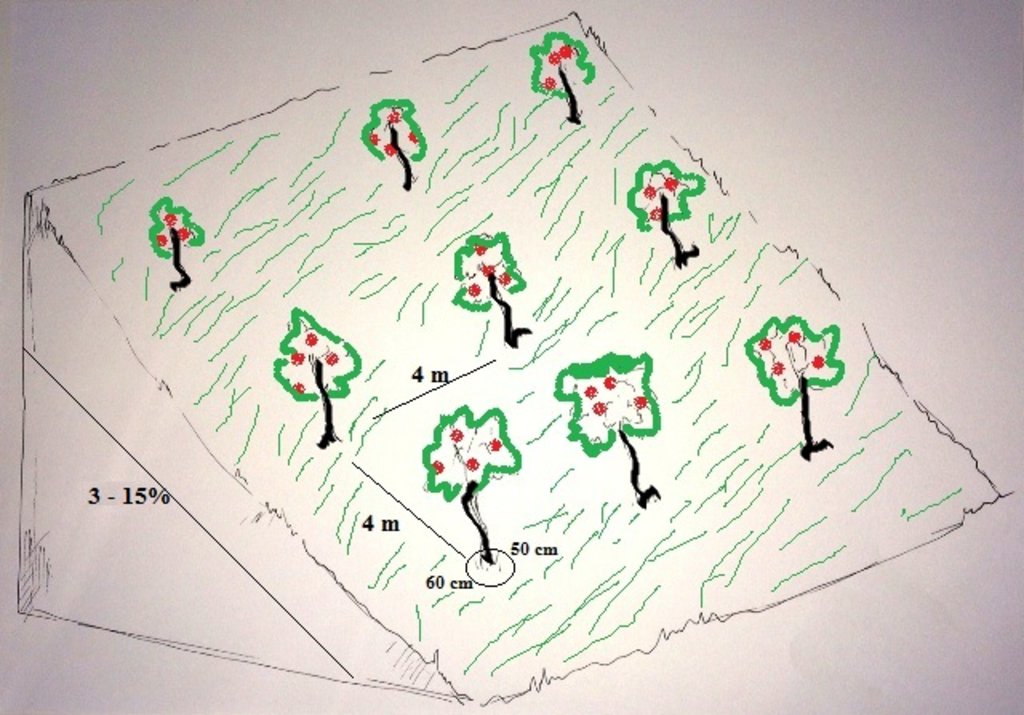
Orchards are established on mountain slopes with gentle (3-5%) and moderate (6-10%) steepness. Considering the medium soil fertility, the first step of tree plantation is application of organic fertilizer. Afterwards, the plot is designed according to 4m x 4 m spacing between rows and trees. Under such parameters, on 1 jirib (0.2 ha) of land 125 fruit tree (apple or pear) seedlings are planted. The depth of the planting pits is 60 x 50 cm. The planted tree is watered and the lower trunk is covered with lime and water solution. Alfalfa is sown under the trees for livestock fodder.
Auteur:
Aslam Qadamov; Roziya Kirgizbekova
Date:
03/04/2017
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
1 ha
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
67,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
5.2-5.3 USD per day
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of the area for orchard (Men) | Fall |
| 2. | Applicatoin of manure (Men) | Fall/Winter |
| 3. | Design of tree spacing in the orchard assisted by project staff (Men) | End of winter |
| 4. | Digging pits for planting (Men/Women) | Spring |
| 5. | Planting of fruit trees (Men/Women) | Spring |
| 6. | Sowing of alfalfa under the trees (Men/Women) | Spring |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Application of manure | person-day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 83,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Design of tree spacing | person-day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Digging pits for planting | person-day | 15,0 | 5,3 | 79,5 | 83,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting trees, sowing alfalfa and watering | person-day | 10,0 | 5,3 | 53,0 | 83,0 |
| Equipements | Meter | piece | 1,0 | 2,25 | 2,25 | |
| Equipements | Rope | Meter | 500,0 | 0,07 | 35,0 | |
| Equipements | Shovel | piece | 2,0 | 3,8 | 7,6 | |
| Equipements | Pick axe | piece | 1,0 | 2,25 | 2,25 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings (apple/pear) | piece | 625,0 | 0,75 | 468,75 | |
| Matériel végétal | Alfalfa seeds | kg | 17,5 | 0,42 | 7,35 | |
| Engrais et biocides | DAP | Kg | 250,0 | 0,9 | 225,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Urea | Kg | 250,0 | 0,45 | 112,5 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Animal manure | ton | 10,0 | 60,0 | 600,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Pesticide | cc | 500,0 | 0,9 | 450,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Lime | Kg | 25,0 | 1,5 | 37,5 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 2133,7 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 31,85 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
Commentaires:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.2- 0.4 ha or 1- 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering of the trees (Men/Women) | 2 times/month/Summer |
| 2. | Weeding (Women) | |
| 3. | Pruning (Men) | |
| 4. | Lime application (Men) | |
| 5. | Hay making (Men/Women) | |
| 6. | Harvesting fruits (Men/Women) |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Irrigation | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Weeding | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Pruning | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Lime application | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Scissors for pruning | piece | 2,0 | 9,0 | 18,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Lime | Kg | 25,0 | 1,5 | 37,5 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 161,5 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 2,41 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des Hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
Commentaires:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.2- 0.4 ha or 1- 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the Technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as agricultural equipment, plant material, fertilizers, etc., are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
580,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Average annual percipitation for the area was calculated with 580 mm, with minimums in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximums in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolut maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the time from 1979 to 2014.
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR), http://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Derived from the publicly available dataset on length of growing period (LGP) (Fischer 2009 / IIASA-FAO). Internet link: http://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P8Cok4qAP1sTVE59/arcgis/rest/services/Length_of_growing_period/MapServer
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Local land users differentiate between the following soil types where orchards and vineyards are established:
- Light soil: moderately deep; texture medium; medium, low organic matter
- Dark soil: moderately deep; texture medium, medium; medium organic matter
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
épisodiquement
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water differs for the three study villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, and Dashti Mirzai. Sari Joy has sources and good surface water availability. Jawaz Khana has poor water availability as water has to be fetched from a lower laying stream. Dashti Mirzai has good water availability also from an irrigation channel.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
- personnes âgées
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
The land users in the area where the Technology is applied belong to the Uzbek ethnic minority group Qarluq.
Although the men are generally the main land users, however, women and children also take active part in the related work. The functions of men and women are clearly distinguished within the Afghan society. At the same time within the family this division of work and functions also results in men and women working hand-in-hand. An improvement of the family’s livelihood situation is expected to positively affect all family members. While, it is recognized that the involvement of women is key in order to secure basic human rights for everyone, to achieve good governance, sustainable development, and to efficiently contribute to poverty reduction (SDC 2004), it is also clear that a context sensitive approach is of high importance.
Women in rural Afghanistan are involved in many production and income generating activities that contribute to the overall household income, however, very few women own resources such as land and livestock, and their income generating options are fewer in comparison to that of men.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
Those who own land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for the water. The payment is made both in kind and in cash to the Mirob - the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The local and new improved varieties of fruit trees planted and managed sustainably give better fruit yields. Enhanced fruit production is also due to proper and timely control of pests and disease.
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The grass (alfalfa and sainfoin), which is planted under the fruit trees is used as fodder for livestock.
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Indirect contribution to animal production is achieved through availability of more fodder for the livestock from the grass in the orchards. Animals also feed on the tree leaves in autumn.
production de bois
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Production of wood is limited. Fuel wood is made from seasonal pruning of the trees.
production forestière non ligneuse
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Multiple varieties of fruit trees are grown, also through grafting techniques.
surface de production
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The new practice of establishing orchards and vineyards ensures better yields. New variety of fruits such as apples, pears, almonds and grapes improve the diversity of household's production and consumption. The households have better opportunity to earn more from selling their fresh and dried fruits on the local market.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Land users learned new methods of planting trees according to the soil conditions and water availability. They were trained with such skills as grafting, pruning, pest and disease control and were introduced to improved verities of fruit trees.
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Female headed households are not included. Technology is implemented on private land, therefore people without land are excluded. However, they have they opportunity to earn income as a hired worker for the SLM implementers.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Sols
perte en sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Improved vegetation cover resulting from the tree plantations and the grass.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
capacité tampon/de filtration
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
These comments apply to 6.1 and 6.2:
- Socio-economic impacts: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits from orchards and vineyards. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in product diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all implementers of orchards are reflected here.
- Similarly for the "ecological impacts" and on "off-site impacts": Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of orchards and vineyards on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by the orchard implementers are reflected here.
- Socio-cultural impacts: This section is answered by the scientists, based on information collected during focus group discussions, and interviews conducted with persons from the 3 villages where the LIPT project implemented the SLM practices.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | très bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Commentaires:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: SLM implementers were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly, well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrixes compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: During the FGD with SLM implementers, a multi-criteria matrix was elaborated, and different SLM practices were rated. In the frame of this exercise, SLM implementers were asked to jointly discuss and rate short term (1-3 years) and long-term (10 years) returns of the SLM practice. As the SLM technology was only implemented 1-2 years ago, it is too early to compare benefits to maintenance costs. Farmers have little experience so far on the actual benefits of the SLM technology. The ratings are mostly based on expected benefits and not on actual benefits.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 1-10%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
6.5 ha
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 11-50%
Commentaires:
Individual SLM implementers were asked whether they received support for implementing the Technology. Each indicated the type of support he received from the proposed options: "Full Support 100%, Some Support, No Support 0%". 18% have adopted the technology without receiving support.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
autre (précisez):
protection
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
Some of the land users built a wall around their orchard. The wall made from locally available clay material, protects the trees and the grass from animal and people intrusion.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| The land users have high expectations about the benefits of the improved practices to grow fruit trees. They see the benefit of growing different types of fruits. Expectations are high about increased fruit yields and increased opportunities to sell more fresh and dried fruits and nuts on the local market. Fruits and nuts sell very well and can generate higher incomes for the households. |
| The ecological benefits of the orchards in protecting the soil from heavy rains is valued by the land users. The villagers mark improved vegetation cover as their villages are becoming greener with the fruit trees and the alfalfa in the orchards. |
| It is appreciated by the land users that they were introduced and provided with new varieties of fruits. They were also trained on planting and maintaining orchards and vineyards in accordance with local conditions and using such techniques as grafting, pruning, mulching, protection from pests and diseases, etc. |
| The orchards not only give fruits, but also are the source of fuel wood, which is made from pruning the trees. Considering that many households keep livestock, the grass under the trees and tree leaves are used to feed the livestock. In return livestock manure is used as organic fertilizer for the trees. |
| Some land users having seen the positive outcome of their work, are interested in enlarging their orchards. Others are ready to support those who want to plant fruit trees by sharing tree saplings or seedlings with them. |
| Women share the expectations of earning more money for their household through growing more fruits and selling them on the local market. In Dashti Mirzai and Jawaz Khana women are particularly excited over their grape, which still need some time to give yields. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Better management practices in growing fruit trees will benefit the land user and the land through strengthening soil resistance to heavy rainfall and prevent erosion. Over the period of few more years the trees and undergrowth grass will significantly enhance infiltration and moisture retention in the soil, which in turn increase the vegetation cover and halt the degradation process. |
| The SLM knowledge obtained through project training is disseminating inside and beyond the villages, along with exchange of seedlings from new varieties of fruit trees. In addition to that, land users are aware of pest and disease control and have access to these services through trained specialist. |
| Households do not have to rely only on wheat and legumes, but are able to diversify their agricultural production even more. The expected opportunity to sell more fruits and nuts has the potential to increase households income. This in turn will enable the family to secure their food supply for longer periods. |
| Female family members' participation is one of the key elements for sustaining orchards and vineyards. Women highly value the importance of their work in orchards and the benefit it provides to their households. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Lack of irrigation water is a crucial issue, especially in Jawaz Khana, which makes it very difficult for the land users to maintain their orchards. | Rehabilitate the Yakhdons. Yakhdon is a local storage method for collecting snow water in winter to be used for drinking and irrigation in spring and summer. One Yakhdon can provide water for up to six months. Several of these Yakhdons are destroyed and their rehabilitation would provide better access to water for Jawaz Khana. |
| The young trees are sensitive to droughts and need to be watered regularly to ensure that they survive. | |
| Establishment of orchards requires hard work and sufficient money from the land user to buy seedlings and in some cases to build a wall around the orchard or build an irrigation canal. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The establishment of orchards is reported as one of the most labour-intensive SLM practice for both men and women. Working in orchards increases the burden of women in addition to their household chores. | |
| Technical knowledge on planting and maintaining fruit trees and grapes is required to ensure tree survival, good productivity and protection from pests and diseases. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Focus group discussions (FGD) were organized by CDE team to collect information from SLM implementers. Total of 17 land users who have implemented terraces participated in the FGDs held in the three villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
Interviews were conducted by the HAFL team to collect information from persons representing all the three study villages. Very detailed interviews were conducted with 41 persons interested in orchard implementation, of which 14 persons are from households that already have implemented orchards.
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
Close collaboration took place during the compilation of this material with the technical staff of the LIPT project in Rustaq.
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
Information provided in the reports of the LIPT project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
27/10/2016
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Guidelines for Focus Group Discussions
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Methods section of the Rustaq NRM study
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé